Liu Yang
School of Computer Science and Engineering, Central South University, Changsha, China
Reinforced Attention Learning
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Post-training with Reinforcement Learning (RL) has substantially improved reasoning in Large Language Models (LLMs) via test-time scaling. However, extending this paradigm to Multimodal LLMs (MLLMs) through verbose rationales yields limited gains for perception and can even degrade performance. We propose Reinforced Attention Learning (RAL), a policy-gradient framework that directly optimizes internal attention distributions rather than output token sequences. By shifting optimization from what to generate to where to attend, RAL promotes effective information allocation and improved grounding in complex multimodal inputs. Experiments across diverse image and video benchmarks show consistent gains over GRPO and other baselines. We further introduce On-Policy Attention Distillation, demonstrating that transferring latent attention behaviors yields stronger cross-modal alignment than standard knowledge distillation. Our results position attention policies as a principled and general alternative for multimodal post-training.
Temporally Coherent Imitation Learning via Latent Action Flow Matching for Robotic Manipulation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Learning long-horizon robotic manipulation requires jointly achieving expressive behavior modeling, real-time inference, and stable execution, which remains challenging for existing generative policies. Diffusion-based approaches provide strong modeling capacity but typically incur high inference latency, while flow matching enables fast one-step generation yet often leads to unstable execution when applied directly in the raw action space. We propose LG-Flow Policy, a trajectory-level imitation learning framework that performs flow matching in a continuous latent action space. By encoding action sequences into temporally regularized latent trajectories and learning an explicit latent-space flow, the proposed approach decouples global motion structure from low-level control noise, resulting in smooth and reliable long-horizon execution. LG-Flow Policy further incorporates geometry-aware point cloud conditioning and execution-time multimodal modulation, with visual cues evaluated as a representative modality in real-world settings. Experimental results in simulation and on physical robot platforms demonstrate that LG-Flow Policy achieves near single-step inference, substantially improves trajectory smoothness and task success over flow-based baselines operating in the raw action space, and remains significantly more efficient than diffusion-based policies.
Reinforced Efficient Reasoning via Semantically Diverse Exploration
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards (RLVR) has proven effective in enhancing the reasoning of large language models (LLMs). Monte Carlo Tree Search (MCTS)-based extensions improve upon vanilla RLVR (e.g., GRPO) by providing tree-based reasoning rollouts that enable fine-grained and segment-level credit assignment. However, existing methods still suffer from limited exploration diversity and inefficient reasoning. To address the above challenges, we propose reinforced efficient reasoning via semantically diverse explorations, i.e., ROSE, for LLMs. To encourage more diverse reasoning exploration, our method incorporates a semantic-entropy-based branching strategy and an $\varepsilon$-exploration mechanism. The former operates on already sampled reasoning rollouts to capture semantic uncertainty and select branching points with high semantic divergence to generate new successive reasoning paths, whereas the latter stochastically initiates reasoning rollouts from the root, preventing the search process from becoming overly local. To improve efficiency, we design a length-aware segment-level advantage estimator that rewards concise and correct reasoning while penalizing unnecessarily long reasoning chains. Extensive experiments on various mathematical reasoning benchmarks with Qwen and Llama models validate the effectiveness and efficiency of ROSE. Codes are available at https://github.com/ZiqiZhao1/ROSE-rl.
Exploiting Radio Frequency Fingerprints for Device Identification: Tackling Cross-receiver Challenges in the Source-data-free Scenario
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:With the rapid proliferation of edge computing, Radio Frequency Fingerprint Identification (RFFI) has become increasingly important for secure device authentication. However, practical deployment of deep learning-based RFFI models is hindered by a critical challenge: their performance often degrades significantly when applied across receivers with different hardware characteristics due to distribution shifts introduced by receiver variation. To address this, we investigate the source-data-free cross-receiver RFFI (SCRFFI) problem, where a model pretrained on labeled signals from a source receiver must adapt to unlabeled signals from a target receiver, without access to any source-domain data during adaptation. We first formulate a novel constrained pseudo-labeling-based SCRFFI adaptation framework, and provide a theoretical analysis of its generalization performance. Our analysis highlights a key insight: the target-domain performance is highly sensitive to the quality of the pseudo-labels generated during adaptation. Motivated by this, we propose Momentum Soft pseudo-label Source Hypothesis Transfer (MS-SHOT), a new method for SCRFFI that incorporates momentum-center-guided soft pseudo-labeling and enforces global structural constraints to encourage confident and diverse predictions. Notably, MS-SHOT effectively addresses scenarios involving label shift or unknown, non-uniform class distributions in the target domain -- a significant limitation of prior methods. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that MS-SHOT consistently outperforms existing approaches in both accuracy and robustness, offering a practical and scalable solution for source-data-free cross-receiver adaptation in RFFI.
Early GVHD Prediction in Liver Transplantation via Multi-Modal Deep Learning on Imbalanced EHR Data
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) is a rare but often fatal complication in liver transplantation, with a very high mortality rate. By harnessing multi-modal deep learning methods to integrate heterogeneous and imbalanced electronic health records (EHR), we aim to advance early prediction of GVHD, paving the way for timely intervention and improved patient outcomes. In this study, we analyzed pre-transplant electronic health records (EHR) spanning the period before surgery for 2,100 liver transplantation patients, including 42 cases of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD), from a cohort treated at Mayo Clinic between 1992 and 2025. The dataset comprised four major modalities: patient demographics, laboratory tests, diagnoses, and medications. We developed a multi-modal deep learning framework that dynamically fuses these modalities, handles irregular records with missing values, and addresses extreme class imbalance through AUC-based optimization. The developed framework outperforms all single-modal and multi-modal machine learning baselines, achieving an AUC of 0.836, an AUPRC of 0.157, a recall of 0.768, and a specificity of 0.803. It also demonstrates the effectiveness of our approach in capturing complementary information from different modalities, leading to improved performance. Our multi-modal deep learning framework substantially improves existing approaches for early GVHD prediction. By effectively addressing the challenges of heterogeneity and extreme class imbalance in real-world EHR, it achieves accurate early prediction. Our proposed multi-modal deep learning method demonstrates promising results for early prediction of a GVHD in liver transplantation, despite the challenge of extremely imbalanced EHR data.
Addressing Personalized Bias for Unbiased Learning to Rank
Aug 28, 2025Abstract:Unbiased learning to rank (ULTR), which aims to learn unbiased ranking models from biased user behavior logs, plays an important role in Web search. Previous research on ULTR has studied a variety of biases in users' clicks, such as position bias, presentation bias, and outlier bias. However, existing work often assumes that the behavior logs are collected from an ``average'' user, neglecting the differences between different users in their search and browsing behaviors. In this paper, we introduce personalized factors into the ULTR framework, which we term the user-aware ULTR problem. Through a formal causal analysis of this problem, we demonstrate that existing user-oblivious methods are biased when different users have different preferences over queries and personalized propensities of examining documents. To address such a personalized bias, we propose a novel user-aware inverse-propensity-score estimator for learning-to-rank objectives. Specifically, our approach models the distribution of user browsing behaviors for each query and aggregates user-weighted examination probabilities to determine propensities. We theoretically prove that the user-aware estimator is unbiased under some mild assumptions and shows lower variance compared to the straightforward way of calculating a user-dependent propensity for each impression. Finally, we empirically verify the effectiveness of our user-aware estimator by conducting extensive experiments on two semi-synthetic datasets and a real-world dataset.
An Out-Of-Distribution Membership Inference Attack Approach for Cross-Domain Graph Attacks
May 26, 2025Abstract:Graph Neural Network-based methods face privacy leakage risks due to the introduction of topological structures about the targets, which allows attackers to bypass the target's prior knowledge of the sensitive attributes and realize membership inference attacks (MIA) by observing and analyzing the topology distribution. As privacy concerns grow, the assumption of MIA, which presumes that attackers can obtain an auxiliary dataset with the same distribution, is increasingly deviating from reality. In this paper, we categorize the distribution diversity issue in real-world MIA scenarios as an Out-Of-Distribution (OOD) problem, and propose a novel Graph OOD Membership Inference Attack (GOOD-MIA) to achieve cross-domain graph attacks. Specifically, we construct shadow subgraphs with distributions from different domains to model the diversity of real-world data. We then explore the stable node representations that remain unchanged under external influences and consider eliminating redundant information from confounding environments and extracting task-relevant key information to more clearly distinguish between the characteristics of training data and unseen data. This OOD-based design makes cross-domain graph attacks possible. Finally, we perform risk extrapolation to optimize the attack's domain adaptability during attack inference to generalize the attack to other domains. Experimental results demonstrate that GOOD-MIA achieves superior attack performance in datasets designed for multiple domains.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
LMME3DHF: Benchmarking and Evaluating Multimodal 3D Human Face Generation with LMMs
May 05, 2025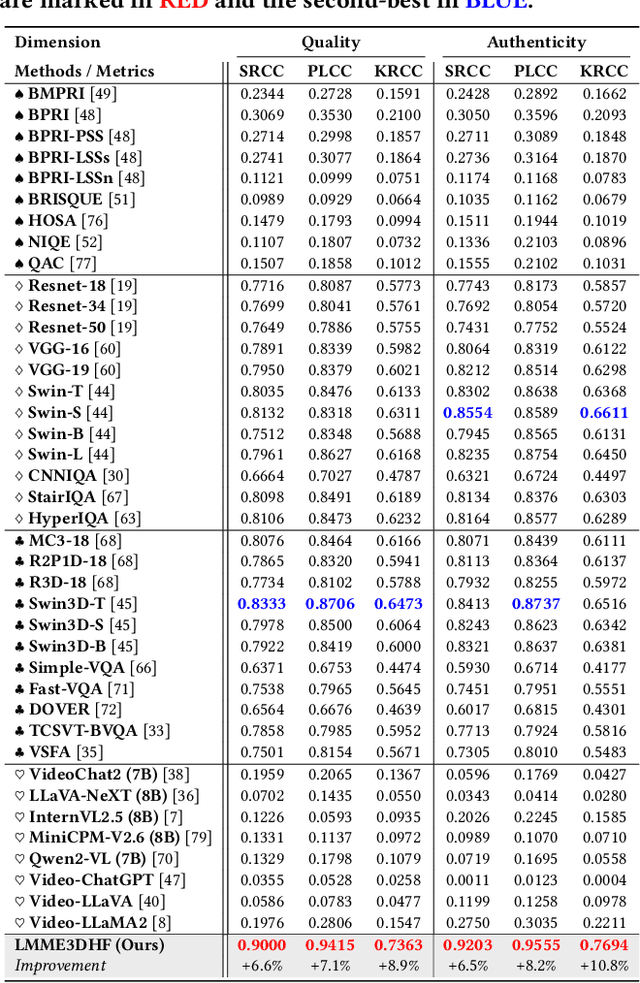
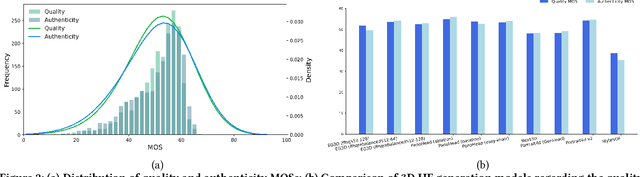
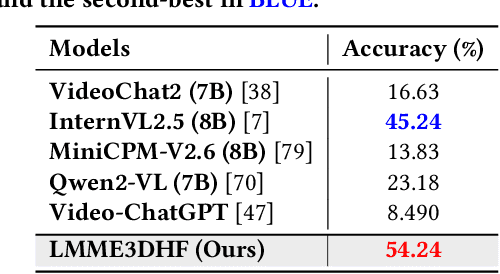
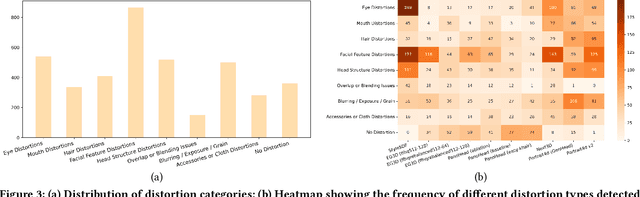
Abstract:The rapid advancement in generative artificial intelligence have enabled the creation of 3D human faces (HFs) for applications including media production, virtual reality, security, healthcare, and game development, etc. However, assessing the quality and realism of these AI-generated 3D human faces remains a significant challenge due to the subjective nature of human perception and innate perceptual sensitivity to facial features. To this end, we conduct a comprehensive study on the quality assessment of AI-generated 3D human faces. We first introduce Gen3DHF, a large-scale benchmark comprising 2,000 videos of AI-Generated 3D Human Faces along with 4,000 Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) collected across two dimensions, i.e., quality and authenticity, 2,000 distortion-aware saliency maps and distortion descriptions. Based on Gen3DHF, we propose LMME3DHF, a Large Multimodal Model (LMM)-based metric for Evaluating 3DHF capable of quality and authenticity score prediction, distortion-aware visual question answering, and distortion-aware saliency prediction. Experimental results show that LMME3DHF achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing methods in both accurately predicting quality scores for AI-generated 3D human faces and effectively identifying distortion-aware salient regions and distortion types, while maintaining strong alignment with human perceptual judgments. Both the Gen3DHF database and the LMME3DHF will be released upon the publication.
LMM4Gen3DHF: Benchmarking and Evaluating Multimodal 3D Human Face Generation with LMMs
Apr 29, 2025



Abstract:The rapid advancement in generative artificial intelligence have enabled the creation of 3D human faces (HFs) for applications including media production, virtual reality, security, healthcare, and game development, etc. However, assessing the quality and realism of these AI-generated 3D human faces remains a significant challenge due to the subjective nature of human perception and innate perceptual sensitivity to facial features. To this end, we conduct a comprehensive study on the quality assessment of AI-generated 3D human faces. We first introduce Gen3DHF, a large-scale benchmark comprising 2,000 videos of AI-Generated 3D Human Faces along with 4,000 Mean Opinion Scores (MOS) collected across two dimensions, i.e., quality and authenticity, 2,000 distortion-aware saliency maps and distortion descriptions. Based on Gen3DHF, we propose LMME3DHF, a Large Multimodal Model (LMM)-based metric for Evaluating 3DHF capable of quality and authenticity score prediction, distortion-aware visual question answering, and distortion-aware saliency prediction. Experimental results show that LMME3DHF achieves state-of-the-art performance, surpassing existing methods in both accurately predicting quality scores for AI-generated 3D human faces and effectively identifying distortion-aware salient regions and distortion types, while maintaining strong alignment with human perceptual judgments. Both the Gen3DHF database and the LMME3DHF will be released upon the publication.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge