Yi Xie
PERM: Psychology-grounded Empathetic Reward Modeling for Large Language Models
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in human-centric applications, yet they often fail to provide substantive emotional support. While Reinforcement Learning (RL) has been utilized to enhance empathy of LLMs, existing reward models typically evaluate empathy from a single perspective, overlooking the inherently bidirectional interaction nature of empathy between the supporter and seeker as defined by Empathy Cycle theory. To address this limitation, we propose Psychology-grounded Empathetic Reward Modeling (PERM). PERM operationalizes empathy evaluation through a bidirectional decomposition: 1) Supporter perspective, assessing internal resonation and communicative expression; 2) Seeker perspective, evaluating emotional reception. Additionally, it incorporates a bystander perspective to monitor overall interaction quality. Extensive experiments on a widely-used emotional intelligence benchmark and an industrial daily conversation dataset demonstrate that PERM outperforms state-of-the-art baselines by over 10\%. Furthermore, a blinded user study reveals a 70\% preference for our approach, highlighting its efficacy in generating more empathetic responses. Our code, dataset, and models are available at https://github.com/ZhengWwwq/PERM.
Modality Dominance-Aware Optimization for Embodied RGB-Infrared Perception
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:RGB-Infrared (RGB-IR) multimodal perception is fundamental to embodied multimedia systems operating in complex physical environments. Although recent cross-modal fusion methods have advanced RGB-IR detection, the optimization dynamics caused by asymmetric modality characteristics remain underexplored. In practice, disparities in information density and feature quality introduce persistent optimization bias, leading training to overemphasize a dominant modality and hindering effective fusion. To quantify this phenomenon, we propose the Modality Dominance Index (MDI), which measures modality dominance by jointly modeling feature entropy and gradient contribution. Based on MDI, we develop a Modality Dominance-Aware Cross-modal Learning (MDACL) framework that regulates cross-modal optimization. MDACL incorporates Hierarchical Cross-modal Guidance (HCG) to enhance feature alignment and Adversarial Equilibrium Regularization (AER) to balance optimization dynamics during fusion. Extensive experiments on three RGB-IR benchmarks demonstrate that MDACL effectively mitigates optimization bias and achieves SOTA performance.
REPAIR: Robust Editing via Progressive Adaptive Intervention and Reintegration
Oct 02, 2025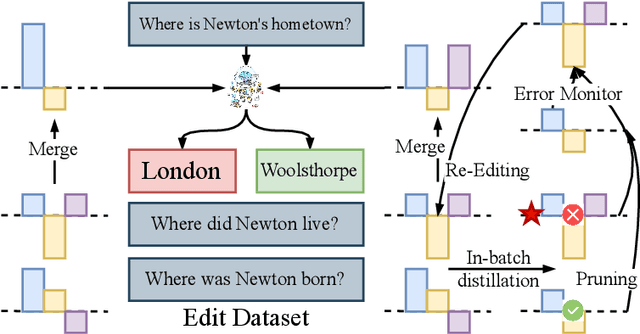
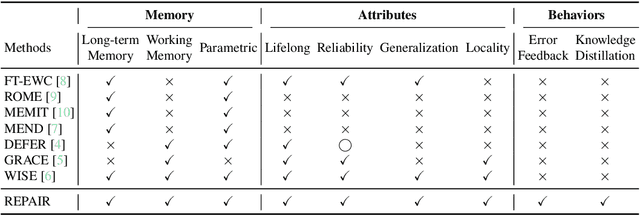
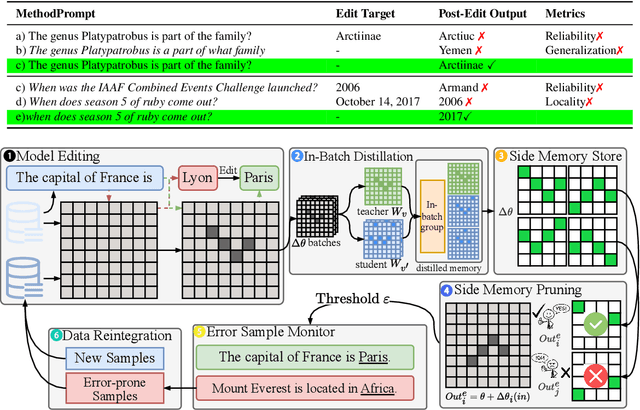
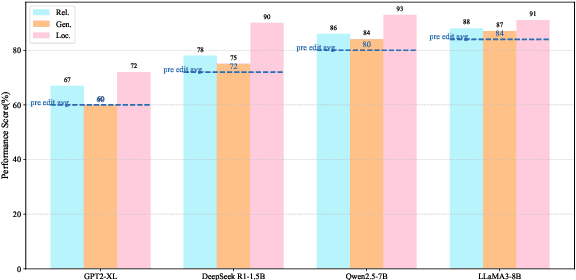
Abstract:Post-training for large language models (LLMs) is constrained by the high cost of acquiring new knowledge or correcting errors and by the unintended side effects that frequently arise from retraining. To address these issues, we introduce REPAIR (Robust Editing via Progressive Adaptive Intervention and Reintegration), a lifelong editing framework designed to support precise and low-cost model updates while preserving non-target knowledge. REPAIR mitigates the instability and conflicts of large-scale sequential edits through a closed-loop feedback mechanism coupled with dynamic memory management. Furthermore, by incorporating frequent knowledge fusion and enforcing strong locality guards, REPAIR effectively addresses the shortcomings of traditional distribution-agnostic approaches that often overlook unintended ripple effects. Our experiments demonstrate that REPAIR boosts editing accuracy by 10%-30% across multiple model families and significantly reduces knowledge forgetting. This work introduces a robust framework for developing reliable, scalable, and continually evolving LLMs.
KLIPA: A Knowledge Graph and LLM-Driven QA Framework for IP Analysis
Sep 09, 2025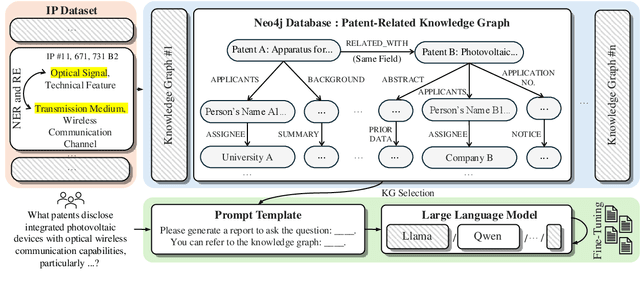
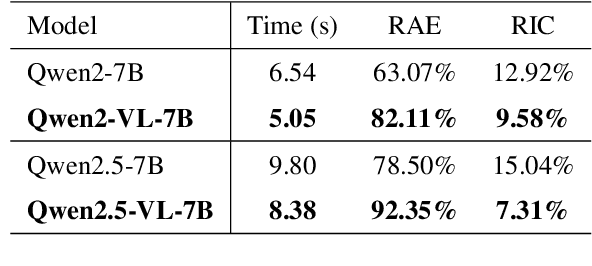
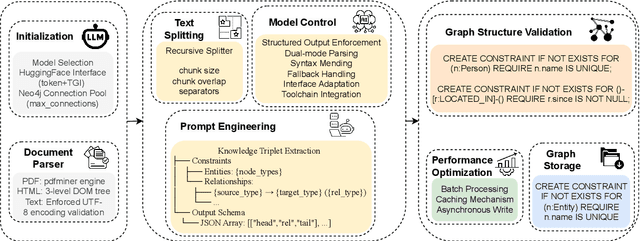
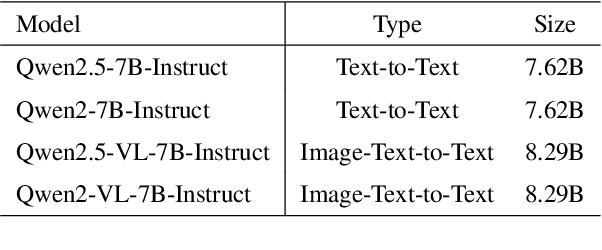
Abstract:Effectively managing intellectual property is a significant challenge. Traditional methods for patent analysis depend on labor-intensive manual searches and rigid keyword matching. These approaches are often inefficient and struggle to reveal the complex relationships hidden within large patent datasets, hindering strategic decision-making. To overcome these limitations, we introduce KLIPA, a novel framework that leverages a knowledge graph and a large language model (LLM) to significantly advance patent analysis. Our approach integrates three key components: a structured knowledge graph to map explicit relationships between patents, a retrieval-augmented generation(RAG) system to uncover contextual connections, and an intelligent agent that dynamically determines the optimal strategy for resolving user queries. We validated KLIPA on a comprehensive, real-world patent database, where it demonstrated substantial improvements in knowledge extraction, discovery of novel connections, and overall operational efficiency. This combination of technologies enhances retrieval accuracy, reduces reliance on domain experts, and provides a scalable, automated solution for any organization managing intellectual property, including technology corporations and legal firms, allowing them to better navigate the complexities of strategic innovation and competitive intelligence.
Three Minds, One Legend: Jailbreak Large Reasoning Model with Adaptive Stacked Ciphers
May 22, 2025Abstract:Recently, Large Reasoning Models (LRMs) have demonstrated superior logical capabilities compared to traditional Large Language Models (LLMs), gaining significant attention. Despite their impressive performance, the potential for stronger reasoning abilities to introduce more severe security vulnerabilities remains largely underexplored. Existing jailbreak methods often struggle to balance effectiveness with robustness against adaptive safety mechanisms. In this work, we propose SEAL, a novel jailbreak attack that targets LRMs through an adaptive encryption pipeline designed to override their reasoning processes and evade potential adaptive alignment. Specifically, SEAL introduces a stacked encryption approach that combines multiple ciphers to overwhelm the models reasoning capabilities, effectively bypassing built-in safety mechanisms. To further prevent LRMs from developing countermeasures, we incorporate two dynamic strategies - random and adaptive - that adjust the cipher length, order, and combination. Extensive experiments on real-world reasoning models, including DeepSeek-R1, Claude Sonnet, and OpenAI GPT-o4, validate the effectiveness of our approach. Notably, SEAL achieves an attack success rate of 80.8% on GPT o4-mini, outperforming state-of-the-art baselines by a significant margin of 27.2%. Warning: This paper contains examples of inappropriate, offensive, and harmful content.
Slow Transition to Low-Dimensional Chaos in Heavy-Tailed Recurrent Neural Networks
May 14, 2025Abstract:Growing evidence suggests that synaptic weights in the brain follow heavy-tailed distributions, yet most theoretical analyses of recurrent neural networks (RNNs) assume Gaussian connectivity. We systematically study the activity of RNNs with random weights drawn from biologically plausible L\'evy alpha-stable distributions. While mean-field theory for the infinite system predicts that the quiescent state is always unstable -- implying ubiquitous chaos -- our finite-size analysis reveals a sharp transition between quiescent and chaotic dynamics. We theoretically predict the gain at which the system transitions from quiescent to chaotic dynamics, and validate it through simulations. Compared to Gaussian networks, heavy-tailed RNNs exhibit a broader parameter regime near the edge of chaos, namely a slow transition to chaos. However, this robustness comes with a tradeoff: heavier tails reduce the Lyapunov dimension of the attractor, indicating lower effective dimensionality. Our results reveal a biologically aligned tradeoff between the robustness of dynamics near the edge of chaos and the richness of high-dimensional neural activity. By analytically characterizing the transition point in finite-size networks -- where mean-field theory breaks down -- we provide a tractable framework for understanding dynamics in realistically sized, heavy-tailed neural circuits.
SCJD: Sparse Correlation and Joint Distillation for Efficient 3D Human Pose Estimation
Mar 18, 2025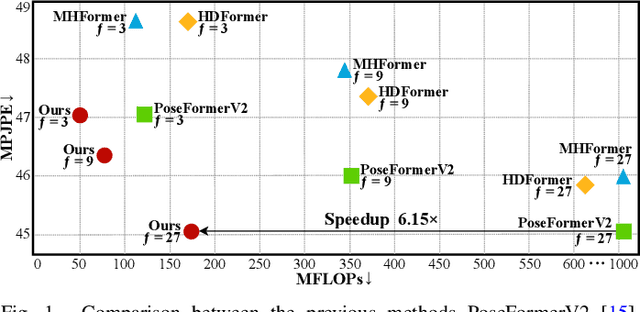
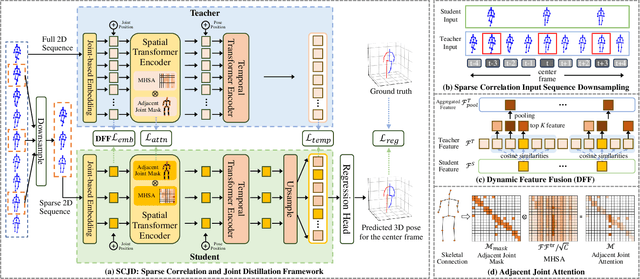
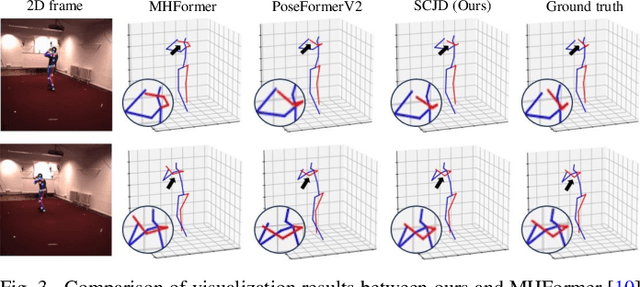
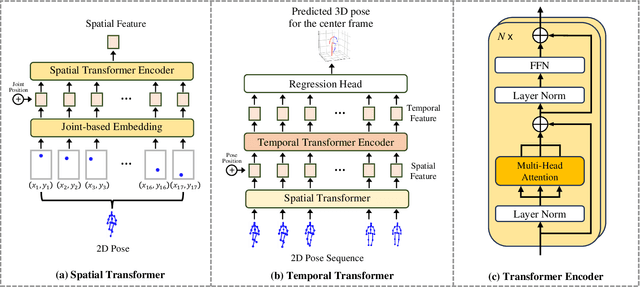
Abstract:Existing 3D Human Pose Estimation (HPE) methods achieve high accuracy but suffer from computational overhead and slow inference, while knowledge distillation methods fail to address spatial relationships between joints and temporal correlations in multi-frame inputs. In this paper, we propose Sparse Correlation and Joint Distillation (SCJD), a novel framework that balances efficiency and accuracy for 3D HPE. SCJD introduces Sparse Correlation Input Sequence Downsampling to reduce redundancy in student network inputs while preserving inter-frame correlations. For effective knowledge transfer, we propose Dynamic Joint Spatial Attention Distillation, which includes Dynamic Joint Embedding Distillation to enhance the student's feature representation using the teacher's multi-frame context feature, and Adjacent Joint Attention Distillation to improve the student network's focus on adjacent joint relationships for better spatial understanding. Additionally, Temporal Consistency Distillation aligns the temporal correlations between teacher and student networks through upsampling and global supervision. Extensive experiments demonstrate that SCJD achieves state-of-the-art performance. Code is available at https://github.com/wileychan/SCJD.
Knowledge Bridger: Towards Training-free Missing Multi-modality Completion
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Previous successful approaches to missing modality completion rely on carefully designed fusion techniques and extensive pre-training on complete data, which can limit their generalizability in out-of-domain (OOD) scenarios. In this study, we pose a new challenge: can we develop a missing modality completion model that is both resource-efficient and robust to OOD generalization? To address this, we present a training-free framework for missing modality completion that leverages large multimodal models (LMMs). Our approach, termed the "Knowledge Bridger", is modality-agnostic and integrates generation and ranking of missing modalities. By defining domain-specific priors, our method automatically extracts structured information from available modalities to construct knowledge graphs. These extracted graphs connect the missing modality generation and ranking modules through the LMM, resulting in high-quality imputations of missing modalities. Experimental results across both general and medical domains show that our approach consistently outperforms competing methods, including in OOD generalization. Additionally, our knowledge-driven generation and ranking techniques demonstrate superiority over variants that directly employ LMMs for generation and ranking, offering insights that may be valuable for applications in other domains.
Enhancing Masked Time-Series Modeling via Dropping Patches
Dec 19, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores how to enhance existing masked time-series modeling by randomly dropping sub-sequence level patches of time series. On this basis, a simple yet effective method named DropPatch is proposed, which has two remarkable advantages: 1) It improves the pre-training efficiency by a square-level advantage; 2) It provides additional advantages for modeling in scenarios such as in-domain, cross-domain, few-shot learning and cold start. This paper conducts comprehensive experiments to verify the effectiveness of the method and analyze its internal mechanism. Empirically, DropPatch strengthens the attention mechanism, reduces information redundancy and serves as an efficient means of data augmentation. Theoretically, it is proved that DropPatch slows down the rate at which the Transformer representations collapse into the rank-1 linear subspace by randomly dropping patches, thus optimizing the quality of the learned representations
TSGaussian: Semantic and Depth-Guided Target-Specific Gaussian Splatting from Sparse Views
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Recent advances in Gaussian Splatting have significantly advanced the field, achieving both panoptic and interactive segmentation of 3D scenes. However, existing methodologies often overlook the critical need for reconstructing specified targets with complex structures from sparse views. To address this issue, we introduce TSGaussian, a novel framework that combines semantic constraints with depth priors to avoid geometry degradation in challenging novel view synthesis tasks. Our approach prioritizes computational resources on designated targets while minimizing background allocation. Bounding boxes from YOLOv9 serve as prompts for Segment Anything Model to generate 2D mask predictions, ensuring semantic accuracy and cost efficiency. TSGaussian effectively clusters 3D gaussians by introducing a compact identity encoding for each Gaussian ellipsoid and incorporating 3D spatial consistency regularization. Leveraging these modules, we propose a pruning strategy to effectively reduce redundancy in 3D gaussians. Extensive experiments demonstrate that TSGaussian outperforms state-of-the-art methods on three standard datasets and a new challenging dataset we collected, achieving superior results in novel view synthesis of specific objects. Code is available at: https://github.com/leon2000-ai/TSGaussian.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge