Huaidong Zhang
SITA: Structurally Imperceptible and Transferable Adversarial Attacks for Stylized Image Generation
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Image generation technology has brought significant advancements across various fields but has also raised concerns about data misuse and potential rights infringements, particularly with respect to creating visual artworks. Current methods aimed at safeguarding artworks often employ adversarial attacks. However, these methods face challenges such as poor transferability, high computational costs, and the introduction of noticeable noise, which compromises the aesthetic quality of the original artwork. To address these limitations, we propose a Structurally Imperceptible and Transferable Adversarial (SITA) attacks. SITA leverages a CLIP-based destylization loss, which decouples and disrupts the robust style representation of the image. This disruption hinders style extraction during stylized image generation, thereby impairing the overall stylization process. Importantly, SITA eliminates the need for a surrogate diffusion model, leading to significantly reduced computational overhead. The method's robust style feature disruption ensures high transferability across diverse models. Moreover, SITA introduces perturbations by embedding noise within the imperceptible structural details of the image. This approach effectively protects against style extraction without compromising the visual quality of the artwork. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SITA offers superior protection for artworks against unauthorized use in stylized generation. It significantly outperforms existing methods in terms of transferability, computational efficiency, and noise imperceptibility. Code is available at https://github.com/A-raniy-day/SITA.
NexusGS: Sparse View Synthesis with Epipolar Depth Priors in 3D Gaussian Splatting
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Neural Radiance Field (NeRF) and 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) have noticeably advanced photo-realistic novel view synthesis using images from densely spaced camera viewpoints. However, these methods struggle in few-shot scenarios due to limited supervision. In this paper, we present NexusGS, a 3DGS-based approach that enhances novel view synthesis from sparse-view images by directly embedding depth information into point clouds, without relying on complex manual regularizations. Exploiting the inherent epipolar geometry of 3DGS, our method introduces a novel point cloud densification strategy that initializes 3DGS with a dense point cloud, reducing randomness in point placement while preventing over-smoothing and overfitting. Specifically, NexusGS comprises three key steps: Epipolar Depth Nexus, Flow-Resilient Depth Blending, and Flow-Filtered Depth Pruning. These steps leverage optical flow and camera poses to compute accurate depth maps, while mitigating the inaccuracies often associated with optical flow. By incorporating epipolar depth priors, NexusGS ensures reliable dense point cloud coverage and supports stable 3DGS training under sparse-view conditions. Experiments demonstrate that NexusGS significantly enhances depth accuracy and rendering quality, surpassing state-of-the-art methods by a considerable margin. Furthermore, we validate the superiority of our generated point clouds by substantially boosting the performance of competing methods. Project page: https://usmizuki.github.io/NexusGS/.
SCJD: Sparse Correlation and Joint Distillation for Efficient 3D Human Pose Estimation
Mar 18, 2025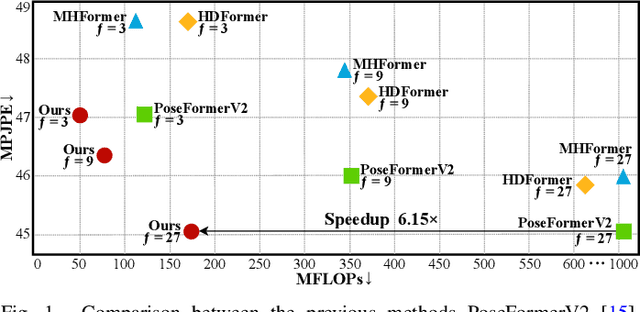
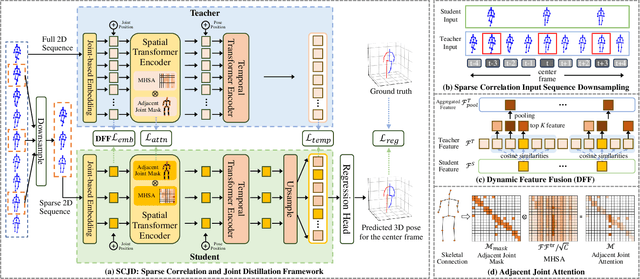
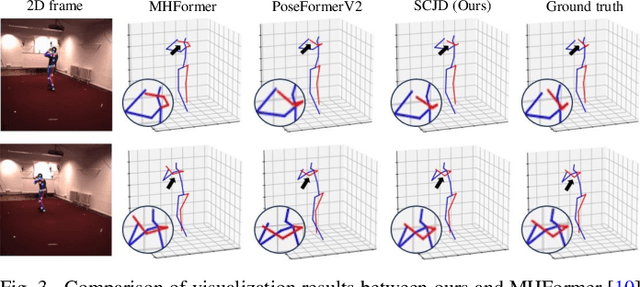
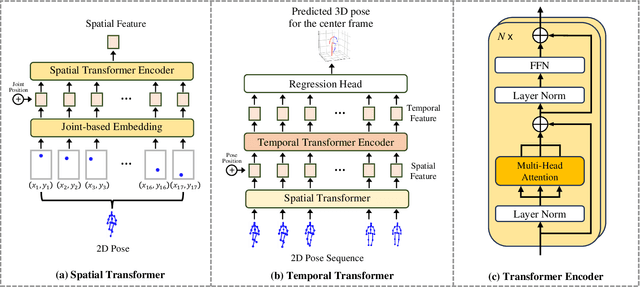
Abstract:Existing 3D Human Pose Estimation (HPE) methods achieve high accuracy but suffer from computational overhead and slow inference, while knowledge distillation methods fail to address spatial relationships between joints and temporal correlations in multi-frame inputs. In this paper, we propose Sparse Correlation and Joint Distillation (SCJD), a novel framework that balances efficiency and accuracy for 3D HPE. SCJD introduces Sparse Correlation Input Sequence Downsampling to reduce redundancy in student network inputs while preserving inter-frame correlations. For effective knowledge transfer, we propose Dynamic Joint Spatial Attention Distillation, which includes Dynamic Joint Embedding Distillation to enhance the student's feature representation using the teacher's multi-frame context feature, and Adjacent Joint Attention Distillation to improve the student network's focus on adjacent joint relationships for better spatial understanding. Additionally, Temporal Consistency Distillation aligns the temporal correlations between teacher and student networks through upsampling and global supervision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SCJD achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code is available at https://github.com/wileychan/SCJD.
Rotation-Adaptive Point Cloud Domain Generalization via Intricate Orientation Learning
Feb 04, 2025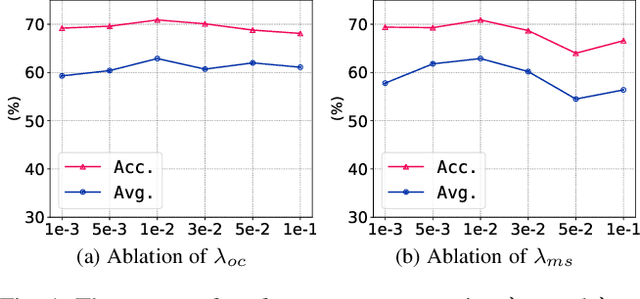



Abstract:The vulnerability of 3D point cloud analysis to unpredictable rotations poses an open yet challenging problem: orientation-aware 3D domain generalization. Cross-domain robustness and adaptability of 3D representations are crucial but not easily achieved through rotation augmentation. Motivated by the inherent advantages of intricate orientations in enhancing generalizability, we propose an innovative rotation-adaptive domain generalization framework for 3D point cloud analysis. Our approach aims to alleviate orientational shifts by leveraging intricate samples in an iterative learning process. Specifically, we identify the most challenging rotation for each point cloud and construct an intricate orientation set by optimizing intricate orientations. Subsequently, we employ an orientation-aware contrastive learning framework that incorporates an orientation consistency loss and a margin separation loss, enabling effective learning of categorically discriminative and generalizable features with rotation consistency. Extensive experiments and ablations conducted on 3D cross-domain benchmarks firmly establish the state-of-the-art performance of our proposed approach in the context of orientation-aware 3D domain generalization.
PersonaMagic: Stage-Regulated High-Fidelity Face Customization with Tandem Equilibrium
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Personalized image generation has made significant strides in adapting content to novel concepts. However, a persistent challenge remains: balancing the accurate reconstruction of unseen concepts with the need for editability according to the prompt, especially when dealing with the complex nuances of facial features. In this study, we delve into the temporal dynamics of the text-to-image conditioning process, emphasizing the crucial role of stage partitioning in introducing new concepts. We present PersonaMagic, a stage-regulated generative technique designed for high-fidelity face customization. Using a simple MLP network, our method learns a series of embeddings within a specific timestep interval to capture face concepts. Additionally, we develop a Tandem Equilibrium mechanism that adjusts self-attention responses in the text encoder, balancing text description and identity preservation, improving both areas. Extensive experiments confirm the superiority of PersonaMagic over state-of-the-art methods in both qualitative and quantitative evaluations. Moreover, its robustness and flexibility are validated in non-facial domains, and it can also serve as a valuable plug-in for enhancing the performance of pretrained personalization models.
MSSDA: Multi-Sub-Source Adaptation for Diabetic Foot Neuropathy Recognition
Sep 21, 2024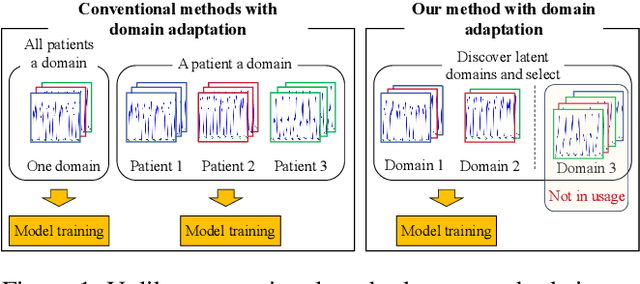
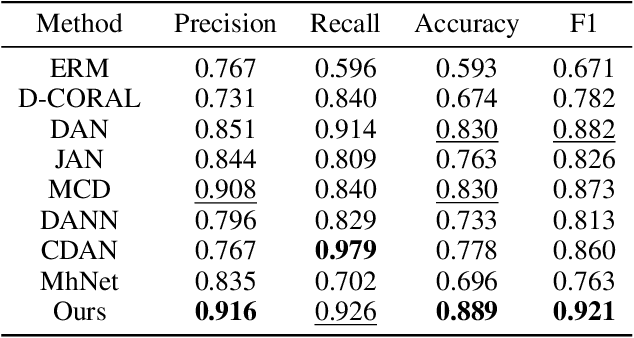
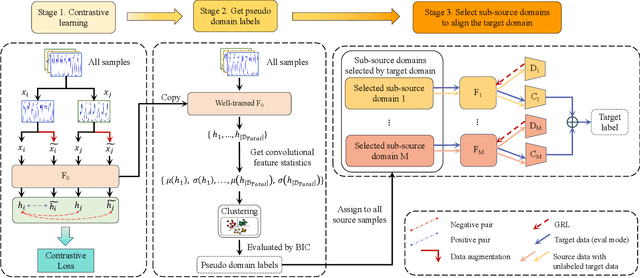
Abstract:Diabetic foot neuropathy (DFN) is a critical factor leading to diabetic foot ulcers, which is one of the most common and severe complications of diabetes mellitus (DM) and is associated with high risks of amputation and mortality. Despite its significance, existing datasets do not directly derive from plantar data and lack continuous, long-term foot-specific information. To advance DFN research, we have collected a novel dataset comprising continuous plantar pressure data to recognize diabetic foot neuropathy. This dataset includes data from 94 DM patients with DFN and 41 DM patients without DFN. Moreover, traditional methods divide datasets by individuals, potentially leading to significant domain discrepancies in some feature spaces due to the absence of mid-domain data. In this paper, we propose an effective domain adaptation method to address this proplem. We split the dataset based on convolutional feature statistics and select appropriate sub-source domains to enhance efficiency and avoid negative transfer. We then align the distributions of each source and target domain pair in specific feature spaces to minimize the domain gap. Comprehensive results validate the effectiveness of our method on both the newly proposed dataset for DFN recognition and an existing dataset.
VrdONE: One-stage Video Visual Relation Detection
Aug 18, 2024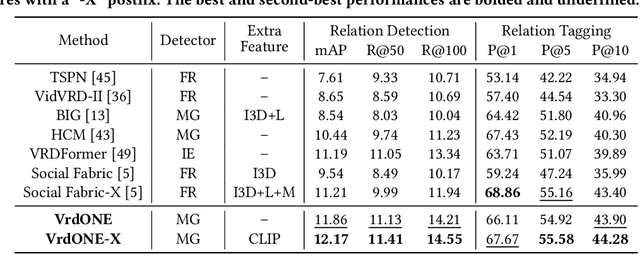

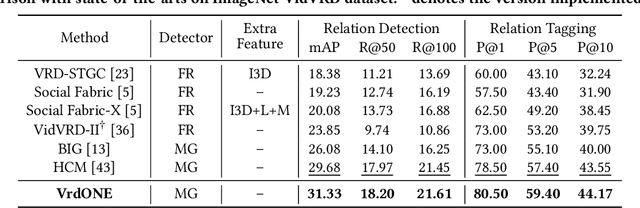

Abstract:Video Visual Relation Detection (VidVRD) focuses on understanding how entities interact over time and space in videos, a key step for gaining deeper insights into video scenes beyond basic visual tasks. Traditional methods for VidVRD, challenged by its complexity, typically split the task into two parts: one for identifying what relation categories are present and another for determining their temporal boundaries. This split overlooks the inherent connection between these elements. Addressing the need to recognize entity pairs' spatiotemporal interactions across a range of durations, we propose VrdONE, a streamlined yet efficacious one-stage model. VrdONE combines the features of subjects and objects, turning predicate detection into 1D instance segmentation on their combined representations. This setup allows for both relation category identification and binary mask generation in one go, eliminating the need for extra steps like proposal generation or post-processing. VrdONE facilitates the interaction of features across various frames, adeptly capturing both short-lived and enduring relations. Additionally, we introduce the Subject-Object Synergy (SOS) module, enhancing how subjects and objects perceive each other before combining. VrdONE achieves state-of-the-art performances on the VidOR benchmark and ImageNet-VidVRD, showcasing its superior capability in discerning relations across different temporal scales. The code is available at \textcolor[RGB]{228,58,136}{\href{https://github.com/lucaspk512/vrdone}{https://github.com/lucaspk512/vrdone}}.
G2Face: High-Fidelity Reversible Face Anonymization via Generative and Geometric Priors
Aug 18, 2024



Abstract:Reversible face anonymization, unlike traditional face pixelization, seeks to replace sensitive identity information in facial images with synthesized alternatives, preserving privacy without sacrificing image clarity. Traditional methods, such as encoder-decoder networks, often result in significant loss of facial details due to their limited learning capacity. Additionally, relying on latent manipulation in pre-trained GANs can lead to changes in ID-irrelevant attributes, adversely affecting data utility due to GAN inversion inaccuracies. This paper introduces G\textsuperscript{2}Face, which leverages both generative and geometric priors to enhance identity manipulation, achieving high-quality reversible face anonymization without compromising data utility. We utilize a 3D face model to extract geometric information from the input face, integrating it with a pre-trained GAN-based decoder. This synergy of generative and geometric priors allows the decoder to produce realistic anonymized faces with consistent geometry. Moreover, multi-scale facial features are extracted from the original face and combined with the decoder using our novel identity-aware feature fusion blocks (IFF). This integration enables precise blending of the generated facial patterns with the original ID-irrelevant features, resulting in accurate identity manipulation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing state-of-the-art techniques in face anonymization and recovery, while preserving high data utility. Code is available at https://github.com/Harxis/G2Face.
D$^4$-VTON: Dynamic Semantics Disentangling for Differential Diffusion based Virtual Try-On
Jul 21, 2024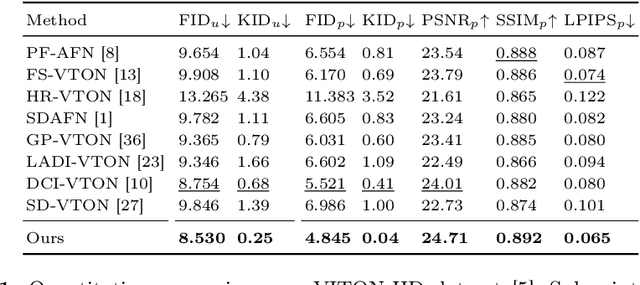
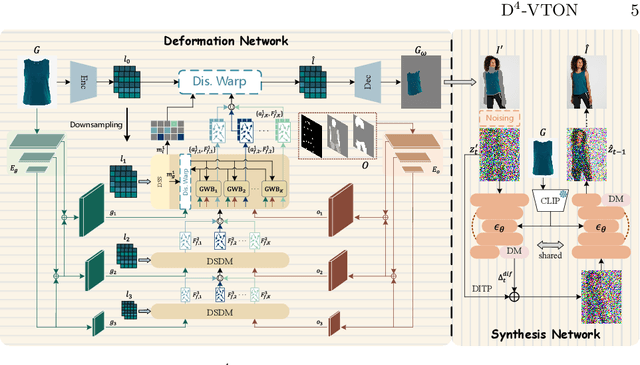
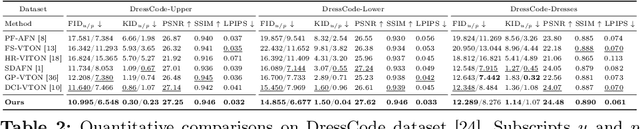
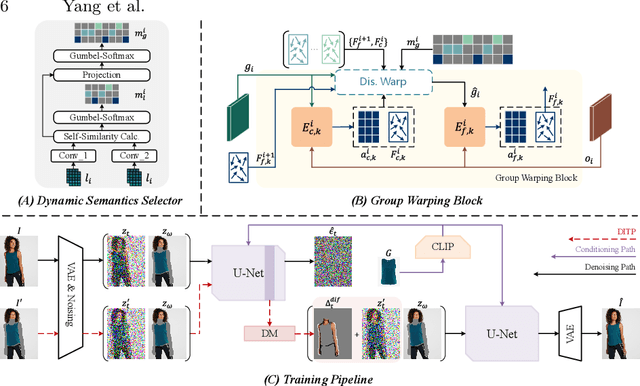
Abstract:In this paper, we introduce D$^4$-VTON, an innovative solution for image-based virtual try-on. We address challenges from previous studies, such as semantic inconsistencies before and after garment warping, and reliance on static, annotation-driven clothing parsers. Additionally, we tackle the complexities in diffusion-based VTON models when handling simultaneous tasks like inpainting and denoising. Our approach utilizes two key technologies: Firstly, Dynamic Semantics Disentangling Modules (DSDMs) extract abstract semantic information from garments to create distinct local flows, improving precise garment warping in a self-discovered manner. Secondly, by integrating a Differential Information Tracking Path (DITP), we establish a novel diffusion-based VTON paradigm. This path captures differential information between incomplete try-on inputs and their complete versions, enabling the network to handle multiple degradations independently, thereby minimizing learning ambiguities and achieving realistic results with minimal overhead. Extensive experiments demonstrate that D$^4$-VTON significantly outperforms existing methods in both quantitative metrics and qualitative evaluations, demonstrating its capability in generating realistic images and ensuring semantic consistency.
Beat-It: Beat-Synchronized Multi-Condition 3D Dance Generation
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:Dance, as an art form, fundamentally hinges on the precise synchronization with musical beats. However, achieving aesthetically pleasing dance sequences from music is challenging, with existing methods often falling short in controllability and beat alignment. To address these shortcomings, this paper introduces Beat-It, a novel framework for beat-specific, key pose-guided dance generation. Unlike prior approaches, Beat-It uniquely integrates explicit beat awareness and key pose guidance, effectively resolving two main issues: the misalignment of generated dance motions with musical beats, and the inability to map key poses to specific beats, critical for practical choreography. Our approach disentangles beat conditions from music using a nearest beat distance representation and employs a hierarchical multi-condition fusion mechanism. This mechanism seamlessly integrates key poses, beats, and music features, mitigating condition conflicts and offering rich, multi-conditioned guidance for dance generation. Additionally, a specially designed beat alignment loss ensures the generated dance movements remain in sync with the designated beats. Extensive experiments confirm Beat-It's superiority over existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of beat alignment and motion controllability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge