Jiale Liu
Veri-Sure: A Contract-Aware Multi-Agent Framework with Temporal Tracing and Formal Verification for Correct RTL Code Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of Electronic Design Automation (EDA), the deployment of Large Language Models (LLMs) for Register-Transfer Level (RTL) design has emerged as a promising direction. However, silicon-grade correctness remains bottlenecked by: (i) limited test coverage and reliability of simulation-centric evaluation, (ii) regressions and repair hallucinations introduced by iterative debugging, and (iii) semantic drift as intent is reinterpreted across agent handoffs. In this work, we propose Veri-Sure, a multi-agent framework that establishes a design contract to align agents' intent and uses a patching mechanism guided by static dependency slicing to perform precise, localized repairs. By integrating a multi-branch verification pipeline that combines trace-driven temporal analysis with formal verification consisting of assertion-based checking and boolean equivalence proofs, Veri-Sure enables functional correctness beyond pure simulations. We also introduce VerilogEval-v2-EXT, extending the original benchmark with 53 more industrial-grade design tasks and stratified difficulty levels, and show that Veri-Sure achieves state-of-the-art verified-correct RTL code generation performance, surpassing standalone LLMs and prior agentic systems.
Do Images Speak Louder than Words? Investigating the Effect of Textual Misinformation in VLMs
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown strong multimodal reasoning capabilities on Visual-Question-Answering (VQA) benchmarks. However, their robustness against textual misinformation remains under-explored. While existing research has studied the effect of misinformation in text-only domains, it is not clear how VLMs arbitrate between contradictory information from different modalities. To bridge the gap, we first propose the CONTEXT-VQA (i.e., Conflicting Text) dataset, consisting of image-question pairs together with systematically generated persuasive prompts that deliberately conflict with visual evidence. Then, a thorough evaluation framework is designed and executed to benchmark the susceptibility of various models to these conflicting multimodal inputs. Comprehensive experiments over 11 state-of-the-art VLMs reveal that these models are indeed vulnerable to misleading textual prompts, often overriding clear visual evidence in favor of the conflicting text, and show an average performance drop of over 48.2% after only one round of persuasive conversation. Our findings highlight a critical limitation in current VLMs and underscore the need for improved robustness against textual manipulation.
Sliding Window Attention Adaptation
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:The self-attention mechanism in Transformer-based Large Language Models (LLMs) scales quadratically with input length, making long-context inference expensive. Sliding window attention (SWA) reduces this cost to linear complexity, but naively enabling complete SWA at inference-time for models pretrained with full attention (FA) causes severe long-context performance degradation due to training-inference mismatch. This makes us wonder: Can FA-pretrained LLMs be well adapted to SWA without pretraining? We investigate this by proposing Sliding Window Attention Adaptation (SWAA), a set of practical recipes that combine five methods for better adaptation: (1) applying SWA only during prefilling; (2) preserving "sink" tokens; (3) interleaving FA/SWA layers; (4) chain-of-thought (CoT); and (5) fine-tuning. Our experiments show that SWA adaptation is feasible while non-trivial: no single method suffices, yet specific synergistic combinations effectively recover the original long-context performance. We further analyze the performance-efficiency trade-offs of different SWAA configurations and provide recommended recipes for diverse scenarios, which can greatly and fundamentally accelerate LLM long-context inference speed by up to 100%. Our code is available at https://github.com/yuyijiong/sliding-window-attention-adaptation
Cross Modal Fine-Grained Alignment via Granularity-Aware and Region-Uncertain Modeling
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Fine-grained image-text alignment is a pivotal challenge in multimodal learning, underpinning key applications such as visual question answering, image captioning, and vision-language navigation. Unlike global alignment, fine-grained alignment requires precise correspondence between localized visual regions and textual tokens, often hindered by noisy attention mechanisms and oversimplified modeling of cross-modal relationships. In this work, we identify two fundamental limitations of existing approaches: the lack of robust intra-modal mechanisms to assess the significance of visual and textual tokens, leading to poor generalization in complex scenes; and the absence of fine-grained uncertainty modeling, which fails to capture the one-to-many and many-to-one nature of region-word correspondences. To address these issues, we propose a unified approach that incorporates significance-aware and granularity-aware modeling and region-level uncertainty modeling. Our method leverages modality-specific biases to identify salient features without relying on brittle cross-modal attention, and represents region features as a mixture of Gaussian distributions to capture fine-grained uncertainty. Extensive experiments on Flickr30K and MS-COCO demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance across various backbone architectures, significantly enhancing the robustness and interpretability of fine-grained image-text alignment.
Exposing Privacy Risks in Graph Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) is a powerful technique for enhancing Large Language Models (LLMs) with external, up-to-date knowledge. Graph RAG has emerged as an advanced paradigm that leverages graph-based knowledge structures to provide more coherent and contextually rich answers. However, the move from plain document retrieval to structured graph traversal introduces new, under-explored privacy risks. This paper investigates the data extraction vulnerabilities of the Graph RAG systems. We design and execute tailored data extraction attacks to probe their susceptibility to leaking both raw text and structured data, such as entities and their relationships. Our findings reveal a critical trade-off: while Graph RAG systems may reduce raw text leakage, they are significantly more vulnerable to the extraction of structured entity and relationship information. We also explore potential defense mechanisms to mitigate these novel attack surfaces. This work provides a foundational analysis of the unique privacy challenges in Graph RAG and offers insights for building more secure systems.
Divide, Optimize, Merge: Fine-Grained LLM Agent Optimization at Scale
May 06, 2025Abstract:LLM-based optimization has shown remarkable potential in enhancing agentic systems. However, the conventional approach of prompting LLM optimizer with the whole training trajectories on training dataset in a single pass becomes untenable as datasets grow, leading to context window overflow and degraded pattern recognition. To address these challenges, we propose Fine-Grained Optimization (FGO), a scalable framework that divides large optimization tasks into manageable subsets, performs targeted optimizations, and systematically combines optimized components through progressive merging. Evaluation across ALFWorld, LogisticsQA, and GAIA benchmarks demonstrate that FGO outperforms existing approaches by 1.6-8.6% while reducing average prompt token consumption by 56.3%. Our framework provides a practical solution for scaling up LLM-based optimization of increasingly sophisticated agent systems. Further analysis demonstrates that FGO achieves the most consistent performance gain in all training dataset sizes, showcasing its scalability and efficiency.
Which Agent Causes Task Failures and When? On Automated Failure Attribution of LLM Multi-Agent Systems
Apr 30, 2025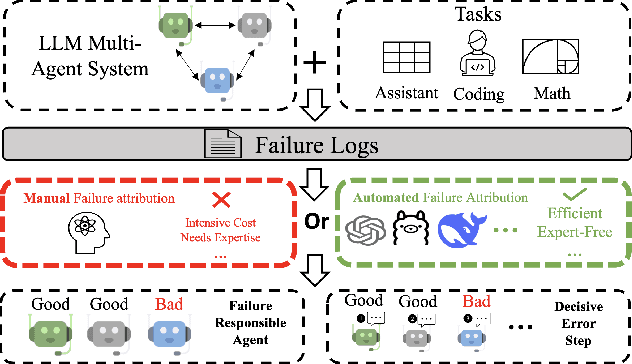
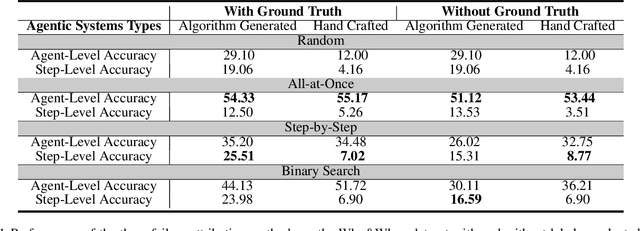
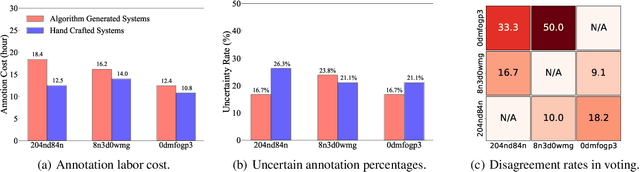

Abstract:Failure attribution in LLM multi-agent systems-identifying the agent and step responsible for task failures-provides crucial clues for systems debugging but remains underexplored and labor-intensive. In this paper, we propose and formulate a new research area: automated failure attribution for LLM multi-agent systems. To support this initiative, we introduce the Who&When dataset, comprising extensive failure logs from 127 LLM multi-agent systems with fine-grained annotations linking failures to specific agents and decisive error steps. Using the Who&When, we develop and evaluate three automated failure attribution methods, summarizing their corresponding pros and cons. The best method achieves 53.5% accuracy in identifying failure-responsible agents but only 14.2% in pinpointing failure steps, with some methods performing below random. Even SOTA reasoning models, such as OpenAI o1 and DeepSeek R1, fail to achieve practical usability. These results highlight the task's complexity and the need for further research in this area. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/mingyin1/Agents_Failure_Attribution
Identifying Trustworthiness Challenges in Deep Learning Models for Continental-Scale Water Quality Prediction
Mar 13, 2025



Abstract:Water quality is foundational to environmental sustainability, ecosystem resilience, and public health. Deep learning models, particularly Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, offer transformative potential for large-scale water quality prediction and scientific insights generation. However, their widespread adoption in high-stakes decision-making, such as pollution mitigation and equitable resource allocation, is prevented by unresolved trustworthiness challenges including fairness, uncertainty, interpretability, robustness, generalizability, and reproducibility. In this work, we present the first comprehensive evaluation of trustworthiness in a continental-scale multi-task LSTM model predicting 20 water quality variables (encompassing physical/chemical processes, geochemical weathering, and nutrient cycling) across 482 U.S. basins. Our investigation uncovers systematic patterns of model performance disparities linked to basin characteristics, the inherent complexity of biogeochemical processes, and variable predictability, emphasizing critical performance fairness concerns. We further propose methodological frameworks for quantitatively evaluating critical aspects of trustworthiness, including uncertainty, interpretability, and robustness, identifying key limitations that could challenge reliable real-world deployment. This work serves as a timely call to action for advancing trustworthy data-driven methods for water resources management and provides a pathway to offering critical insights for researchers, decision-makers, and practitioners seeking to leverage artificial intelligence (AI) responsibly in environmental management.
CovNet: Covariance Information-Assisted CSI Feedback for FDD Massive MIMO Systems
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel covariance information-assisted channel state information (CSI) feedback scheme for frequency-division duplex (FDD) massive multi-input multi-output (MIMO) systems. Unlike most existing CSI feedback schemes, which rely on instantaneous CSI only, the proposed CovNet leverages CSI covariance information to achieve high-performance CSI reconstruction, primarily consisting of convolutional neural network (CNN) and Transformer architecture. To efficiently utilize covariance information, we propose a covariance information processing procedure and sophisticatedly design the covariance information processing network (CIPN) to further process it. Moreover, the feed-forward network (FFN) in CovNet is designed to jointly leverage the 2D characteristics of the CSI matrix in the angle and delay domains. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed network effectively leverages covariance information and outperforms the state-of-the-art (SOTA) scheme across the full compression ratio (CR) range.
Memory-Augmented Agent Training for Business Document Understanding
Dec 17, 2024



Abstract:Traditional enterprises face significant challenges in processing business documents, where tasks like extracting transport references from invoices remain largely manual despite their crucial role in logistics operations. While Large Language Models offer potential automation, their direct application to specialized business domains often yields unsatisfactory results. We introduce Matrix (Memory-Augmented agent Training through Reasoning and Iterative eXploration), a novel paradigm that enables LLM agents to progressively build domain expertise through experience-driven memory refinement and iterative learning. To validate this approach, we collaborate with one of the world's largest logistics companies to create a dataset of Universal Business Language format invoice documents, focusing on the task of transport reference extraction. Experiments demonstrate that Matrix outperforms prompting a single LLM by 30.3%, vanilla LLM agent by 35.2%. We further analyze the metrics of the optimized systems and observe that the agent system requires less API calls, fewer costs and can analyze longer documents on average. Our methods establish a new approach to transform general-purpose LLMs into specialized business tools through systematic memory enhancement in document processing tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge