Kyle Lo
Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence
Olmo 3
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:We introduce Olmo 3, a family of state-of-the-art, fully-open language models at the 7B and 32B parameter scales. Olmo 3 model construction targets long-context reasoning, function calling, coding, instruction following, general chat, and knowledge recall. This release includes the entire model flow, i.e., the full lifecycle of the family of models, including every stage, checkpoint, data point, and dependency used to build it. Our flagship model, Olmo 3 Think 32B, is the strongest fully-open thinking model released to-date.
olmOCR 2: Unit Test Rewards for Document OCR
Oct 22, 2025Abstract:We present olmOCR 2, the latest in our family of powerful OCR systems for converting digitized print documents, like PDFs, into clean, naturally ordered plain text. olmOCR 2 is powered by olmOCR-2-7B-1025, a specialized, 7B vision language model (VLM) trained using reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR), where our rewards are a diverse set of binary unit tests. To scale unit test creation, we develop a pipeline for generating synthetic documents with diverse and challenging layouts, known ground-truth HTML source code, and extracted test cases. We show that RL training on these test cases results in state-of-the-art performance on olmOCR-Bench, our English-language OCR benchmark, with the largest improvements in math formula conversion, table parsing, and multi-column layouts compared to previous versions. We release our model, data and code under permissive open licenses.
Signal and Noise: A Framework for Reducing Uncertainty in Language Model Evaluation
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:Developing large language models is expensive and involves making decisions with small experiments, typically by evaluating on large, multi-task evaluation suites. In this work, we analyze specific properties which make a benchmark more reliable for such decisions, and interventions to design higher-quality evaluation benchmarks. We introduce two key metrics that show differences in current benchmarks: signal, a benchmark's ability to separate better models from worse models, and noise, a benchmark's sensitivity to random variability between training steps. We demonstrate that benchmarks with a better signal-to-noise ratio are more reliable when making decisions at small scale, and those with less noise have lower scaling law prediction error. These results suggest that improving signal or noise will lead to more useful benchmarks, so we introduce three interventions designed to directly affect signal or noise. For example, we propose that switching to a metric that has better signal and noise (e.g., perplexity rather than accuracy) leads to better reliability and improved scaling law error. We also find that filtering noisy subtasks, to improve an aggregate signal-to-noise ratio, leads to more reliable multi-task evaluations. We also find that averaging the output of a model's intermediate checkpoints to reduce noise leads to consistent improvements. We conclude by recommending that those creating new benchmarks, or selecting which existing benchmarks to use, aim for high signal and low noise. We use 30 benchmarks for these experiments, and 375 open-weight language models from 60M to 32B parameters, resulting in a new, publicly available dataset of 900K evaluation benchmark results, totaling 200M instances.
FlexOlmo: Open Language Models for Flexible Data Use
Jul 09, 2025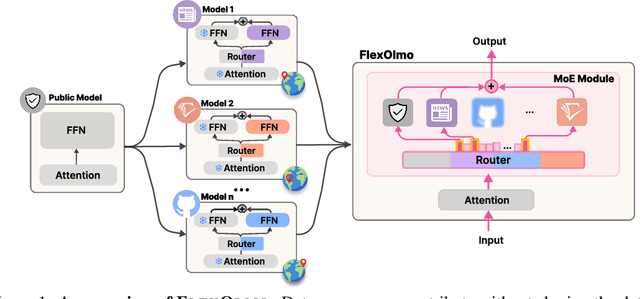
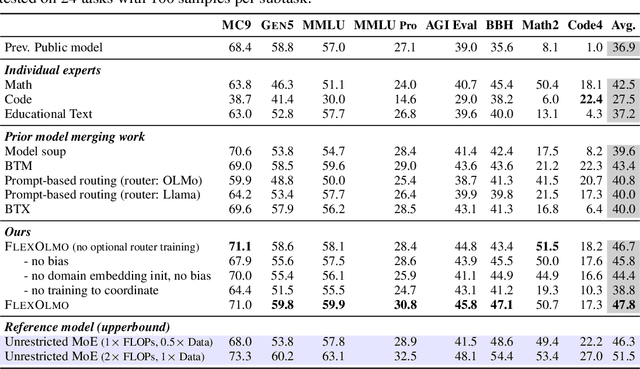
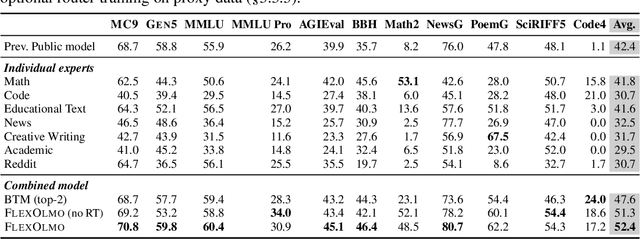
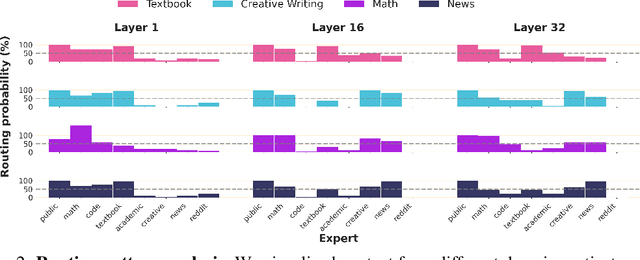
Abstract:We introduce FlexOlmo, a new class of language models (LMs) that supports (1) distributed training without data sharing, where different model parameters are independently trained on closed datasets, and (2) data-flexible inference, where these parameters along with their associated data can be flexibly included or excluded from model inferences with no further training. FlexOlmo employs a mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture where each expert is trained independently on closed datasets and later integrated through a new domain-informed routing without any joint training. FlexOlmo is trained on FlexMix, a corpus we curate comprising publicly available datasets alongside seven domain-specific sets, representing realistic approximations of closed sets. We evaluate models with up to 37 billion parameters (20 billion active) on 31 diverse downstream tasks. We show that a general expert trained on public data can be effectively combined with independently trained experts from other data owners, leading to an average 41% relative improvement while allowing users to opt out of certain data based on data licensing or permission requirements. Our approach also outperforms prior model merging methods by 10.1% on average and surpasses the standard MoE trained without data restrictions using the same training FLOPs. Altogether, this research presents a solution for both data owners and researchers in regulated industries with sensitive or protected data. FlexOlmo enables benefiting from closed data while respecting data owners' preferences by keeping their data local and supporting fine-grained control of data access during inference.
Automatic Detection of Research Values from Scientific Abstracts Across Computer Science Subfields
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:The field of Computer science (CS) has rapidly evolved over the past few decades, providing computational tools and methodologies to various fields and forming new interdisciplinary communities. This growth in CS has significantly impacted institutional practices and relevant research communities. Therefore, it is crucial to explore what specific research values, known as basic and fundamental beliefs that guide or motivate research attitudes or actions, CS-related research communities promote. Prior research has manually analyzed research values from a small sample of machine learning papers. No prior work has studied the automatic detection of research values in CS from large-scale scientific texts across different research subfields. This paper introduces a detailed annotation scheme featuring ten research values that guide CS-related research. Based on the scheme, we build value classifiers to scale up the analysis and present a systematic study over 226,600 paper abstracts from 32 CS-related subfields and 86 popular publishing venues over ten years.
olmOCR: Unlocking Trillions of Tokens in PDFs with Vision Language Models
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:PDF documents have the potential to provide trillions of novel, high-quality tokens for training language models. However, these documents come in a diversity of types with differing formats and visual layouts that pose a challenge when attempting to extract and faithfully represent the underlying content for language model use. We present olmOCR, an open-source Python toolkit for processing PDFs into clean, linearized plain text in natural reading order while preserving structured content like sections, tables, lists, equations, and more. Our toolkit runs a fine-tuned 7B vision language model (VLM) trained on a sample of 260,000 pages from over 100,000 crawled PDFs with diverse properties, including graphics, handwritten text and poor quality scans. olmOCR is optimized for large-scale batch processing, able to scale flexibly to different hardware setups and convert a million PDF pages for only $190 USD. We release all components of olmOCR including VLM weights, data and training code, as well as inference code built on serving frameworks including vLLM and SGLang.
DrawEduMath: Evaluating Vision Language Models with Expert-Annotated Students' Hand-Drawn Math Images
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:In real-world settings, vision language models (VLMs) should robustly handle naturalistic, noisy visual content as well as domain-specific language and concepts. For example, K-12 educators using digital learning platforms may need to examine and provide feedback across many images of students' math work. To assess the potential of VLMs to support educators in settings like this one, we introduce DrawEduMath, an English-language dataset of 2,030 images of students' handwritten responses to K-12 math problems. Teachers provided detailed annotations, including free-form descriptions of each image and 11,661 question-answer (QA) pairs. These annotations capture a wealth of pedagogical insights, ranging from students' problem-solving strategies to the composition of their drawings, diagrams, and writing. We evaluate VLMs on teachers' QA pairs, as well as 44,362 synthetic QA pairs derived from teachers' descriptions using language models (LMs). We show that even state-of-the-art VLMs leave much room for improvement on DrawEduMath questions. We also find that synthetic QAs, though imperfect, can yield similar model rankings as teacher-written QAs. We release DrawEduMath to support the evaluation of VLMs' abilities to reason mathematically over images gathered with educational contexts in mind.
2 OLMo 2 Furious
Dec 31, 2024
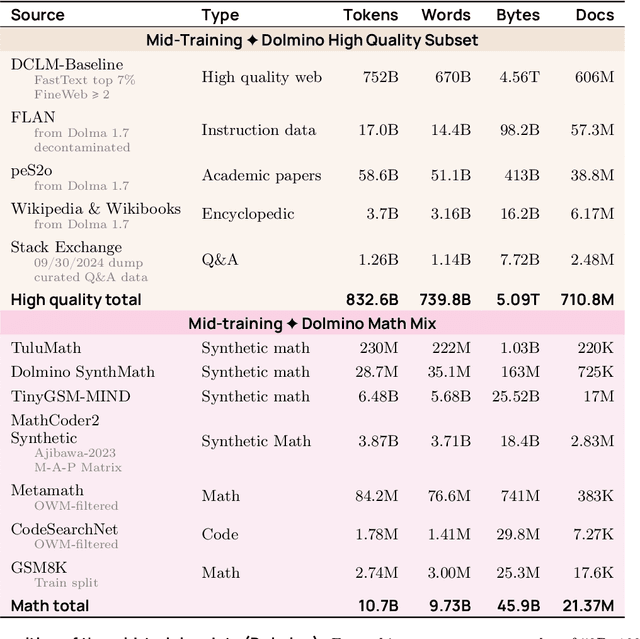
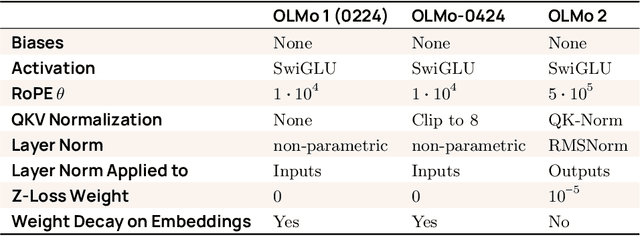

Abstract:We present OLMo 2, the next generation of our fully open language models. OLMo 2 includes dense autoregressive models with improved architecture and training recipe, pretraining data mixtures, and instruction tuning recipes. Our modified model architecture and training recipe achieve both better training stability and improved per-token efficiency. Our updated pretraining data mixture introduces a new, specialized data mix called Dolmino Mix 1124, which significantly improves model capabilities across many downstream task benchmarks when introduced via late-stage curriculum training (i.e. specialized data during the annealing phase of pretraining). Finally, we incorporate best practices from T\"ulu 3 to develop OLMo 2-Instruct, focusing on permissive data and extending our final-stage reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR). Our OLMo 2 base models sit at the Pareto frontier of performance to compute, often matching or outperforming open-weight only models like Llama 3.1 and Qwen 2.5 while using fewer FLOPs and with fully transparent training data, code, and recipe. Our fully open OLMo 2-Instruct models are competitive with or surpassing open-weight only models of comparable size, including Qwen 2.5, Llama 3.1 and Gemma 2. We release all OLMo 2 artifacts openly -- models at 7B and 13B scales, both pretrained and post-trained, including their full training data, training code and recipes, training logs and thousands of intermediate checkpoints. The final instruction model is available on the Ai2 Playground as a free research demo.
OpenScholar: Synthesizing Scientific Literature with Retrieval-augmented LMs
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:Scientific progress depends on researchers' ability to synthesize the growing body of literature. Can large language models (LMs) assist scientists in this task? We introduce OpenScholar, a specialized retrieval-augmented LM that answers scientific queries by identifying relevant passages from 45 million open-access papers and synthesizing citation-backed responses. To evaluate OpenScholar, we develop ScholarQABench, the first large-scale multi-domain benchmark for literature search, comprising 2,967 expert-written queries and 208 long-form answers across computer science, physics, neuroscience, and biomedicine. On ScholarQABench, OpenScholar-8B outperforms GPT-4o by 5% and PaperQA2 by 7% in correctness, despite being a smaller, open model. While GPT4o hallucinates citations 78 to 90% of the time, OpenScholar achieves citation accuracy on par with human experts. OpenScholar's datastore, retriever, and self-feedback inference loop also improves off-the-shelf LMs: for instance, OpenScholar-GPT4o improves GPT-4o's correctness by 12%. In human evaluations, experts preferred OpenScholar-8B and OpenScholar-GPT4o responses over expert-written ones 51% and 70% of the time, respectively, compared to GPT4o's 32%. We open-source all of our code, models, datastore, data and a public demo.
Contextualized Evaluations: Taking the Guesswork Out of Language Model Evaluations
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Language model users often issue queries that lack specification, where the context under which a query was issued -- such as the user's identity, the query's intent, and the criteria for a response to be useful -- is not explicit. For instance, a good response to a subjective query like "What book should I read next?" would depend on the user's preferences, and a good response to an open-ended query like "How do antibiotics work against bacteria?" would depend on the user's expertise. This makes evaluation of responses to such queries an ill-posed task, as evaluators may make arbitrary judgments about the response quality. To remedy this, we present contextualized evaluations, a protocol that synthetically constructs context surrounding an underspecified query and provides it during evaluation. We find that the presence of context can 1) alter conclusions drawn from evaluation, even flipping win rates between model pairs, 2) nudge evaluators to make fewer judgments based on surface-level criteria, like style, and 3) provide new insights about model behavior across diverse contexts. Specifically, our procedure uncovers an implicit bias towards WEIRD contexts in models' "default" responses and we find that models are not equally sensitive to following different contexts, even when they are provided in prompts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge