Shijing He
Privacy in Human-AI Romantic Relationships: Concerns, Boundaries, and Agency
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:An increasing number of LLM-based applications are being developed to facilitate romantic relationships with AI partners, yet the safety and privacy risks in these partnerships remain largely underexplored. In this work, we investigate privacy in human-AI romantic relationships through an interview study (N=17), examining participants' experiences and privacy perceptions across stages of exploration, intimacy, and dissolution, alongside platforms they used. We found that these relationships took varied forms, from one-to-one to one-to-many, and were shaped by multiple actors, including creators, platforms, and moderators. AI partners were perceived as having agency, actively negotiating privacy boundaries with participants and sometimes encouraging disclosure of personal details. As intimacy deepened, these boundaries became more permeable, though some participants voiced concerns such as conversation exposure and sought to preserve anonymity. Overall, platform affordances and diverse romantic dynamics expand the privacy landscape, underscoring the need to rethink how privacy is constructed in human-AI intimacy.
MAC-Gaze: Motion-Aware Continual Calibration for Mobile Gaze Tracking
May 28, 2025Abstract:Mobile gaze tracking faces a fundamental challenge: maintaining accuracy as users naturally change their postures and device orientations. Traditional calibration approaches, like one-off, fail to adapt to these dynamic conditions, leading to degraded performance over time. We present MAC-Gaze, a Motion-Aware continual Calibration approach that leverages smartphone Inertial measurement unit (IMU) sensors and continual learning techniques to automatically detect changes in user motion states and update the gaze tracking model accordingly. Our system integrates a pre-trained visual gaze estimator and an IMU-based activity recognition model with a clustering-based hybrid decision-making mechanism that triggers recalibration when motion patterns deviate significantly from previously encountered states. To enable accumulative learning of new motion conditions while mitigating catastrophic forgetting, we employ replay-based continual learning, allowing the model to maintain performance across previously encountered motion conditions. We evaluate our system through extensive experiments on the publicly available RGBDGaze dataset and our own 10-hour multimodal MotionGaze dataset (481K+ images, 800K+ IMU readings), encompassing a wide range of postures under various motion conditions including sitting, standing, lying, and walking. Results demonstrate that our method reduces gaze estimation error by 19.9% on RGBDGaze (from 1.73 cm to 1.41 cm) and by 31.7% on MotionGaze (from 2.81 cm to 1.92 cm) compared to traditional calibration approaches. Our framework provides a robust solution for maintaining gaze estimation accuracy in mobile scenarios.
An End-to-End Review of Gaze Estimation and its Interactive Applications on Handheld Mobile Devices
Jun 30, 2023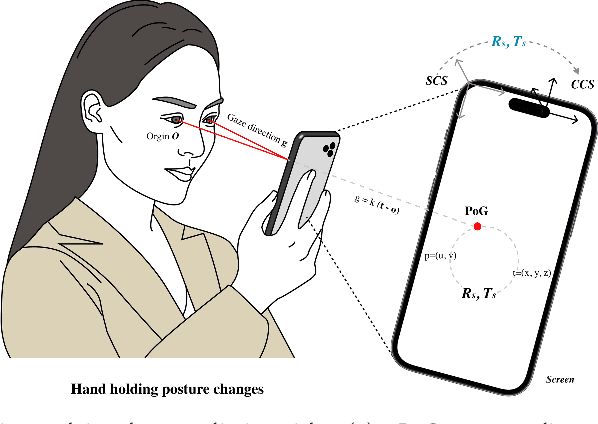
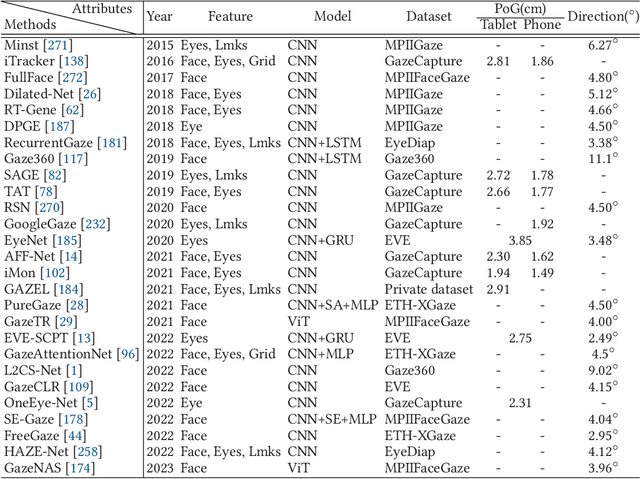

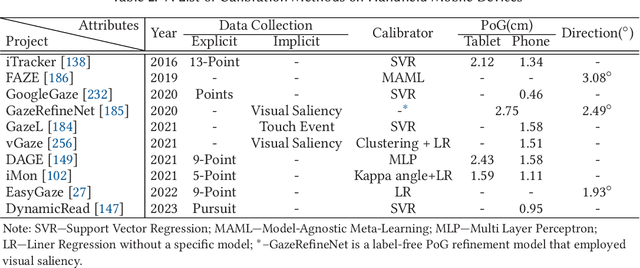
Abstract:In recent years we have witnessed an increasing number of interactive systems on handheld mobile devices which utilise gaze as a single or complementary interaction modality. This trend is driven by the enhanced computational power of these devices, higher resolution and capacity of their cameras, and improved gaze estimation accuracy obtained from advanced machine learning techniques, especially in deep learning. As the literature is fast progressing, there is a pressing need to review the state of the art, delineate the boundary, and identify the key research challenges and opportunities in gaze estimation and interaction. This paper aims to serve this purpose by presenting an end-to-end holistic view in this area, from gaze capturing sensors, to gaze estimation workflows, to deep learning techniques, and to gaze interactive applications.
* 37 Pages, Paper accepted by ACM Computing Surveys
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge