Ya Zhang
Multi-Source Retrieval and Reasoning for Legal Sentencing Prediction
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Legal judgment prediction (LJP) aims to predict judicial outcomes from case facts and typically includes law article, charge, and sentencing prediction. While recent methods perform well on the first two subtasks, legal sentencing prediction (LSP) remains difficult due to its need for fine-grained objective knowledge and flexible subjective reasoning. To address these limitations, we propose $MSR^2$, a framework that integrates multi-source retrieval and reasoning in LLMs with reinforcement learning. $MSR^2$ enables LLMs to perform multi-source retrieval based on reasoning needs and applies a process-level reward to guide intermediate subjective reasoning steps. Experiments on two real-world datasets show that $MSR^2$ improves both accuracy and interpretability in LSP, providing a promising step toward practical legal AI. Our code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MSR2-FC3B.
LegalOne: A Family of Foundation Models for Reliable Legal Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive general capabilities, their direct application in the legal domain is often hindered by a lack of precise domain knowledge and complexity of performing rigorous multi-step judicial reasoning. To address this gap, we present LegalOne, a family of foundational models specifically tailored for the Chinese legal domain. LegalOne is developed through a comprehensive three-phase pipeline designed to master legal reasoning. First, during mid-training phase, we propose Plasticity-Adjusted Sampling (PAS) to address the challenge of domain adaptation. This perplexity-based scheduler strikes a balance between the acquisition of new knowledge and the retention of original capabilities, effectively establishing a robust legal foundation. Second, during supervised fine-tuning, we employ Legal Agentic CoT Distillation (LEAD) to distill explicit reasoning from raw legal texts. Unlike naive distillation, LEAD utilizes an agentic workflow to convert complex judicial processes into structured reasoning trajectories, thereby enforcing factual grounding and logical rigor. Finally, we implement a Curriculum Reinforcement Learning (RL) strategy. Through a progressive reinforcement process spanning memorization, understanding, and reasoning, LegalOne evolves from simple pattern matching to autonomous and reliable legal reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that LegalOne achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of legal tasks, surpassing general-purpose LLMs with vastly larger parameter counts through enhanced knowledge density and efficiency. We publicly release the LegalOne weights and the LegalKit evaluation framework to advance the field of Legal AI, paving the way for deploying trustworthy and interpretable foundation models in high-stakes judicial applications.
Miner:Mining Intrinsic Mastery for Data-Efficient RL in Large Reasoning Models
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Current critic-free RL methods for large reasoning models suffer from severe inefficiency when training on positive homogeneous prompts (where all rollouts are correct), resulting in waste of rollouts due to zero advantage estimates. We introduce a radically simple yet powerful solution to \uline{M}ine \uline{in}trinsic mast\uline{er}y (Miner), that repurposes the policy's intrinsic uncertainty as a self-supervised reward signal, with no external supervision, auxiliary models, or additional inference cost. Our method pioneers two key innovations: (1) a token-level focal credit assignment mechanism that dynamically amplifies gradients on critical uncertain tokens while suppressing overconfident ones, and (2) adaptive advantage calibration to seamlessly integrate intrinsic and verifiable rewards. Evaluated across six reasoning benchmarks on Qwen3-4B and Qwen3-8B base models, Miner achieves state-of-the-art performance among the other four algorithms, yielding up to \textbf{4.58} absolute gains in Pass@1 and \textbf{6.66} gains in Pass@K compared to GRPO. Comparison with other methods targeted at exploration enhancement further discloses the superiority of the two newly proposed innovations. This demonstrates that latent uncertainty exploitation is both necessary and sufficient for efficient and scalable RL training of reasoning models.
Automatic Reward Shaping from Multi-Objective Human Heuristics
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Designing effective reward functions remains a central challenge in reinforcement learning, especially in multi-objective environments. In this work, we propose Multi-Objective Reward Shaping with Exploration (MORSE), a general framework that automatically combines multiple human-designed heuristic rewards into a unified reward function. MORSE formulates the shaping process as a bi-level optimization problem: the inner loop trains a policy to maximize the current shaped reward, while the outer loop updates the reward function to optimize task performance. To encourage exploration in the reward space and avoid suboptimal local minima, MORSE introduces stochasticity into the shaping process, injecting noise guided by task performance and the prediction error of a fixed, randomly initialized neural network. Experimental results in MuJoCo and Isaac Sim environments show that MORSE effectively balances multiple objectives across various robotic tasks, achieving task performance comparable to those obtained with manually tuned reward functions.
CoPAD : Multi-source Trajectory Fusion and Cooperative Trajectory Prediction with Anchor-oriented Decoder in V2X Scenarios
Sep 19, 2025Abstract:Recently, data-driven trajectory prediction methods have achieved remarkable results, significantly advancing the development of autonomous driving. However, the instability of single-vehicle perception introduces certain limitations to trajectory prediction. In this paper, a novel lightweight framework for cooperative trajectory prediction, CoPAD, is proposed. This framework incorporates a fusion module based on the Hungarian algorithm and Kalman filtering, along with the Past Time Attention (PTA) module, mode attention module and anchor-oriented decoder (AoD). It effectively performs early fusion on multi-source trajectory data from vehicles and road infrastructure, enabling the trajectories with high completeness and accuracy. The PTA module can efficiently capture potential interaction information among historical trajectories, and the mode attention module is proposed to enrich the diversity of predictions. Additionally, the decoder based on sparse anchors is designed to generate the final complete trajectories. Extensive experiments show that CoPAD achieves the state-of-the-art performance on the DAIR-V2X-Seq dataset, validating the effectiveness of the model in cooperative trajectory prediction in V2X scenarios.
Visual Programmability: A Guide for Code-as-Thought in Chart Understanding
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:Chart understanding presents a critical test to the reasoning capabilities of Vision-Language Models (VLMs). Prior approaches face critical limitations: some rely on external tools, making them brittle and constrained by a predefined toolkit, while others fine-tune specialist models that often adopt a single reasoning strategy, such as text-based chain-of-thought (CoT). The intermediate steps of text-based reasoning are difficult to verify, which complicates the use of reinforcement-learning signals that reward factual accuracy. To address this, we propose a Code-as-Thought (CaT) approach to represent the visual information of a chart in a verifiable, symbolic format. Our key insight is that this strategy must be adaptive: a fixed, code-only implementation consistently fails on complex charts where symbolic representation is unsuitable. This finding leads us to introduce Visual Programmability: a learnable property that determines if a chart-question pair is better solved with code or direct visual analysis. We implement this concept in an adaptive framework where a VLM learns to choose between the CaT pathway and a direct visual reasoning pathway. The selection policy of the model is trained with reinforcement learning using a novel dual-reward system. This system combines a data-accuracy reward to ground the model in facts and prevent numerical hallucination, with a decision reward that teaches the model when to use each strategy, preventing it from defaulting to a single reasoning mode. Experiments demonstrate strong and robust performance across diverse chart-understanding benchmarks. Our work shows that VLMs can be taught not only to reason but also how to reason, dynamically selecting the optimal reasoning pathway for each task.
Wide-In, Narrow-Out: Revokable Decoding for Efficient and Effective DLLMs
Jul 24, 2025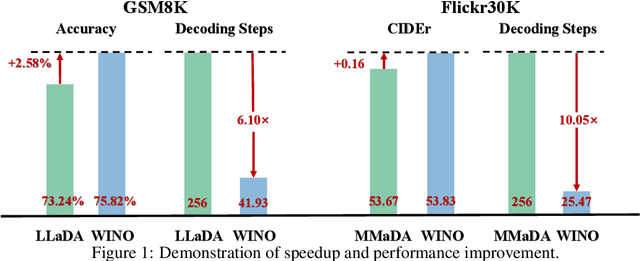
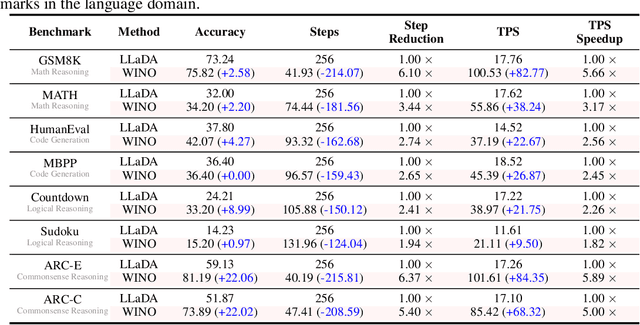
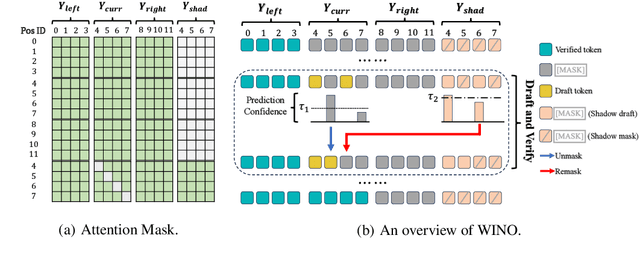
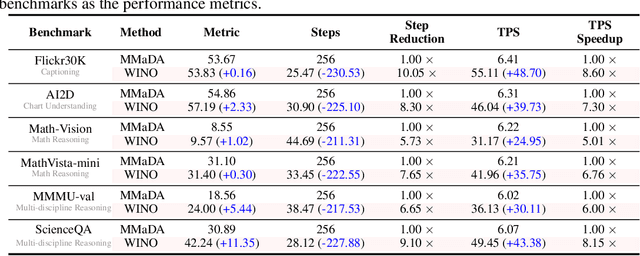
Abstract:Diffusion Large Language Models (DLLMs) have emerged as a compelling alternative to Autoregressive models, designed for fast parallel generation. However, existing DLLMs are plagued by a severe quality-speed trade-off, where faster parallel decoding leads to significant performance degradation. We attribute this to the irreversibility of standard decoding in DLLMs, which is easily polarized into the wrong decoding direction along with early error context accumulation. To resolve this, we introduce Wide-In, Narrow-Out (WINO), a training-free decoding algorithm that enables revokable decoding in DLLMs. WINO employs a parallel draft-and-verify mechanism, aggressively drafting multiple tokens while simultaneously using the model's bidirectional context to verify and re-mask suspicious ones for refinement. Verified in open-source DLLMs like LLaDA and MMaDA, WINO is shown to decisively improve the quality-speed trade-off. For instance, on the GSM8K math benchmark, it accelerates inference by 6$\times$ while improving accuracy by 2.58%; on Flickr30K captioning, it achieves a 10$\times$ speedup with higher performance. More comprehensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the superiority and provide an in-depth understanding of WINO.
Differential-informed Sample Selection Accelerates Multimodal Contrastive Learning
Jul 17, 2025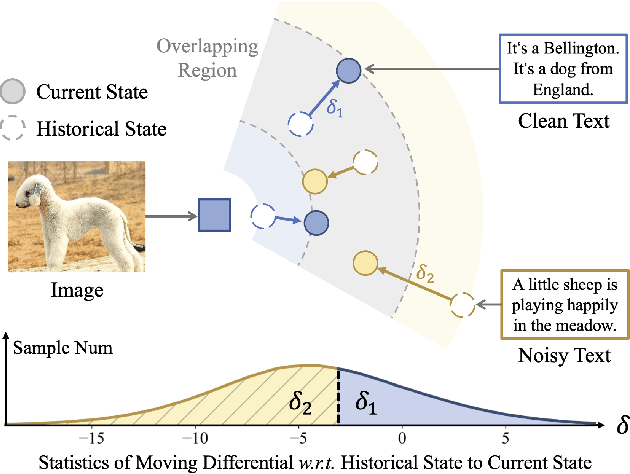
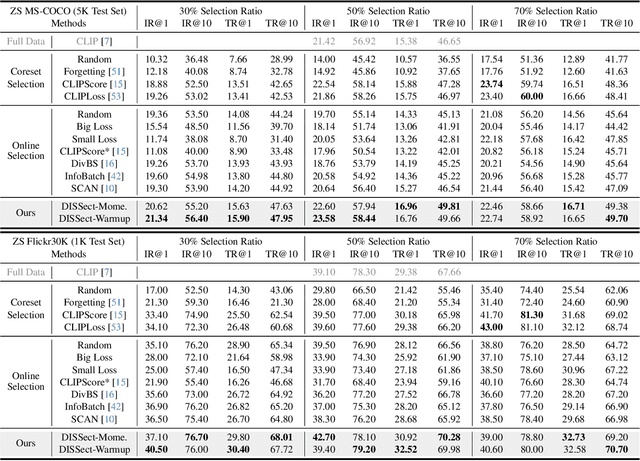
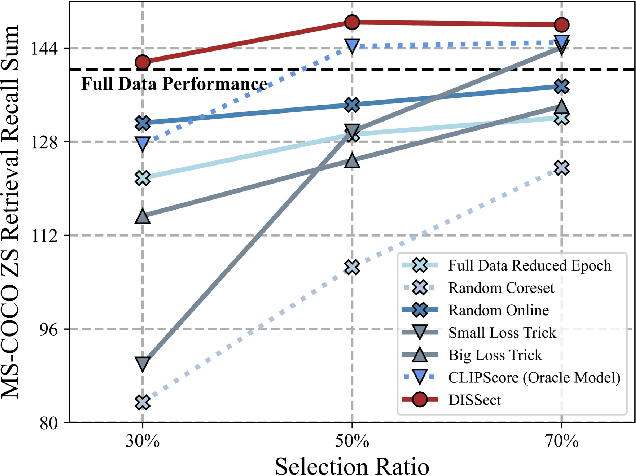
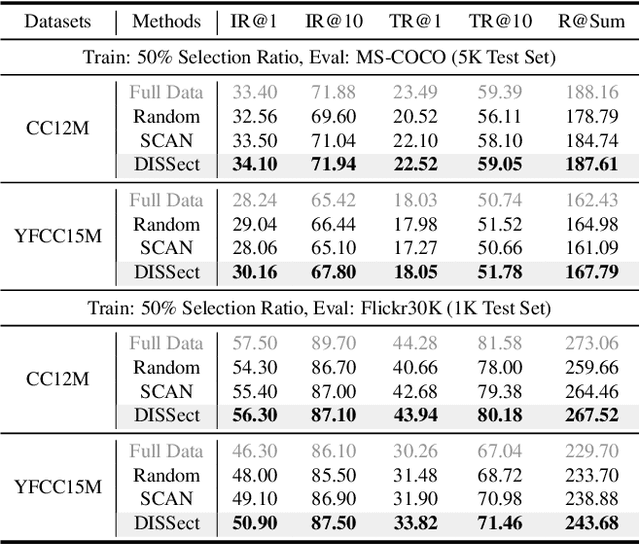
Abstract:The remarkable success of contrastive-learning-based multimodal models has been greatly driven by training on ever-larger datasets with expensive compute consumption. Sample selection as an alternative efficient paradigm plays an important direction to accelerate the training process. However, recent advances on sample selection either mostly rely on an oracle model to offline select a high-quality coreset, which is limited in the cold-start scenarios, or focus on online selection based on real-time model predictions, which has not sufficiently or efficiently considered the noisy correspondence. To address this dilemma, we propose a novel Differential-Informed Sample Selection (DISSect) method, which accurately and efficiently discriminates the noisy correspondence for training acceleration. Specifically, we rethink the impact of noisy correspondence on contrastive learning and propose that the differential between the predicted correlation of the current model and that of a historical model is more informative to characterize sample quality. Based on this, we construct a robust differential-based sample selection and analyze its theoretical insights. Extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets and various downstream tasks demonstrate the consistent superiority of DISSect over current state-of-the-art methods. Source code is available at: https://github.com/MediaBrain-SJTU/DISSect.
ConText: Driving In-context Learning for Text Removal and Segmentation
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:This paper presents the first study on adapting the visual in-context learning (V-ICL) paradigm to optical character recognition tasks, specifically focusing on text removal and segmentation. Most existing V-ICL generalists employ a reasoning-as-reconstruction approach: they turn to using a straightforward image-label compositor as the prompt and query input, and then masking the query label to generate the desired output. This direct prompt confines the model to a challenging single-step reasoning process. To address this, we propose a task-chaining compositor in the form of image-removal-segmentation, providing an enhanced prompt that elicits reasoning with enriched intermediates. Additionally, we introduce context-aware aggregation, integrating the chained prompt pattern into the latent query representation, thereby strengthening the model's in-context reasoning. We also consider the issue of visual heterogeneity, which complicates the selection of homogeneous demonstrations in text recognition. Accordingly, this is effectively addressed through a simple self-prompting strategy, preventing the model's in-context learnability from devolving into specialist-like, context-free inference. Collectively, these insights culminate in our ConText model, which achieves new state-of-the-art across both in- and out-of-domain benchmarks. The code is available at https://github.com/Ferenas/ConText.
SpatialScore: Towards Unified Evaluation for Multimodal Spatial Understanding
May 22, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have achieved impressive success in question-answering tasks, yet their capabilities for spatial understanding are less explored. This work investigates a critical question: do existing MLLMs possess 3D spatial perception and understanding abilities? Concretely, we make the following contributions in this paper: (i) we introduce VGBench, a benchmark specifically designed to assess MLLMs for visual geometry perception, e.g., camera pose and motion estimation; (ii) we propose SpatialScore, the most comprehensive and diverse multimodal spatial understanding benchmark to date, integrating VGBench with relevant data from the other 11 existing datasets. This benchmark comprises 28K samples across various spatial understanding tasks, modalities, and QA formats, along with a carefully curated challenging subset, SpatialScore-Hard; (iii) we develop SpatialAgent, a novel multi-agent system incorporating 9 specialized tools for spatial understanding, supporting both Plan-Execute and ReAct reasoning paradigms; (iv) we conduct extensive evaluations to reveal persistent challenges in spatial reasoning while demonstrating the effectiveness of SpatialAgent. We believe SpatialScore will offer valuable insights and serve as a rigorous benchmark for the next evolution of MLLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge