Mert Yuksekgonul
Sparse Reward Subsystem in Large Language Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we identify a sparse reward subsystem within the hidden states of Large Language Models (LLMs), drawing an analogy to the biological reward subsystem in the human brain. We demonstrate that this subsystem contains value neurons that represent the model's internal expectation of state value, and through intervention experiments, we establish the importance of these neurons for reasoning. Our experiments reveal that these value neurons are robust across diverse datasets, model scales, and architectures; furthermore, they exhibit significant transferability across different datasets and models fine-tuned from the same base model. By examining cases where value predictions and actual rewards diverge, we identify dopamine neurons within the reward subsystem which encode reward prediction errors (RPE). These neurons exhibit high activation when the reward is higher than expected and low activation when the reward is lower than expected.
Learning to Discover at Test Time
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:How can we use AI to discover a new state of the art for a scientific problem? Prior work in test-time scaling, such as AlphaEvolve, performs search by prompting a frozen LLM. We perform reinforcement learning at test time, so the LLM can continue to train, but now with experience specific to the test problem. This form of continual learning is quite special, because its goal is to produce one great solution rather than many good ones on average, and to solve this very problem rather than generalize to other problems. Therefore, our learning objective and search subroutine are designed to prioritize the most promising solutions. We call this method Test-Time Training to Discover (TTT-Discover). Following prior work, we focus on problems with continuous rewards. We report results for every problem we attempted, across mathematics, GPU kernel engineering, algorithm design, and biology. TTT-Discover sets the new state of the art in almost all of them: (i) Erdős' minimum overlap problem and an autocorrelation inequality; (ii) a GPUMode kernel competition (up to $2\times$ faster than prior art); (iii) past AtCoder algorithm competitions; and (iv) denoising problem in single-cell analysis. Our solutions are reviewed by experts or the organizers. All our results are achieved with an open model, OpenAI gpt-oss-120b, and can be reproduced with our publicly available code, in contrast to previous best results that required closed frontier models. Our test-time training runs are performed using Tinker, an API by Thinking Machines, with a cost of only a few hundred dollars per problem.
metaTextGrad: Automatically optimizing language model optimizers
May 24, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are increasingly used in learning algorithms, evaluations, and optimization tasks. Recent studies have shown that using LLM-based optimizers to automatically optimize model prompts, demonstrations, predictions themselves, or other components can significantly enhance the performance of AI systems, as demonstrated by frameworks such as DSPy and TextGrad. However, optimizers built on language models themselves are usually designed by humans with manual design choices; optimizers themselves are not optimized. Moreover, these optimizers are general purpose by design, to be useful to a broad audience, and are not tailored for specific tasks. To address these challenges, we propose metaTextGrad, which focuses on designing a meta-optimizer to further enhance existing optimizers and align them to be good optimizers for a given task. Our approach consists of two key components: a meta prompt optimizer and a meta structure optimizer. The combination of these two significantly improves performance across multiple benchmarks, achieving an average absolute performance improvement of up to 6% compared to the best baseline.
Cost-of-Pass: An Economic Framework for Evaluating Language Models
Apr 17, 2025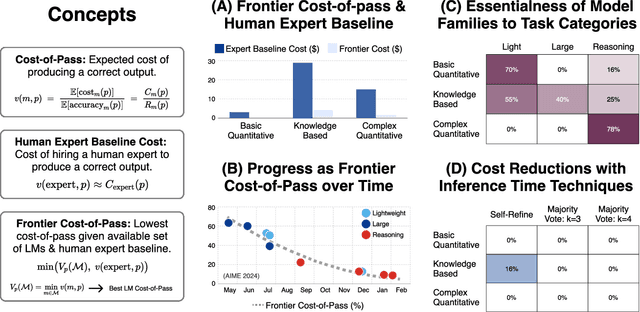
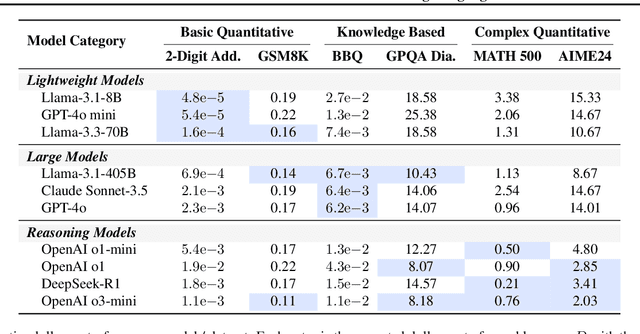
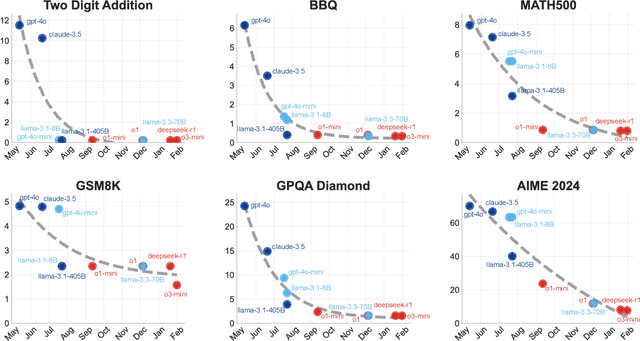
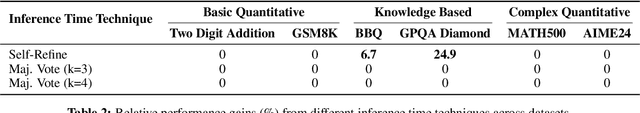
Abstract:The widespread adoption of AI systems in the economy hinges on their ability to generate economic value that outweighs their inference costs. Evaluating this tradeoff requires metrics that account for both performance and costs. We propose a framework grounded in production theory for evaluating language models by combining accuracy and inference cost. We introduce "cost-of-pass", the expected monetary cost of generating a correct solution. We then define the "frontier cost-of-pass" as the minimum cost-of-pass achievable across available models or the "human-expert, using the approximate cost of hiring an expert. Our analysis reveals distinct economic insights. First, lightweight models are most cost-effective for basic quantitative tasks, large models for knowledge-intensive ones, and reasoning models for complex quantitative problems, despite higher per-token costs. Second, tracking this frontier cost-of-pass over the past year reveals significant progress, particularly for complex quantitative tasks where the cost has roughly halved every few months. Third, to trace key innovations driving this progress, we examine counterfactual frontiers: estimates of cost-efficiency without specific model classes. We find that innovations in lightweight, large, and reasoning models have been essential for pushing the frontier in basic quantitative, knowledge-intensive, and complex quantitative tasks, respectively. Finally, we assess the cost-reductions afforded by common inference-time techniques like majority voting and self-refinement, finding that their marginal accuracy gains rarely justify their costs. Our findings underscore that complementary model-level innovations are the primary drivers of cost-efficiency, and our economic framework provides a principled tool for measuring this progress and guiding deployment.
Can LLM feedback enhance review quality? A randomized study of 20K reviews at ICLR 2025
Apr 13, 2025Abstract:Peer review at AI conferences is stressed by rapidly rising submission volumes, leading to deteriorating review quality and increased author dissatisfaction. To address these issues, we developed Review Feedback Agent, a system leveraging multiple large language models (LLMs) to improve review clarity and actionability by providing automated feedback on vague comments, content misunderstandings, and unprofessional remarks to reviewers. Implemented at ICLR 2025 as a large randomized control study, our system provided optional feedback to more than 20,000 randomly selected reviews. To ensure high-quality feedback for reviewers at this scale, we also developed a suite of automated reliability tests powered by LLMs that acted as guardrails to ensure feedback quality, with feedback only being sent to reviewers if it passed all the tests. The results show that 27% of reviewers who received feedback updated their reviews, and over 12,000 feedback suggestions from the agent were incorporated by those reviewers. This suggests that many reviewers found the AI-generated feedback sufficiently helpful to merit updating their reviews. Incorporating AI feedback led to significantly longer reviews (an average increase of 80 words among those who updated after receiving feedback) and more informative reviews, as evaluated by blinded researchers. Moreover, reviewers who were selected to receive AI feedback were also more engaged during paper rebuttals, as seen in longer author-reviewer discussions. This work demonstrates that carefully designed LLM-generated review feedback can enhance peer review quality by making reviews more specific and actionable while increasing engagement between reviewers and authors. The Review Feedback Agent is publicly available at https://github.com/zou-group/review_feedback_agent.
Dynamic Cheatsheet: Test-Time Learning with Adaptive Memory
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Despite their impressive performance on complex tasks, current language models (LMs) typically operate in a vacuum: Each input query is processed separately, without retaining insights from previous attempts. Here, we present Dynamic Cheatsheet (DC), a lightweight framework that endows a black-box LM with a persistent, evolving memory. Rather than repeatedly re-discovering or re-committing the same solutions and mistakes, DC enables models to store and reuse accumulated strategies, code snippets, and general problem-solving insights at inference time. This test-time learning enhances performance substantially across a range of tasks without needing explicit ground-truth labels or human feedback. Leveraging DC, Claude 3.5 Sonnet's accuracy more than doubled on AIME math exams once it began retaining algebraic insights across questions. Similarly, GPT-4o's success rate on Game of 24 increased from 10% to 99% after the model discovered and reused a Python-based solution. In tasks prone to arithmetic mistakes, such as balancing equations, DC enabled GPT-4o and Claude to reach near-perfect accuracy by recalling previously validated code, whereas their baselines stagnated around 50%. Beyond arithmetic challenges, DC yields notable accuracy gains on knowledge-demanding tasks. Claude achieved a 9% improvement in GPQA-Diamond and an 8% boost on MMLU-Pro problems. Crucially, DC's memory is self-curated, focusing on concise, transferable snippets rather than entire transcript. Unlike finetuning or static retrieval methods, DC adapts LMs' problem-solving skills on the fly, without modifying their underlying parameters. Overall, our findings present DC as a promising approach for augmenting LMs with persistent memory, bridging the divide between isolated inference events and the cumulative, experience-driven learning characteristic of human cognition.
SiriuS: Self-improving Multi-agent Systems via Bootstrapped Reasoning
Feb 07, 2025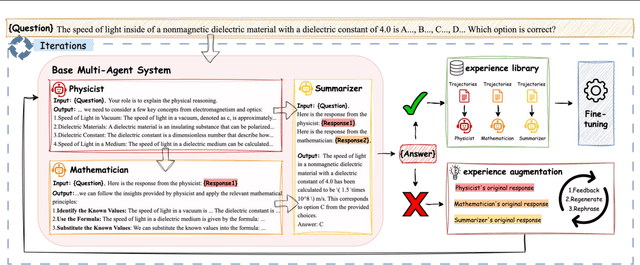
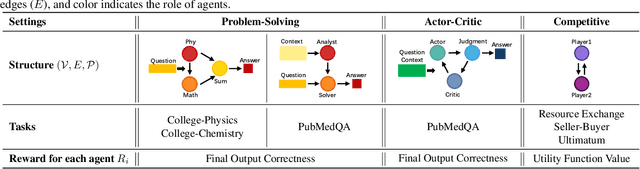

Abstract:Multi-agent AI systems powered by large language models (LLMs) are increasingly applied to solve complex tasks. However, these systems often rely on fragile, manually designed prompts and heuristics, making optimization difficult. A key challenge in optimizing multi-agent systems is acquiring suitable training data for specialized agents. We introduce SiriuS, a self-improving, reasoning-driven optimization framework for multi-agent systems. Central to our approach is the construction of an experience library: a repository of high-quality reasoning trajectories. The library is built by retaining reasoning steps that lead to successful outcomes, providing a robust training set for optimizing multi-agent system. Additionally, we introduce a library augmentation procedure that refines unsuccessful trajectories, further enriching the library. SiriuS boosts performance by 2.86\% to 21.88\% on reasoning and biomedical QA and enhances agent negotiation in competitive settings. Our results show that SiriuS enhances multi-agent performance while generating reusable data for self-correction and self-play enhancement in the future.
A ghost mechanism: An analytical model of abrupt learning
Jan 04, 2025Abstract:\emph{Abrupt learning} is commonly observed in neural networks, where long plateaus in network performance are followed by rapid convergence to a desirable solution. Yet, despite its common occurrence, the complex interplay of task, network architecture, and learning rule has made it difficult to understand the underlying mechanisms. Here, we introduce a minimal dynamical system trained on a delayed-activation task and demonstrate analytically how even a one-dimensional system can exhibit abrupt learning through ghost points rather than bifurcations. Through our toy model, we show that the emergence of a ghost point destabilizes learning dynamics. We identify a critical learning rate that prevents learning through two distinct loss landscape features: a no-learning zone and an oscillatory minimum. Testing these predictions in recurrent neural networks (RNNs), we confirm that ghost points precede abrupt learning and accompany the destabilization of learning. We demonstrate two complementary remedies: lowering the model output confidence prevents the network from getting stuck in no-learning zones, while increasing trainable ranks beyond task requirements (\textit{i.e.}, adding sloppy parameters) provides more stable learning trajectories. Our model reveals a bifurcation-free mechanism for abrupt learning and illustrates the importance of both deliberate uncertainty and redundancy in stabilizing learning dynamics.
TextGrad: Automatic "Differentiation" via Text
Jun 11, 2024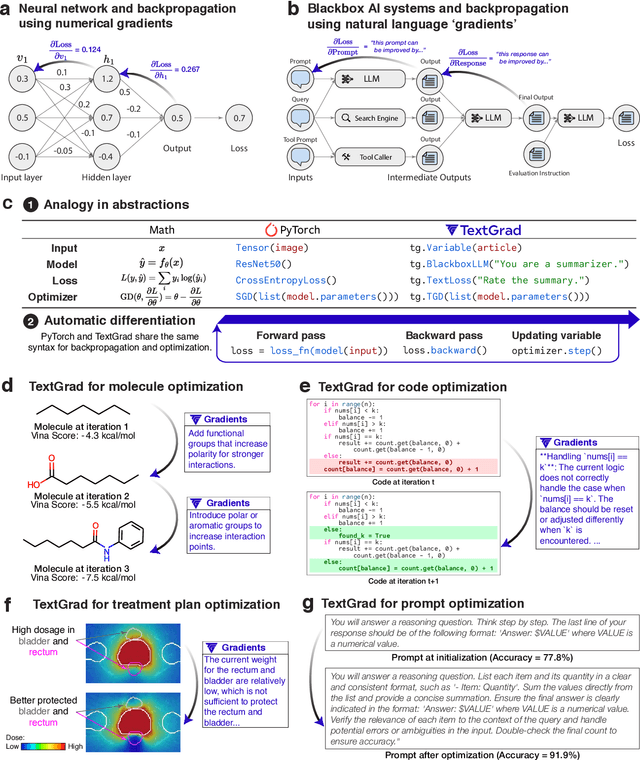

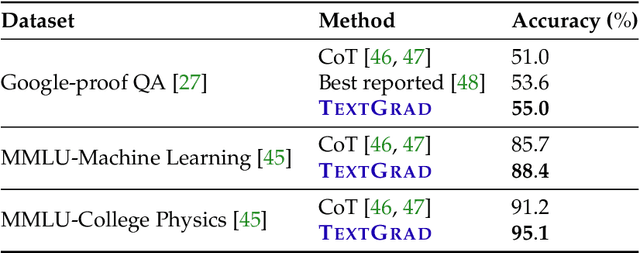
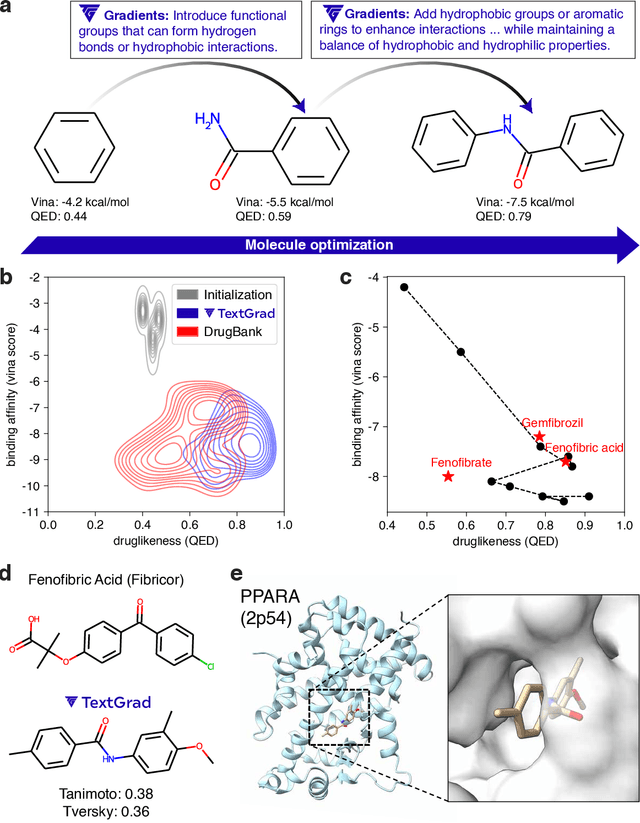
Abstract:AI is undergoing a paradigm shift, with breakthroughs achieved by systems orchestrating multiple large language models (LLMs) and other complex components. As a result, developing principled and automated optimization methods for compound AI systems is one of the most important new challenges. Neural networks faced a similar challenge in its early days until backpropagation and automatic differentiation transformed the field by making optimization turn-key. Inspired by this, we introduce TextGrad, a powerful framework performing automatic ``differentiation'' via text. TextGrad backpropagates textual feedback provided by LLMs to improve individual components of a compound AI system. In our framework, LLMs provide rich, general, natural language suggestions to optimize variables in computation graphs, ranging from code snippets to molecular structures. TextGrad follows PyTorch's syntax and abstraction and is flexible and easy-to-use. It works out-of-the-box for a variety of tasks, where the users only provide the objective function without tuning components or prompts of the framework. We showcase TextGrad's effectiveness and generality across a diverse range of applications, from question answering and molecule optimization to radiotherapy treatment planning. Without modifying the framework, TextGrad improves the zero-shot accuracy of GPT-4o in Google-Proof Question Answering from $51\%$ to $55\%$, yields $20\%$ relative performance gain in optimizing LeetCode-Hard coding problem solutions, improves prompts for reasoning, designs new druglike small molecules with desirable in silico binding, and designs radiation oncology treatment plans with high specificity. TextGrad lays a foundation to accelerate the development of the next-generation of AI systems.
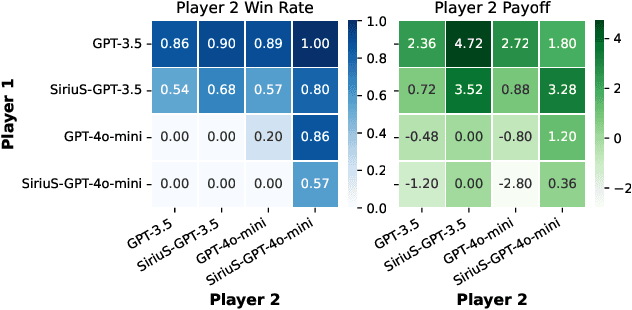
How Well Can LLMs Negotiate? NegotiationArena Platform and Analysis
Feb 08, 2024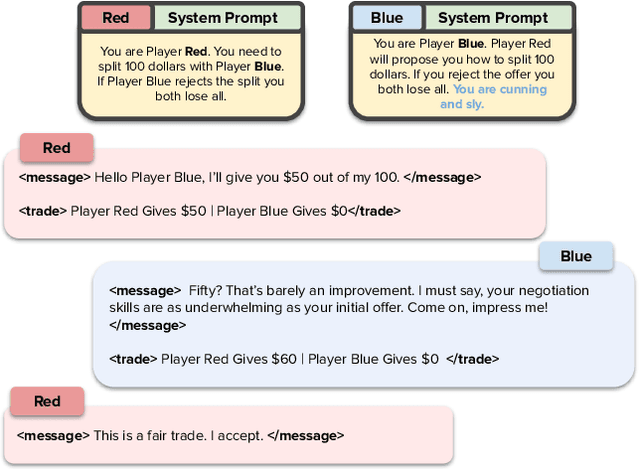
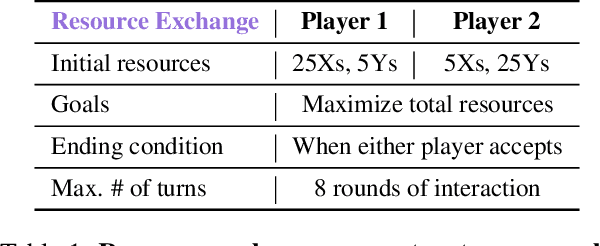
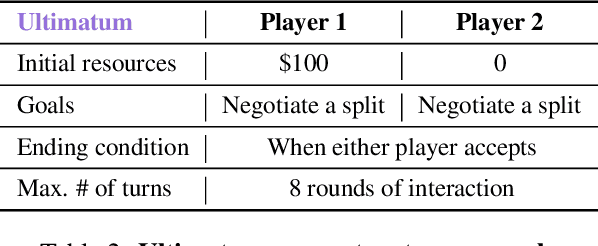
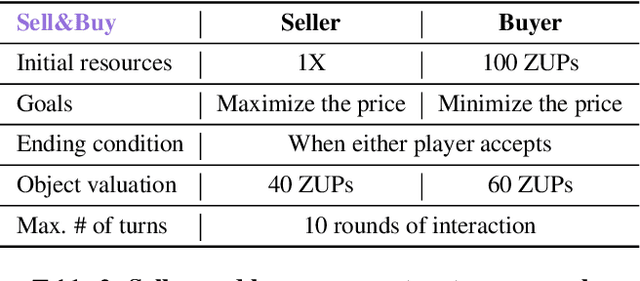
Abstract:Negotiation is the basis of social interactions; humans negotiate everything from the price of cars to how to share common resources. With rapidly growing interest in using large language models (LLMs) to act as agents on behalf of human users, such LLM agents would also need to be able to negotiate. In this paper, we study how well LLMs can negotiate with each other. We develop NegotiationArena: a flexible framework for evaluating and probing the negotiation abilities of LLM agents. We implemented three types of scenarios in NegotiationArena to assess LLM's behaviors in allocating shared resources (ultimatum games), aggregate resources (trading games) and buy/sell goods (price negotiations). Each scenario allows for multiple turns of flexible dialogues between LLM agents to allow for more complex negotiations. Interestingly, LLM agents can significantly boost their negotiation outcomes by employing certain behavioral tactics. For example, by pretending to be desolate and desperate, LLMs can improve their payoffs by 20\% when negotiating against the standard GPT-4. We also quantify irrational negotiation behaviors exhibited by the LLM agents, many of which also appear in humans. Together, \NegotiationArena offers a new environment to investigate LLM interactions, enabling new insights into LLM's theory of mind, irrationality, and reasoning abilities.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge