Dan Jurafsky
Beyond Tokens: Concept-Level Training Objectives for LLMs
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:The next-token prediction (NTP) objective has been foundational in the development of modern large language models (LLMs), driving advances in fluency and generalization. However, NTP operates at the \textit{token} level, treating deviations from a single reference continuation as errors even when alternative continuations are equally plausible or semantically equivalent (e.g., ``mom'' vs. ``mother''). As a result, token-level loss can penalize valid abstractions, paraphrases, or conceptually correct reasoning paths, biasing models toward surface form rather than underlying meaning. This mismatch between the training signal and semantic correctness motivates learning objectives that operate over higher-level representations. We propose a shift from token-level to concept-level prediction, where concepts group multiple surface forms of the same idea (e.g., ``mom,'' ``mommy,'' ``mother'' $\rightarrow$ \textit{MOTHER}). We introduce various methods for integrating conceptual supervision into LLM training and show that concept-aware models achieve lower perplexity, improved robustness under domain shift, and stronger performance than NTP-based models on diverse NLP benchmarks. This suggests \textit{concept-level supervision} as an improved training signal that better aligns LLMs with human semantic abstractions.
The Roots of Performance Disparity in Multilingual Language Models: Intrinsic Modeling Difficulty or Design Choices?
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Multilingual language models (LMs) promise broader NLP access, yet current systems deliver uneven performance across the world's languages. This survey examines why these gaps persist and whether they reflect intrinsic linguistic difficulty or modeling artifacts. We organize the literature around two questions: do linguistic disparities arise from representation and allocation choices (e.g., tokenization, encoding, data exposure, parameter sharing) rather than inherent complexity; and which design choices mitigate inequities across typologically diverse languages. We review linguistic features, such as orthography, morphology, lexical diversity, syntax, information density, and typological distance, linking each to concrete modeling mechanisms. Gaps often shrink when segmentation, encoding, and data exposure are normalized, suggesting much apparent difficulty stems from current modeling choices. We synthesize these insights into design recommendations for tokenization, sampling, architectures, and evaluation to support more balanced multilingual LMs.
Categorize Early, Integrate Late: Divergent Processing Strategies in Automatic Speech Recognition
Jan 11, 2026Abstract:In speech language modeling, two architectures dominate the frontier: the Transformer and the Conformer. However, it remains unknown whether their comparable performance stems from convergent processing strategies or distinct architectural inductive biases. We introduce Architectural Fingerprinting, a probing framework that isolates the effect of architecture on representation, and apply it to a controlled suite of 24 pre-trained encoders (39M-3.3B parameters). Our analysis reveals divergent hierarchies: Conformers implement a "Categorize Early" strategy, resolving phoneme categories 29% earlier in depth and speaker gender by 16% depth. In contrast, Transformers "Integrate Late," deferring phoneme, accent, and duration encoding to deep layers (49-57%). These fingerprints suggest design heuristics: Conformers' front-loaded categorization may benefit low-latency streaming, while Transformers' deep integration may favor tasks requiring rich context and cross-utterance normalization.
Accommodation and Epistemic Vigilance: A Pragmatic Account of Why LLMs Fail to Challenge Harmful Beliefs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) frequently fail to challenge users' harmful beliefs in domains ranging from medical advice to social reasoning. We argue that these failures can be understood and addressed pragmatically as consequences of LLMs defaulting to accommodating users' assumptions and exhibiting insufficient epistemic vigilance. We show that social and linguistic factors known to influence accommodation in humans (at-issueness, linguistic encoding, and source reliability) similarly affect accommodation in LLMs, explaining performance differences across three safety benchmarks that test models' ability to challenge harmful beliefs, spanning misinformation (Cancer-Myth, SAGE-Eval) and sycophancy (ELEPHANT). We further show that simple pragmatic interventions, such as adding the phrase "wait a minute", significantly improve performance on these benchmarks while preserving low false-positive rates. Our results highlight the importance of considering pragmatics for evaluating LLM behavior and improving LLM safety.
Generation Space Size: Understanding and Calibrating Open-Endedness of LLM Generations
Oct 14, 2025



Abstract:Different open-ended generation tasks require different degrees of output diversity. However, current LLMs are often miscalibrated. They collapse to overly homogeneous outputs for creative tasks and hallucinate diverse but incorrect responses for factual tasks. We argue that these two failure modes are unified by, and can both be addressed by, the notion of effective generation space size (GSS) -- the set of semantically distinct outputs a model considers for a prompt. We present GSSBench, a task suite of prompt pairs with ground-truth GSS relationships to assess different metrics and understand where models diverge from desired behavior. We find that hallucination detection metrics, particularly EigenScore, consistently outperform standard diversity and uncertainty quantification metrics, while using only model internals, providing interpretable insights into a model's internal task representations. We demonstrate three applications of GSS: (1) detecting prompt ambiguity and predicting clarification questions for better grounding, (2) interpreting overthinking and underthinking in reasoning models, and (3) steering models to expand their generation space to yield high-quality and diverse outputs.
Sycophantic AI Decreases Prosocial Intentions and Promotes Dependence
Oct 01, 2025



Abstract:Both the general public and academic communities have raised concerns about sycophancy, the phenomenon of artificial intelligence (AI) excessively agreeing with or flattering users. Yet, beyond isolated media reports of severe consequences, like reinforcing delusions, little is known about the extent of sycophancy or how it affects people who use AI. Here we show the pervasiveness and harmful impacts of sycophancy when people seek advice from AI. First, across 11 state-of-the-art AI models, we find that models are highly sycophantic: they affirm users' actions 50% more than humans do, and they do so even in cases where user queries mention manipulation, deception, or other relational harms. Second, in two preregistered experiments (N = 1604), including a live-interaction study where participants discuss a real interpersonal conflict from their life, we find that interaction with sycophantic AI models significantly reduced participants' willingness to take actions to repair interpersonal conflict, while increasing their conviction of being in the right. However, participants rated sycophantic responses as higher quality, trusted the sycophantic AI model more, and were more willing to use it again. This suggests that people are drawn to AI that unquestioningly validate, even as that validation risks eroding their judgment and reducing their inclination toward prosocial behavior. These preferences create perverse incentives both for people to increasingly rely on sycophantic AI models and for AI model training to favor sycophancy. Our findings highlight the necessity of explicitly addressing this incentive structure to mitigate the widespread risks of AI sycophancy.
The ML-SUPERB 2.0 Challenge: Towards Inclusive ASR Benchmarking for All Language Varieties
Sep 08, 2025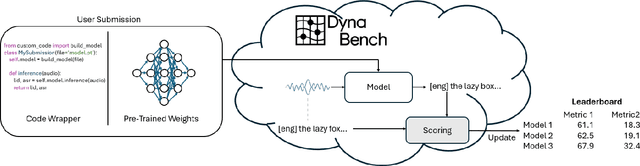
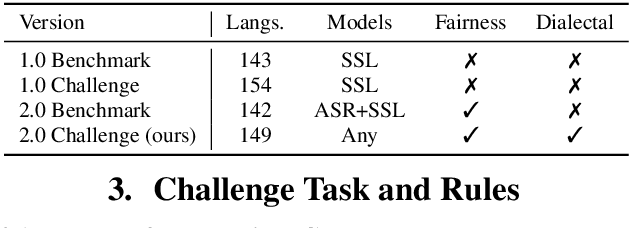
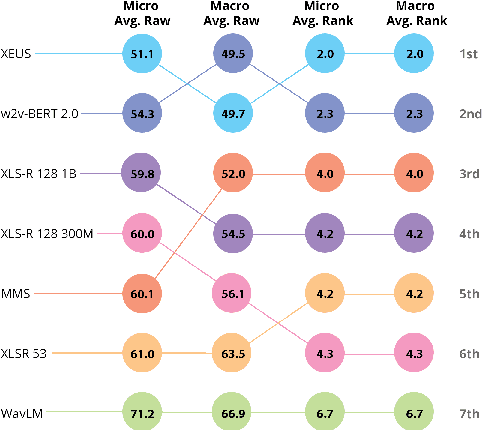
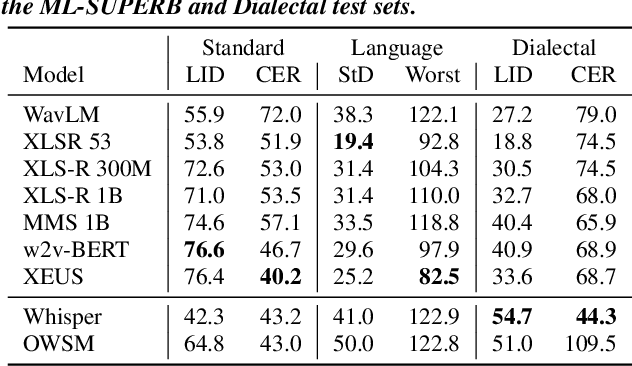
Abstract:Recent improvements in multilingual ASR have not been equally distributed across languages and language varieties. To advance state-of-the-art (SOTA) ASR models, we present the Interspeech 2025 ML-SUPERB 2.0 Challenge. We construct a new test suite that consists of data from 200+ languages, accents, and dialects to evaluate SOTA multilingual speech models. The challenge also introduces an online evaluation server based on DynaBench, allowing for flexibility in model design and architecture for participants. The challenge received 5 submissions from 3 teams, all of which outperformed our baselines. The best-performing submission achieved an absolute improvement in LID accuracy of 23% and a reduction in CER of 18% when compared to the best baseline on a general multilingual test set. On accented and dialectal data, the best submission obtained 30.2% lower CER and 15.7% higher LID accuracy, showing the importance of community challenges in making speech technologies more inclusive.
Humans overrely on overconfident language models, across languages
Jul 08, 2025



Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) are deployed globally, it is crucial that their responses are calibrated across languages to accurately convey uncertainty and limitations. Previous work has shown that LLMs are linguistically overconfident in English, leading users to overrely on confident generations. However, the usage and interpretation of epistemic markers (e.g., 'It's definitely,' 'I think') can differ sharply across languages. Here, we study the risks of multilingual linguistic (mis)calibration, overconfidence, and overreliance across five languages to evaluate the safety of LLMs in a global context. We find that overreliance risks are high across all languages. We first analyze the distribution of LLM-generated epistemic markers, and observe that while LLMs are cross-linguistically overconfident, they are also sensitive to documented linguistic variation. For example, models generate the most markers of uncertainty in Japanese and the most markers of certainty in German and Mandarin. We then measure human reliance rates across languages, finding that while users strongly rely on confident LLM generations in all languages, reliance behaviors differ cross-linguistically: for example, users rely significantly more on expressions of uncertainty in Japanese than in English. Taken together, these results indicate high risk of reliance on overconfident model generations across languages. Our findings highlight the challenges of multilingual linguistic calibration and stress the importance of culturally and linguistically contextualized model safety evaluations.
Mechanistic evaluation of Transformers and state space models
May 21, 2025Abstract:State space models (SSMs) for language modelling promise an efficient and performant alternative to quadratic-attention Transformers, yet show variable performance on recalling basic information from the context. While performance on synthetic tasks like Associative Recall (AR) can point to this deficiency, behavioural metrics provide little information as to why--on a mechanistic level--certain architectures fail and others succeed. To address this, we conduct experiments on AR and find that only Transformers and Based SSM models fully succeed at AR, with Mamba a close third, whereas the other SSMs (H3, Hyena) fail. We then use causal interventions to explain why. We find that Transformers and Based learn to store key-value associations in-context using induction heads. By contrast, the SSMs compute these associations only at the last state, with only Mamba succeeding because of its short convolution component. To extend and deepen these findings, we introduce Associative Treecall (ATR), a synthetic task similar to AR based on PCFG induction. ATR introduces language-like hierarchical structure into the AR setting. We find that all architectures learn the same mechanism as they did for AR, and the same three models succeed at the task. These results reveal that architectures with similar accuracy may still have substantive differences, motivating the adoption of mechanistic evaluations.
From Tokens to Thoughts: How LLMs and Humans Trade Compression for Meaning
May 21, 2025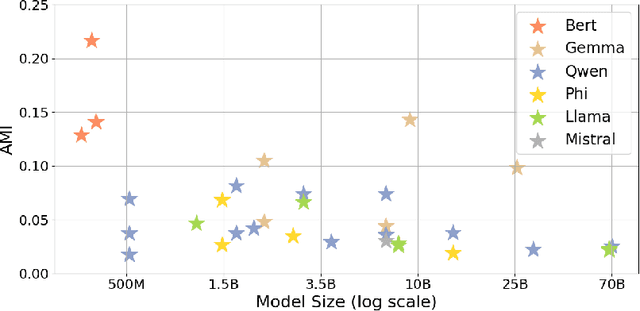
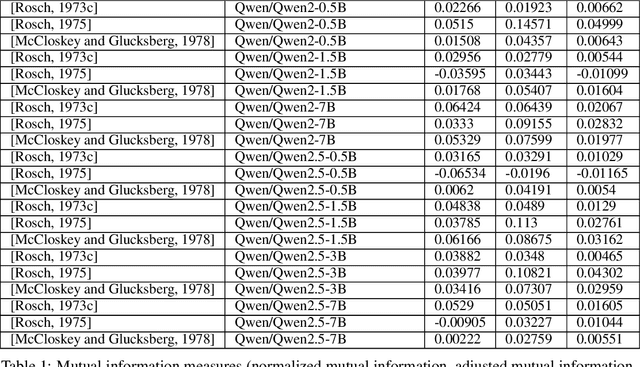
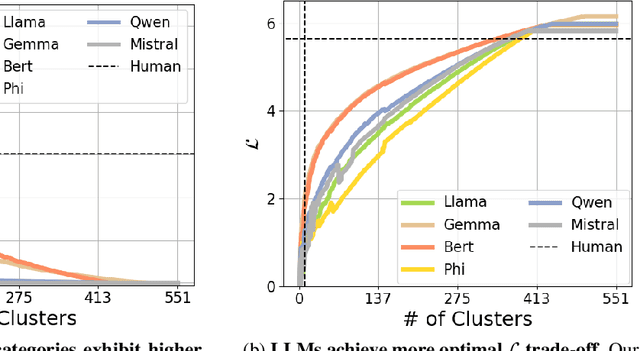
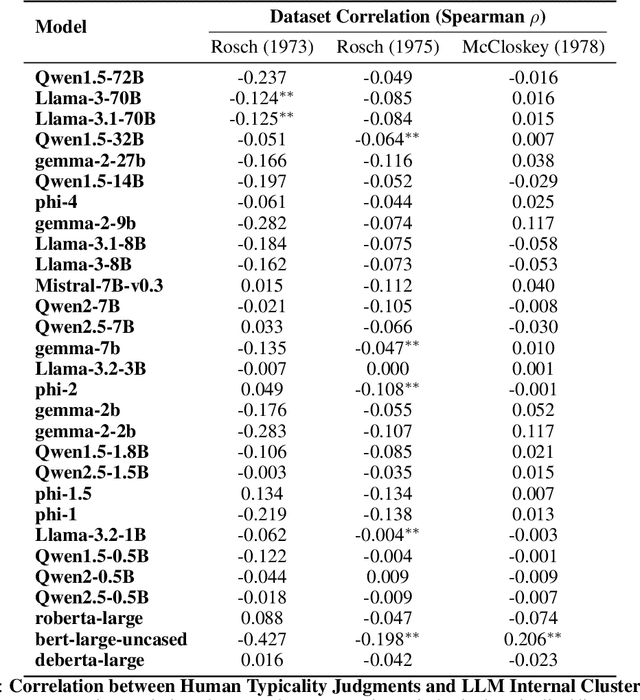
Abstract:Humans organize knowledge into compact categories through semantic compression by mapping diverse instances to abstract representations while preserving meaning (e.g., robin and blue jay are both birds; most birds can fly). These concepts reflect a trade-off between expressive fidelity and representational simplicity. Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable linguistic abilities, yet whether their internal representations strike a human-like trade-off between compression and semantic fidelity is unclear. We introduce a novel information-theoretic framework, drawing from Rate-Distortion Theory and the Information Bottleneck principle, to quantitatively compare these strategies. Analyzing token embeddings from a diverse suite of LLMs against seminal human categorization benchmarks, we uncover key divergences. While LLMs form broad conceptual categories that align with human judgment, they struggle to capture the fine-grained semantic distinctions crucial for human understanding. More fundamentally, LLMs demonstrate a strong bias towards aggressive statistical compression, whereas human conceptual systems appear to prioritize adaptive nuance and contextual richness, even if this results in lower compressional efficiency by our measures. These findings illuminate critical differences between current AI and human cognitive architectures, guiding pathways toward LLMs with more human-aligned conceptual representations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge