Aniruddha Kembhavi
Eval3D: Interpretable and Fine-grained Evaluation for 3D Generation
Apr 25, 2025Abstract:Despite the unprecedented progress in the field of 3D generation, current systems still often fail to produce high-quality 3D assets that are visually appealing and geometrically and semantically consistent across multiple viewpoints. To effectively assess the quality of the generated 3D data, there is a need for a reliable 3D evaluation tool. Unfortunately, existing 3D evaluation metrics often overlook the geometric quality of generated assets or merely rely on black-box multimodal large language models for coarse assessment. In this paper, we introduce Eval3D, a fine-grained, interpretable evaluation tool that can faithfully evaluate the quality of generated 3D assets based on various distinct yet complementary criteria. Our key observation is that many desired properties of 3D generation, such as semantic and geometric consistency, can be effectively captured by measuring the consistency among various foundation models and tools. We thus leverage a diverse set of models and tools as probes to evaluate the inconsistency of generated 3D assets across different aspects. Compared to prior work, Eval3D provides pixel-wise measurement, enables accurate 3D spatial feedback, and aligns more closely with human judgments. We comprehensively evaluate existing 3D generation models using Eval3D and highlight the limitations and challenges of current models.
ReSpec: Relevance and Specificity Grounded Online Filtering for Learning on Video-Text Data Streams
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of video-text data presents challenges in storage and computation during training. Online learning, which processes streaming data in real-time, offers a promising solution to these issues while also allowing swift adaptations in scenarios demanding real-time responsiveness. One strategy to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of learning involves identifying and prioritizing data that enhances performance on target downstream tasks. We propose Relevance and Specificity-based online filtering framework (ReSpec) that selects data based on four criteria: (i) modality alignment for clean data, (ii) task relevance for target focused data, (iii) specificity for informative and detailed data, and (iv) efficiency for low-latency processing. Relevance is determined by the probabilistic alignment of incoming data with downstream tasks, while specificity employs the distance to a root embedding representing the least specific data as an efficient proxy for informativeness. By establishing reference points from target task data, ReSpec filters incoming data in real-time, eliminating the need for extensive storage and compute. Evaluating on large-scale datasets WebVid2M and VideoCC3M, ReSpec attains state-of-the-art performance on five zeroshot video retrieval tasks, using as little as 5% of the data while incurring minimal compute. The source code is available at https://github.com/cdjkim/ReSpec.
Scaling Text-Rich Image Understanding via Code-Guided Synthetic Multimodal Data Generation
Feb 20, 2025Abstract:Reasoning about images with rich text, such as charts and documents, is a critical application of vision-language models (VLMs). However, VLMs often struggle in these domains due to the scarcity of diverse text-rich vision-language data. To address this challenge, we present CoSyn, a framework that leverages the coding capabilities of text-only large language models (LLMs) to automatically create synthetic text-rich multimodal data. Given input text describing a target domain (e.g., "nutrition fact labels"), CoSyn prompts an LLM to generate code (Python, HTML, LaTeX, etc.) for rendering synthetic images. With the underlying code as textual representations of the synthetic images, CoSyn can generate high-quality instruction-tuning data, again relying on a text-only LLM. Using CoSyn, we constructed a dataset comprising 400K images and 2.7M rows of vision-language instruction-tuning data. Comprehensive experiments on seven benchmarks demonstrate that models trained on our synthetic data achieve state-of-the-art performance among competitive open-source models, including Llama 3.2, and surpass proprietary models such as GPT-4V and Gemini 1.5 Flash. Furthermore, CoSyn can produce synthetic pointing data, enabling VLMs to ground information within input images, showcasing its potential for developing multimodal agents capable of acting in real-world environments.
The One RING: a Robotic Indoor Navigation Generalist
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Modern robots vary significantly in shape, size, and sensor configurations used to perceive and interact with their environments. However, most navigation policies are embodiment-specific; a policy learned using one robot's configuration does not typically gracefully generalize to another. Even small changes in the body size or camera viewpoint may cause failures. With the recent surge in custom hardware developments, it is necessary to learn a single policy that can be transferred to other embodiments, eliminating the need to (re)train for each specific robot. In this paper, we introduce RING (Robotic Indoor Navigation Generalist), an embodiment-agnostic policy, trained solely in simulation with diverse randomly initialized embodiments at scale. Specifically, we augment the AI2-THOR simulator with the ability to instantiate robot embodiments with controllable configurations, varying across body size, rotation pivot point, and camera configurations. In the visual object-goal navigation task, RING achieves robust performance on real unseen robot platforms (Stretch RE-1, LoCoBot, Unitree's Go1), achieving an average of 72.1% and 78.9% success rate across 5 embodiments in simulation and 4 robot platforms in the real world. (project website: https://one-ring-policy.allen.ai/)
Generate Any Scene: Evaluating and Improving Text-to-Vision Generation with Scene Graph Programming
Dec 11, 2024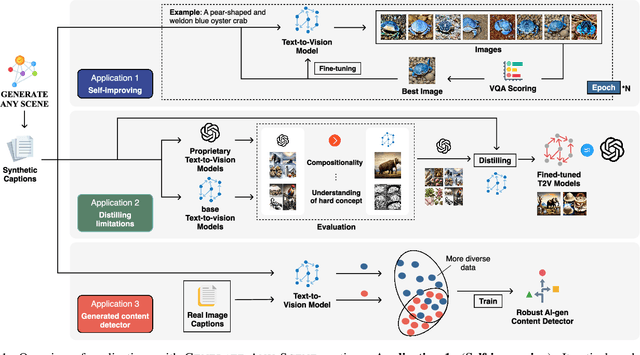
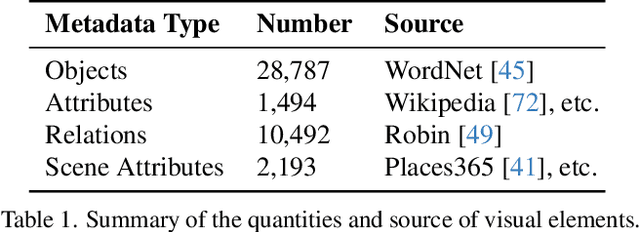
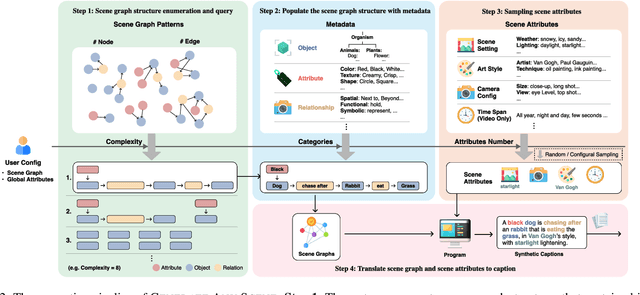
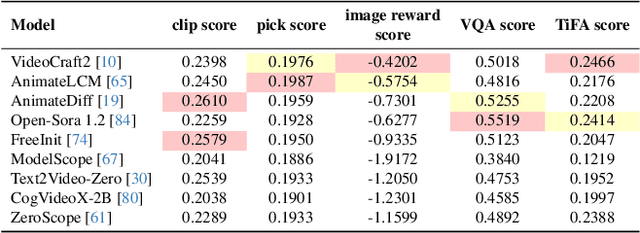
Abstract:DALL-E and Sora have gained attention by producing implausible images, such as "astronauts riding a horse in space." Despite the proliferation of text-to-vision models that have inundated the internet with synthetic visuals, from images to 3D assets, current benchmarks predominantly evaluate these models on real-world scenes paired with captions. We introduce Generate Any Scene, a framework that systematically enumerates scene graphs representing a vast array of visual scenes, spanning realistic to imaginative compositions. Generate Any Scene leverages 'scene graph programming', a method for dynamically constructing scene graphs of varying complexity from a structured taxonomy of visual elements. This taxonomy includes numerous objects, attributes, and relations, enabling the synthesis of an almost infinite variety of scene graphs. Using these structured representations, Generate Any Scene translates each scene graph into a caption, enabling scalable evaluation of text-to-vision models through standard metrics. We conduct extensive evaluations across multiple text-to-image, text-to-video, and text-to-3D models, presenting key findings on model performance. We find that DiT-backbone text-to-image models align more closely with input captions than UNet-backbone models. Text-to-video models struggle with balancing dynamics and consistency, while both text-to-video and text-to-3D models show notable gaps in human preference alignment. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Generate Any Scene by conducting three practical applications leveraging captions generated by Generate Any Scene: 1) a self-improving framework where models iteratively enhance their performance using generated data, 2) a distillation process to transfer specific strengths from proprietary models to open-source counterparts, and 3) improvements in content moderation by identifying and generating challenging synthetic data.
SAT: Spatial Aptitude Training for Multimodal Language Models
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Spatial perception is a fundamental component of intelligence. While many studies highlight that large multimodal language models (MLMs) struggle to reason about space, they only test for static spatial reasoning, such as categorizing the relative positions of objects. Meanwhile, real-world deployment requires dynamic capabilities like perspective-taking and egocentric action recognition. As a roadmap to improving spatial intelligence, we introduce SAT, Spatial Aptitude Training, which goes beyond static relative object position questions to the more dynamic tasks. SAT contains 218K question-answer pairs for 22K synthetic scenes across a training and testing set. Generated using a photo-realistic physics engine, our dataset can be arbitrarily scaled and easily extended to new actions, scenes, and 3D assets. We find that even MLMs that perform relatively well on static questions struggle to accurately answer dynamic spatial questions. Further, we show that SAT instruction-tuning data improves not only dynamic spatial reasoning on SAT, but also zero-shot performance on existing real-image spatial benchmarks: $23\%$ on CVBench, $8\%$ on the harder BLINK benchmark, and $18\%$ on VSR. When instruction-tuned on SAT, our 13B model matches larger proprietary MLMs like GPT4-V and Gemini-3-1.0 in spatial reasoning. Our data/code is available at http://arijitray1993.github.io/SAT/ .
From an Image to a Scene: Learning to Imagine the World from a Million 360 Videos
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Three-dimensional (3D) understanding of objects and scenes play a key role in humans' ability to interact with the world and has been an active area of research in computer vision, graphics, and robotics. Large scale synthetic and object-centric 3D datasets have shown to be effective in training models that have 3D understanding of objects. However, applying a similar approach to real-world objects and scenes is difficult due to a lack of large-scale data. Videos are a potential source for real-world 3D data, but finding diverse yet corresponding views of the same content has shown to be difficult at scale. Furthermore, standard videos come with fixed viewpoints, determined at the time of capture. This restricts the ability to access scenes from a variety of more diverse and potentially useful perspectives. We argue that large scale 360 videos can address these limitations to provide: scalable corresponding frames from diverse views. In this paper, we introduce 360-1M, a 360 video dataset, and a process for efficiently finding corresponding frames from diverse viewpoints at scale. We train our diffusion-based model, Odin, on 360-1M. Empowered by the largest real-world, multi-view dataset to date, Odin is able to freely generate novel views of real-world scenes. Unlike previous methods, Odin can move the camera through the environment, enabling the model to infer the geometry and layout of the scene. Additionally, we show improved performance on standard novel view synthesis and 3D reconstruction benchmarks.
One Diffusion to Generate Them All
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:We introduce OneDiffusion, a versatile, large-scale diffusion model that seamlessly supports bidirectional image synthesis and understanding across diverse tasks. It enables conditional generation from inputs such as text, depth, pose, layout, and semantic maps, while also handling tasks like image deblurring, upscaling, and reverse processes such as depth estimation and segmentation. Additionally, OneDiffusion allows for multi-view generation, camera pose estimation, and instant personalization using sequential image inputs. Our model takes a straightforward yet effective approach by treating all tasks as frame sequences with varying noise scales during training, allowing any frame to act as a conditioning image at inference time. Our unified training framework removes the need for specialized architectures, supports scalable multi-task training, and adapts smoothly to any resolution, enhancing both generalization and scalability. Experimental results demonstrate competitive performance across tasks in both generation and prediction such as text-to-image, multiview generation, ID preservation, depth estimation and camera pose estimation despite relatively small training dataset. Our code and checkpoint are freely available at https://github.com/lehduong/OneDiffusion
Molmo and PixMo: Open Weights and Open Data for State-of-the-Art Multimodal Models
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:Today's most advanced multimodal models remain proprietary. The strongest open-weight models rely heavily on synthetic data from proprietary VLMs to achieve good performance, effectively distilling these closed models into open ones. As a result, the community is still missing foundational knowledge about how to build performant VLMs from scratch. We present Molmo, a new family of VLMs that are state-of-the-art in their class of openness. Our key innovation is a novel, highly detailed image caption dataset collected entirely from human annotators using speech-based descriptions. To enable a wide array of user interactions, we also introduce a diverse dataset mixture for fine-tuning that includes in-the-wild Q&A and innovative 2D pointing data. The success of our approach relies on careful choices for the model architecture details, a well-tuned training pipeline, and, most critically, the quality of our newly collected datasets, all of which will be released. The best-in-class 72B model within the Molmo family not only outperforms others in the class of open weight and data models but also compares favorably against proprietary systems like GPT-4o, Claude 3.5, and Gemini 1.5 on both academic benchmarks and human evaluation. We will be releasing all of our model weights, captioning and fine-tuning data, and source code in the near future. Select model weights, inference code, and demo are available at https://molmo.allenai.org.
FLaRe: Achieving Masterful and Adaptive Robot Policies with Large-Scale Reinforcement Learning Fine-Tuning
Sep 25, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, the Robotics field has initiated several efforts toward building generalist robot policies through large-scale multi-task Behavior Cloning. However, direct deployments of these policies have led to unsatisfactory performance, where the policy struggles with unseen states and tasks. How can we break through the performance plateau of these models and elevate their capabilities to new heights? In this paper, we propose FLaRe, a large-scale Reinforcement Learning fine-tuning framework that integrates robust pre-trained representations, large-scale training, and gradient stabilization techniques. Our method aligns pre-trained policies towards task completion, achieving state-of-the-art (SoTA) performance both on previously demonstrated and on entirely novel tasks and embodiments. Specifically, on a set of long-horizon mobile manipulation tasks, FLaRe achieves an average success rate of 79.5% in unseen environments, with absolute improvements of +23.6% in simulation and +30.7% on real robots over prior SoTA methods. By utilizing only sparse rewards, our approach can enable generalizing to new capabilities beyond the pretraining data with minimal human effort. Moreover, we demonstrate rapid adaptation to new embodiments and behaviors with less than a day of fine-tuning. Videos can be found on the project website at https://robot-flare.github.io/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge