Xinyang Li
Deeper detection limits in astronomical imaging using self-supervised spatiotemporal denoising
Feb 19, 2026Abstract:The detection limit of astronomical imaging observations is limited by several noise sources. Some of that noise is correlated between neighbouring image pixels and exposures, so in principle could be learned and corrected. We present an astronomical self-supervised transformer-based denoising algorithm (ASTERIS), that integrates spatiotemporal information across multiple exposures. Benchmarking on mock data indicates that ASTERIS improves detection limits by 1.0 magnitude at 90% completeness and purity, while preserving the point spread function and photometric accuracy. Observational validation using data from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) and Subaru telescope identifies previously undetectable features, including low-surface-brightness galaxy structures and gravitationally-lensed arcs. Applied to deep JWST images, ASTERIS identifies three times more redshift > 9 galaxy candidates, with rest-frame ultraviolet luminosity 1.0 magnitude fainter, than previous methods.
Real-Time Multi-Target Detection and Tracking with mmWave 5G NR Waveforms on RFSoC
Dec 27, 2025Abstract:We demonstrate a real-time implementation of multi-target detection and tracking using 5G New Radio (NR) physical downlink shared channel (PDSCH) waveform with 400 MHz bandwidth at 28 GHz carrier frequency. The hardware platform is built on a radio frequency system-on-chip (RFSoC) 4x2 board connected with a pair of Sivers EVK02001 mmWave beamformers for transmission and reception. The entire sensing transceiver processing and fast beam control are realized purely in the programmable logic (PL) part of the RFSoC, enabling low-latency and fully hardware-accelerated operation. The continuously acquired sensing data constitute 3D range-angle (RA) tensors, which are processed on a host PC using adaptive background subtraction, cell-averaging constant false alarm rate (CA-CFAR) detection with density-based spatial clustering of applications with noise (DBSCAN) clustering, and extended Kalman filtering (EKF), to detect and track targets in the environment. Our software-defined radio (SDR) testbed integrates heterogeneous computing resources, including CPUs, GPUs, and FPGAs, thereby providing design flexibility for a wide range of tasks.
Variational Secret Common Randomness Extraction
Oct 02, 2025Abstract:This paper studies the problem of extracting common randomness (CR) or secret keys from correlated random sources observed by two legitimate parties, Alice and Bob, through public discussion in the presence of an eavesdropper, Eve. We propose a practical two-stage CR extraction framework. In the first stage, the variational probabilistic quantization (VPQ) step is introduced, where Alice and Bob employ probabilistic neural network (NN) encoders to map their observations into discrete, nearly uniform random variables (RVs) with high agreement probability while minimizing information leakage to Eve. This is realized through a variational learning objective combined with adversarial training. In the second stage, a secure sketch using code-offset construction reconciles the encoder outputs into identical secret keys, whose secrecy is guaranteed by the VPQ objective. As a representative application, we study physical layer key (PLK) generation. Beyond the traditional methods, which rely on the channel reciprocity principle and require two-way channel probing, thus suffering from large protocol overhead and being unsuitable in high mobility scenarios, we propose a sensing-based PLK generation method for integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) systems, where paired range-angle (RA) maps measured at Alice and Bob serve as correlated sources. The idea is verified through both end-to-end simulations and real-world software-defined radio (SDR) measurements, including scenarios where Eve has partial knowledge about Bob's position. The results demonstrate the feasibility and convincing performance of both the proposed CR extraction framework and sensing-based PLK generation method.
JCo-MVTON: Jointly Controllable Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer for Mask-Free Virtual Try-on
Aug 25, 2025
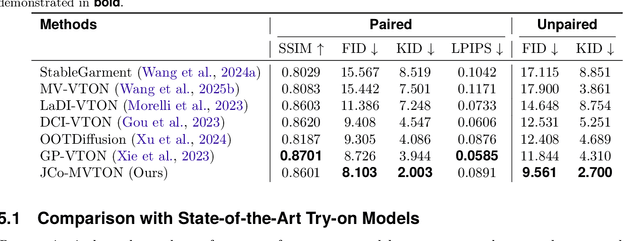
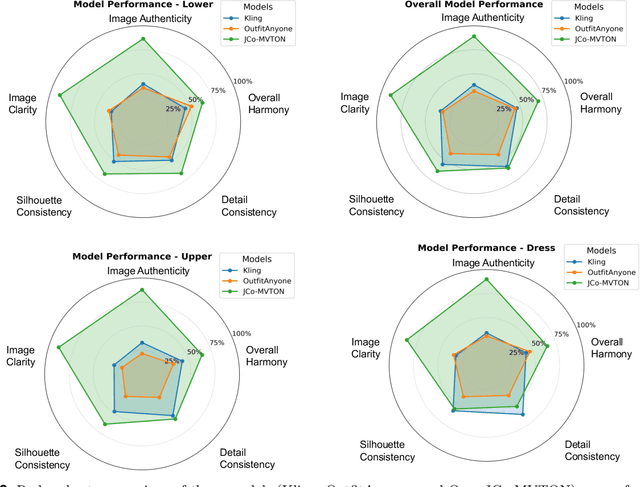
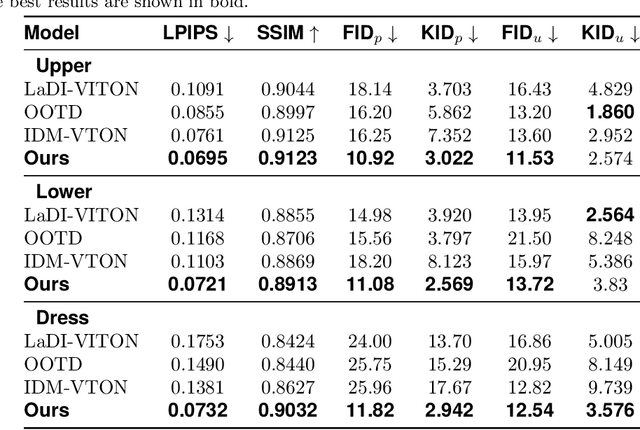
Abstract:Virtual try-on systems have long been hindered by heavy reliance on human body masks, limited fine-grained control over garment attributes, and poor generalization to real-world, in-the-wild scenarios. In this paper, we propose JCo-MVTON (Jointly Controllable Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer for Mask-Free Virtual Try-On), a novel framework that overcomes these limitations by integrating diffusion-based image generation with multi-modal conditional fusion. Built upon a Multi-Modal Diffusion Transformer (MM-DiT) backbone, our approach directly incorporates diverse control signals -- such as the reference person image and the target garment image -- into the denoising process through dedicated conditional pathways that fuse features within the self-attention layers. This fusion is further enhanced with refined positional encodings and attention masks, enabling precise spatial alignment and improved garment-person integration. To address data scarcity and quality, we introduce a bidirectional generation strategy for dataset construction: one pipeline uses a mask-based model to generate realistic reference images, while a symmetric ``Try-Off'' model, trained in a self-supervised manner, recovers the corresponding garment images. The synthesized dataset undergoes rigorous manual curation, allowing iterative improvement in visual fidelity and diversity. Experiments demonstrate that JCo-MVTON achieves state-of-the-art performance on public benchmarks including DressCode, significantly outperforming existing methods in both quantitative metrics and human evaluations. Moreover, it shows strong generalization in real-world applications, surpassing commercial systems.
XSpecMesh: Quality-Preserving Auto-Regressive Mesh Generation Acceleration via Multi-Head Speculative Decoding
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Current auto-regressive models can generate high-quality, topologically precise meshes; however, they necessitate thousands-or even tens of thousands-of next-token predictions during inference, resulting in substantial latency. We introduce XSpecMesh, a quality-preserving acceleration method for auto-regressive mesh generation models. XSpecMesh employs a lightweight, multi-head speculative decoding scheme to predict multiple tokens in parallel within a single forward pass, thereby accelerating inference. We further propose a verification and resampling strategy: the backbone model verifies each predicted token and resamples any tokens that do not meet the quality criteria. In addition, we propose a distillation strategy that trains the lightweight decoding heads by distilling from the backbone model, encouraging their prediction distributions to align and improving the success rate of speculative predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves a 1.7x speedup without sacrificing generation quality. Our code will be released.
DeOcc-1-to-3: 3D De-Occlusion from a Single Image via Self-Supervised Multi-View Diffusion
Jun 26, 2025Abstract:Reconstructing 3D objects from a single image is a long-standing challenge, especially under real-world occlusions. While recent diffusion-based view synthesis models can generate consistent novel views from a single RGB image, they generally assume fully visible inputs and fail when parts of the object are occluded. This leads to inconsistent views and degraded 3D reconstruction quality. To overcome this limitation, we propose an end-to-end framework for occlusion-aware multi-view generation. Our method directly synthesizes six structurally consistent novel views from a single partially occluded image, enabling downstream 3D reconstruction without requiring prior inpainting or manual annotations. We construct a self-supervised training pipeline using the Pix2Gestalt dataset, leveraging occluded-unoccluded image pairs and pseudo-ground-truth views to teach the model structure-aware completion and view consistency. Without modifying the original architecture, we fully fine-tune the view synthesis model to jointly learn completion and multi-view generation. Additionally, we introduce the first benchmark for occlusion-aware reconstruction, encompassing diverse occlusion levels, object categories, and mask patterns. This benchmark provides a standardized protocol for evaluating future methods under partial occlusions. Our code is available at https://github.com/Quyans/DeOcc123.
From Black Boxes to Transparent Minds: Evaluating and Enhancing the Theory of Mind in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:As large language models evolve, there is growing anticipation that they will emulate human-like Theory of Mind (ToM) to assist with routine tasks. However, existing methods for evaluating machine ToM focus primarily on unimodal models and largely treat these models as black boxes, lacking an interpretative exploration of their internal mechanisms. In response, this study adopts an approach based on internal mechanisms to provide an interpretability-driven assessment of ToM in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Specifically, we first construct a multimodal ToM test dataset, GridToM, which incorporates diverse belief testing tasks and perceptual information from multiple perspectives. Next, our analysis shows that attention heads in multimodal large models can distinguish cognitive information across perspectives, providing evidence of ToM capabilities. Furthermore, we present a lightweight, training-free approach that significantly enhances the model's exhibited ToM by adjusting in the direction of the attention head.
Label-efficient Single Photon Images Classification via Active Learning
May 07, 2025Abstract:Single-photon LiDAR achieves high-precision 3D imaging in extreme environments through quantum-level photon detection technology. Current research primarily focuses on reconstructing 3D scenes from sparse photon events, whereas the semantic interpretation of single-photon images remains underexplored, due to high annotation costs and inefficient labeling strategies. This paper presents the first active learning framework for single-photon image classification. The core contribution is an imaging condition-aware sampling strategy that integrates synthetic augmentation to model variability across imaging conditions. By identifying samples where the model is both uncertain and sensitive to these conditions, the proposed method selectively annotates only the most informative examples. Experiments on both synthetic and real-world datasets show that our approach outperforms all baselines and achieves high classification accuracy with significantly fewer labeled samples. Specifically, our approach achieves 97% accuracy on synthetic single-photon data using only 1.5% labeled samples. On real-world data, we maintain 90.63% accuracy with just 8% labeled samples, which is 4.51% higher than the best-performing baseline. This illustrates that active learning enables the same level of classification performance on single-photon images as on classical images, opening doors to large-scale integration of single-photon data in real-world applications.
SynergyAmodal: Deocclude Anything with Text Control
Apr 28, 2025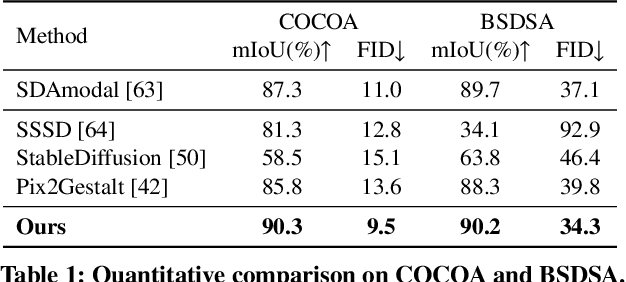

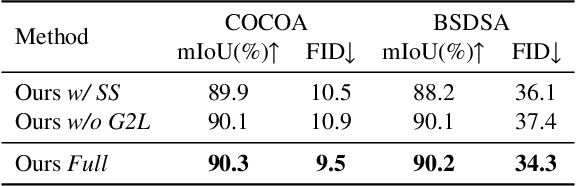
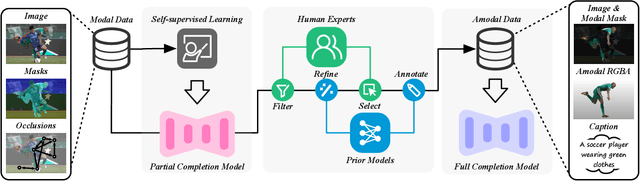
Abstract:Image deocclusion (or amodal completion) aims to recover the invisible regions (\ie, shape and appearance) of occluded instances in images. Despite recent advances, the scarcity of high-quality data that balances diversity, plausibility, and fidelity remains a major obstacle. To address this challenge, we identify three critical elements: leveraging in-the-wild image data for diversity, incorporating human expertise for plausibility, and utilizing generative priors for fidelity. We propose SynergyAmodal, a novel framework for co-synthesizing in-the-wild amodal datasets with comprehensive shape and appearance annotations, which integrates these elements through a tripartite data-human-model collaboration. First, we design an occlusion-grounded self-supervised learning algorithm to harness the diversity of in-the-wild image data, fine-tuning an inpainting diffusion model into a partial completion diffusion model. Second, we establish a co-synthesis pipeline to iteratively filter, refine, select, and annotate the initial deocclusion results of the partial completion diffusion model, ensuring plausibility and fidelity through human expert guidance and prior model constraints. This pipeline generates a high-quality paired amodal dataset with extensive category and scale diversity, comprising approximately 16K pairs. Finally, we train a full completion diffusion model on the synthesized dataset, incorporating text prompts as conditioning signals. Extensive experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our framework in achieving zero-shot generalization and textual controllability. Our code, dataset, and models will be made publicly available at https://github.com/imlixinyang/SynergyAmodal.
Computation of Capacity-Distortion-Cost Functions for Continuous Memoryless Channels
Apr 28, 2025


Abstract:This paper aims at computing the capacity-distortion-cost (CDC) function for continuous memoryless channels, which is defined as the supremum of the mutual information between channel input and output, constrained by an input cost and an expected distortion of estimating channel state. Solving the optimization problem is challenging because the input distribution does not lie in a finite-dimensional Euclidean space and the optimal estimation function has no closed form in general. We propose to adopt the Wasserstein proximal point method and parametric models such as neural networks (NNs) to update the input distribution and estimation function alternately. To implement it in practice, the importance sampling (IS) technique is used to calculate integrals numerically, and the Wasserstein gradient descent is approximated by pushing forward particles. The algorithm is then applied to an integrated sensing and communications (ISAC) system, validating theoretical results at minimum and maximum distortion as well as the random-deterministic trade-off.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge