Soonyoung Lee
Adaptive Information Routing for Multimodal Time Series Forecasting
Dec 23, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting is a critical task for artificial intelligence with numerous real-world applications. Traditional approaches primarily rely on historical time series data to predict the future values. However, in practical scenarios, this is often insufficient for accurate predictions due to the limited information available. To address this challenge, multimodal time series forecasting methods which incorporate additional data modalities, mainly text data, alongside time series data have been explored. In this work, we introduce the Adaptive Information Routing (AIR) framework, a novel approach for multimodal time series forecasting. Unlike existing methods that treat text data on par with time series data as interchangeable auxiliary features for forecasting, AIR leverages text information to dynamically guide the time series model by controlling how and to what extent multivariate time series information should be combined. We also present a text-refinement pipeline that employs a large language model to convert raw text data into a form suitable for multimodal forecasting, and we introduce a benchmark that facilitates multimodal forecasting experiments based on this pipeline. Experiment results with the real world market data such as crude oil price and exchange rates demonstrate that AIR effectively modulates the behavior of the time series model using textual inputs, significantly enhancing forecasting accuracy in various time series forecasting tasks.
EXAONE Path 2.5: Pathology Foundation Model with Multi-Omics Alignment
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Cancer progression arises from interactions across multiple biological layers, especially beyond morphological and across molecular layers that remain invisible to image-only models. To capture this broader biological landscape, we present EXAONE Path 2.5, a pathology foundation model that jointly models histologic, genomic, epigenetic and transcriptomic modalities, producing an integrated patient representation that reflects tumor biology more comprehensively. Our approach incorporates three key components: (1) multimodal SigLIP loss enabling all-pairwise contrastive learning across heterogeneous modalities, (2) a fragment-aware rotary positional encoding (F-RoPE) module that preserves spatial structure and tissue-fragment topology in WSI, and (3) domain-specialized internal foundation models for both WSI and RNA-seq to provide biologically grounded embeddings for robust multimodal alignment. We evaluate EXAONE Path 2.5 against six leading pathology foundation models across two complementary benchmarks: an internal real-world clinical dataset and the Patho-Bench benchmark covering 80 tasks. Our framework demonstrates high data and parameter efficiency, achieving on-par performance with state-of-the-art foundation models on Patho-Bench while exhibiting the highest adaptability in the internal clinical setting. These results highlight the value of biologically informed multimodal design and underscore the potential of integrated genotype-to-phenotype modeling for next-generation precision oncology.
ReTabAD: A Benchmark for Restoring Semantic Context in Tabular Anomaly Detection
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:In tabular anomaly detection (AD), textual semantics often carry critical signals, as the definition of an anomaly is closely tied to domain-specific context. However, existing benchmarks provide only raw data points without semantic context, overlooking rich textual metadata such as feature descriptions and domain knowledge that experts rely on in practice. This limitation restricts research flexibility and prevents models from fully leveraging domain knowledge for detection. ReTabAD addresses this gap by restoring textual semantics to enable context-aware tabular AD research. We provide (1) 20 carefully curated tabular datasets enriched with structured textual metadata, together with implementations of state-of-the-art AD algorithms including classical, deep learning, and LLM-based approaches, and (2) a zero-shot LLM framework that leverages semantic context without task-specific training, establishing a strong baseline for future research. Furthermore, this work provides insights into the role and utility of textual metadata in AD through experiments and analysis. Results show that semantic context improves detection performance and enhances interpretability by supporting domain-aware reasoning. These findings establish ReTabAD as a benchmark for systematic exploration of context-aware AD.
EXAONE Path 2.0: Pathology Foundation Model with End-to-End Supervision
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:In digital pathology, whole-slide images (WSIs) are often difficult to handle due to their gigapixel scale, so most approaches train patch encoders via self-supervised learning (SSL) and then aggregate the patch-level embeddings via multiple instance learning (MIL) or slide encoders for downstream tasks. However, patch-level SSL may overlook complex domain-specific features that are essential for biomarker prediction, such as mutation status and molecular characteristics, as SSL methods rely only on basic augmentations selected for natural image domains on small patch-level area. Moreover, SSL methods remain less data efficient than fully supervised approaches, requiring extensive computational resources and datasets to achieve competitive performance. To address these limitations, we present EXAONE Path 2.0, a pathology foundation model that learns patch-level representations under direct slide-level supervision. Using only 37k WSIs for training, EXAONE Path 2.0 achieves state-of-the-art average performance across 10 biomarker prediction tasks, demonstrating remarkable data efficiency.
MolMole: Molecule Mining from Scientific Literature
May 08, 2025Abstract:The extraction of molecular structures and reaction data from scientific documents is challenging due to their varied, unstructured chemical formats and complex document layouts. To address this, we introduce MolMole, a vision-based deep learning framework that unifies molecule detection, reaction diagram parsing, and optical chemical structure recognition (OCSR) into a single pipeline for automating the extraction of chemical data directly from page-level documents. Recognizing the lack of a standard page-level benchmark and evaluation metric, we also present a testset of 550 pages annotated with molecule bounding boxes, reaction labels, and MOLfiles, along with a novel evaluation metric. Experimental results demonstrate that MolMole outperforms existing toolkits on both our benchmark and public datasets. The benchmark testset will be publicly available, and the MolMole toolkit will be accessible soon through an interactive demo on the LG AI Research website. For commercial inquiries, please contact us at \href{mailto:contact_ddu@lgresearch.ai}{contact\_ddu@lgresearch.ai}.
ReSpec: Relevance and Specificity Grounded Online Filtering for Learning on Video-Text Data Streams
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of video-text data presents challenges in storage and computation during training. Online learning, which processes streaming data in real-time, offers a promising solution to these issues while also allowing swift adaptations in scenarios demanding real-time responsiveness. One strategy to enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of learning involves identifying and prioritizing data that enhances performance on target downstream tasks. We propose Relevance and Specificity-based online filtering framework (ReSpec) that selects data based on four criteria: (i) modality alignment for clean data, (ii) task relevance for target focused data, (iii) specificity for informative and detailed data, and (iv) efficiency for low-latency processing. Relevance is determined by the probabilistic alignment of incoming data with downstream tasks, while specificity employs the distance to a root embedding representing the least specific data as an efficient proxy for informativeness. By establishing reference points from target task data, ReSpec filters incoming data in real-time, eliminating the need for extensive storage and compute. Evaluating on large-scale datasets WebVid2M and VideoCC3M, ReSpec attains state-of-the-art performance on five zeroshot video retrieval tasks, using as little as 5% of the data while incurring minimal compute. The source code is available at https://github.com/cdjkim/ReSpec.
ChatEXAONEPath: An Expert-level Multimodal Large Language Model for Histopathology Using Whole Slide Images
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:Recent studies have made significant progress in developing large language models (LLMs) in the medical domain, which can answer expert-level questions and demonstrate the potential to assist clinicians in real-world clinical scenarios. Studies have also witnessed the importance of integrating various modalities with the existing LLMs for a better understanding of complex clinical contexts, which are innately multi-faceted by nature. Although studies have demonstrated the ability of multimodal LLMs in histopathology to answer questions from given images, they lack in understanding of thorough clinical context due to the patch-level data with limited information from public datasets. Thus, developing WSI-level MLLMs is significant in terms of the scalability and applicability of MLLMs in histopathology. In this study, we introduce an expert-level MLLM for histopathology using WSIs, dubbed as ChatEXAONEPath. We present a retrieval-based data generation pipeline using 10,094 pairs of WSIs and histopathology reports from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). We also showcase an AI-based evaluation protocol for a comprehensive understanding of the medical context from given multimodal information and evaluate generated answers compared to the original histopathology reports. We demonstrate the ability of diagnosing the given histopathology images using ChatEXAONEPath with the acceptance rate of 62.9% from 1,134 pairs of WSIs and reports. Our proposed model can understand pan-cancer WSIs and clinical context from various cancer types. We argue that our proposed model has the potential to assist clinicians by comprehensively understanding complex morphology of WSIs for cancer diagnosis through the integration of multiple modalities.
MASH-VLM: Mitigating Action-Scene Hallucination in Video-LLMs through Disentangled Spatial-Temporal Representations
Mar 20, 2025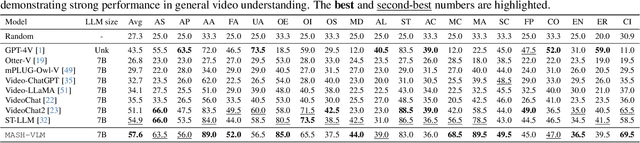
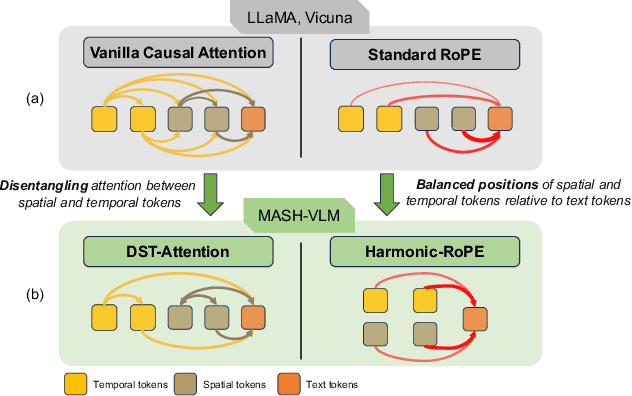
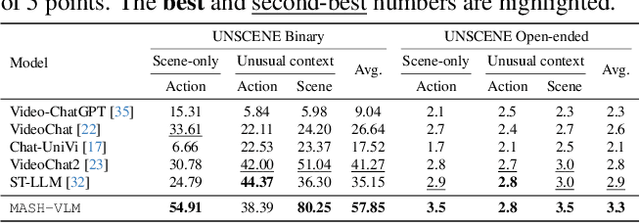
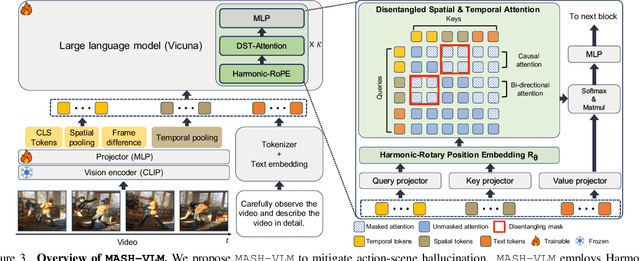
Abstract:In this work, we tackle action-scene hallucination in Video Large Language Models (Video-LLMs), where models incorrectly predict actions based on the scene context or scenes based on observed actions. We observe that existing Video-LLMs often suffer from action-scene hallucination due to two main factors. First, existing Video-LLMs intermingle spatial and temporal features by applying an attention operation across all tokens. Second, they use the standard Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE), which causes the text tokens to overemphasize certain types of tokens depending on their sequential orders. To address these issues, we introduce MASH-VLM, Mitigating Action-Scene Hallucination in Video-LLMs through disentangled spatial-temporal representations. Our approach includes two key innovations: (1) DST-attention, a novel attention mechanism that disentangles the spatial and temporal tokens within the LLM by using masked attention to restrict direct interactions between the spatial and temporal tokens; (2) Harmonic-RoPE, which extends the dimensionality of the positional IDs, allowing the spatial and temporal tokens to maintain balanced positions relative to the text tokens. To evaluate the action-scene hallucination in Video-LLMs, we introduce the UNSCENE benchmark with 1,320 videos and 4,078 QA pairs. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MASH-VLM achieves state-of-the-art results on the UNSCENE benchmark, as well as on existing video understanding benchmarks.
See It All: Contextualized Late Aggregation for 3D Dense Captioning
Aug 14, 2024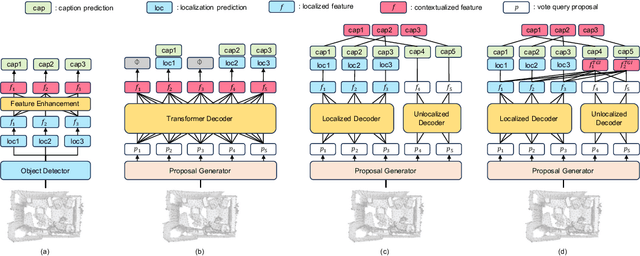
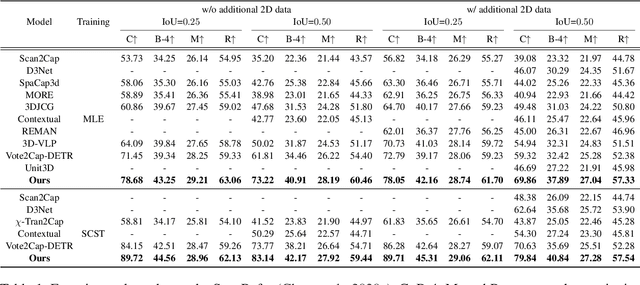
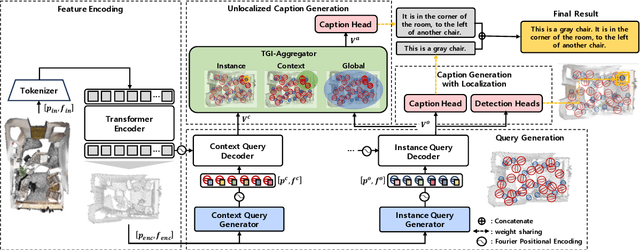
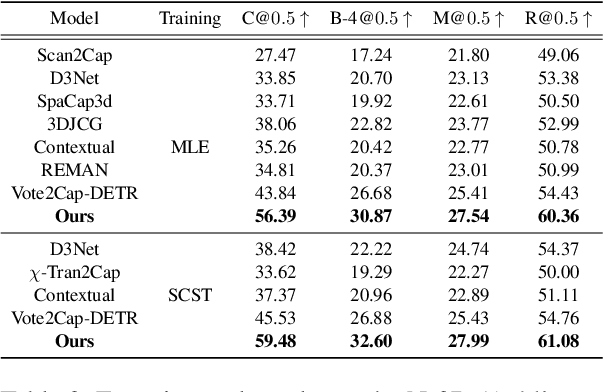
Abstract:3D dense captioning is a task to localize objects in a 3D scene and generate descriptive sentences for each object. Recent approaches in 3D dense captioning have adopted transformer encoder-decoder frameworks from object detection to build an end-to-end pipeline without hand-crafted components. However, these approaches struggle with contradicting objectives where a single query attention has to simultaneously view both the tightly localized object regions and contextual environment. To overcome this challenge, we introduce SIA (See-It-All), a transformer pipeline that engages in 3D dense captioning with a novel paradigm called late aggregation. SIA simultaneously decodes two sets of queries-context query and instance query. The instance query focuses on localization and object attribute descriptions, while the context query versatilely captures the region-of-interest of relationships between multiple objects or with the global scene, then aggregated afterwards (i.e., late aggregation) via simple distance-based measures. To further enhance the quality of contextualized caption generation, we design a novel aggregator to generate a fully informed caption based on the surrounding context, the global environment, and object instances. Extensive experiments on two of the most widely-used 3D dense captioning datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves a significant improvement over prior methods.
Bi-directional Contextual Attention for 3D Dense Captioning
Aug 13, 2024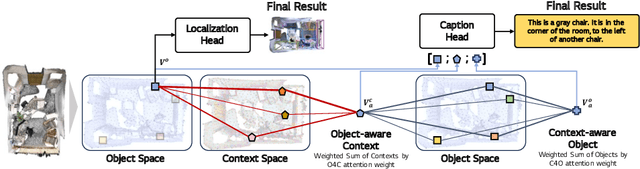
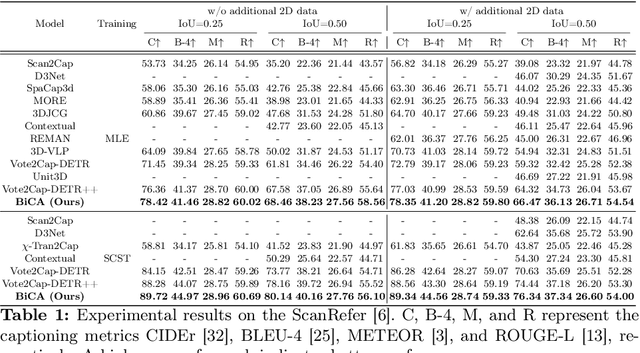
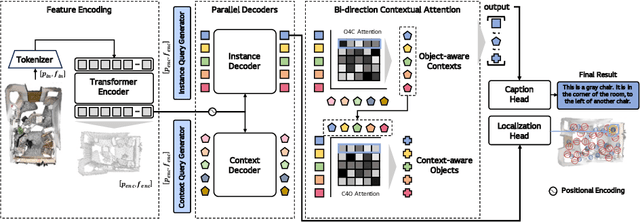
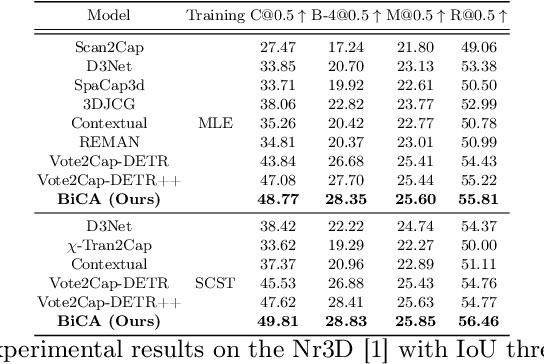
Abstract:3D dense captioning is a task involving the localization of objects and the generation of descriptions for each object in a 3D scene. Recent approaches have attempted to incorporate contextual information by modeling relationships with object pairs or aggregating the nearest neighbor features of an object. However, the contextual information constructed in these scenarios is limited in two aspects: first, objects have multiple positional relationships that exist across the entire global scene, not only near the object itself. Second, it faces with contradicting objectives--where localization and attribute descriptions are generated better with tight localization, while descriptions involving global positional relations are generated better with contextualized features of the global scene. To overcome this challenge, we introduce BiCA, a transformer encoder-decoder pipeline that engages in 3D dense captioning for each object with Bi-directional Contextual Attention. Leveraging parallelly decoded instance queries for objects and context queries for non-object contexts, BiCA generates object-aware contexts, where the contexts relevant to each object is summarized, and context-aware objects, where the objects relevant to the summarized object-aware contexts are aggregated. This extension relieves previous methods from the contradicting objectives, enhancing both localization performance and enabling the aggregation of contextual features throughout the global scene; thus improving caption generation performance simultaneously. Extensive experiments on two of the most widely-used 3D dense captioning datasets demonstrate that our proposed method achieves a significant improvement over prior methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge