Guoxin Wang
TinyDrop: Tiny Model Guided Token Dropping for Vision Transformers
Sep 03, 2025Abstract:Vision Transformers (ViTs) achieve strong performance in image classification but incur high computational costs from processing all image tokens. To reduce inference costs in large ViTs without compromising accuracy, we propose TinyDrop, a training-free token dropping framework guided by a lightweight vision model. The guidance model estimates the importance of tokens while performing inference, thereby selectively discarding low-importance tokens if large vit models need to perform attention calculations. The framework operates plug-and-play, requires no architectural modifications, and is compatible with diverse ViT architectures. Evaluations on standard image classification benchmarks demonstrate that our framework reduces FLOPs by up to 80% for ViTs with minimal accuracy degradation, highlighting its generalization capability and practical utility for efficient ViT-based classification.
Optimal Brain Connection: Towards Efficient Structural Pruning
Aug 07, 2025Abstract:Structural pruning has been widely studied for its effectiveness in compressing neural networks. However, existing methods often neglect the interconnections among parameters. To address this limitation, this paper proposes a structural pruning framework termed Optimal Brain Connection. First, we introduce the Jacobian Criterion, a first-order metric for evaluating the saliency of structural parameters. Unlike existing first-order methods that assess parameters in isolation, our criterion explicitly captures both intra-component interactions and inter-layer dependencies. Second, we propose the Equivalent Pruning mechanism, which utilizes autoencoders to retain the contributions of all original connection--including pruned ones--during fine-tuning. Experimental results demonstrate that the Jacobian Criterion outperforms several popular metrics in preserving model performance, while the Equivalent Pruning mechanism effectively mitigates performance degradation after fine-tuning. Code: https://github.com/ShaowuChen/Optimal_Brain_Connection
JoyTTS: LLM-based Spoken Chatbot With Voice Cloning
Jul 03, 2025Abstract:JoyTTS is an end-to-end spoken chatbot that combines large language models (LLM) with text-to-speech (TTS) technology, featuring voice cloning capabilities. This project is built upon the open-source MiniCPM-o and CosyVoice2 models and trained on 2000 hours of conversational data. We have also provided the complete training code to facilitate further development and optimization by the community. On the testing machine seed-tts-zh, it achieves a SS (speaker similarity) score of 0.73 and a WER (Word Error Rate) of 5.09. The code and models, along with training and inference scripts, are available at https://github.com/jdh-algo/JoyTTS.git.
ORXE: Orchestrating Experts for Dynamically Configurable Efficiency
May 07, 2025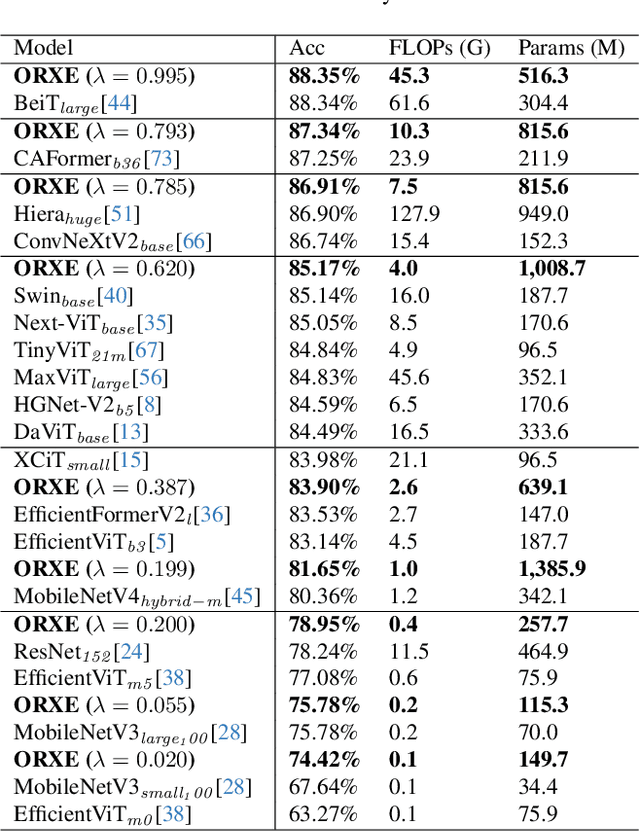
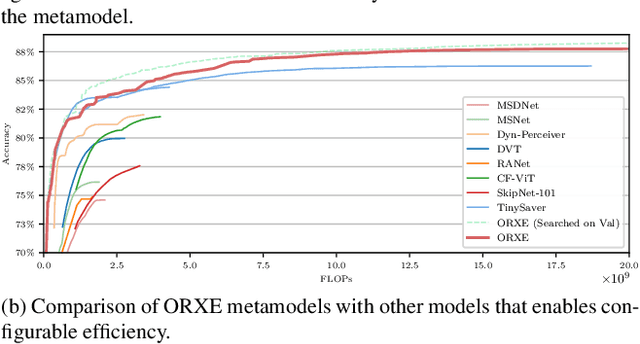
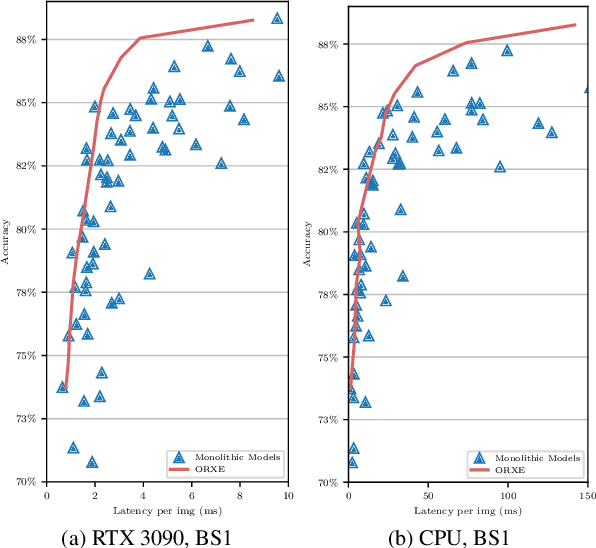
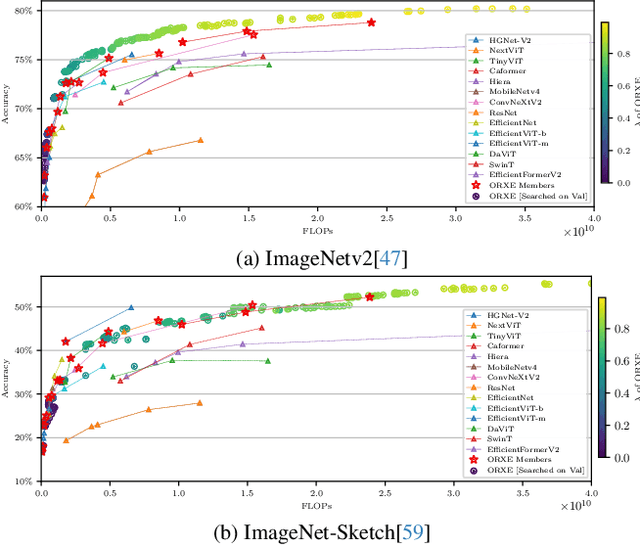
Abstract:This paper presents ORXE, a modular and adaptable framework for achieving real-time configurable efficiency in AI models. By leveraging a collection of pre-trained experts with diverse computational costs and performance levels, ORXE dynamically adjusts inference pathways based on the complexity of input samples. Unlike conventional approaches that require complex metamodel training, ORXE achieves high efficiency and flexibility without complicating the development process. The proposed system utilizes a confidence-based gating mechanism to allocate appropriate computational resources for each input. ORXE also supports adjustments to the preference between inference cost and prediction performance across a wide range during runtime. We implemented a training-free ORXE system for image classification tasks, evaluating its efficiency and accuracy across various devices. The results demonstrate that ORXE achieves superior performance compared to individual experts and other dynamic models in most cases. This approach can be extended to other applications, providing a scalable solution for diverse real-world deployment scenarios.
Citrus: Leveraging Expert Cognitive Pathways in a Medical Language Model for Advanced Medical Decision Support
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs), particularly those with reasoning capabilities, have rapidly advanced in recent years, demonstrating significant potential across a wide range of applications. However, their deployment in healthcare, especially in disease reasoning tasks, is hindered by the challenge of acquiring expert-level cognitive data. In this paper, we introduce Citrus, a medical language model that bridges the gap between clinical expertise and AI reasoning by emulating the cognitive processes of medical experts. The model is trained on a large corpus of simulated expert disease reasoning data, synthesized using a novel approach that accurately captures the decision-making pathways of clinicians. This approach enables Citrus to better simulate the complex reasoning processes involved in diagnosing and treating medical conditions. To further address the lack of publicly available datasets for medical reasoning tasks, we release the last-stage training data, including a custom-built medical diagnostic dialogue dataset. This open-source contribution aims to support further research and development in the field. Evaluations using authoritative benchmarks such as MedQA, covering tasks in medical reasoning and language understanding, show that Citrus achieves superior performance compared to other models of similar size. These results highlight Citrus potential to significantly enhance medical decision support systems, providing a more accurate and efficient tool for clinical decision-making.
JoyVASA: Portrait and Animal Image Animation with Diffusion-Based Audio-Driven Facial Dynamics and Head Motion Generation
Nov 14, 2024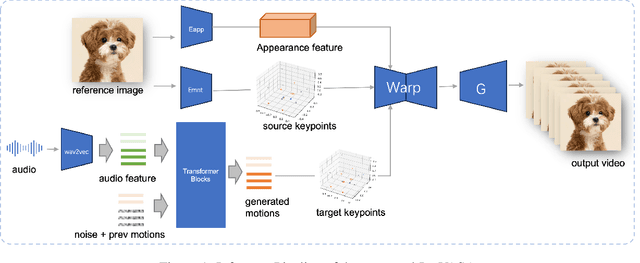
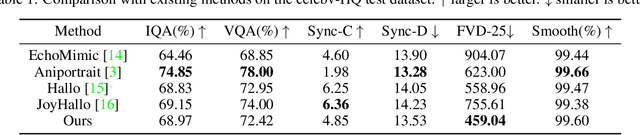
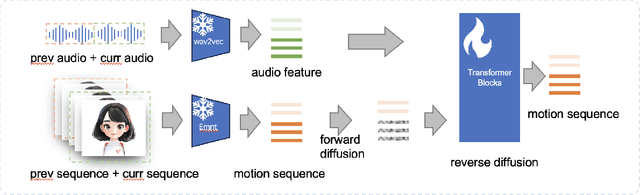
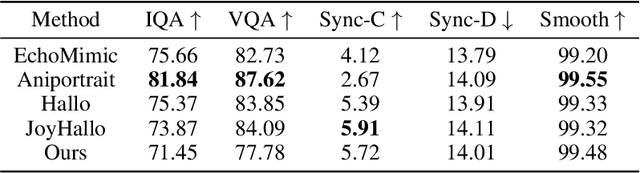
Abstract:Audio-driven portrait animation has made significant advances with diffusion-based models, improving video quality and lipsync accuracy. However, the increasing complexity of these models has led to inefficiencies in training and inference, as well as constraints on video length and inter-frame continuity. In this paper, we propose JoyVASA, a diffusion-based method for generating facial dynamics and head motion in audio-driven facial animation. Specifically, in the first stage, we introduce a decoupled facial representation framework that separates dynamic facial expressions from static 3D facial representations. This decoupling allows the system to generate longer videos by combining any static 3D facial representation with dynamic motion sequences. Then, in the second stage, a diffusion transformer is trained to generate motion sequences directly from audio cues, independent of character identity. Finally, a generator trained in the first stage uses the 3D facial representation and the generated motion sequences as inputs to render high-quality animations. With the decoupled facial representation and the identity-independent motion generation process, JoyVASA extends beyond human portraits to animate animal faces seamlessly. The model is trained on a hybrid dataset of private Chinese and public English data, enabling multilingual support. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of our approach. Future work will focus on improving real-time performance and refining expression control, further expanding the applications in portrait animation. The code will be available at: https://jdhalgo.github.io/JoyVASA.
JoyType: A Robust Design for Multilingual Visual Text Creation
Sep 26, 2024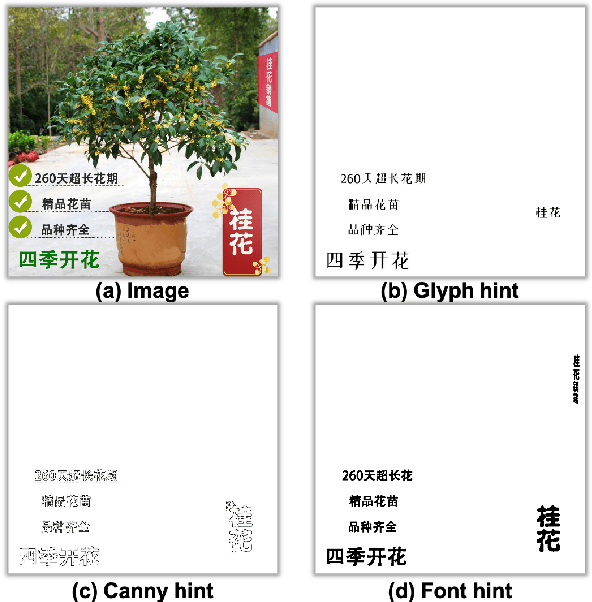
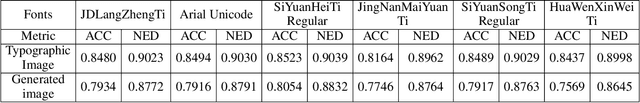

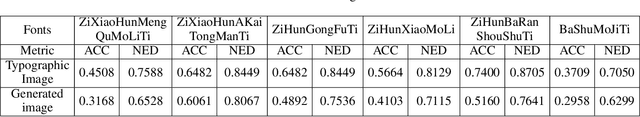
Abstract:Generating images with accurately represented text, especially in non-Latin languages, poses a significant challenge for diffusion models. Existing approaches, such as the integration of hint condition diagrams via auxiliary networks (e.g., ControlNet), have made strides towards addressing this issue. However, diffusion models often fall short in tasks requiring controlled text generation, such as specifying particular fonts or producing text in small fonts. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach for multilingual visual text creation, named JoyType, designed to maintain the font style of text during the image generation process. Our methodology begins with assembling a training dataset, JoyType-1M, comprising 1 million pairs of data. Each pair includes an image, its description, and glyph instructions corresponding to the font style within the image. We then developed a text control network, Font ControlNet, tasked with extracting font style information to steer the image generation. To further enhance our model's ability to maintain font style, notably in generating small-font text, we incorporated a multi-layer OCR-aware loss into the diffusion process. This enhancement allows JoyType to direct text rendering using low-level descriptors. Our evaluations, based on both visual and accuracy metrics, demonstrate that JoyType significantly outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods. Additionally, JoyType can function as a plugin, facilitating the creation of varied image styles in conjunction with other stable diffusion models on HuggingFace and CivitAI. Our project is open-sourced on https://jdh-algo.github.io/JoyType/.
MHAD: Multimodal Home Activity Dataset with Multi-Angle Videos and Synchronized Physiological Signals
Sep 14, 2024



Abstract:Video-based physiology, exemplified by remote photoplethysmography (rPPG), extracts physiological signals such as pulse and respiration by analyzing subtle changes in video recordings. This non-contact, real-time monitoring method holds great potential for home settings. Despite the valuable contributions of public benchmark datasets to this technology, there is currently no dataset specifically designed for passive home monitoring. Existing datasets are often limited to close-up, static, frontal recordings and typically include only 1-2 physiological signals. To advance video-based physiology in real home settings, we introduce the MHAD dataset. It comprises 1,440 videos from 40 subjects, capturing 6 typical activities from 3 angles in a real home environment. Additionally, 5 physiological signals were recorded, making it a comprehensive video-based physiology dataset. MHAD is compatible with the rPPG-toolbox and has been validated using several unsupervised and supervised methods. Our dataset is publicly available at https://github.com/jdh-algo/MHAD-Dataset.
ECG Biometric Authentication Using Self-Supervised Learning for IoT Edge Sensors
Sep 09, 2024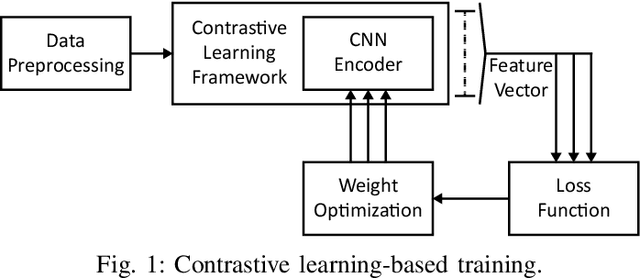
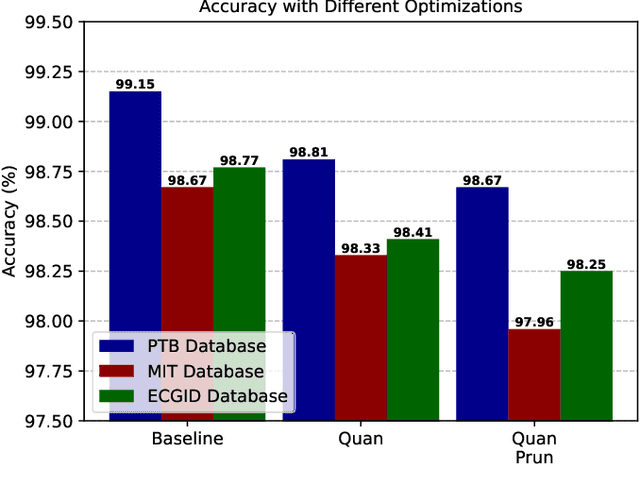
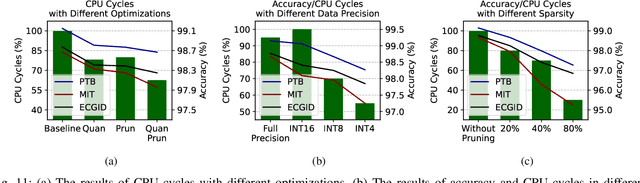
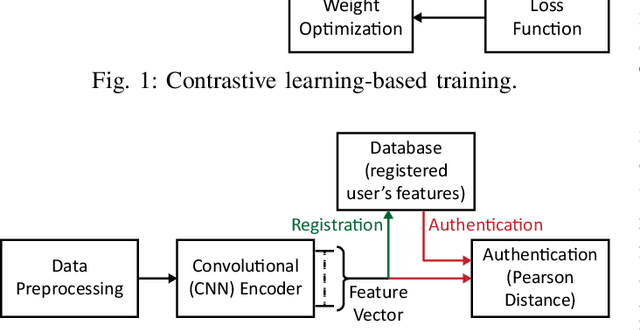
Abstract:Wearable Internet of Things (IoT) devices are gaining ground for continuous physiological data acquisition and health monitoring. These physiological signals can be used for security applications to achieve continuous authentication and user convenience due to passive data acquisition. This paper investigates an electrocardiogram (ECG) based biometric user authentication system using features derived from the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and self-supervised contrastive learning. Contrastive learning enables us to use large unlabeled datasets to train the model and establish its generalizability. We propose approaches enabling the CNN encoder to extract appropriate features that distinguish the user from other subjects. When evaluated using the PTB ECG database with 290 subjects, the proposed technique achieved an authentication accuracy of 99.15%. To test its generalizability, we applied the model to two new datasets, the MIT-BIH Arrhythmia Database and the ECG-ID Database, achieving over 98.5% accuracy without any modifications. Furthermore, we show that repeating the authentication step three times can increase accuracy to nearly 100% for both PTBDB and ECGIDDB. This paper also presents model optimizations for embedded device deployment, which makes the system more relevant to real-world scenarios. To deploy our model in IoT edge sensors, we optimized the model complexity by applying quantization and pruning. The optimized model achieves 98.67% accuracy on PTBDB, with 0.48% accuracy loss and 62.6% CPU cycles compared to the unoptimized model. An accuracy-vs-time-complexity tradeoff analysis is performed, and results are presented for different optimization levels.
3SHNet: Boosting Image-Sentence Retrieval via Visual Semantic-Spatial Self-Highlighting
Apr 26, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a novel visual Semantic-Spatial Self-Highlighting Network (termed 3SHNet) for high-precision, high-efficiency and high-generalization image-sentence retrieval. 3SHNet highlights the salient identification of prominent objects and their spatial locations within the visual modality, thus allowing the integration of visual semantics-spatial interactions and maintaining independence between two modalities. This integration effectively combines object regions with the corresponding semantic and position layouts derived from segmentation to enhance the visual representation. And the modality-independence guarantees efficiency and generalization. Additionally, 3SHNet utilizes the structured contextual visual scene information from segmentation to conduct the local (region-based) or global (grid-based) guidance and achieve accurate hybrid-level retrieval. Extensive experiments conducted on MS-COCO and Flickr30K benchmarks substantiate the superior performances, inference efficiency and generalization of the proposed 3SHNet when juxtaposed with contemporary state-of-the-art methodologies. Specifically, on the larger MS-COCO 5K test set, we achieve 16.3%, 24.8%, and 18.3% improvements in terms of rSum score, respectively, compared with the state-of-the-art methods using different image representations, while maintaining optimal retrieval efficiency. Moreover, our performance on cross-dataset generalization improves by 18.6%. Data and code are available at https://github.com/XuriGe1995/3SHNet.
* Accepted Information Processing and Management (IP&M), 10 pages, 9 figures and 8 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge