Joemon M. Jose
Benchmarking Multimodal Large Language Models for Missing Modality Completion in Product Catalogues
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Missing-modality information on e-commerce platforms, such as absent product images or textual descriptions, often arises from annotation errors or incomplete metadata, impairing both product presentation and downstream applications such as recommendation systems. Motivated by the multimodal generative capabilities of recent Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), this work investigates a fundamental yet underexplored question: can MLLMs generate missing modalities for products in e-commerce scenarios? We propose the Missing Modality Product Completion Benchmark (MMPCBench), which consists of two sub-benchmarks: a Content Quality Completion Benchmark and a Recommendation Benchmark. We further evaluate six state-of-the-art MLLMs from the Qwen2.5-VL and Gemma-3 model families across nine real-world e-commerce categories, focusing on image-to-text and text-to-image completion tasks. Experimental results show that while MLLMs can capture high-level semantics, they struggle with fine-grained word-level and pixel- or patch-level alignment. In addition, performance varies substantially across product categories and model scales, and we observe no trivial correlation between model size and performance, in contrast to trends commonly reported in mainstream benchmarks. We also explore Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) to better align MLLMs with this task. GRPO improves image-to-text completion but does not yield gains for text-to-image completion. Overall, these findings expose the limitations of current MLLMs in real-world cross-modal generation and represent an early step toward more effective missing-modality product completion.
Differentiable Semantic ID for Generative Recommendation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Generative recommendation provides a novel paradigm in which each item is represented by a discrete semantic ID (SID) learned from rich content. Most existing methods treat SIDs as predefined and train recommenders under static indexing. In practice, SIDs are typically optimized only for content reconstruction rather than recommendation accuracy. This leads to an objective mismatch: the system optimizes an indexing loss to learn the SID and a recommendation loss for interaction prediction, but because the tokenizer is trained independently, the recommendation loss cannot update it. A natural approach is to make semantic indexing differentiable so that recommendation gradients can directly influence SID learning, but this often causes codebook collapse, where only a few codes are used. We attribute this issue to early deterministic assignments that limit codebook exploration, resulting in imbalance and unstable optimization. In this paper, we propose DIGER (Differentiable Semantic ID for Generative Recommendation), a first step toward effective differentiable semantic IDs for generative recommendation. DIGER introduces Gumbel noise to explicitly encourage early-stage exploration over codes, mitigating codebook collapse and improving code utilization. To balance exploration and convergence, we further design two uncertainty decay strategies that gradually reduce the Gumbel noise, enabling a smooth transition from early exploration to exploitation of learned SIDs. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate consistent improvements from differentiable semantic IDs. These results confirm the effectiveness of aligning indexing and recommendation objectives through differentiable SIDs and highlight differentiable semantic indexing as a promising research direction.
Focal-RegionFace: Generating Fine-Grained Multi-attribute Descriptions for Arbitrarily Selected Face Focal Regions
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:In this paper, we introduce an underexplored problem in facial analysis: generating and recognizing multi-attribute natural language descriptions, containing facial action units (AUs), emotional states, and age estimation, for arbitrarily selected face regions (termed FaceFocalDesc). We argue that the system's ability to focus on individual facial areas leads to better understanding and control. To achieve this capability, we construct a new multi-attribute description dataset for arbitrarily selected face regions, providing rich region-level annotations and natural language descriptions. Further, we propose a fine-tuned vision-language model based on Qwen2.5-VL, called Focal-RegionFace for facial state analysis, which incrementally refines its focus on localized facial features through multiple progressively fine-tuning stages, resulting in interpretable age estimation, FAU and emotion detection. Experimental results show that Focal-RegionFace achieves the best performance on the new benchmark in terms of traditional and widely used metrics, as well as new proposed metrics. This fully verifies its effectiveness and versatility in fine-grained multi-attribute face region-focal analysis scenarios.
Are Multimodal Embeddings Truly Beneficial for Recommendation? A Deep Dive into Whole vs. Individual Modalities
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Multimodal recommendation (MMRec) has emerged as a mainstream paradigm, typically leveraging text and visual embeddings extracted from pre-trained models such as Sentence-BERT, Vision Transformers, and ResNet. This approach is founded on the intuitive assumption that incorporating multimodal embeddings can enhance recommendation performance. However, despite its popularity, this assumption lacks comprehensive empirical verification. This presents a critical research gap. To address it, we pose the central research question of this paper: Are multimodal embeddings truly beneficial for recommendation? To answer this question, we conduct a large-scale empirical study examining the role of text and visual embeddings in modern MMRec models, both as a whole and individually. Specifically, we pose two key research questions: (1) Do multimodal embeddings as a whole improve recommendation performance? (2) Is each individual modality - text and image - useful when used alone? To isolate the effect of individual modalities - text or visual - we employ a modality knockout strategy by setting the corresponding embeddings to either constant values or random noise. To ensure the scale and comprehensiveness of our study, we evaluate 14 widely used state-of-the-art MMRec models. Our findings reveal that: (1) multimodal embeddings generally enhance recommendation performance - particularly when integrated through more sophisticated graph-based fusion models. Surprisingly, commonly adopted baseline models with simple fusion schemes, such as VBPR and BM3, show only limited gains. (2) The text modality alone achieves performance comparable to the full multimodal setting in most cases, whereas the image modality alone does not. These results offer foundational insights and practical guidance for the MMRec community. We will release our code and datasets to facilitate future research.
Beyond One-Size-Fits-All: A Study of Neural and Behavioural Variability Across Different Recommendation Categories
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Traditionally, Recommender Systems (RS) have primarily measured performance based on the accuracy and relevance of their recommendations. However, this algorithmic-centric approach overlooks how different types of recommendations impact user engagement and shape the overall quality of experience. In this paper, we shift the focus to the user and address for the first time the challenge of decoding the neural and behavioural variability across distinct recommendation categories, considering more than just relevance. Specifically, we conducted a controlled study using a comprehensive e-commerce dataset containing various recommendation types, and collected Electroencephalography and behavioural data. We analysed both neural and behavioural responses to recommendations that were categorised as Exact, Substitute, Complement, or Irrelevant products within search query results. Our findings offer novel insights into user preferences and decision-making processes, revealing meaningful relationships between behavioural and neural patterns for each category, but also indicate inter-subject variability.
The 1st EReL@MIR Workshop on Efficient Representation Learning for Multimodal Information Retrieval
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:Multimodal representation learning has garnered significant attention in the AI community, largely due to the success of large pre-trained multimodal foundation models like LLaMA, GPT, Mistral, and CLIP. These models have achieved remarkable performance across various tasks of multimodal information retrieval (MIR), including web search, cross-modal retrieval, and recommender systems, etc. However, due to their enormous parameter sizes, significant efficiency challenges emerge across training, deployment, and inference stages when adapting these models' representation for IR tasks. These challenges present substantial obstacles to the practical adaptation of foundation models for representation learning in information retrieval tasks. To address these pressing issues, we propose organizing the first EReL@MIR workshop at the Web Conference 2025, inviting participants to explore novel solutions, emerging problems, challenges, efficiency evaluation metrics and benchmarks. This workshop aims to provide a platform for both academic and industry researchers to engage in discussions, share insights, and foster collaboration toward achieving efficient and effective representation learning for multimodal information retrieval in the era of large foundation models.
Multimodal Representation Learning Techniques for Comprehensive Facial State Analysis
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Multimodal foundation models have significantly improved feature representation by integrating information from multiple modalities, making them highly suitable for a broader set of applications. However, the exploration of multimodal facial representation for understanding perception has been limited. Understanding and analyzing facial states, such as Action Units (AUs) and emotions, require a comprehensive and robust framework that bridges visual and linguistic modalities. In this paper, we present a comprehensive pipeline for multimodal facial state analysis. First, we compile a new Multimodal Face Dataset (MFA) by generating detailed multilevel language descriptions of face, incorporating Action Unit (AU) and emotion descriptions, by leveraging GPT-4o. Second, we introduce a novel Multilevel Multimodal Face Foundation model (MF^2) tailored for Action Unit (AU) and emotion recognition. Our model incorporates comprehensive visual feature modeling at both local and global levels of face image, enhancing its ability to represent detailed facial appearances. This design aligns visual representations with structured AU and emotion descriptions, ensuring effective cross-modal integration. Third, we develop a Decoupled Fine-Tuning Network (DFN) that efficiently adapts MF^2 across various tasks and datasets. This approach not only reduces computational overhead but also broadens the applicability of the foundation model to diverse scenarios. Experimentation show superior performance for AU and emotion detection tasks.
* Accepted by ICME2025
CROSSAN: Towards Efficient and Effective Adaptation of Multiple Multimodal Foundation Models for Sequential Recommendation
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Multimodal Foundation Models (MFMs) excel at representing diverse raw modalities (e.g., text, images, audio, videos, etc.). As recommender systems increasingly incorporate these modalities, leveraging MFMs to generate better representations has great potential. However, their application in sequential recommendation remains largely unexplored. This is primarily because mainstream adaptation methods, such as Fine-Tuning and even Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) techniques (e.g., Adapter and LoRA), incur high computational costs, especially when integrating multiple modality encoders, thus hindering research progress. As a result, it remains unclear whether we can efficiently and effectively adapt multiple (>2) MFMs for the sequential recommendation task. To address this, we propose a plug-and-play Cross-modal Side Adapter Network (CROSSAN). Leveraging the fully decoupled side adapter-based paradigm, CROSSAN achieves high efficiency while enabling cross-modal learning across diverse modalities. To optimize the final stage of multimodal fusion across diverse modalities, we adopt the Mixture of Modality Expert Fusion (MOMEF) mechanism. CROSSAN achieves superior performance on the public datasets for adapting four foundation models with raw modalities. Performance consistently improves as more MFMs are adapted. We will release our code and datasets to facilitate future research.
Enhancing Interpretability in Generative AI Through Search-Based Data Influence Analysis
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:Generative AI models offer powerful capabilities but often lack transparency, making it difficult to interpret their output. This is critical in cases involving artistic or copyrighted content. This work introduces a search-inspired approach to improve the interpretability of these models by analysing the influence of training data on their outputs. Our method provides observational interpretability by focusing on a model's output rather than on its internal state. We consider both raw data and latent-space embeddings when searching for the influence of data items in generated content. We evaluate our method by retraining models locally and by demonstrating the method's ability to uncover influential subsets in the training data. This work lays the groundwork for future extensions, including user-based evaluations with domain experts, which is expected to improve observational interpretability further.
LLMPopcorn: An Empirical Study of LLMs as Assistants for Popular Micro-video Generation
Feb 19, 2025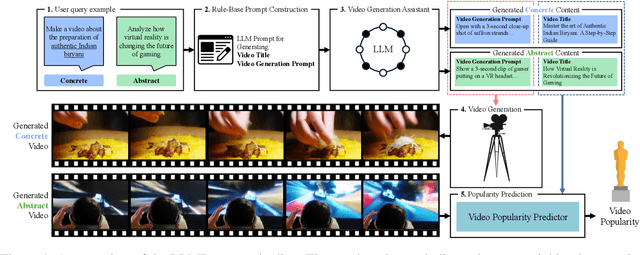
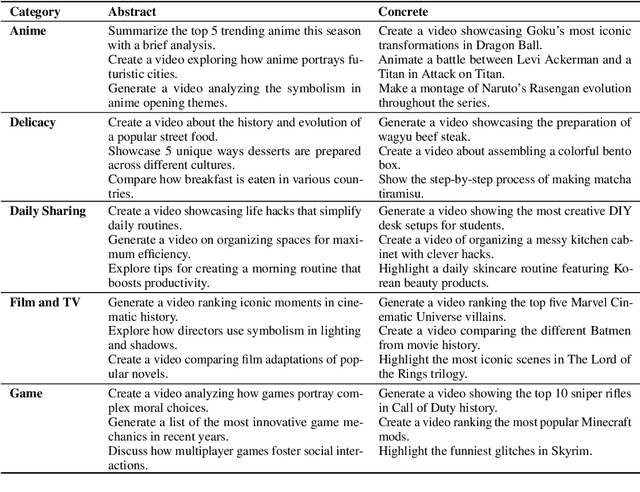
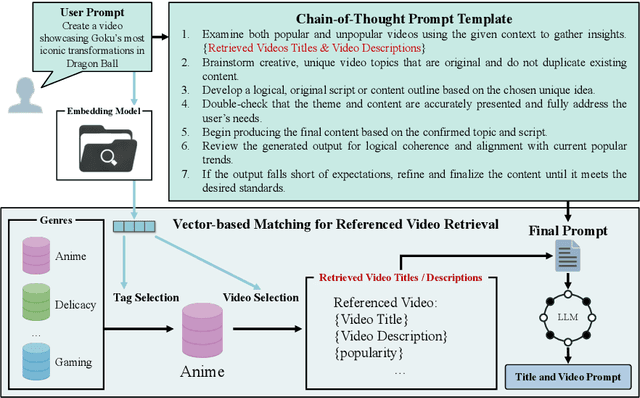
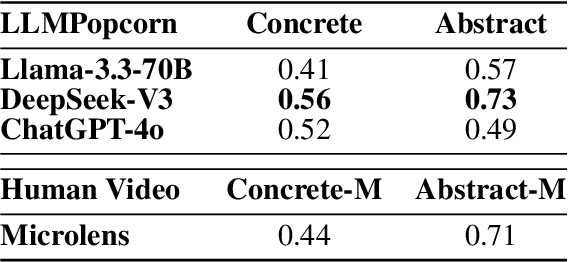
Abstract:Popular Micro-videos, dominant on platforms like TikTok and YouTube, hold significant commercial value. The rise of high-quality AI-generated content has spurred interest in AI-driven micro-video creation. However, despite the advanced capabilities of large language models (LLMs) like ChatGPT and DeepSeek in text generation and reasoning, their potential to assist the creation of popular micro-videos remains largely unexplored. In this paper, we conduct an empirical study on LLM-assisted popular micro-video generation (LLMPopcorn). Specifically, we investigate the following research questions: (i) How can LLMs be effectively utilized to assist popular micro-video generation? (ii) To what extent can prompt-based enhancements optimize the LLM-generated content for higher popularity? (iii) How well do various LLMs and video generators perform in the popular micro-video generation task? By exploring these questions, we show that advanced LLMs like DeepSeek-V3 enable micro-video generation to achieve popularity comparable to human-created content. Prompt enhancements further boost popularity, and benchmarking highlights DeepSeek-V3 and DeepSeek-R1 among LLMs, while LTX-Video and HunyuanVideo lead in video generation. This pioneering work advances AI-assisted micro-video creation, uncovering new research opportunities. We will release the code and datasets to support future studies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge