Abdulhady Abas Abdullah
Speaker Diarization for Low-Resource Languages Through Wav2vec Fine-Tuning
Apr 23, 2025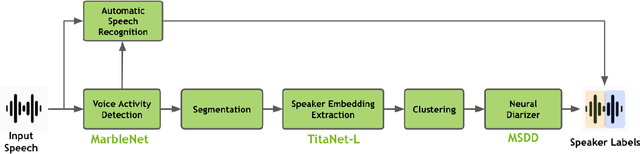

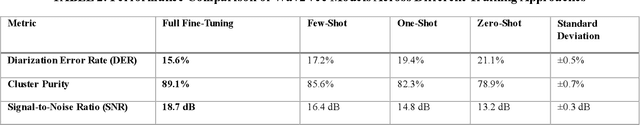
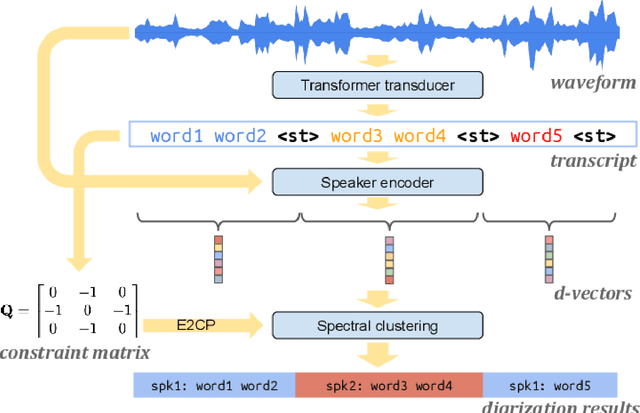
Abstract:Speaker diarization is a fundamental task in speech processing that involves dividing an audio stream by speaker. Although state-of-the-art models have advanced performance in high-resource languages, low-resource languages such as Kurdish pose unique challenges due to limited annotated data, multiple dialects and frequent code-switching. In this study, we address these issues by training the Wav2Vec 2.0 self-supervised learning model on a dedicated Kurdish corpus. By leveraging transfer learning, we adapted multilingual representations learned from other languages to capture the phonetic and acoustic characteristics of Kurdish speech. Relative to a baseline method, our approach reduced the diarization error rate by seven point two percent and improved cluster purity by thirteen percent. These findings demonstrate that enhancements to existing models can significantly improve diarization performance for under-resourced languages. Our work has practical implications for developing transcription services for Kurdish-language media and for speaker segmentation in multilingual call centers, teleconferencing and video-conferencing systems. The results establish a foundation for building effective diarization systems in other understudied languages, contributing to greater equity in speech technology.
From Dialect Gaps to Identity Maps: Tackling Variability in Speaker Verification
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:The complexity and difficulties of Kurdish speaker detection among its several dialects are investigated in this work. Because of its great phonetic and lexical differences, Kurdish with several dialects including Kurmanji, Sorani, and Hawrami offers special challenges for speaker recognition systems. The main difficulties in building a strong speaker identification system capable of precisely identifying speakers across several dialects are investigated in this work. To raise the accuracy and dependability of these systems, it also suggests solutions like sophisticated machine learning approaches, data augmentation tactics, and the building of thorough dialect-specific corpus. The results show that customized strategies for every dialect together with cross-dialect training greatly enhance recognition performance.
Effect of Information Technology on Job Creation to Support Economic: Case Studies of Graduates in Universities (2023-2024) of the KRG of Iraq
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:The aim of this study is to assess the impact of information technology (IT) on university graduates in terms of employment development, which will aid in economic issues. This study uses a descriptive research methodology and a quantitative approach to understand variables. The focus of this study is to ascertain how graduates of Kurdistan regional universities might use IT to secure employment and significantly contribute to the nation's economic revival. The sample size was established by the use of judgmental sampling procedure and consisted of 314 people. The researcher prepared the questionnaire to collect data, and then SPSS statistical software, version 22, and Excel 2010 were used to modify, compile, and tabulate the results. The study's outcome showed that information technology is incredibly inventive, has a promising future, and makes life much easier for everyone. It also proved that a deep academic understanding of information technology and its constituent parts helps graduates of Kurdistan Regional University find suitable careers. More importantly, though, anyone looking for work or a means of support will find great benefit from possessing credentials and understanding of IT. The study's final finding was that information technology has actively advanced the country's economy. Not only is IT helping to boost youth employment, but it is also turning into a worthwhile investment for economic growth.
A novel Facial Recognition technique with Focusing on Masked Faces
Jan 08, 2025


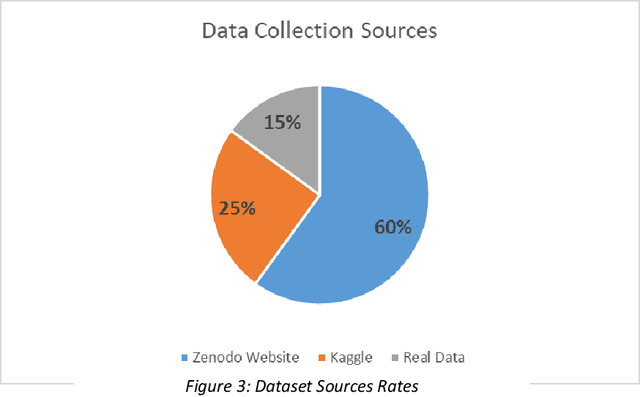
Abstract:Recognizing the same faces with and without masks is important for ensuring consistent identification in security, access control, and public safety. This capability is crucial in scenarios like law enforcement, healthcare, and surveillance, where accurate recognition must be maintained despite facial occlusion. This research focuses on the challenge of recognizing the same faces with and without masks by employing cosine similarity as the primary technique. With the increased use of masks, traditional facial recognition systems face significant accuracy issues, making it crucial to develop methods that can reliably identify individuals in masked conditions. For that reason, this study proposed Masked-Unmasked Face Matching Model (MUFM). This model employs transfer learning using the Visual Geometry Group (VGG16) model to extract significant facial features, which are subsequently classified utilizing the K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN) algorithm. The cosine similarity metric is employed to compare masked and unmasked faces of the same individuals. This approach represents a novel contribution, as the task of recognizing the same individual with and without a mask using cosine similarity has not been previously addressed. By integrating these advanced methodologies, the research demonstrates effective identification of individuals despite the presence of masks, addressing a significant limitation in traditional systems. Using data is another essential part of this work, by collecting and preparing an image dataset from three different sources especially some of those data are real provided a comprehensive power of this research. The image dataset used were already collected in three different datasets of masked and unmasked for the same faces.
NER- RoBERTa: Fine-Tuning RoBERTa for Named Entity Recognition (NER) within low-resource languages
Dec 15, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, Natural Language Processing (NLP) is an important tool for most people's daily life routines, ranging from understanding speech, translation, named entity recognition (NER), and text categorization, to generative text models such as ChatGPT. Due to the existence of big data and consequently large corpora for widely used languages like English, Spanish, Turkish, Persian, and many more, these applications have been developed accurately. However, the Kurdish language still requires more corpora and large datasets to be included in NLP applications. This is because Kurdish has a rich linguistic structure, varied dialects, and a limited dataset, which poses unique challenges for Kurdish NLP (KNLP) application development. While several studies have been conducted in KNLP for various applications, Kurdish NER (KNER) remains a challenge for many KNLP tasks, including text analysis and classification. In this work, we address this limitation by proposing a methodology for fine-tuning the pre-trained RoBERTa model for KNER. To this end, we first create a Kurdish corpus, followed by designing a modified model architecture and implementing the training procedures. To evaluate the trained model, a set of experiments is conducted to demonstrate the performance of the KNER model using different tokenization methods and trained models. The experimental results show that fine-tuned RoBERTa with the SentencePiece tokenization method substantially improves KNER performance, achieving a 12.8% improvement in F1-score compared to traditional models, and consequently establishes a new benchmark for KNLP.
End-to-End Transformer-based Automatic Speech Recognition for Northern Kurdish: A Pioneering Approach
Oct 19, 2024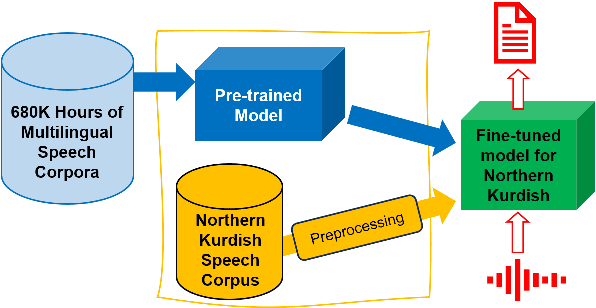
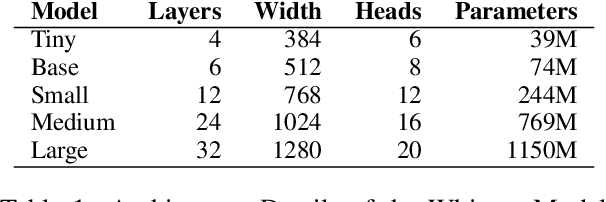
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) for low-resource languages remains a challenging task due to limited training data. This paper introduces a comprehensive study exploring the effectiveness of Whisper, a pre-trained ASR model, for Northern Kurdish (Kurmanji) an under-resourced language spoken in the Middle East. We investigate three fine-tuning strategies: vanilla, specific parameters, and additional modules. Using a Northern Kurdish fine-tuning speech corpus containing approximately 68 hours of validated transcribed data, our experiments demonstrate that the additional module fine-tuning strategy significantly improves ASR accuracy on a specialized test set, achieving a Word Error Rate (WER) of 10.5% and Character Error Rate (CER) of 5.7% with Whisper version 3. These results underscore the potential of sophisticated transformer models for low-resource ASR and emphasize the importance of tailored fine-tuning techniques for optimal performance.
Advanced Clustering Techniques for Speech Signal Enhancement: A Review and Metanalysis of Fuzzy C-Means, K-Means, and Kernel Fuzzy C-Means Methods
Sep 28, 2024



Abstract:Speech signal processing is a cornerstone of modern communication technologies, tasked with improving the clarity and comprehensibility of audio data in noisy environments. The primary challenge in this field is the effective separation and recognition of speech from background noise, crucial for applications ranging from voice-activated assistants to automated transcription services. The quality of speech recognition directly impacts user experience and accessibility in technology-driven communication. This review paper explores advanced clustering techniques, particularly focusing on the Kernel Fuzzy C-Means (KFCM) method, to address these challenges. Our findings indicate that KFCM, compared to traditional methods like K-Means (KM) and Fuzzy C-Means (FCM), provides superior performance in handling non-linear and non-stationary noise conditions in speech signals. The most notable outcome of this review is the adaptability of KFCM to various noisy environments, making it a robust choice for speech enhancement applications. Additionally, the paper identifies gaps in current methodologies, such as the need for more dynamic clustering algorithms that can adapt in real time to changing noise conditions without compromising speech recognition quality. Key contributions include a detailed comparative analysis of current clustering algorithms and suggestions for further integrating hybrid models that combine KFCM with neural networks to enhance speech recognition accuracy. Through this review, we advocate for a shift towards more sophisticated, adaptive clustering techniques that can significantly improve speech enhancement and pave the way for more resilient speech processing systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge