Valentin Hofmann
Can Large Language Models Generalize Procedures Across Representations?
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are trained and tested extensively on symbolic representations such as code and graphs, yet real-world user tasks are often specified in natural language. To what extent can LLMs generalize across these representations? Here, we approach this question by studying isomorphic tasks involving procedures represented in code, graphs, and natural language (e.g., scheduling steps in planning). We find that training LLMs with popular post-training methods on graphs or code data alone does not reliably generalize to corresponding natural language tasks, while training solely on natural language can lead to inefficient performance gains. To address this gap, we propose a two-stage data curriculum that first trains on symbolic, then natural language data. The curriculum substantially improves model performance across model families and tasks. Remarkably, a 1.5B Qwen model trained by our method can closely match zero-shot GPT-4o in naturalistic planning. Finally, our analysis suggests that successful cross-representation generalization can be interpreted as a form of generative analogy, which our curriculum effectively encourages.
Demographic Probing of Large Language Models Lacks Construct Validity
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Demographic probing is widely used to study how large language models (LLMs) adapt their behavior to signaled demographic attributes. This approach typically uses a single demographic cue in isolation (e.g., a name or dialect) as a signal for group membership, implicitly assuming strong construct validity: that such cues are interchangeable operationalizations of the same underlying, demographically conditioned behavior. We test this assumption in realistic advice-seeking interactions, focusing on race and gender in a U.S. context. We find that cues intended to represent the same demographic group induce only partially overlapping changes in model behavior, while differentiation between groups within a given cue is weak and uneven. Consequently, estimated disparities are unstable, with both magnitude and direction varying across cues. We further show that these inconsistencies partly arise from variation in how strongly cues encode demographic attributes and from linguistic confounders that independently shape model behavior. Together, our findings suggest that demographic probing lacks construct validity: it does not yield a single, stable characterization of how LLMs condition on demographic information, which may reflect a misspecified or fragmented construct. We conclude by recommending the use of multiple, ecologically valid cues and explicit control of confounders to support more defensible claims about demographic effects in LLMs.
Bolmo: Byteifying the Next Generation of Language Models
Dec 17, 2025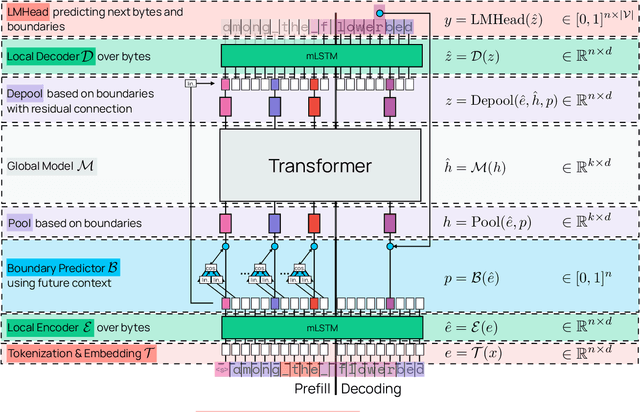
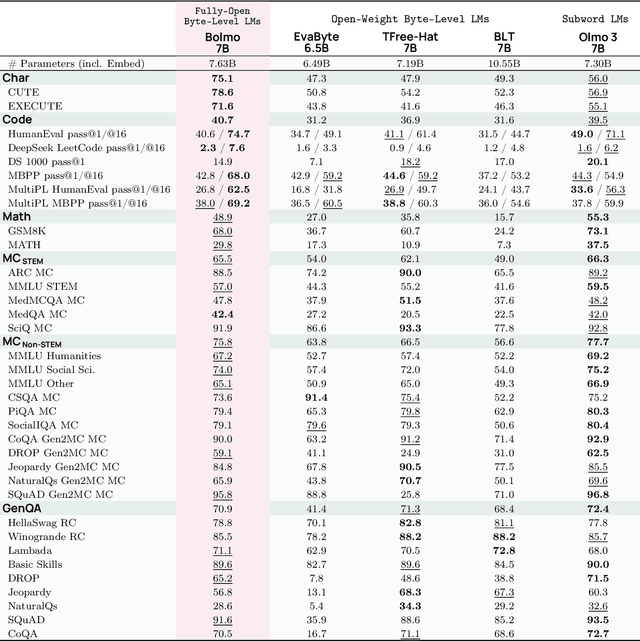
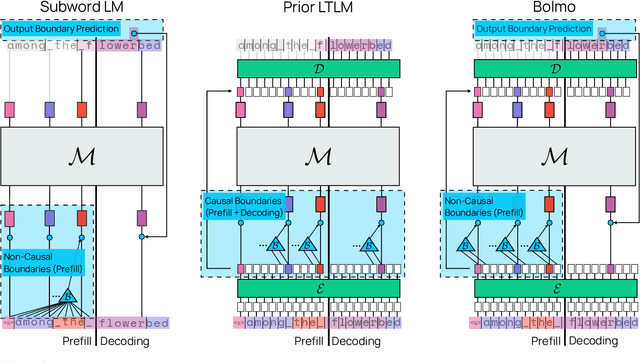
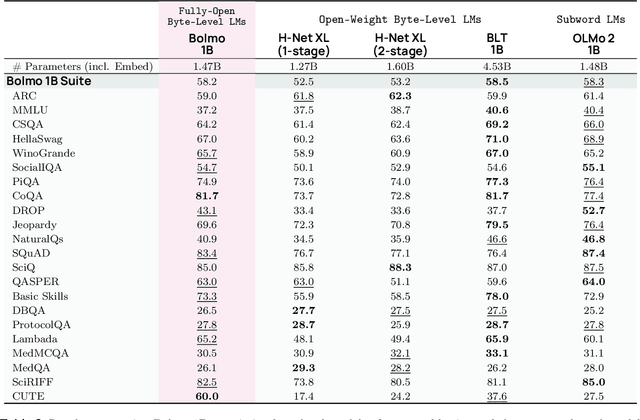
Abstract:We introduce Bolmo, the first family of competitive fully open byte-level language models (LMs) at the 1B and 7B parameter scales. In contrast to prior research on byte-level LMs, which focuses predominantly on training from scratch, we train Bolmo by byteifying existing subword-level LMs. Byteification enables overcoming the limitations of subword tokenization - such as insufficient character understanding and efficiency constraints due to the fixed subword vocabulary - while performing at the level of leading subword-level LMs. Bolmo is specifically designed for byteification: our architecture resolves a mismatch between the expressivity of prior byte-level architectures and subword-level LMs, which makes it possible to employ an effective exact distillation objective between Bolmo and the source subword model. This allows for converting a subword-level LM to a byte-level LM by investing less than 1\% of a typical pretraining token budget. Bolmo substantially outperforms all prior byte-level LMs of comparable size, and outperforms the source subword-level LMs on character understanding and, in some cases, coding, while coming close to matching the original LMs' performance on other tasks. Furthermore, we show that Bolmo can achieve inference speeds competitive with subword-level LMs by training with higher token compression ratios, and can be cheaply and effectively post-trained by leveraging the existing ecosystem around the source subword-level LM. Our results finally make byte-level LMs a practical choice competitive with subword-level LMs across a wide set of use cases.
Large Language Models Discriminate Against Speakers of German Dialects
Sep 17, 2025Abstract:Dialects represent a significant component of human culture and are found across all regions of the world. In Germany, more than 40% of the population speaks a regional dialect (Adler and Hansen, 2022). However, despite cultural importance, individuals speaking dialects often face negative societal stereotypes. We examine whether such stereotypes are mirrored by large language models (LLMs). We draw on the sociolinguistic literature on dialect perception to analyze traits commonly associated with dialect speakers. Based on these traits, we assess the dialect naming bias and dialect usage bias expressed by LLMs in two tasks: an association task and a decision task. To assess a model's dialect usage bias, we construct a novel evaluation corpus that pairs sentences from seven regional German dialects (e.g., Alemannic and Bavarian) with their standard German counterparts. We find that: (1) in the association task, all evaluated LLMs exhibit significant dialect naming and dialect usage bias against German dialect speakers, reflected in negative adjective associations; (2) all models reproduce these dialect naming and dialect usage biases in their decision making; and (3) contrary to prior work showing minimal bias with explicit demographic mentions, we find that explicitly labeling linguistic demographics--German dialect speakers--amplifies bias more than implicit cues like dialect usage.
Signal and Noise: A Framework for Reducing Uncertainty in Language Model Evaluation
Aug 18, 2025Abstract:Developing large language models is expensive and involves making decisions with small experiments, typically by evaluating on large, multi-task evaluation suites. In this work, we analyze specific properties which make a benchmark more reliable for such decisions, and interventions to design higher-quality evaluation benchmarks. We introduce two key metrics that show differences in current benchmarks: signal, a benchmark's ability to separate better models from worse models, and noise, a benchmark's sensitivity to random variability between training steps. We demonstrate that benchmarks with a better signal-to-noise ratio are more reliable when making decisions at small scale, and those with less noise have lower scaling law prediction error. These results suggest that improving signal or noise will lead to more useful benchmarks, so we introduce three interventions designed to directly affect signal or noise. For example, we propose that switching to a metric that has better signal and noise (e.g., perplexity rather than accuracy) leads to better reliability and improved scaling law error. We also find that filtering noisy subtasks, to improve an aggregate signal-to-noise ratio, leads to more reliable multi-task evaluations. We also find that averaging the output of a model's intermediate checkpoints to reduce noise leads to consistent improvements. We conclude by recommending that those creating new benchmarks, or selecting which existing benchmarks to use, aim for high signal and low noise. We use 30 benchmarks for these experiments, and 375 open-weight language models from 60M to 32B parameters, resulting in a new, publicly available dataset of 900K evaluation benchmark results, totaling 200M instances.
BLAB: Brutally Long Audio Bench
May 05, 2025Abstract:Developing large audio language models (LMs) capable of understanding diverse spoken interactions is essential for accommodating the multimodal nature of human communication and can increase the accessibility of language technologies across different user populations. Recent work on audio LMs has primarily evaluated their performance on short audio segments, typically under 30 seconds, with limited exploration of long-form conversational speech segments that more closely reflect natural user interactions with these models. We introduce Brutally Long Audio Bench (BLAB), a challenging long-form audio benchmark that evaluates audio LMs on localization, duration estimation, emotion, and counting tasks using audio segments averaging 51 minutes in length. BLAB consists of 833+ hours of diverse, full-length audio clips, each paired with human-annotated, text-based natural language questions and answers. Our audio data were collected from permissively licensed sources and underwent a human-assisted filtering process to ensure task compliance. We evaluate six open-source and proprietary audio LMs on BLAB and find that all of them, including advanced models such as Gemini 2.0 Pro and GPT-4o, struggle with the tasks in BLAB. Our comprehensive analysis reveals key insights into the trade-offs between task difficulty and audio duration. In general, we find that audio LMs struggle with long-form speech, with performance declining as duration increases. They perform poorly on localization, temporal reasoning, counting, and struggle to understand non-phonemic information, relying more on prompts than audio content. BLAB serves as a challenging evaluation framework to develop audio LMs with robust long-form audio understanding capabilities.
SuperBPE: Space Travel for Language Models
Mar 17, 2025



Abstract:The assumption across nearly all language model (LM) tokenization schemes is that tokens should be subwords, i.e., contained within word boundaries. While providing a seemingly reasonable inductive bias, is this common practice limiting the potential of modern LMs? Whitespace is not a reliable delimiter of meaning, as evidenced by multi-word expressions (e.g., "by the way"), crosslingual variation in the number of words needed to express a concept (e.g., "spacesuit helmet" in German is "raumanzughelm"), and languages that do not use whitespace at all (e.g., Chinese). To explore the potential of tokenization beyond subwords, we introduce a "superword" tokenizer, SuperBPE, which incorporates a simple pretokenization curriculum into the byte-pair encoding (BPE) algorithm to first learn subwords, then superwords that bridge whitespace. This brings dramatic improvements in encoding efficiency: when fixing the vocabulary size to 200k, SuperBPE encodes a fixed piece of text with up to 33% fewer tokens than BPE on average. In experiments, we pretrain 8B transformer LMs from scratch while fixing the model size, vocabulary size, and train compute, varying *only* the algorithm for learning the vocabulary. Our model trained with SuperBPE achieves an average +4.0% absolute improvement over the BPE baseline across 30 downstream tasks (including +8.2% on MMLU), while simultaneously requiring 27% less compute at inference time. In analysis, we find that SuperBPE results in segmentations of text that are more uniform in per-token difficulty. Qualitatively, this may be because SuperBPE tokens often capture common multi-word expressions that function semantically as a single unit. SuperBPE is a straightforward, local modification to tokenization that improves both encoding efficiency and downstream performance, yielding better language models overall.
IssueBench: Millions of Realistic Prompts for Measuring Issue Bias in LLM Writing Assistance
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are helping millions of users write texts about diverse issues, and in doing so expose users to different ideas and perspectives. This creates concerns about issue bias, where an LLM tends to present just one perspective on a given issue, which in turn may influence how users think about this issue. So far, it has not been possible to measure which issue biases LLMs actually manifest in real user interactions, making it difficult to address the risks from biased LLMs. Therefore, we create IssueBench: a set of 2.49m realistic prompts for measuring issue bias in LLM writing assistance, which we construct based on 3.9k templates (e.g. "write a blog about") and 212 political issues (e.g. "AI regulation") from real user interactions. Using IssueBench, we show that issue biases are common and persistent in state-of-the-art LLMs. We also show that biases are remarkably similar across models, and that all models align more with US Democrat than Republican voter opinion on a subset of issues. IssueBench can easily be adapted to include other issues, templates, or tasks. By enabling robust and realistic measurement, we hope that IssueBench can bring a new quality of evidence to ongoing discussions about LLM biases and how to address them.
Derivational Morphology Reveals Analogical Generalization in Large Language Models
Nov 12, 2024



Abstract:What mechanisms underlie linguistic generalization in large language models (LLMs)? This question has attracted considerable attention, with most studies analyzing the extent to which the language skills of LLMs resemble rules. As of yet, it is not known whether linguistic generalization in LLMs could equally well be explained as the result of analogical processes, which can be formalized as similarity operations on stored exemplars. A key shortcoming of prior research is its focus on linguistic phenomena with a high degree of regularity, for which rule-based and analogical approaches make the same predictions. Here, we instead examine derivational morphology, specifically English adjective nominalization, which displays notable variability. We introduce a new method for investigating linguistic generalization in LLMs: focusing on GPT-J, we fit cognitive models that instantiate rule-based and analogical learning to the LLM training data and compare their predictions on a set of nonce adjectives with those of the LLM, allowing us to draw direct conclusions regarding underlying mechanisms. As expected, rule-based and analogical models explain the predictions of GPT-J equally well for adjectives with regular nominalization patterns. However, for adjectives with variable nominalization patterns, the analogical model provides a much better match. Furthermore, GPT-J's behavior is sensitive to the individual word frequencies, even for regular forms, a behavior that is consistent with an analogical account of regular forms but not a rule-based one. These findings refute the hypothesis that GPT-J's linguistic generalization on adjective nominalization involves rules, suggesting similarity operations on stored exemplars as the underlying mechanism. Overall, our study suggests that analogical processes play a bigger role in the linguistic generalization of LLMs than previously thought.
One Language, Many Gaps: Evaluating Dialect Fairness and Robustness of Large Language Models in Reasoning Tasks
Oct 14, 2024


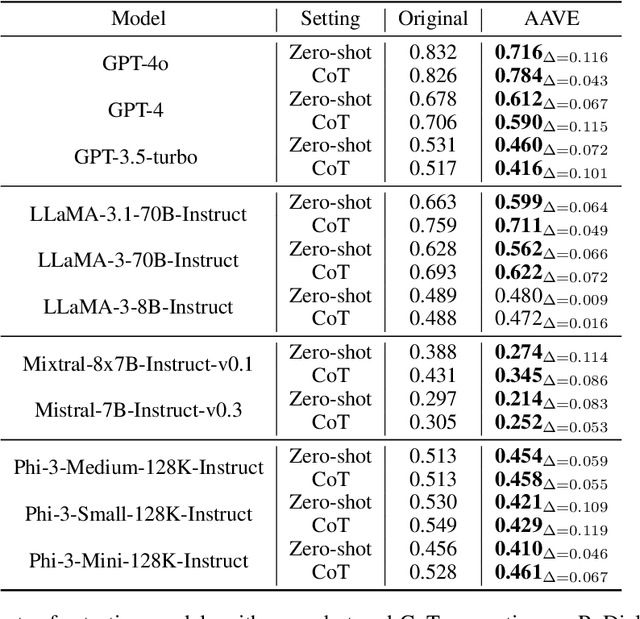
Abstract:Language is not monolithic. While many benchmarks are used as proxies to systematically estimate Large Language Models' (LLM) performance in real-life tasks, they tend to ignore the nuances of within-language variation and thus fail to model the experience of speakers of minority dialects. Focusing on African American Vernacular English (AAVE), we present the first study on LLMs' fairness and robustness to a dialect in canonical reasoning tasks (algorithm, math, logic, and comprehensive reasoning). We hire AAVE speakers, including experts with computer science backgrounds, to rewrite seven popular benchmarks, such as HumanEval and GSM8K. The result of this effort is ReDial, a dialectal benchmark comprising $1.2K+$ parallel query pairs in Standardized English and AAVE. We use ReDial to evaluate state-of-the-art LLMs, including GPT-4o/4/3.5-turbo, LLaMA-3.1/3, Mistral, and Phi-3. We find that, compared to Standardized English, almost all of these widely used models show significant brittleness and unfairness to queries in AAVE. Furthermore, AAVE queries can degrade performance more substantially than misspelled texts in Standardized English, even when LLMs are more familiar with the AAVE queries. Finally, asking models to rephrase questions in Standardized English does not close the performance gap but generally introduces higher costs. Overall, our findings indicate that LLMs provide unfair service to dialect users in complex reasoning tasks. Code can be found at https://github.com/fangru-lin/redial_dialect_robustness_fairness.git.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge