Dihan Li
OpenFedLLM: Training Large Language Models on Decentralized Private Data via Federated Learning
Feb 10, 2024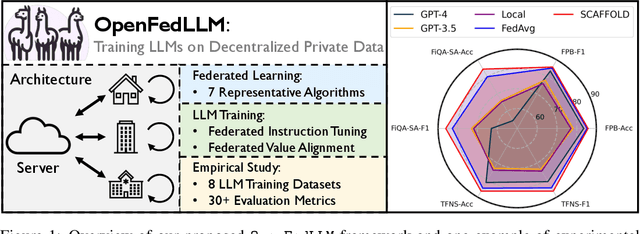
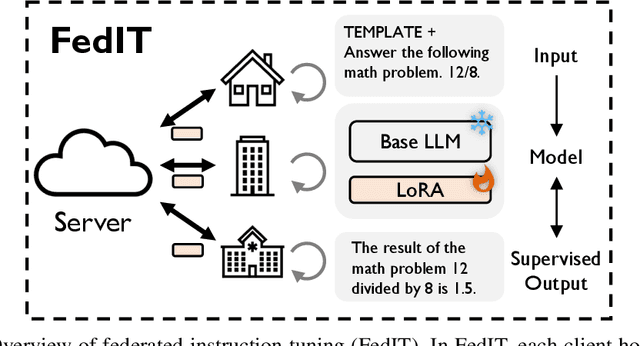
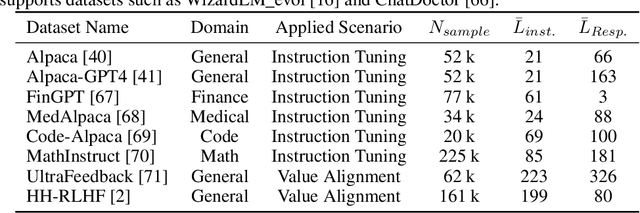
Abstract:Trained on massive publicly available data, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated tremendous success across various fields. While more data contributes to better performance, a disconcerting reality is that high-quality public data will be exhausted in a few years. In this paper, we offer a potential next step for contemporary LLMs: collaborative and privacy-preserving LLM training on the underutilized distributed private data via federated learning (FL), where multiple data owners collaboratively train a shared model without transmitting raw data. To achieve this, we build a concise, integrated, and research-friendly framework/codebase, named OpenFedLLM. It covers federated instruction tuning for enhancing instruction-following capability, federated value alignment for aligning with human values, and 7 representative FL algorithms. Besides, OpenFedLLM supports training on diverse domains, where we cover 8 training datasets; and provides comprehensive evaluations, where we cover 30+ evaluation metrics. Through extensive experiments, we observe that all FL algorithms outperform local training on training LLMs, demonstrating a clear performance improvement across a variety of settings. Notably, in a financial benchmark, Llama2-7B fine-tuned by applying any FL algorithm can outperform GPT-4 by a significant margin while the model obtained through individual training cannot, demonstrating strong motivation for clients to participate in FL. The code is available at https://github.com/rui-ye/OpenFedLLM.
TFCNs: A CNN-Transformer Hybrid Network for Medical Image Segmentation
Jul 07, 2022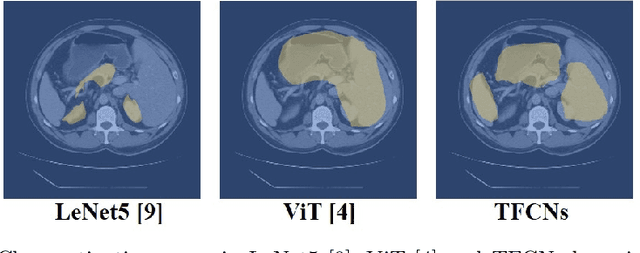
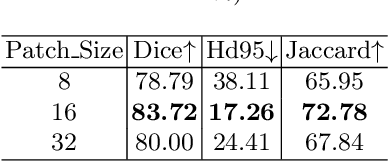
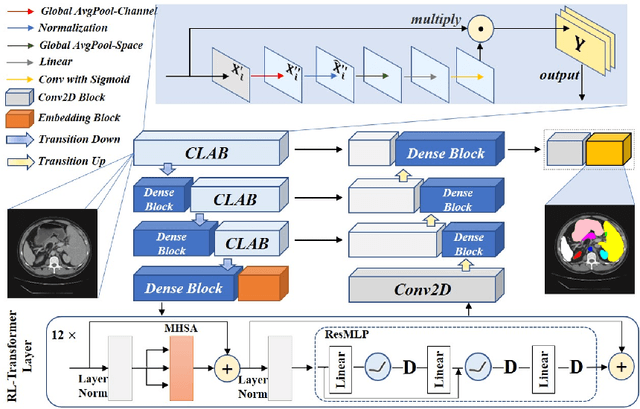
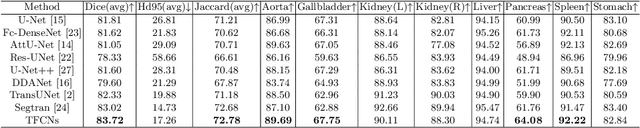
Abstract:Medical image segmentation is one of the most fundamental tasks concerning medical information analysis. Various solutions have been proposed so far, including many deep learning-based techniques, such as U-Net, FC-DenseNet, etc. However, high-precision medical image segmentation remains a highly challenging task due to the existence of inherent magnification and distortion in medical images as well as the presence of lesions with similar density to normal tissues. In this paper, we propose TFCNs (Transformers for Fully Convolutional denseNets) to tackle the problem by introducing ResLinear-Transformer (RL-Transformer) and Convolutional Linear Attention Block (CLAB) to FC-DenseNet. TFCNs is not only able to utilize more latent information from the CT images for feature extraction, but also can capture and disseminate semantic features and filter non-semantic features more effectively through the CLAB module. Our experimental results show that TFCNs can achieve state-of-the-art performance with dice scores of 83.72\% on the Synapse dataset. In addition, we evaluate the robustness of TFCNs for lesion area effects on the COVID-19 public datasets. The Python code will be made publicly available on https://github.com/HUANGLIZI/TFCNs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge