Zhaochun Ren
Differentiable Semantic ID for Generative Recommendation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Generative recommendation provides a novel paradigm in which each item is represented by a discrete semantic ID (SID) learned from rich content. Most existing methods treat SIDs as predefined and train recommenders under static indexing. In practice, SIDs are typically optimized only for content reconstruction rather than recommendation accuracy. This leads to an objective mismatch: the system optimizes an indexing loss to learn the SID and a recommendation loss for interaction prediction, but because the tokenizer is trained independently, the recommendation loss cannot update it. A natural approach is to make semantic indexing differentiable so that recommendation gradients can directly influence SID learning, but this often causes codebook collapse, where only a few codes are used. We attribute this issue to early deterministic assignments that limit codebook exploration, resulting in imbalance and unstable optimization. In this paper, we propose DIGER (Differentiable Semantic ID for Generative Recommendation), a first step toward effective differentiable semantic IDs for generative recommendation. DIGER introduces Gumbel noise to explicitly encourage early-stage exploration over codes, mitigating codebook collapse and improving code utilization. To balance exploration and convergence, we further design two uncertainty decay strategies that gradually reduce the Gumbel noise, enabling a smooth transition from early exploration to exploitation of learned SIDs. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets demonstrate consistent improvements from differentiable semantic IDs. These results confirm the effectiveness of aligning indexing and recommendation objectives through differentiable SIDs and highlight differentiable semantic indexing as a promising research direction.
Unifying Search and Recommendation in LLMs via Gradient Multi-Subspace Tuning
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Search and recommendation (S&R) are core to online platforms, addressing explicit intent through queries and modeling implicit intent from behaviors, respectively. Their complementary roles motivate a unified modeling paradigm. Early studies to unify S&R adopt shared encoders with task-specific heads, while recent efforts reframe item ranking in both S&R as conditional generation. The latter holds particular promise, enabling end-to-end optimization and leveraging the semantic understanding of LLMs. However, existing methods rely on full fine-tuning, which is computationally expensive and limits scalability. Parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) offers a more practical alternative but faces two critical challenges in unifying S&R: (1) gradient conflicts across tasks due to divergent optimization objectives, and (2) shifts in user intent understanding caused by overfitting to fine-tuning data, which distort general-domain knowledge and weaken LLM reasoning. To address the above issues, we propose Gradient Multi-Subspace Tuning (GEMS), a novel framework that unifies S&R with LLMs while alleviating gradient conflicts and preserving general-domain knowledge. GEMS introduces (1) \textbf{Multi-Subspace Decomposition}, which disentangles shared and task-specific optimization signals into complementary low-rank subspaces, thereby reducing destructive gradient interference, and (2) \textbf{Null-Space Projection}, which constrains parameter updates to a subspace orthogonal to the general-domain knowledge space, mitigating shifts in user intent understanding. Extensive experiments on benchmark datasets show that GEMS consistently outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines across both search and recommendation tasks, achieving superior effectiveness.
Reinforced Efficient Reasoning via Semantically Diverse Exploration
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has proven effective in enhancing the reasoning of large language models (LLMs). Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-based extensions improve upon vanilla RLVR (e.g., GRPO) by providing tree-based reasoning rollouts that enable fine-grained and segment-level credit assignment. However, existing methods still suffer from limited exploration diversity and inefficient reasoning. To address the above challenges, we propose reinforced efficient reasoning via semantically diverse explorations, i.e., ROSE, for LLMs. To encourage more diverse reasoning exploration, our method incorporates a semantic-entropy-based branching strategy and an $\varepsilon$-exploration mechanism. The former operates on already sampled reasoning rollouts to capture semantic uncertainty and select branching points with high semantic divergence to generate new successive reasoning paths, whereas the latter stochastically initiates reasoning rollouts from the root, preventing the search process from becoming overly local. To improve efficiency, we design a length-aware segment-level advantage estimator that rewards concise and correct reasoning while penalizing unnecessarily long reasoning chains. Extensive experiments on various mathematical reasoning benchmarks with Qwen and Llama models validate the effectiveness and efficiency of ROSE. Codes are available at https://github.com/ZiqiZhao1/ROSE-rl.
DiffuGR: Generative Document Retrieval with Diffusion Language Models
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Generative retrieval (GR) re-frames document retrieval as a sequence-based document identifier (DocID) generation task, memorizing documents with model parameters and enabling end-to-end retrieval without explicit indexing. Existing GR methods are based on auto-regressive generative models, i.e., the token generation is performed from left to right. However, such auto-regressive methods suffer from: (1) mismatch between DocID generation and natural language generation, e.g., an incorrect DocID token generated in early left steps would lead to totally erroneous retrieval; and (2) failure to balance the trade-off between retrieval efficiency and accuracy dynamically, which is crucial for practical applications. To address these limitations, we propose generative document retrieval with diffusion language models, dubbed DiffuGR. It models DocID generation as a discrete diffusion process: during training, DocIDs are corrupted through a stochastic masking process, and a diffusion language model is learned to recover them under a retrieval-aware objective. For inference, DiffuGR attempts to generate DocID tokens in parallel and refines them through a controllable number of denoising steps. In contrast to conventional left-to-right auto-regressive decoding, DiffuGR provides a novel mechanism to first generate more confident DocID tokens and refine the generation through diffusion-based denoising. Moreover, DiffuGR also offers explicit runtime control over the qualitylatency tradeoff. Extensive experiments on benchmark retrieval datasets show that DiffuGR is competitive with strong auto-regressive generative retrievers, while offering flexible speed and accuracy tradeoffs through variable denoising budgets. Overall, our results indicate that non-autoregressive diffusion models are a practical and effective alternative for generative document retrieval.
Have We Really Understood Collaborative Information? An Empirical Investigation
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Collaborative information serves as the cornerstone of recommender systems which typically focus on capturing it from user-item interactions to deliver personalized services. However, current understanding of this crucial resource remains limited. Specifically, a quantitative definition of collaborative information is missing, its manifestation within user-item interactions remains unclear, and its impact on recommendation performance is largely unknown. To bridge this gap, this work conducts a systematic investigation of collaborative information. We begin by clarifying collaborative information in terms of item co-occurrence patterns, identifying its main characteristics, and presenting a quantitative definition. We then estimate the distribution of collaborative information from several aspects, shedding light on how collaborative information is structured in practice. Furthermore, we evaluate the impact of collaborative information on the performance of various recommendation algorithms. Finally, we highlight challenges in effectively capturing collaborative information and outlook promising directions for future research. By establishing an empirical framework, we uncover many insightful observations that advance our understanding of collaborative information and offer valuable guidelines for developing more effective recommender systems.
Bridging the Capability Gap: Joint Alignment Tuning for Harmonizing LLM-based Multi-Agent Systems
Sep 11, 2025Abstract:The advancement of large language models (LLMs) has enabled the construction of multi-agent systems to solve complex tasks by dividing responsibilities among specialized agents, such as a planning agent for subgoal generation and a grounding agent for executing tool-use actions. Most existing methods typically fine-tune these agents independently, leading to capability gaps among them with poor coordination. To address this, we propose MOAT, a Multi-Agent Joint Alignment Tuning framework that improves agents collaboration through iterative alignment. MOAT alternates between two key stages: (1) Planning Agent Alignment, which optimizes the planning agent to generate subgoal sequences that better guide the grounding agent; and (2) Grounding Agent Improving, which fine-tunes the grounding agent using diverse subgoal-action pairs generated by the agent itself to enhance its generalization capablity. Theoretical analysis proves that MOAT ensures a non-decreasing and progressively convergent training process. Experiments across six benchmarks demonstrate that MOAT outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, achieving average improvements of 3.1% on held-in tasks and 4.4% on held-out tasks.
A Comprehensive Survey of Self-Evolving AI Agents: A New Paradigm Bridging Foundation Models and Lifelong Agentic Systems
Aug 10, 2025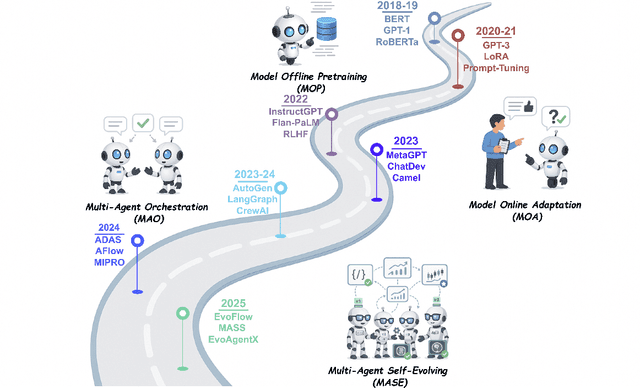
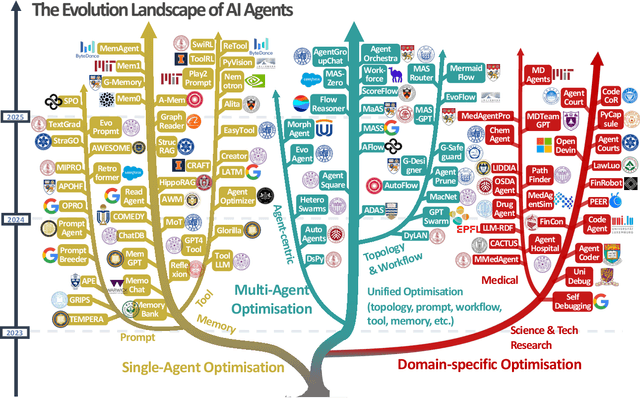
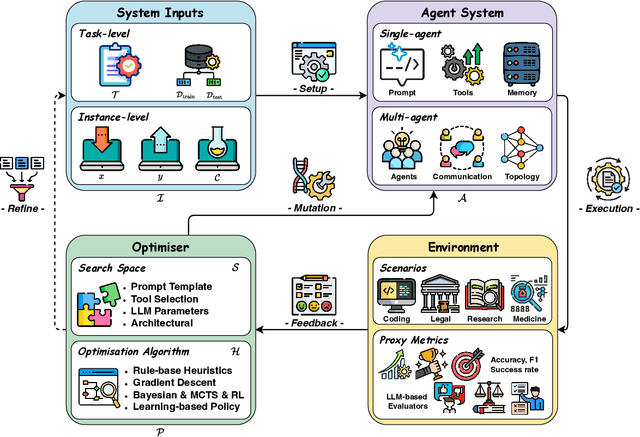
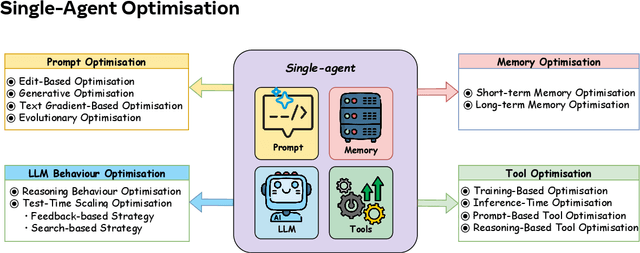
Abstract:Recent advances in large language models have sparked growing interest in AI agents capable of solving complex, real-world tasks. However, most existing agent systems rely on manually crafted configurations that remain static after deployment, limiting their ability to adapt to dynamic and evolving environments. To this end, recent research has explored agent evolution techniques that aim to automatically enhance agent systems based on interaction data and environmental feedback. This emerging direction lays the foundation for self-evolving AI agents, which bridge the static capabilities of foundation models with the continuous adaptability required by lifelong agentic systems. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of existing techniques for self-evolving agentic systems. Specifically, we first introduce a unified conceptual framework that abstracts the feedback loop underlying the design of self-evolving agentic systems. The framework highlights four key components: System Inputs, Agent System, Environment, and Optimisers, serving as a foundation for understanding and comparing different strategies. Based on this framework, we systematically review a wide range of self-evolving techniques that target different components of the agent system. We also investigate domain-specific evolution strategies developed for specialised fields such as biomedicine, programming, and finance, where optimisation objectives are tightly coupled with domain constraints. In addition, we provide a dedicated discussion on the evaluation, safety, and ethical considerations for self-evolving agentic systems, which are critical to ensuring their effectiveness and reliability. This survey aims to provide researchers and practitioners with a systematic understanding of self-evolving AI agents, laying the foundation for the development of more adaptive, autonomous, and lifelong agentic systems.
Iterative Self-Incentivization Empowers Large Language Models as Agentic Searchers
May 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely integrated into information retrieval to advance traditional techniques. However, effectively enabling LLMs to seek accurate knowledge in complex tasks remains a challenge due to the complexity of multi-hop queries as well as the irrelevant retrieved content. To address these limitations, we propose EXSEARCH, an agentic search framework, where the LLM learns to retrieve useful information as the reasoning unfolds through a self-incentivized process. At each step, the LLM decides what to retrieve (thinking), triggers an external retriever (search), and extracts fine-grained evidence (recording) to support next-step reasoning. To enable LLM with this capability, EXSEARCH adopts a Generalized Expectation-Maximization algorithm. In the E-step, the LLM generates multiple search trajectories and assigns an importance weight to each; the M-step trains the LLM on them with a re-weighted loss function. This creates a self-incentivized loop, where the LLM iteratively learns from its own generated data, progressively improving itself for search. We further theoretically analyze this training process, establishing convergence guarantees. Extensive experiments on four knowledge-intensive benchmarks show that EXSEARCH substantially outperforms baselines, e.g., +7.8% improvement on exact match score. Motivated by these promising results, we introduce EXSEARCH-Zoo, an extension that extends our method to broader scenarios, to facilitate future work.
Disentangling Knowledge Representations for Large Language Model Editing
May 24, 2025Abstract:Knowledge Editing has emerged as a promising solution for efficiently updating embedded knowledge in large language models (LLMs). While existing approaches demonstrate effectiveness in integrating new knowledge and preserving the original capabilities of LLMs, they fail to maintain fine-grained irrelevant knowledge facts that share the same subject as edited knowledge but differ in relation and object. This challenge arises because subject representations inherently encode multiple attributes, causing the target and fine-grained irrelevant knowledge to become entangled in the representation space, and thus vulnerable to unintended alterations during editing. To address this, we propose DiKE, a novel approach that Disentangles Knowledge representations for LLM Editing (DiKE). DiKE consists of two key components: a Knowledge Representation Disentanglement (KRD) module that decomposes the subject representation into target-knowledgerelated and -unrelated components, and a Disentanglement-based Knowledge Edit (DKE) module that updates only the target-related component while explicitly preserving the unrelated one. We further derive a closed-form, rank-one parameter update based on matrix theory to enable efficient and minimally invasive edits. To rigorously evaluate fine-grained irrelevant knowledge preservation, we construct FINE-KED, a new benchmark comprising fine-grained irrelevant knowledge at different levels of relational similarity to the edited knowledge. Extensive experiments across multiple LLMs demonstrate that DiKE substantially improves fine-grained irrelevant knowledge preservation while maintaining competitive general editing performance.
Joint Flashback Adaptation for Forgetting-Resistant Instruction Tuning
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large language models have achieved remarkable success in various tasks. However, it is challenging for them to learn new tasks incrementally due to catastrophic forgetting. Existing approaches rely on experience replay, optimization constraints, or task differentiation, which encounter strict limitations in real-world scenarios. To address these issues, we propose Joint Flashback Adaptation. We first introduce flashbacks -- a limited number of prompts from old tasks -- when adapting to new tasks and constrain the deviations of the model outputs compared to the original one. We then interpolate latent tasks between flashbacks and new tasks to enable jointly learning relevant latent tasks, new tasks, and flashbacks, alleviating data sparsity in flashbacks and facilitating knowledge sharing for smooth adaptation. Our method requires only a limited number of flashbacks without access to the replay data and is task-agnostic. We conduct extensive experiments on state-of-the-art large language models across 1000+ instruction-following tasks, arithmetic reasoning tasks, and general reasoning tasks. The results demonstrate the superior performance of our method in improving generalization on new tasks and reducing forgetting in old tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge