Yafei Wang
Multi-Satellite Multi-Stream Beamspace Massive MIMO Transmission
Dec 26, 2025Abstract:This paper studies multi-satellite multi-stream (MSMS) beamspace transmission, where multiple satellites cooperate to form a distributed multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) system and jointly deliver multiple data streams to multi-antenna user terminals (UTs), and beamspace transmission combines earth-moving beamforming with beam-domain precoding. For the first time, we formulate the signal model for MSMS beamspace MIMO transmission. Under synchronization errors, multi-antenna UTs enable the distributed MIMO channel to exhibit higher rank, supporting multiple data streams. Beamspace MIMO retains conventional codebook based beamforming while providing the performance gains of precoding. Based on the signal model, we propose statistical channel state information (sCSI)-based optimization of satellite clustering, beam selection, and transmit precoding, using a sum-rate upper-bound approximation. With given satellite clustering and beam selection, we cast precoder design as an equivalent covariance decomposition-based weighted minimum mean square error (CDWMMSE) problem. To obtain tractable algorithms, we develop a closed-form covariance decomposition required by CDWMMSE and derive an iterative MSMS beam-domain precoder under sCSI. Following this, we further propose several heuristic closed-form precoders to avoid iterative cost. For satellite clustering, we enhance a competition-based algorithm by introducing a mechanism to regulate the number of satellites serving certain UT. Furthermore, we design a two-stage low-complexity beam selection algorithm focused on enhancing the effective channel power. Simulations under practical configurations validate the proposed methods across the number of data streams, receive antennas, serving satellites, and active beams, and show that beamspace transmission approaches conventional MIMO performance at lower complexity.
QoS-Aware Hierarchical Reinforcement Learning for Joint Link Selection and Trajectory Optimization in SAGIN-Supported UAV Mobility Management
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Due to the significant variations in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) altitude and horizontal mobility, it becomes difficult for any single network to ensure continuous and reliable threedimensional coverage. Towards that end, the space-air-ground integrated network (SAGIN) has emerged as an essential architecture for enabling ubiquitous UAV connectivity. To address the pronounced disparities in coverage and signal characteristics across heterogeneous networks, this paper formulates UAV mobility management in SAGIN as a constrained multi-objective joint optimization problem. The formulation couples discrete link selection with continuous trajectory optimization. Building on this, we propose a two-level multi-agent hierarchical deep reinforcement learning (HDRL) framework that decomposes the problem into two alternately solvable subproblems. To map complex link selection decisions into a compact discrete action space, we conceive a double deep Q-network (DDQN) algorithm in the top-level, which achieves stable and high-quality policy learning through double Q-value estimation. To handle the continuous trajectory action space while satisfying quality of service (QoS) constraints, we integrate the maximum-entropy mechanism of the soft actor-critic (SAC) and employ a Lagrangian-based constrained SAC (CSAC) algorithm in the lower-level that dynamically adjusts the Lagrange multipliers to balance constraint satisfaction and policy optimization. Moreover, the proposed algorithm can be extended to multi-UAV scenarios under the centralized training and decentralized execution (CTDE) paradigm, which enables more generalizable policies. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed scheme substantially outperforms existing benchmarks in throughput, link switching frequency and QoS satisfaction.
Unlocking Symbol-Level Precoding Efficiency Through Tensor Equivariant Neural Network
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:Although symbol-level precoding (SLP) based on constructive interference (CI) exploitation offers performance gains, its high complexity remains a bottleneck. This paper addresses this challenge with an end-to-end deep learning (DL) framework with low inference complexity that leverages the structure of the optimal SLP solution in the closed-form and its inherent tensor equivariance (TE), where TE denotes that a permutation of the input induces the corresponding permutation of the output. Building upon the computationally efficient model-based formulations, as well as their known closed-form solutions, we analyze their relationship with linear precoding (LP) and investigate the corresponding optimality condition. We then construct a mapping from the problem formulation to the solution and prove its TE, based on which the designed networks reveal a specific parameter-sharing pattern that delivers low computational complexity and strong generalization. Leveraging these, we propose the backbone of the framework with an attention-based TE module, achieving linear computational complexity. Furthermore, we demonstrate that such a framework is also applicable to imperfect CSI scenarios, where we design a TE-based network to map the CSI, statistics, and symbols to auxiliary variables. Simulation results show that the proposed framework captures substantial performance gains of optimal SLP, while achieving an approximately 80-times speedup over conventional methods and maintaining strong generalization across user numbers and symbol block lengths.
Tensor-Structured Bayesian Channel Prediction for Upper Mid-Band XL-MIMO Systems
Aug 11, 2025Abstract:The upper mid-band balances coverage and capacity for the future cellular systems and also embraces XL-MIMO systems, offering enhanced spectral and energy efficiency. However, these benefits are significantly degraded under mobility due to channel aging, and further exacerbated by the unique near-field (NF) and spatial non-stationarity (SnS) propagation in such systems. To address this challenge, we propose a novel channel prediction approach that incorporates dedicated channel modeling, probabilistic representations, and Bayesian inference algorithms for this emerging scenario. Specifically, we develop tensor-structured channel models in both the spatial-frequency-temporal (SFT) and beam-delay-Doppler (BDD) domains, which leverage temporal correlations among multiple pilot symbols for channel prediction. The factor matrices of multi-linear transformations are parameterized by BDD domain grids and SnS factors, where beam domain grids are jointly determined by angles and slopes under spatial-chirp based NF representations. To enable tractable inference, we replace environment-dependent BDD domain grids with uniformly sampled ones, and introduce perturbation parameters in each domain to mitigate grid mismatch. We further propose a hybrid beam domain strategy that integrates angle-only sampling with slope hyperparameterization to avoid the computational burden of explicit slope sampling. Based on the probabilistic models, we develop tensor-structured bi-layer inference (TS-BLI) algorithm under the expectation-maximization (EM) framework, which reduces computational complexity via tensor operations by leveraging the bi-layer factor graph for approximate E-step inference and an alternating strategy with closed-form updates in the M-step. Numerical simulations based on the near-practical channel simulator demonstrate the superior channel prediction performance of the proposed algorithm.
Free Energy-Inspired Cognitive Risk Integration for AV Navigation in Pedestrian-Rich Environments
Jul 28, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in autonomous vehicle (AV) behavior planning have shown impressive social interaction capabilities when interacting with other road users. However, achieving human-like prediction and decision-making in interactions with vulnerable road users remains a key challenge in complex multi-agent interactive environments. Existing research focuses primarily on crowd navigation for small mobile robots, which cannot be directly applied to AVs due to inherent differences in their decision-making strategies and dynamic boundaries. Moreover, pedestrians in these multi-agent simulations follow fixed behavior patterns that cannot dynamically respond to AV actions. To overcome these limitations, this paper proposes a novel framework for modeling interactions between the AV and multiple pedestrians. In this framework, a cognitive process modeling approach inspired by the Free Energy Principle is integrated into both the AV and pedestrian models to simulate more realistic interaction dynamics. Specifically, the proposed pedestrian Cognitive-Risk Social Force Model adjusts goal-directed and repulsive forces using a fused measure of cognitive uncertainty and physical risk to produce human-like trajectories. Meanwhile, the AV leverages this fused risk to construct a dynamic, risk-aware adjacency matrix for a Graph Convolutional Network within a Soft Actor-Critic architecture, allowing it to make more reasonable and informed decisions. Simulation results indicate that our proposed framework effectively improves safety, efficiency, and smoothness of AV navigation compared to the state-of-the-art method.
Interference in Spectrum-Sharing Integrated Terrestrial and Satellite Networks: Modeling, Approximation, and Robust Transmit Beamforming
Jun 13, 2025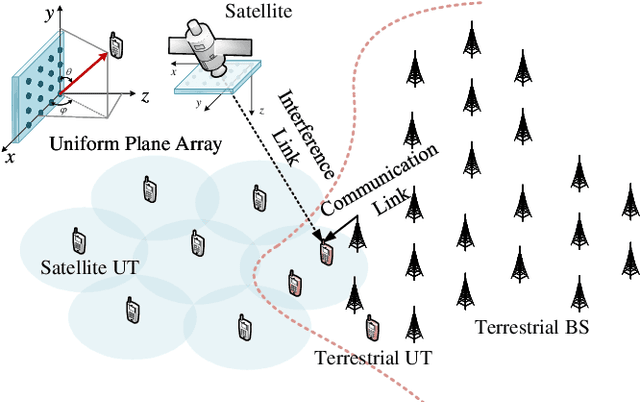
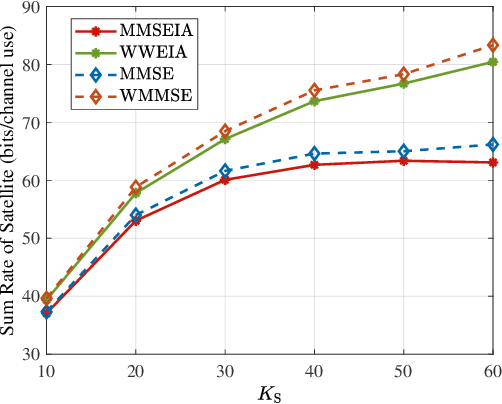
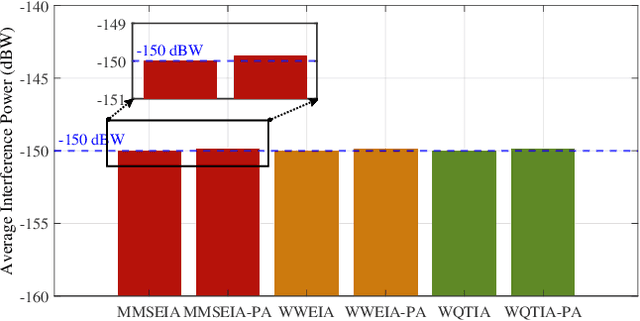
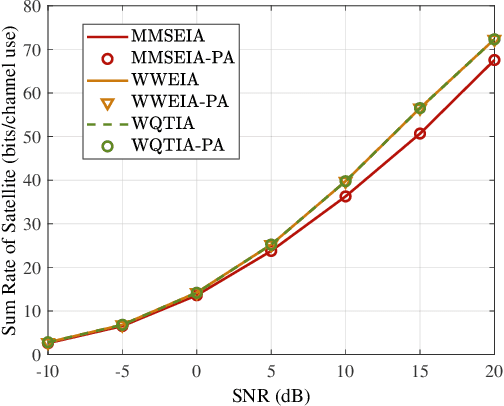
Abstract:This paper investigates robust transmit (TX) beamforming from the satellite to user terminals (UTs), based on statistical channel state information (CSI). The proposed design specifically targets the mitigation of satellite-to-terrestrial interference in spectrum-sharing integrated terrestrial and satellite networks. By leveraging the distribution information of terrestrial UTs, we first establish an interference model from the satellite to terrestrial systems without shared CSI. Based on this, robust TX beamforming schemes are developed under both the interference threshold and the power budget. Two optimization criteria are considered: satellite weighted sum rate maximization and mean square error minimization. The former achieves a superior achievable rate performance through an iterative optimization framework, whereas the latter enables a low-complexity closed-form solution at the expense of reduced rate, with interference constraints satisfied via a bisection method. To avoid complex integral calculations and the dependence on user distribution information in inter-system interference evaluations, we propose a terrestrial base station position-aided approximation method, and the approximation errors are subsequently analyzed. Numerical simulations validate the effectiveness of our proposed schemes.
MAC-Gaze: Motion-Aware Continual Calibration for Mobile Gaze Tracking
May 28, 2025Abstract:Mobile gaze tracking faces a fundamental challenge: maintaining accuracy as users naturally change their postures and device orientations. Traditional calibration approaches, like one-off, fail to adapt to these dynamic conditions, leading to degraded performance over time. We present MAC-Gaze, a Motion-Aware continual Calibration approach that leverages smartphone Inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensors and continual learning techniques to automatically detect changes in user motion states and update the gaze tracking model accordingly. Our system integrates a pre-trained visual gaze estimator and an IMU-based activity recognition model with a clustering-based hybrid decision-making mechanism that triggers recalibration when motion patterns deviate significantly from previously encountered states. To enable accumulative learning of new motion conditions while mitigating catastrophic forgetting, we employ replay-based continual learning, allowing the model to maintain performance across previously encountered motion conditions. We evaluate our system through extensive experiments on the publicly available RGBDGaze dataset and our own 10-hour multimodal MotionGaze dataset (481K+ images, 800K+ IMU readings), encompassing a wide range of postures under various motion conditions including sitting, standing, lying, and walking. Results demonstrate that our method reduces gaze estimation error by 19.9% on RGBDGaze (from 1.73 cm to 1.41 cm) and by 31.7% on MotionGaze (from 2.81 cm to 1.92 cm) compared to traditional calibration approaches. Our framework provides a robust solution for maintaining gaze estimation accuracy in mobile scenarios.
Time-Continuous Frequency Allocation for Feeder Links of Mega Constellations with Multi-Antenna Gateway Stations
May 18, 2025Abstract:With the recent rapid advancement of mega low earth orbit (LEO) satellite constellations, multi-antenna gateway station (MAGS) has emerged as a key enabler to support extremely high system capacity via massive feeder links. However, the densification of both space and ground segment leads to reduced spatial separation between links, posing unprecedented challenges of interference exacerbation. This paper investigates graph coloring-based frequency allocation methods for interference mitigation (IM) of mega LEO systems. We first reveal the characteristics of MAGS interference pattern and formulate the IM problem into a $K$-coloring problem using an adaptive threshold method. Then we propose two tailored graph coloring algorithms, namely Generalized Global (GG) and Clique-Based Tabu Search (CTS), to solve this problem. GG employs a low-complexity greedy conflict avoidance strategy, while CTS leverages the unique clique structure brought by MAGSs to enhance IM performance. Subsequently, we innovatively modify them to achieve time-continuous frequency allocation, which is crucial to ensure the stability of feeder links. Moreover, we further devise two mega constellation decomposition methods to alleviate the complexity burden of satellite operators. Finally, we propose a list coloring-based vacant subchannel utilization method to further improve spectrum efficiency and system capacity. Simulation results on Starlink constellation of the first and second generations with 34396 satellites demonstrate the effectiveness and superiority of the proposed methodology.
Extract the Best, Discard the Rest: CSI Feedback with Offline Large AI Models
May 13, 2025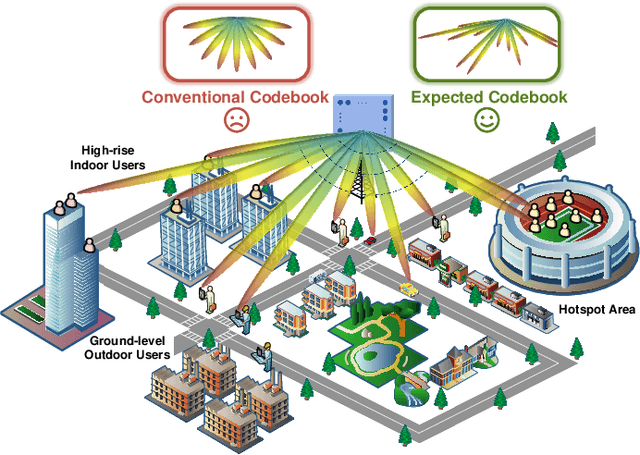
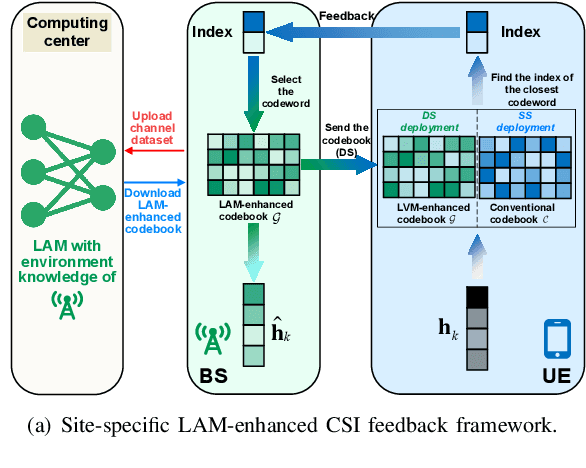
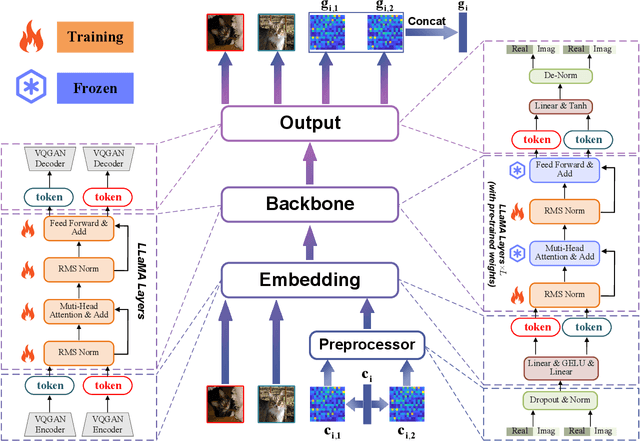
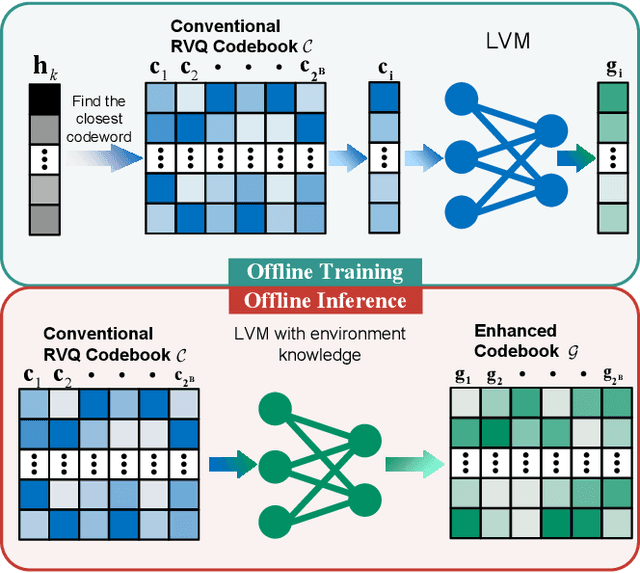
Abstract:Large AI models (LAMs) have shown strong potential in wireless communication tasks, but their practical deployment remains hindered by latency and computational constraints. In this work, we focus on the challenge of integrating LAMs into channel state information (CSI) feedback for frequency-division duplex (FDD) massive multiple-intput multiple-output (MIMO) systems. To this end, we propose two offline frameworks, namely site-specific LAM-enhanced CSI feedback (SSLCF) and multi-scenario LAM-enhanced CSI feedback (MSLCF), that incorporate LAMs into the codebook-based CSI feedback paradigm without requiring real-time inference. Specifically, SSLCF generates a site-specific enhanced codebook through fine-tuning on locally collected CSI data, while MSLCF improves generalization by pre-generating a set of environment-aware codebooks. Both of these frameworks build upon the LAM with vision-based backbone, which is pre-trained on large-scale image datasets and fine-tuned with CSI data to generate customized codebooks. This resulting network named LVM4CF captures the structural similarity between CSI and image, allowing the LAM to refine codewords tailored to the specific environments. To optimize the codebook refinement capability of LVM4CF under both single- and dual-side deployment modes, we further propose corresponding training and inference algorithms. Simulation results show that our frameworks significantly outperform existing schemes in both reconstruction accuracy and system throughput, without introducing additional inference latency or computational overhead. These results also support the core design methodology of our proposed frameworks, extracting the best and discarding the rest, as a promising pathway for integrating LAMs into future wireless systems.
Statistical CSI-Based Distributed Precoding Design for OFDM-Cooperative Multi-Satellite Systems
May 12, 2025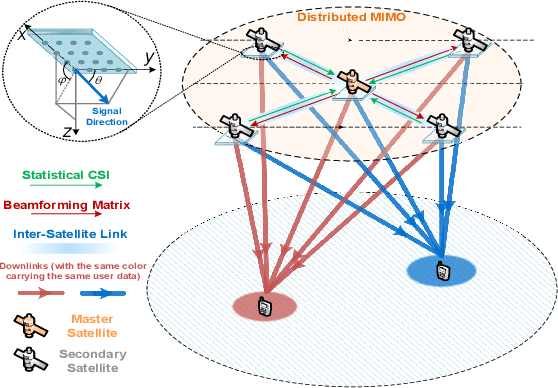
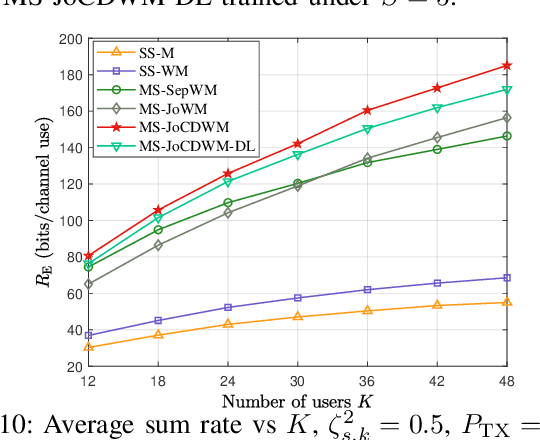
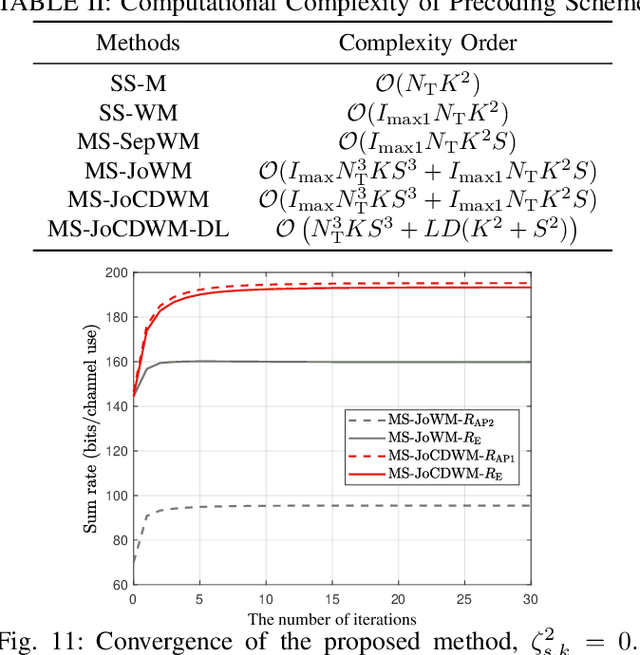
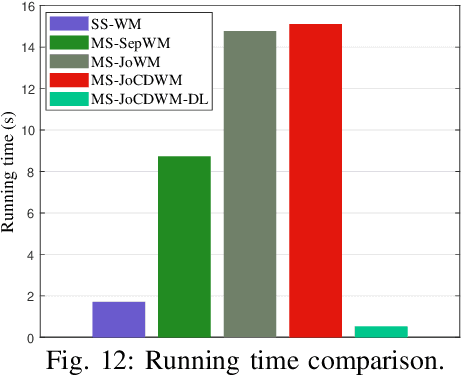
Abstract:This paper investigates the design of distributed precoding for multi-satellite massive MIMO transmissions. We first conduct a detailed analysis of the transceiver model, in which delay and Doppler precompensation is introduced to ensure coherent transmission. In this analysis, we examine the impact of precompensation errors on the transmission model, emphasize the near-independence of inter-satellite interference, and ultimately derive the received signal model. Based on such signal model, we formulate an approximate expected rate maximization problem that considers both statistical channel state information (sCSI) and compensation errors. Unlike conventional approaches that recast such problems as weighted minimum mean square error (WMMSE) minimization, we demonstrate that this transformation fails to maintain equivalence in the considered scenario. To address this, we introduce an equivalent covariance decomposition-based WMMSE (CDWMMSE) formulation derived based on channel covariance matrix decomposition. Taking advantage of the channel characteristics, we develop a low-complexity decomposition method and propose an optimization algorithm. To further reduce computational complexity, we introduce a model-driven scalable deep learning (DL) approach that leverages the equivariance of the mapping from sCSI to the unknown variables in the optimal closed-form solution, enhancing performance through novel dense Transformer network and scaling-invariant loss function design. Simulation results validate the effectiveness and robustness of the proposed method in some practical scenarios. We also demonstrate that the DL approach can adapt to dynamic settings with varying numbers of users and satellites.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge