Yinda Xu
H2R: A Human-to-Robot Data Augmentation for Robot Pre-training from Videos
May 17, 2025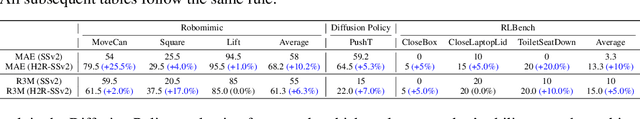
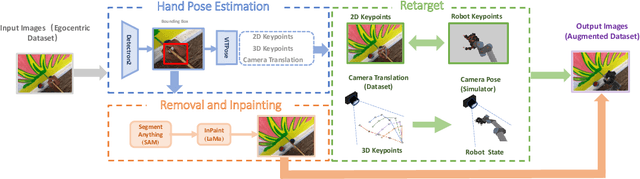

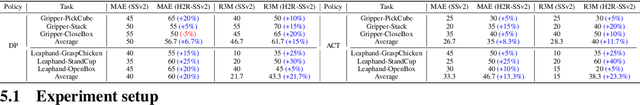
Abstract:Large-scale pre-training using videos has proven effective for robot learning. However, the models pre-trained on such data can be suboptimal for robot learning due to the significant visual gap between human hands and those of different robots. To remedy this, we propose H2R, a simple data augmentation technique that detects human hand keypoints, synthesizes robot motions in simulation, and composites rendered robots into egocentric videos. This process explicitly bridges the visual gap between human and robot embodiments during pre-training. We apply H2R to augment large-scale egocentric human video datasets such as Ego4D and SSv2, replacing human hands with simulated robotic arms to generate robot-centric training data. Based on this, we construct and release a family of 1M-scale datasets covering multiple robot embodiments (UR5 with gripper/Leaphand, Franka) and data sources (SSv2, Ego4D). To verify the effectiveness of the augmentation pipeline, we introduce a CLIP-based image-text similarity metric that quantitatively evaluates the semantic fidelity of robot-rendered frames to the original human actions. We validate H2R across three simulation benchmarks: Robomimic, RLBench and PushT and real-world manipulation tasks with a UR5 robot equipped with Gripper and Leaphand end-effectors. H2R consistently improves downstream success rates, yielding gains of 5.0%-10.2% in simulation and 6.7%-23.3% in real-world tasks across various visual encoders and policy learning methods. These results indicate that H2R improves the generalization ability of robotic policies by mitigating the visual discrepancies between human and robot domains.
Efficient Model-agnostic Alignment via Bayesian Persuasion
May 29, 2024Abstract:With recent advancements in large language models (LLMs), alignment has emerged as an effective technique for keeping LLMs consensus with human intent. Current methods primarily involve direct training through Supervised Fine-tuning (SFT) or Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF), both of which require substantial computational resources and extensive ground truth data. This paper explores an efficient method for aligning black-box large models using smaller models, introducing a model-agnostic and lightweight Bayesian Persuasion Alignment framework. We formalize this problem as an optimization of the signaling strategy from the small model's perspective. In the persuasion process, the small model (Advisor) observes the information item (i.e., state) and persuades large models (Receiver) to elicit improved responses. The Receiver then generates a response based on the input, the signal from the Advisor, and its updated belief about the information item. Through training using our framework, we demonstrate that the Advisor can significantly enhance the performance of various Receivers across a range of tasks. We theoretically analyze our persuasion framework and provide an upper bound on the Advisor's regret, confirming its effectiveness in learning the optimal signaling strategy. Our Empirical results demonstrates that GPT-2 can significantly improve the performance of various models, achieving an average enhancement of 16.1% in mathematical reasoning ability and 13.7% in code generation. We hope our work can provide an initial step toward rethinking the alignment framework from the Bayesian Persuasion perspective.
Towards Collaborative Autonomous Driving: Simulation Platform and End-to-End System
Apr 15, 2024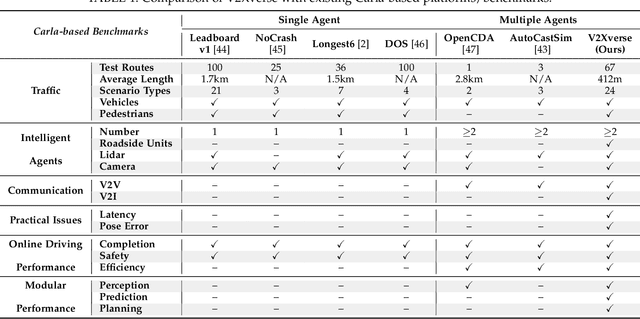
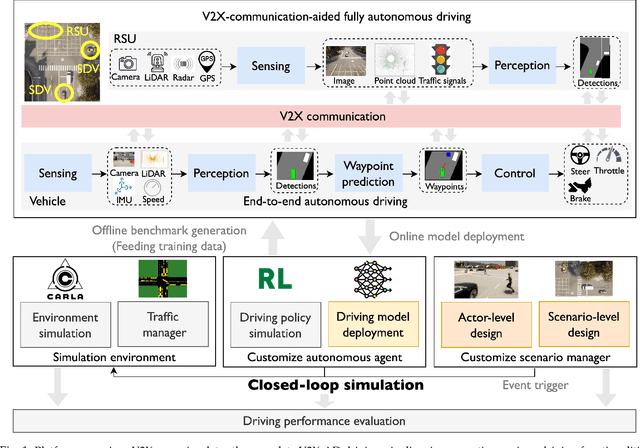

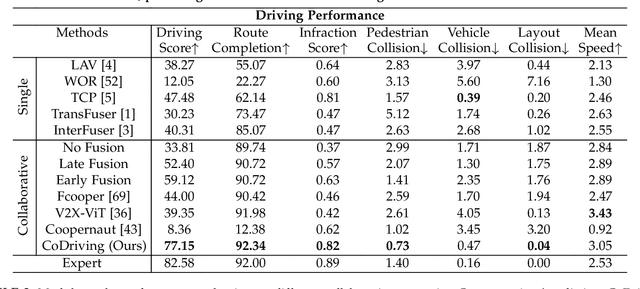
Abstract:Vehicle-to-everything-aided autonomous driving (V2X-AD) has a huge potential to provide a safer driving solution. Despite extensive researches in transportation and communication to support V2X-AD, the actual utilization of these infrastructures and communication resources in enhancing driving performances remains largely unexplored. This highlights the necessity of collaborative autonomous driving: a machine learning approach that optimizes the information sharing strategy to improve the driving performance of each vehicle. This effort necessitates two key foundations: a platform capable of generating data to facilitate the training and testing of V2X-AD, and a comprehensive system that integrates full driving-related functionalities with mechanisms for information sharing. From the platform perspective, we present V2Xverse, a comprehensive simulation platform for collaborative autonomous driving. This platform provides a complete pipeline for collaborative driving. From the system perspective, we introduce CoDriving, a novel end-to-end collaborative driving system that properly integrates V2X communication over the entire autonomous pipeline, promoting driving with shared perceptual information. The core idea is a novel driving-oriented communication strategy. Leveraging this strategy, CoDriving improves driving performance while optimizing communication efficiency. We make comprehensive benchmarks with V2Xverse, analyzing both modular performance and closed-loop driving performance. Experimental results show that CoDriving: i) significantly improves the driving score by 62.49% and drastically reduces the pedestrian collision rate by 53.50% compared to the SOTA end-to-end driving method, and ii) achieves sustaining driving performance superiority over dynamic constraint communication conditions.
OpenFedLLM: Training Large Language Models on Decentralized Private Data via Federated Learning
Feb 10, 2024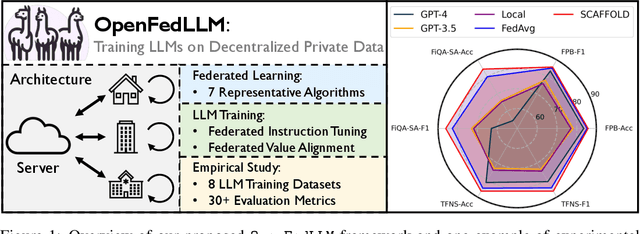
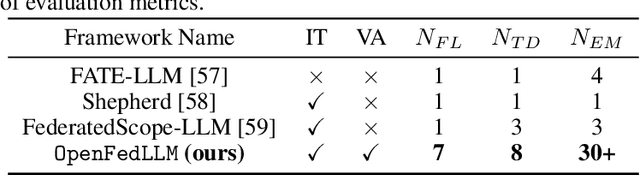
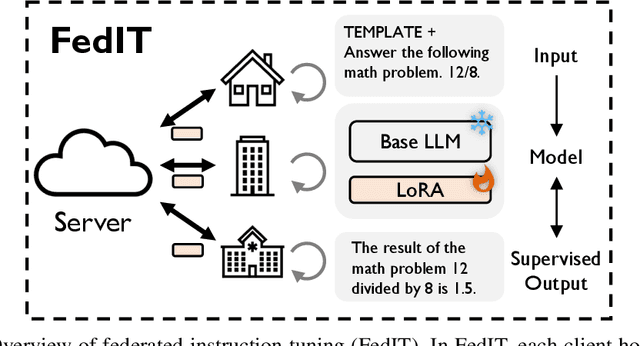
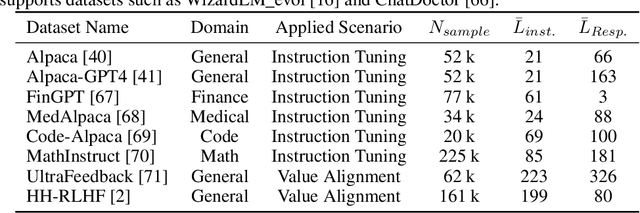
Abstract:Trained on massive publicly available data, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated tremendous success across various fields. While more data contributes to better performance, a disconcerting reality is that high-quality public data will be exhausted in a few years. In this paper, we offer a potential next step for contemporary LLMs: collaborative and privacy-preserving LLM training on the underutilized distributed private data via federated learning (FL), where multiple data owners collaboratively train a shared model without transmitting raw data. To achieve this, we build a concise, integrated, and research-friendly framework/codebase, named OpenFedLLM. It covers federated instruction tuning for enhancing instruction-following capability, federated value alignment for aligning with human values, and 7 representative FL algorithms. Besides, OpenFedLLM supports training on diverse domains, where we cover 8 training datasets; and provides comprehensive evaluations, where we cover 30+ evaluation metrics. Through extensive experiments, we observe that all FL algorithms outperform local training on training LLMs, demonstrating a clear performance improvement across a variety of settings. Notably, in a financial benchmark, Llama2-7B fine-tuned by applying any FL algorithm can outperform GPT-4 by a significant margin while the model obtained through individual training cannot, demonstrating strong motivation for clients to participate in FL. The code is available at https://github.com/rui-ye/OpenFedLLM.
DRL-Based Trajectory Tracking for Motion-Related Modules in Autonomous Driving
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:Autonomous driving systems are always built on motion-related modules such as the planner and the controller. An accurate and robust trajectory tracking method is indispensable for these motion-related modules as a primitive routine. Current methods often make strong assumptions about the model such as the context and the dynamics, which are not robust enough to deal with the changing scenarios in a real-world system. In this paper, we propose a Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL)-based trajectory tracking method for the motion-related modules in autonomous driving systems. The representation learning ability of DL and the exploration nature of RL bring strong robustness and improve accuracy. Meanwhile, it enhances versatility by running the trajectory tracking in a model-free and data-driven manner. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate both the efficiency and effectiveness of our method compared to current methods.
SiamFC++: Towards Robust and Accurate Visual Tracking with Target Estimation Guidelines
Jan 02, 2020



Abstract:Visual tracking problem demands to efficiently perform robust classification and accurate target state estimation over a given target at the same time. Former methods have proposed various ways of target state estimation, yet few of them took the particularity of the visual tracking problem itself into consideration. After a careful analysis, we propose a set of practical guidelines of target state estimation for high-performance generic object tracker design. Following these guidelines, we design our Fully Convolutional Siamese tracker++ (SiamFC++) by introducing both classification and target state estimation branch(G1), classification score without ambiguity(G2), tracking without prior knowledge(G3), and estimation quality score(G4). Extensive analysis and ablation studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed guidelines. Without bells and whistles, our SiamFC++ tracker achieves state-of-the-art performance on five challenging benchmarks(OTB2015, VOT2018, LaSOT, GOT-10k, TrackingNet), which proves both the tracking and generalization ability of the tracker. Particularly, on the large-scale TrackingNet dataset, SiamFC++ achieves a previously unseen AUC score of 75.4 while running at over 90 FPS, which is far above the real-time requirement. Code and models are available at: https://github.com/MegviiDetection/video_analyst .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge