Jieyu Zhang
Theory of Space: Can Foundation Models Construct Spatial Beliefs through Active Exploration?
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Spatial embodied intelligence requires agents to act to acquire information under partial observability. While multimodal foundation models excel at passive perception, their capacity for active, self-directed exploration remains understudied. We propose Theory of Space, defined as an agent's ability to actively acquire information through self-directed, active exploration and to construct, revise, and exploit a spatial belief from sequential, partial observations. We evaluate this through a benchmark where the goal is curiosity-driven exploration to build an accurate cognitive map. A key innovation is spatial belief probing, which prompts models to reveal their internal spatial representations at each step. Our evaluation of state-of-the-art models reveals several critical bottlenecks. First, we identify an Active-Passive Gap, where performance drops significantly when agents must autonomously gather information. Second, we find high inefficiency, as models explore unsystematically compared to program-based proxies. Through belief probing, we diagnose that while perception is an initial bottleneck, global beliefs suffer from instability that causes spatial knowledge to degrade over time. Finally, using a false belief paradigm, we uncover Belief Inertia, where agents fail to update obsolete priors with new evidence. This issue is present in text-based agents but is particularly severe in vision-based models. Our findings suggest that current foundation models struggle to maintain coherent, revisable spatial beliefs during active exploration.
Molmo2: Open Weights and Data for Vision-Language Models with Video Understanding and Grounding
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Today's strongest video-language models (VLMs) remain proprietary. The strongest open-weight models either rely on synthetic data from proprietary VLMs, effectively distilling from them, or do not disclose their training data or recipe. As a result, the open-source community lacks the foundations needed to improve on the state-of-the-art video (and image) language models. Crucially, many downstream applications require more than just high-level video understanding; they require grounding -- either by pointing or by tracking in pixels. Even proprietary models lack this capability. We present Molmo2, a new family of VLMs that are state-of-the-art among open-source models and demonstrate exceptional new capabilities in point-driven grounding in single image, multi-image, and video tasks. Our key contribution is a collection of 7 new video datasets and 2 multi-image datasets, including a dataset of highly detailed video captions for pre-training, a free-form video Q&A dataset for fine-tuning, a new object tracking dataset with complex queries, and an innovative new video pointing dataset, all collected without the use of closed VLMs. We also present a training recipe for this data utilizing an efficient packing and message-tree encoding scheme, and show bi-directional attention on vision tokens and a novel token-weight strategy improves performance. Our best-in-class 8B model outperforms others in the class of open weight and data models on short videos, counting, and captioning, and is competitive on long-videos. On video-grounding Molmo2 significantly outperforms existing open-weight models like Qwen3-VL (35.5 vs 29.6 accuracy on video counting) and surpasses proprietary models like Gemini 3 Pro on some tasks (38.4 vs 20.0 F1 on video pointing and 56.2 vs 41.1 J&F on video tracking).
SAGE: Training Smart Any-Horizon Agents for Long Video Reasoning with Reinforcement Learning
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:As humans, we are natural any-horizon reasoners, i.e., we can decide whether to iteratively skim long videos or watch short ones in full when necessary for a given task. With this in mind, one would expect video reasoning models to reason flexibly across different durations. However, SOTA models are still trained to predict answers in a single turn while processing a large number of frames, akin to watching an entire long video, requiring significant resources. This raises the question: Is it possible to develop performant any-horizon video reasoning systems? Inspired by human behavior, we first propose SAGE, an agent system that performs multi-turn reasoning on long videos while handling simpler problems in a single turn. Secondly, we introduce an easy synthetic data generation pipeline using Gemini-2.5-Flash to train the orchestrator, SAGE-MM, which lies at the core of SAGE. We further propose an effective RL post-training recipe essential for instilling any-horizon reasoning ability in SAGE-MM. Thirdly, we curate SAGE-Bench with an average duration of greater than 700 seconds for evaluating video reasoning ability in real-world entertainment use cases. Lastly, we empirically validate the effectiveness of our system, data, and RL recipe, observing notable improvements of up to 6.1% on open-ended video reasoning tasks, as well as an impressive 8.2% improvement on videos longer than 10 minutes.
MolmoAct: Action Reasoning Models that can Reason in Space
Aug 12, 2025



Abstract:Reasoning is central to purposeful action, yet most robotic foundation models map perception and instructions directly to control, which limits adaptability, generalization, and semantic grounding. We introduce Action Reasoning Models (ARMs), a class of robotic foundation models that integrate perception, planning, and control through a structured three-stage pipeline. Our model, MolmoAct, encodes observations and instructions into depth-aware perception tokens, generates mid-level spatial plans as editable trajectory traces, and predicts precise low-level actions, enabling explainable and steerable behavior. MolmoAct-7B-D achieves strong performance across simulation and real-world settings: 70.5% zero-shot accuracy on SimplerEnv Visual Matching tasks, surpassing closed-source Pi-0 and GR00T N1; 86.6% average success on LIBERO, including an additional 6.3% gain over ThinkAct on long-horizon tasks; and in real-world fine-tuning, an additional 10% (single-arm) and an additional 22.7% (bimanual) task progression over Pi-0-FAST. It also outperforms baselines by an additional 23.3% on out-of-distribution generalization and achieves top human-preference scores for open-ended instruction following and trajectory steering. Furthermore, we release, for the first time, the MolmoAct Dataset -- a mid-training robot dataset comprising over 10,000 high quality robot trajectories across diverse scenarios and tasks. Training with this dataset yields an average 5.5% improvement in general performance over the base model. We release all model weights, training code, our collected dataset, and our action reasoning dataset, establishing MolmoAct as both a state-of-the-art robotics foundation model and an open blueprint for building ARMs that transform perception into purposeful action through structured reasoning. Blogpost: https://allenai.org/blog/molmoact
CoAct-1: Computer-using Agents with Coding as Actions
Aug 05, 2025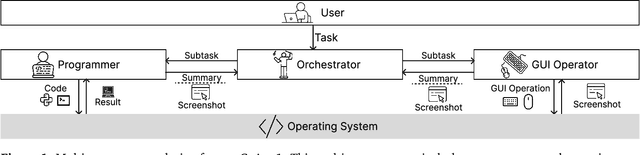
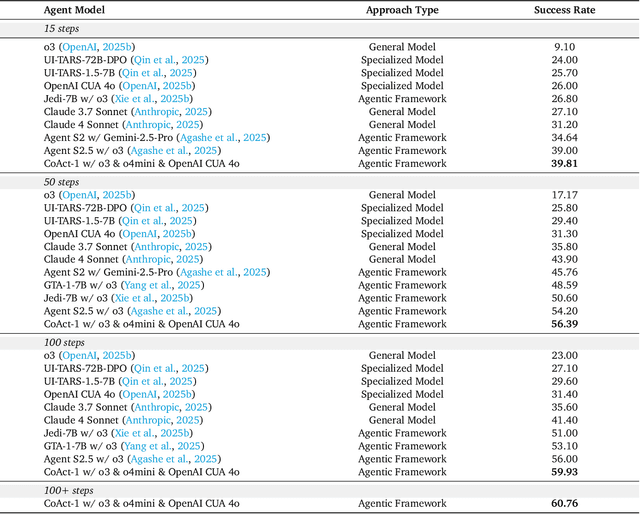
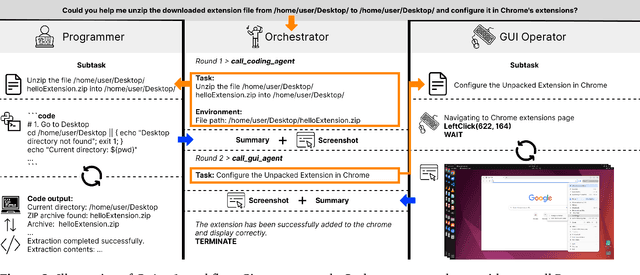
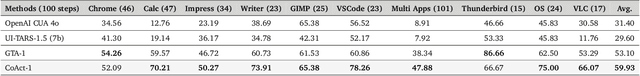
Abstract:Autonomous agents that operate computers via Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) often struggle with efficiency and reliability on complex, long-horizon tasks. While augmenting these agents with planners can improve task decomposition, they remain constrained by the inherent limitations of performing all actions through GUI manipulation, leading to brittleness and inefficiency. In this work, we introduce a more robust and flexible paradigm: enabling agents to use coding as a enhanced action. We present CoAct-1, a novel multi-agent system that synergistically combines GUI-based control with direct programmatic execution. CoAct-1 features an Orchestrator that dynamically delegates subtasks to either a conventional GUI Operator or a specialized Programmer agent, which can write and execute Python or Bash scripts. This hybrid approach allows the agent to bypass inefficient GUI action sequences for tasks like file management and data processing, while still leveraging visual interaction when necessary. We evaluate our system on the challenging OSWorld benchmark, where CoAct-1 achieves a new state-of-the-art success rate of 60.76%, significantly outperforming prior methods. Furthermore, our approach dramatically improves efficiency, reducing the average number of steps required to complete a task to just 10.15, compared to 15 for leading GUI agents. Our results demonstrate that integrating coding as a core action provides a more powerful, efficient, and scalable path toward generalized computer automation.
Spatial Mental Modeling from Limited Views
Jun 26, 2025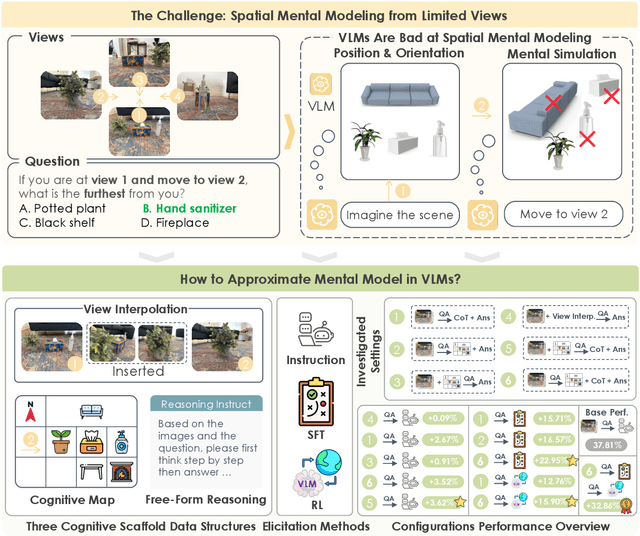
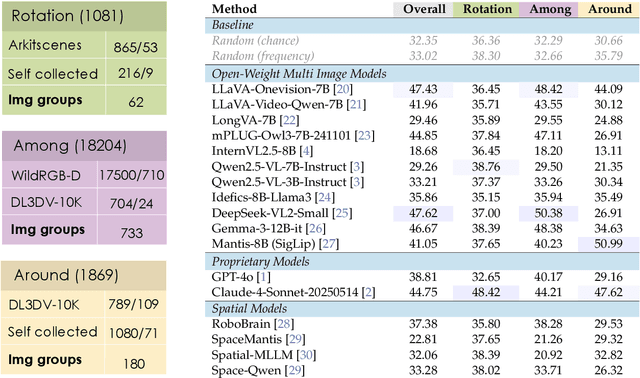
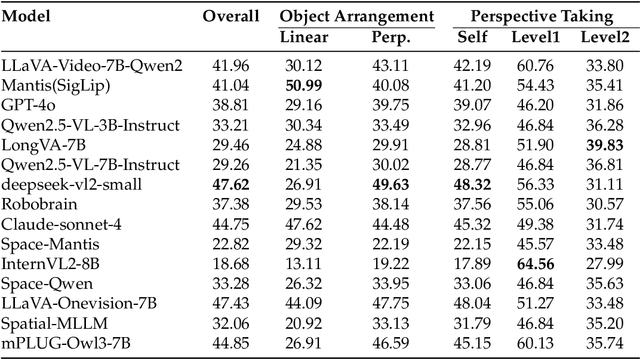
Abstract:Can Vision Language Models (VLMs) imagine the full scene from just a few views, like humans do? Humans form spatial mental models, internal representations of unseen space, to reason about layout, perspective, and motion. Our new MindCube benchmark with 21,154 questions across 3,268 images exposes this critical gap, where existing VLMs exhibit near-random performance. Using MindCube, we systematically evaluate how well VLMs build robust spatial mental models through representing positions (cognitive mapping), orientations (perspective-taking), and dynamics (mental simulation for "what-if" movements). We then explore three approaches to help VLMs approximate spatial mental models, including unseen intermediate views, natural language reasoning chains, and cognitive maps. The significant improvement comes from a synergistic approach, "map-then-reason", that jointly trains the model to first generate a cognitive map and then reason upon it. By training models to reason over these internal maps, we boosted accuracy from 37.8% to 60.8% (+23.0%). Adding reinforcement learning pushed performance even further to 70.7% (+32.9%). Our key insight is that such scaffolding of spatial mental models, actively constructing and utilizing internal structured spatial representations with flexible reasoning processes, significantly improves understanding of unobservable space.
One Trajectory, One Token: Grounded Video Tokenization via Panoptic Sub-object Trajectory
May 29, 2025Abstract:Effective video tokenization is critical for scaling transformer models for long videos. Current approaches tokenize videos using space-time patches, leading to excessive tokens and computational inefficiencies. The best token reduction strategies degrade performance and barely reduce the number of tokens when the camera moves. We introduce grounded video tokenization, a paradigm that organizes tokens based on panoptic sub-object trajectories rather than fixed patches. Our method aligns with fundamental perceptual principles, ensuring that tokenization reflects scene complexity rather than video duration. We propose TrajViT, a video encoder that extracts object trajectories and converts them into semantically meaningful tokens, significantly reducing redundancy while maintaining temporal coherence. Trained with contrastive learning, TrajViT significantly outperforms space-time ViT (ViT3D) across multiple video understanding benchmarks, e.g., TrajViT outperforms ViT3D by a large margin of 6% top-5 recall in average at video-text retrieval task with 10x token deduction. We also show TrajViT as a stronger model than ViT3D for being the video encoder for modern VideoLLM, obtaining an average of 5.2% performance improvement across 6 VideoQA benchmarks while having 4x faster training time and 18x less inference FLOPs. TrajViT is the first efficient encoder to consistently outperform ViT3D across diverse video analysis tasks, making it a robust and scalable solution.
H2R: A Human-to-Robot Data Augmentation for Robot Pre-training from Videos
May 17, 2025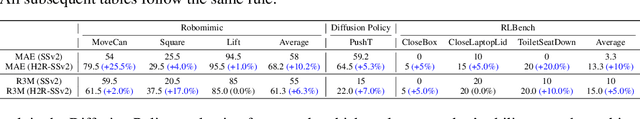
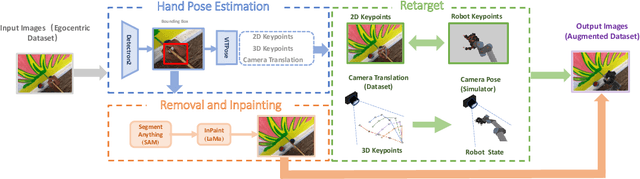

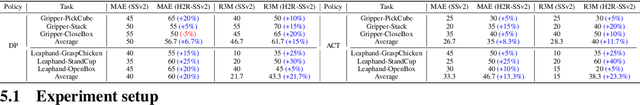
Abstract:Large-scale pre-training using videos has proven effective for robot learning. However, the models pre-trained on such data can be suboptimal for robot learning due to the significant visual gap between human hands and those of different robots. To remedy this, we propose H2R, a simple data augmentation technique that detects human hand keypoints, synthesizes robot motions in simulation, and composites rendered robots into egocentric videos. This process explicitly bridges the visual gap between human and robot embodiments during pre-training. We apply H2R to augment large-scale egocentric human video datasets such as Ego4D and SSv2, replacing human hands with simulated robotic arms to generate robot-centric training data. Based on this, we construct and release a family of 1M-scale datasets covering multiple robot embodiments (UR5 with gripper/Leaphand, Franka) and data sources (SSv2, Ego4D). To verify the effectiveness of the augmentation pipeline, we introduce a CLIP-based image-text similarity metric that quantitatively evaluates the semantic fidelity of robot-rendered frames to the original human actions. We validate H2R across three simulation benchmarks: Robomimic, RLBench and PushT and real-world manipulation tasks with a UR5 robot equipped with Gripper and Leaphand end-effectors. H2R consistently improves downstream success rates, yielding gains of 5.0%-10.2% in simulation and 6.7%-23.3% in real-world tasks across various visual encoders and policy learning methods. These results indicate that H2R improves the generalization ability of robotic policies by mitigating the visual discrepancies between human and robot domains.
Which Agent Causes Task Failures and When? On Automated Failure Attribution of LLM Multi-Agent Systems
Apr 30, 2025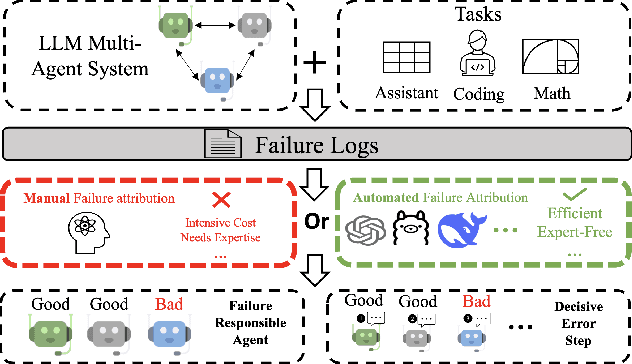
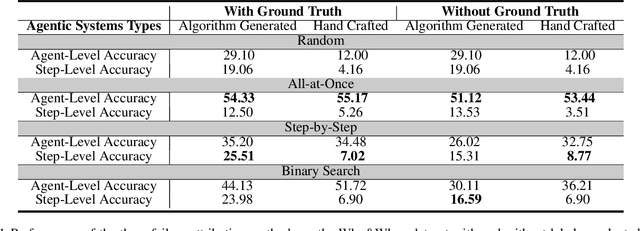
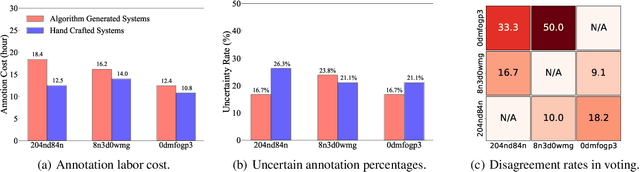

Abstract:Failure attribution in LLM multi-agent systems-identifying the agent and step responsible for task failures-provides crucial clues for systems debugging but remains underexplored and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose and formulate a new research area: automated failure attribution for LLM multi-agent systems. To support this initiative, we introduce the Who&When dataset, comprising extensive failure logs from 127 LLM multi-agent systems with fine-grained annotations linking failures to specific agents and decisive error steps. Using the Who&When, we develop and evaluate three automated failure attribution methods, summarizing their corresponding pros and cons. The best method achieves 53.5% accuracy in identifying failure-responsible agents but only 14.2% in pinpointing failure steps, with some methods performing below random. Even SOTA reasoning models, such as OpenAI o1 and DeepSeek R1, fail to achieve practical usability. These results highlight the task's complexity and the need for further research in this area. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/mingyin1/Agents_Failure_Attribution
Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1: Tool-Using Language Models with Reinforced Reasoning
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Enabling large language models with external tools has become a pivotal strategy for extending their functionality beyond text generation tasks. Prior work typically enhances tool-use abilities by either applying supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to enforce tool-call correctness or distilling reasoning traces from stronger models for SFT. However, both approaches fall short, either omitting reasoning entirely or producing imitative reasoning that limits generalization. Inspired by the success of DeepSeek-R1 in eliciting reasoning through rule-based reinforcement learning, we develop the Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1 series of tool-using language models using a similar training paradigm. Instead of restrictively supervising intermediate reasoning traces distilled from stronger models, Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1 is optimized with a binary reward that evaluates only the structural validity and functional correctness of tool invocations. This lightweight supervision allows the model to autonomously internalize reasoning strategies, without the need for annotated reasoning trajectories. Experiments on the BFCL and API-Bank benchmarks show that Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1-7B and Nemotron-Research-Tool-N1-14B, built on Qwen-2.5-7B/14B-Instruct, achieve state-of-the-art results, outperforming GPT-4o on both evaluations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge