Dana A Abdullah
A novel Facial Recognition technique with Focusing on Masked Faces
Jan 08, 2025


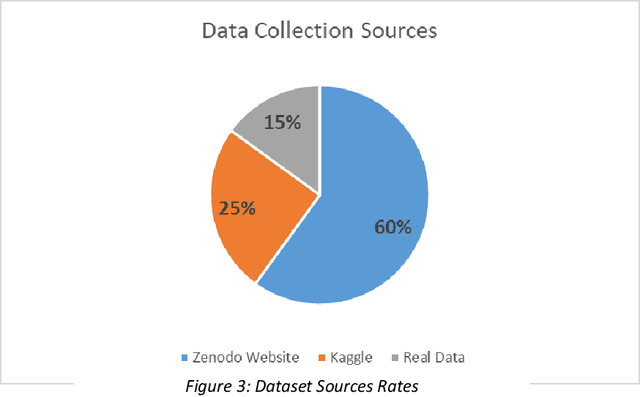
Abstract:Recognizing the same faces with and without masks is important for ensuring consistent identification in security, access control, and public safety. This capability is crucial in scenarios like law enforcement, healthcare, and surveillance, where accurate recognition must be maintained despite facial occlusion. This research focuses on the challenge of recognizing the same faces with and without masks by employing cosine similarity as the primary technique. With the increased use of masks, traditional facial recognition systems face significant accuracy issues, making it crucial to develop methods that can reliably identify individuals in masked conditions. For that reason, this study proposed Masked-Unmasked Face Matching Model (MUFM). This model employs transfer learning using the Visual Geometry Group (VGG16) model to extract significant facial features, which are subsequently classified utilizing the K-Nearest Neighbors (K-NN) algorithm. The cosine similarity metric is employed to compare masked and unmasked faces of the same individuals. This approach represents a novel contribution, as the task of recognizing the same individual with and without a mask using cosine similarity has not been previously addressed. By integrating these advanced methodologies, the research demonstrates effective identification of individuals despite the presence of masks, addressing a significant limitation in traditional systems. Using data is another essential part of this work, by collecting and preparing an image dataset from three different sources especially some of those data are real provided a comprehensive power of this research. The image dataset used were already collected in three different datasets of masked and unmasked for the same faces.
Effect of Information Technology on Job Creation to Support Economic: Case Studies of Graduates in Universities (2023-2024) of the KRG of Iraq
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:The aim of this study is to assess the impact of information technology (IT) on university graduates in terms of employment development, which will aid in economic issues. This study uses a descriptive research methodology and a quantitative approach to understand variables. The focus of this study is to ascertain how graduates of Kurdistan regional universities might use IT to secure employment and significantly contribute to the nation's economic revival. The sample size was established by the use of judgmental sampling procedure and consisted of 314 people. The researcher prepared the questionnaire to collect data, and then SPSS statistical software, version 22, and Excel 2010 were used to modify, compile, and tabulate the results. The study's outcome showed that information technology is incredibly inventive, has a promising future, and makes life much easier for everyone. It also proved that a deep academic understanding of information technology and its constituent parts helps graduates of Kurdistan Regional University find suitable careers. More importantly, though, anyone looking for work or a means of support will find great benefit from possessing credentials and understanding of IT. The study's final finding was that information technology has actively advanced the country's economy. Not only is IT helping to boost youth employment, but it is also turning into a worthwhile investment for economic growth.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge