Hadi Veisi
LIA
NER- RoBERTa: Fine-Tuning RoBERTa for Named Entity Recognition (NER) within low-resource languages
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an important tool for most people's daily life routines, ranging from understanding speech, translation, named entity recognition (NER), and text categorization, to generative text models such as ChatGPT. Due to the existence of big data and consequently large corpora for widely used languages like English, Spanish, Turkish, Persian, and many more, these applications have been developed accurately. However, the Kurdish language still requires more corpora and large datasets to be included in NLP applications. This is because Kurdish has a rich linguistic structure, varied dialects, and a limited dataset, which poses unique challenges for Kurdish NLP (KNLP) application development. While several studies have been conducted in KNLP for various applications, Kurdish NER (KNER) remains a challenge for many KNLP tasks, including text analysis and classification. In this work, we address this limitation by proposing a methodology for fine-tuning the pre-trained RoBERTa model for KNER. To this end, we first create a Kurdish corpus, followed by designing a modified model architecture and implementing the training procedures. To evaluate the trained model, a set of experiments is conducted to demonstrate the performance of the KNER model using different tokenization methods and trained models. The experimental results show that fine-tuned RoBERTa with the SentencePiece tokenization method substantially improves KNER performance, achieving a 12.8% improvement in F1-score compared to traditional models, and consequently establishes a new benchmark for KNLP.
End-to-End Transformer-based Automatic Speech Recognition for Northern Kurdish: A Pioneering Approach
Oct 19, 2024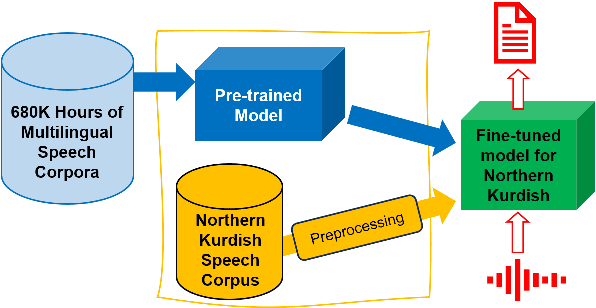
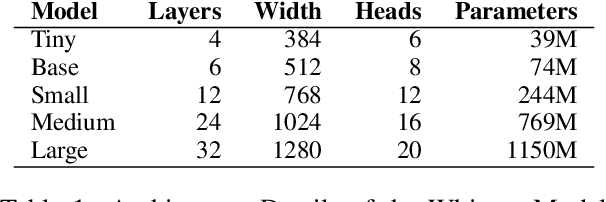
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) for low-resource languages remains a challenging task due to limited training data. This paper introduces a comprehensive study exploring the effectiveness of Whisper, a pre-trained ASR model, for Northern Kurdish (Kurmanji) an under-resourced language spoken in the Middle East. We investigate three fine-tuning strategies: vanilla, specific parameters, and additional modules. Using a Northern Kurdish fine-tuning speech corpus containing approximately 68 hours of validated transcribed data, our experiments demonstrate that the additional module fine-tuning strategy significantly improves ASR accuracy on a specialized test set, achieving a Word Error Rate (WER) of 10.5% and Character Error Rate (CER) of 5.7% with Whisper version 3. These results underscore the potential of sophisticated transformer models for low-resource ASR and emphasize the importance of tailored fine-tuning techniques for optimal performance.
Advanced Clustering Techniques for Speech Signal Enhancement: A Review and Metanalysis of Fuzzy C-Means, K-Means, and Kernel Fuzzy C-Means Methods
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:Speech signal processing is a cornerstone of modern communication technologies, tasked with improving the clarity and comprehensibility of audio data in noisy environments. The primary challenge in this field is the effective separation and recognition of speech from background noise, crucial for applications ranging from voice-activated assistants to automated transcription services. The quality of speech recognition directly impacts user experience and accessibility in technology-driven communication. This review paper explores advanced clustering techniques, particularly focusing on the Kernel Fuzzy C-Means (KFCM) method, to address these challenges. Our findings indicate that KFCM, compared to traditional methods like K-Means (KM) and Fuzzy C-Means (FCM), provides superior performance in handling non-linear and non-stationary noise conditions in speech signals. The most notable outcome of this review is the adaptability of KFCM to various noisy environments, making it a robust choice for speech enhancement applications. Additionally, the paper identifies gaps in current methodologies, such as the need for more dynamic clustering algorithms that can adapt in real time to changing noise conditions without compromising speech recognition quality. Key contributions include a detailed comparative analysis of current clustering algorithms and suggestions for further integrating hybrid models that combine KFCM with neural networks to enhance speech recognition accuracy. Through this review, we advocate for a shift towards more sophisticated, adaptive clustering techniques that can significantly improve speech enhancement and pave the way for more resilient speech processing systems.
Gammatonegram Representation for End-to-End Dysarthric Speech Processing Tasks: Speech Recognition, Speaker Identification, and Intelligibility Assessment
Jul 06, 2023Abstract:Dysarthria is a disability that causes a disturbance in the human speech system and reduces the quality and intelligibility of a person's speech. Because of this effect, the normal speech processing systems can not work properly on impaired speech. This disability is usually associated with physical disabilities. Therefore, designing a system that can perform some tasks by receiving voice commands in the smart home can be a significant achievement. In this work, we introduce gammatonegram as an effective method to represent audio files with discriminative details, which is used as input for the convolutional neural network. On the other word, we convert each speech file into an image and propose image recognition system to classify speech in different scenarios. Proposed CNN is based on the transfer learning method on the pre-trained Alexnet. In this research, the efficiency of the proposed system for speech recognition, speaker identification, and intelligibility assessment is evaluated. According to the results on the UA dataset, the proposed speech recognition system achieved 91.29% accuracy in speaker-dependent mode, the speaker identification system acquired 87.74% accuracy in text-dependent mode, and the intelligibility assessment system achieved 96.47% accuracy in two-class mode. Finally, we propose a multi-network speech recognition system that works fully automatically. This system is located in a cascade arrangement with the two-class intelligibility assessment system, and the output of this system activates each one of the speech recognition networks. This architecture achieves an accuracy of 92.3% WRR. The source code of this paper is available.
Adjustable Privacy using Autoencoder-based Learning Structure
Apr 07, 2023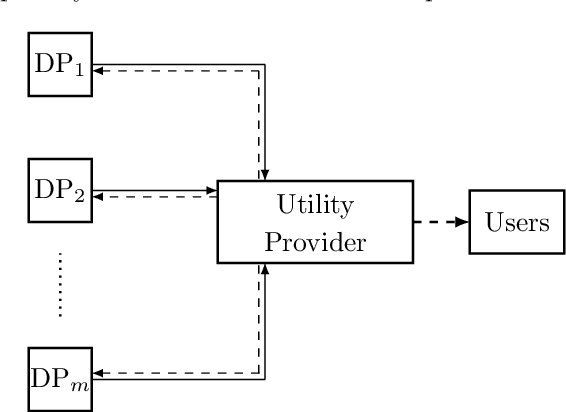
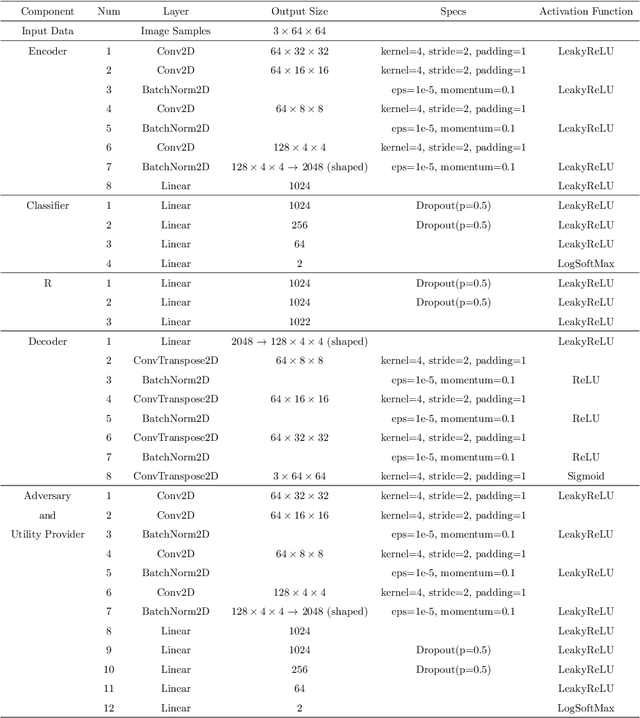
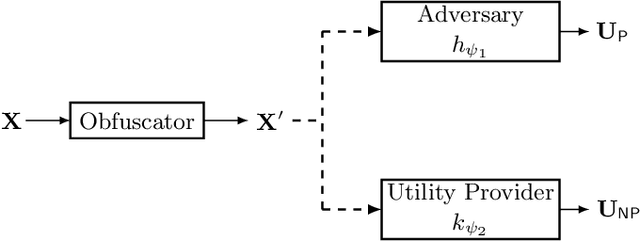
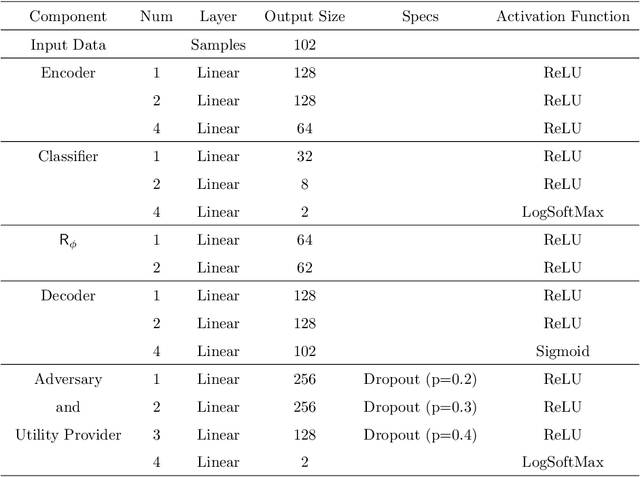
Abstract:Inference centers need more data to have a more comprehensive and beneficial learning model, and for this purpose, they need to collect data from data providers. On the other hand, data providers are cautious about delivering their datasets to inference centers in terms of privacy considerations. In this paper, by modifying the structure of the autoencoder, we present a method that manages the utility-privacy trade-off well. To be more precise, the data is first compressed using the encoder, then confidential and non-confidential features are separated and uncorrelated using the classifier. The confidential feature is appropriately combined with noise, and the non-confidential feature is enhanced, and at the end, data with the original data format is produced by the decoder. The proposed architecture also allows data providers to set the level of privacy required for confidential features. The proposed method has been examined for both image and categorical databases, and the results show a significant performance improvement compared to previous methods.
Fake news detection using parallel BERT deep neural networks
Apr 10, 2022



Abstract:Fake news is a growing challenge for social networks and media. Detection of fake news always has been a problem for many years, but after the evolution of social networks and increasing speed of news dissemination in recent years has been considered again. There are several approaches to solving this problem, one of which is to detect fake news based on its text style using deep neural networks. In recent years, one of the most used forms of deep neural networks for natural language processing is transfer learning with transformers. BERT is one of the most promising transformers who outperforms other models in many NLP benchmarks. This article, we introduce MWPBert, which uses two parallel BERT networks to perform veracity detection on full-text news articles. One of the BERT networks encodes news headline, and another encodes news body. Since the input length of the BERT network is limited and constant and the news body is usually a long text, we cannot fed the whole news text into the BERT. Therefore, using the MaxWorth algorithm, we selected the part of the news text that is more valuable for fact-checking, and fed it into the BERT network. Finally, we encode the output of the two BERT networks to an output network to classify the news. The experiment results showed that the proposed model outperformed previous models in terms of accuracy and other performance measures.
CKMorph: A Comprehensive Morphological Analyzer for Central Kurdish
Sep 17, 2021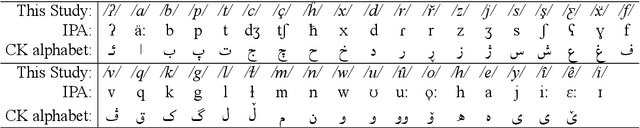
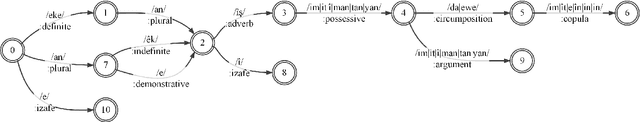
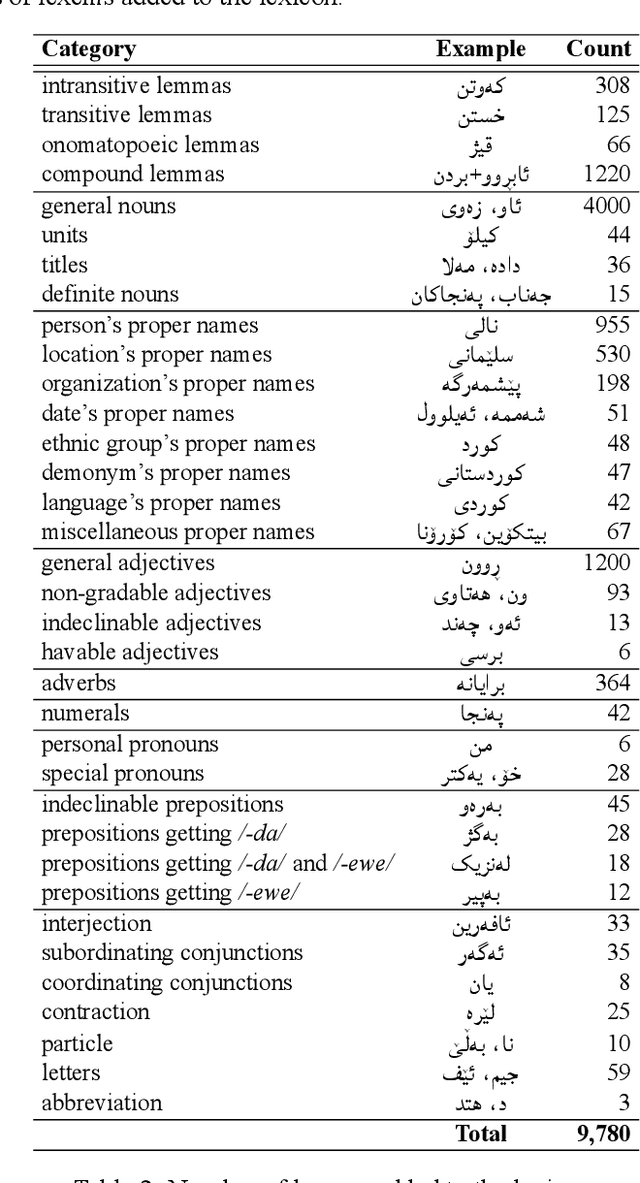
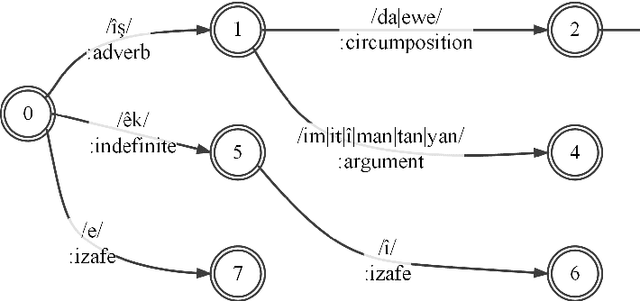
Abstract:A morphological analyzer, which is a significant component of many natural language processing applications especially for morphologically rich languages, divides an input word into all its composing morphemes and identifies their morphological roles. In this paper, we introduce a comprehensive morphological analyzer for Central Kurdish (CK), a low-resourced language with a rich morphology. Building upon the limited existing literature, we first assembled and systematically categorized a comprehensive collection of the morphological and morphophonological rules of the language. Additionally, we collected and manually labeled a generative lexicon containing nearly 10,000 verb, noun and adjective stems, named entities, and other types of word stems. We used these rule sets and resources to implement CKMorph Analyzer based on finite-state transducers. In order to provide a benchmark for future research, we collected, manually labeled, and publicly shared test sets for evaluating accuracy and coverage of the analyzer. CKMorph was able to correctly analyze 95.9% of the accuracy test set, containing 1,000 CK words morphologically analyzed according to the context. Moreover, CKMorph gave at least one analysis for 95.5% of 4.22M CK tokens of the coverage test set. The demonstration of the application and resources including CK verb database and test sets are openly accessible at https://github.com/CKMorph.
Persian Rhetorical Structure Theory
Jun 25, 2021

Abstract:Over the past years, interest in discourse analysis and discourse parsing has steadily grown, and many discourse-annotated corpora and, as a result, discourse parsers have been built. In this paper, we present a discourse-annotated corpus for the Persian language built in the framework of Rhetorical Structure Theory as well as a discourse parser built upon the DPLP parser, an open-source discourse parser. Our corpus consists of 150 journalistic texts, each text having an average of around 400 words. Corpus texts were annotated using 18 discourse relations and based on the annotation guideline of the English RST Discourse Treebank corpus. Our text-level discourse parser is trained using gold segmentation and is built upon the DPLP discourse parser, which uses a large-margin transition-based approach to solve the problem of discourse parsing. The performance of our discourse parser in span (S), nuclearity (N) and relation (R) detection is around 78%, 64%, 44% respectively, in terms of F1 measure.
Automatic Meter Classification of Kurdish Poems
Feb 24, 2021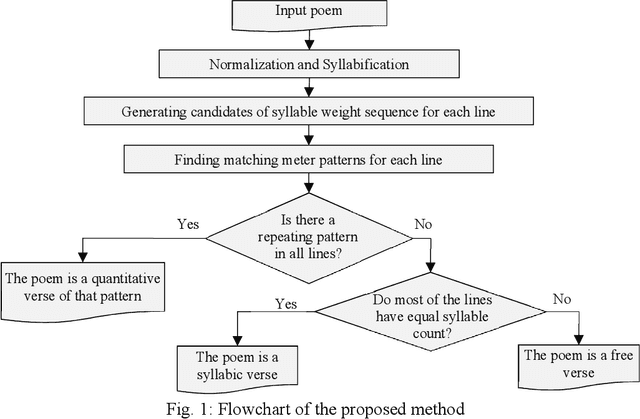
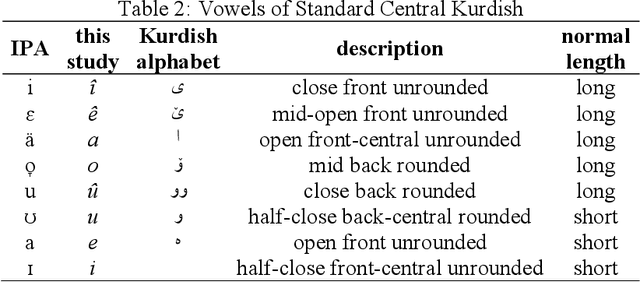
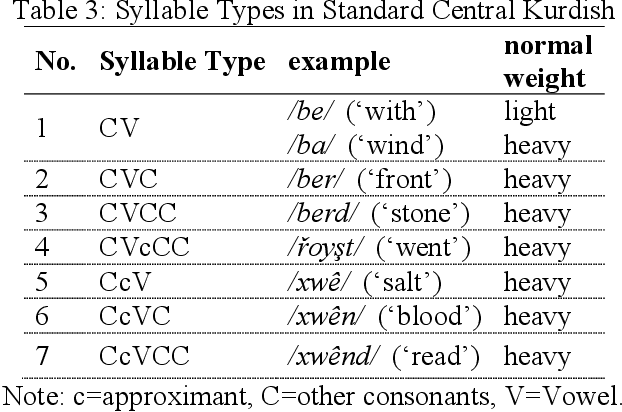
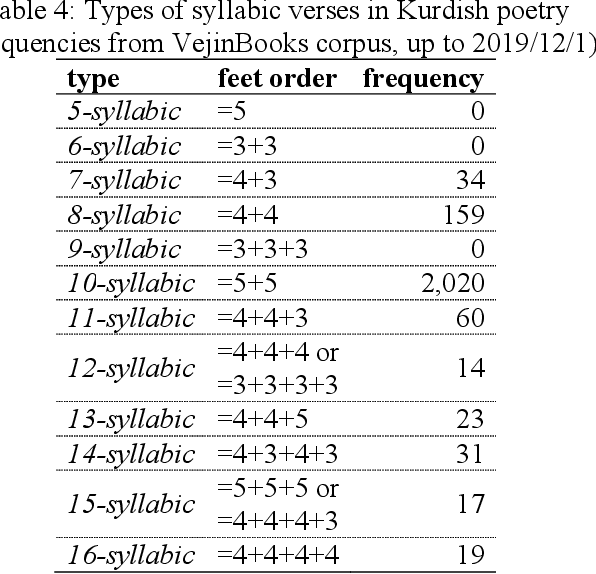
Abstract:Most of the classic texts in Kurdish literature are poems. Knowing the meter of the poems is helpful for correct reading, a better understanding of the meaning, and avoidance of ambiguity. This paper presents a rule-based method for automatic classification of the poem meter for the Central Kurdish language. The metrical system of Kurdish poetry is divided into three classes of quantitative, syllabic, and free verses. As the vowel length is not phonemic in the language, there are uncertainties in syllable weight and meter identification. The proposed method generates all the possible situations and then, by considering all lines of the input poem and the common meter patterns of Kurdish poetry, identifies the most probable meter type and pattern of the input poem. Evaluation of the method on a dataset from VejinBooks Kurdish corpus resulted in 97.3% of precision in meter type and 96.2% of precision in pattern identification.
Jira: a Kurdish Speech Recognition System Designing and Building Speech Corpus and Pronunciation Lexicon
Feb 15, 2021
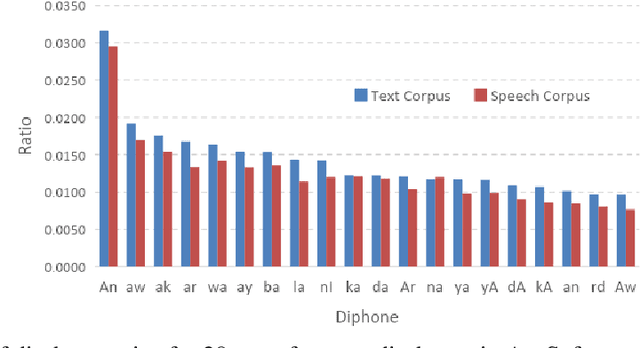
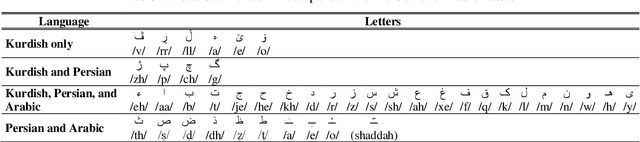
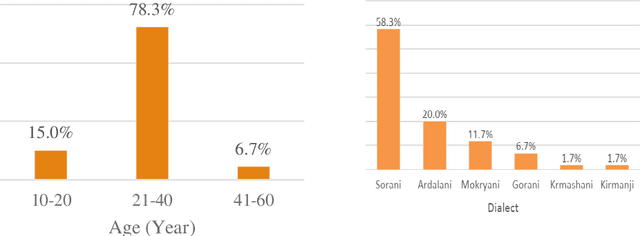
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce the first large vocabulary speech recognition system (LVSR) for the Central Kurdish language, named Jira. The Kurdish language is an Indo-European language spoken by more than 30 million people in several countries, but due to the lack of speech and text resources, there is no speech recognition system for this language. To fill this gap, we introduce the first speech corpus and pronunciation lexicon for the Kurdish language. Regarding speech corpus, we designed a sentence collection in which the ratio of di-phones in the collection resembles the real data of the Central Kurdish language. The designed sentences are uttered by 576 speakers in a controlled environment with noise-free microphones (called AsoSoft Speech-Office) and in Telegram social network environment using mobile phones (denoted as AsoSoft Speech-Crowdsourcing), resulted in 43.68 hours of speech. Besides, a test set including 11 different document topics is designed and recorded in two corresponding speech conditions (i.e., Office and Crowdsourcing). Furthermore, a 60K pronunciation lexicon is prepared in this research in which we faced several challenges and proposed solutions for them. The Kurdish language has several dialects and sub-dialects that results in many lexical variations. Our methods for script standardization of lexical variations and automatic pronunciation of the lexicon tokens are presented in detail. To setup the recognition engine, we used the Kaldi toolkit. A statistical tri-gram language model that is extracted from the AsoSoft text corpus is used in the system. Several standard recipes including HMM-based models (i.e., mono, tri1, tr2, tri2, tri3), SGMM, and DNN methods are used to generate the acoustic model. These methods are trained with AsoSoft Speech-Office and AsoSoft Speech-Crowdsourcing and a combination of them. The best performance achieved by the SGMM acoustic model which results in 13.9% of the average word error rate (on different document topics) and 4.9% for the general topic.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge