Ziqi Zhao
LoR-LUT: Learning Compact 3D Lookup Tables via Low-Rank Residuals
Feb 26, 2026Abstract:We present LoR-LUT, a unified low-rank formulation for compact and interpretable 3D lookup table (LUT) generation. Unlike conventional 3D-LUT-based techniques that rely on fusion of basis LUTs, which are usually dense tensors, our unified approach extends the current framework by jointly using residual corrections, which are in fact low-rank tensors, together with a set of basis LUTs. The approach described here improves the existing perceptual quality of an image, which is primarily due to the technique's novel use of residual corrections. At the same time, we achieve the same level of trilinear interpolation complexity, using a significantly smaller number of network, residual corrections, and LUT parameters. The experimental results obtained from LoR-LUT, which is trained on the MIT-Adobe FiveK dataset, reproduce expert-level retouching characteristics with high perceptual fidelity and a sub-megabyte model size. Furthermore, we introduce an interactive visualization tool, termed LoR-LUT Viewer, which transforms an input image into the LUT-adjusted output image, via a number of slidebars that control different parameters. The tool provides an effective way to enhance interpretability and user confidence in the visual results. Overall, our proposed formulation offers a compact, interpretable, and efficient direction for future LUT-based image enhancement and style transfer.
Reinforced Efficient Reasoning via Semantically Diverse Exploration
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has proven effective in enhancing the reasoning of large language models (LLMs). Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-based extensions improve upon vanilla RLVR (e.g., GRPO) by providing tree-based reasoning rollouts that enable fine-grained and segment-level credit assignment. However, existing methods still suffer from limited exploration diversity and inefficient reasoning. To address the above challenges, we propose reinforced efficient reasoning via semantically diverse explorations, i.e., ROSE, for LLMs. To encourage more diverse reasoning exploration, our method incorporates a semantic-entropy-based branching strategy and an $\varepsilon$-exploration mechanism. The former operates on already sampled reasoning rollouts to capture semantic uncertainty and select branching points with high semantic divergence to generate new successive reasoning paths, whereas the latter stochastically initiates reasoning rollouts from the root, preventing the search process from becoming overly local. To improve efficiency, we design a length-aware segment-level advantage estimator that rewards concise and correct reasoning while penalizing unnecessarily long reasoning chains. Extensive experiments on various mathematical reasoning benchmarks with Qwen and Llama models validate the effectiveness and efficiency of ROSE. Codes are available at https://github.com/ZiqiZhao1/ROSE-rl.
A Multi-scale Representation Learning Framework for Long-Term Time Series Forecasting
May 13, 2025Abstract:Long-term time series forecasting (LTSF) offers broad utility in practical settings like energy consumption and weather prediction. Accurately predicting long-term changes, however, is demanding due to the intricate temporal patterns and inherent multi-scale variations within time series. This work confronts key issues in LTSF, including the suboptimal use of multi-granularity information, the neglect of channel-specific attributes, and the unique nature of trend and seasonal components, by introducing a proficient MLP-based forecasting framework. Our method adeptly disentangles complex temporal dynamics using clear, concurrent predictions across various scales. These multi-scale forecasts are then skillfully integrated through a system that dynamically assigns importance to information from different granularities, sensitive to individual channel characteristics. To manage the specific features of temporal patterns, a two-pronged structure is utilized to model trend and seasonal elements independently. Experimental results on eight LTSF benchmarks demonstrate that MDMixer improves average MAE performance by 4.64% compared to the recent state-of-the-art MLP-based method (TimeMixer), while achieving an effective balance between training efficiency and model interpretability.
Improving Sequential Recommenders through Counterfactual Augmentation of System Exposure
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:In sequential recommendation (SR), system exposure refers to items that are exposed to the user. Typically, only a few of the exposed items would be interacted with by the user. Although SR has achieved great success in predicting future user interests, existing SR methods still fail to fully exploit system exposure data. Most methods only model items that have been interacted with, while the large volume of exposed but non-interacted items is overlooked. Even methods that consider the whole system exposure typically train the recommender using only the logged historical system exposure, without exploring unseen user interests. In this paper, we propose counterfactual augmentation over system exposure for sequential recommendation (CaseRec). To better model historical system exposure, CaseRec introduces reinforcement learning to account for different exposure rewards. CaseRec uses a decision transformer-based sequential model to take an exposure sequence as input and assigns different rewards according to the user feedback. To further explore unseen user interests, CaseRec proposes to perform counterfactual augmentation, where exposed original items are replaced with counterfactual items. Then, a transformer-based user simulator is proposed to predict the user feedback reward for the augmented items. Augmentation, together with the user simulator, constructs counterfactual exposure sequences to uncover new user interests. Finally, CaseRec jointly uses the logged exposure sequences with the counterfactual exposure sequences to train a decision transformer-based sequential model for generating recommendation. Experiments on three real-world benchmarks show the effectiveness of CaseRec. Our code is available at https://github.com/ZiqiZhao1/CaseRec.
HealthiVert-GAN: A Novel Framework of Pseudo-Healthy Vertebral Image Synthesis for Interpretable Compression Fracture Grading
Mar 08, 2025Abstract:Osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (VCFs) are prevalent in the elderly population, typically assessed on computed tomography (CT) scans by evaluating vertebral height loss. This assessment helps determine the fracture's impact on spinal stability and the need for surgical intervention. However, clinical data indicate that many VCFs exhibit irregular compression, complicating accurate diagnosis. While deep learning methods have shown promise in aiding VCFs screening, they often lack interpretability and sufficient sensitivity, limiting their clinical applicability. To address these challenges, we introduce a novel vertebra synthesis-height loss quantification-VCFs grading framework. Our proposed model, HealthiVert-GAN, utilizes a coarse-to-fine synthesis network designed to generate pseudo-healthy vertebral images that simulate the pre-fracture state of fractured vertebrae. This model integrates three auxiliary modules that leverage the morphology and height information of adjacent healthy vertebrae to ensure anatomical consistency. Additionally, we introduce the Relative Height Loss of Vertebrae (RHLV) as a quantification metric, which divides each vertebra into three sections to measure height loss between pre-fracture and post-fracture states, followed by fracture severity classification using a Support Vector Machine (SVM). Our approach achieves state-of-the-art classification performance on both the Verse2019 dataset and our private dataset, and it provides cross-sectional distribution maps of vertebral height loss. This practical tool enhances diagnostic sensitivity in clinical settings and assisting in surgical decision-making. Our code is available: https://github.com/zhibaishouheilab/HealthiVert-GAN.
A Cooperative Multi-Agent Framework for Zero-Shot Named Entity Recognition
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Zero-shot named entity recognition (NER) aims to develop entity recognition systems from unannotated text corpora. This task presents substantial challenges due to minimal human intervention. Recent work has adapted large language models (LLMs) for zero-shot NER by crafting specialized prompt templates. It advances model self-learning abilities by incorporating self-annotated demonstrations. However, two important challenges persist: (i) Correlations between contexts surrounding entities are overlooked, leading to wrong type predictions or entity omissions. (ii) The indiscriminate use of task demonstrations, retrieved through shallow similarity-based strategies, severely misleads LLMs during inference. In this paper, we introduce the cooperative multi-agent system (CMAS), a novel framework for zero-shot NER that uses the collective intelligence of multiple agents to address the challenges outlined above. CMAS has four main agents: (i) a self-annotator, (ii) a type-related feature (TRF) extractor, (iii) a demonstration discriminator, and (iv) an overall predictor. To explicitly capture correlations between contexts surrounding entities, CMAS reformulates NER into two subtasks: recognizing named entities and identifying entity type-related features within the target sentence. To enable controllable utilization of demonstrations, a demonstration discriminator is established to incorporate the self-reflection mechanism, automatically evaluating helpfulness scores for the target sentence. Experimental results show that CMAS significantly improves zero-shot NER performance across six benchmarks, including both domain-specific and general-domain scenarios. Furthermore, CMAS demonstrates its effectiveness in few-shot settings and with various LLM backbones.
Omni Differential Drive for Simultaneous Reconfiguration and Omnidirectional Mobility of Wheeled Robots
Dec 14, 2024Abstract:Wheeled robots are highly efficient in human living environments. However, conventional wheeled designs, limited by degrees of freedom, struggle to meet varying footprint needs and achieve omnidirectional mobility. This paper proposes a novel robot drive model inspired by human movements, termed as the Omni Differential Drive (ODD). The ODD model innovatively utilizes a lateral differential drive to adjust wheel spacing without adding additional actuators to the existing omnidirectional drive. This approach enables wheeled robots to achieve both simultaneous reconfiguration and omnidirectional mobility. Additionally, a prototype was developed to validate the ODD, followed by kinematic analysis. Control systems for self-balancing and motion were designed and implemented. Experimental validations confirmed the feasibility of the ODD mechanism and the effectiveness of the control strategies. The results underline the potential of this innovative drive system to enhance the mobility and adaptability of robotic platforms.
Geminio: Language-Guided Gradient Inversion Attacks in Federated Learning
Nov 22, 2024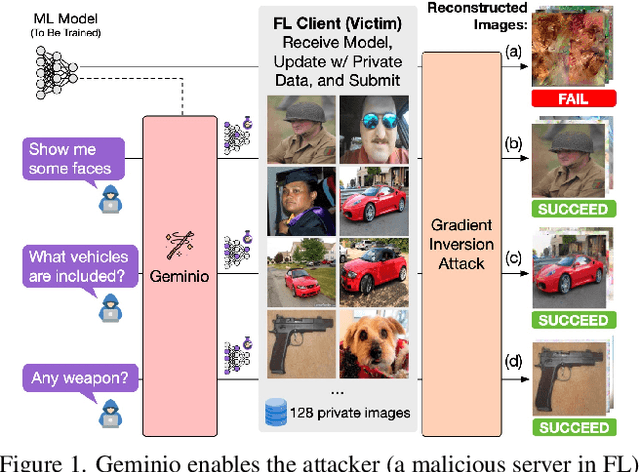

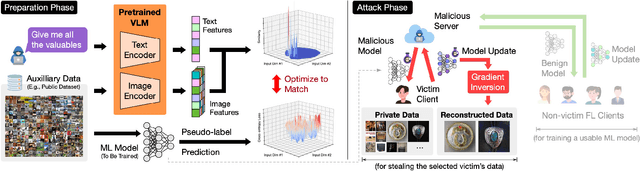
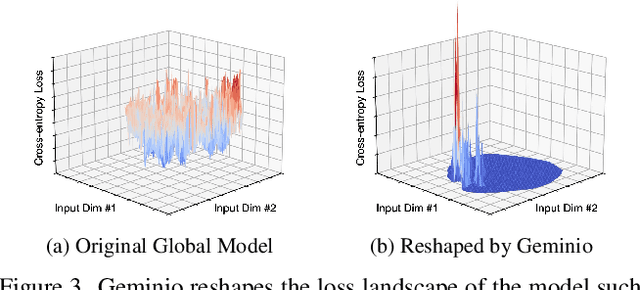
Abstract:Foundation models that bridge vision and language have made significant progress, inspiring numerous life-enriching applications. However, their potential for misuse to introduce new threats remains largely unexplored. This paper reveals that vision-language models (VLMs) can be exploited to overcome longstanding limitations in gradient inversion attacks (GIAs) within federated learning (FL), where an FL server reconstructs private data samples from gradients shared by victim clients. Current GIAs face challenges in reconstructing high-resolution images, especially when the victim has a large local data batch. While focusing reconstruction on valuable samples rather than the entire batch is promising, existing methods lack the flexibility to allow attackers to specify their target data. In this paper, we introduce Geminio, the first approach to transform GIAs into semantically meaningful, targeted attacks. Geminio enables a brand new privacy attack experience: attackers can describe, in natural language, the types of data they consider valuable, and Geminio will prioritize reconstruction to focus on those high-value samples. This is achieved by leveraging a pretrained VLM to guide the optimization of a malicious global model that, when shared with and optimized by a victim, retains only gradients of samples that match the attacker-specified query. Extensive experiments demonstrate Geminio's effectiveness in pinpointing and reconstructing targeted samples, with high success rates across complex datasets under FL and large batch sizes and showing resilience against existing defenses.
AnywhereDoor: Multi-Target Backdoor Attacks on Object Detection
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:As object detection becomes integral to many safety-critical applications, understanding its vulnerabilities is essential. Backdoor attacks, in particular, pose a significant threat by implanting hidden backdoor in a victim model, which adversaries can later exploit to trigger malicious behaviors during inference. However, current backdoor techniques are limited to static scenarios where attackers must define a malicious objective before training, locking the attack into a predetermined action without inference-time adaptability. Given the expressive output space in object detection, including object existence detection, bounding box estimation, and object classification, the feasibility of implanting a backdoor that provides inference-time control with a high degree of freedom remains unexplored. This paper introduces AnywhereDoor, a flexible backdoor attack tailored for object detection. Once implanted, AnywhereDoor enables adversaries to specify different attack types (object vanishing, fabrication, or misclassification) and configurations (untargeted or targeted with specific classes) to dynamically control detection behavior. This flexibility is achieved through three key innovations: (i) objective disentanglement to support a broader range of attack combinations well beyond what existing methods allow; (ii) trigger mosaicking to ensure backdoor activations are robust, even against those object detectors that extract localized regions from the input image for recognition; and (iii) strategic batching to address object-level data imbalances that otherwise hinders a balanced manipulation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that AnywhereDoor provides attackers with a high degree of control, achieving an attack success rate improvement of nearly 80% compared to adaptations of existing methods for such flexible control.
Collaborative Fall Detection and Response using Wi-Fi Sensing and Mobile Companion Robot
Jul 17, 2024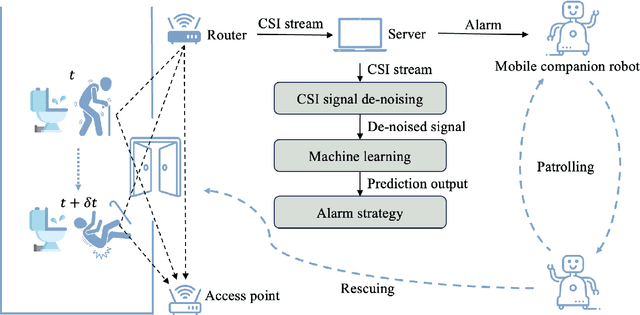
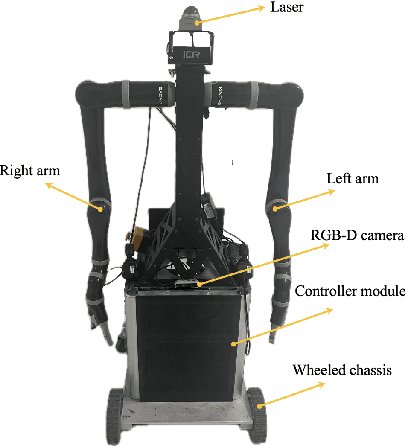
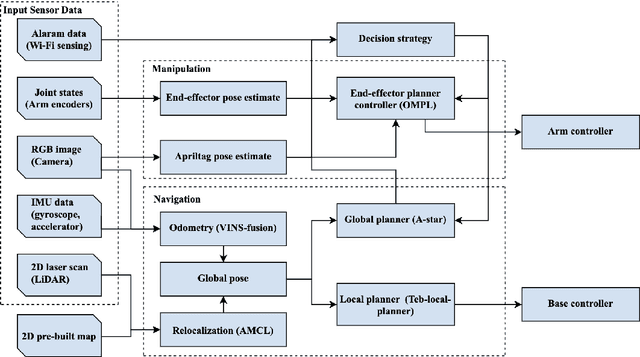
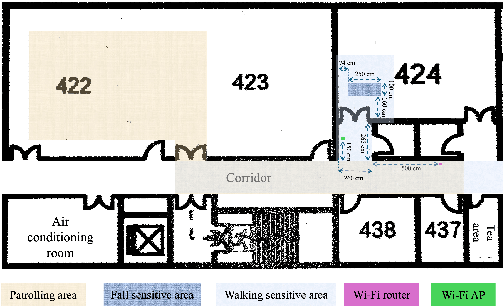
Abstract:This paper presents a collaborative fall detection and response system integrating Wi-Fi sensing with robotic assistance. The proposed system leverages channel state information (CSI) disruptions caused by movements to detect falls in non-line-of-sight (NLOS) scenarios, offering non-intrusive monitoring. Besides, a companion robot is utilized to provide assistance capabilities to navigate and respond to incidents autonomously, improving efficiency in providing assistance in various environments. The experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed system in detecting falls and responding effectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge