Siqi Liu
Step 3.5 Flash: Open Frontier-Level Intelligence with 11B Active Parameters
Feb 11, 2026Abstract:We introduce Step 3.5 Flash, a sparse Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) model that bridges frontier-level agentic intelligence and computational efficiency. We focus on what matters most when building agents: sharp reasoning and fast, reliable execution. Step 3.5 Flash pairs a 196B-parameter foundation with 11B active parameters for efficient inference. It is optimized with interleaved 3:1 sliding-window/full attention and Multi-Token Prediction (MTP-3) to reduce the latency and cost of multi-round agentic interactions. To reach frontier-level intelligence, we design a scalable reinforcement learning framework that combines verifiable signals with preference feedback, while remaining stable under large-scale off-policy training, enabling consistent self-improvement across mathematics, code, and tool use. Step 3.5 Flash demonstrates strong performance across agent, coding, and math tasks, achieving 85.4% on IMO-AnswerBench, 86.4% on LiveCodeBench-v6 (2024.08-2025.05), 88.2% on tau2-Bench, 69.0% on BrowseComp (with context management), and 51.0% on Terminal-Bench 2.0, comparable to frontier models such as GPT-5.2 xHigh and Gemini 3.0 Pro. By redefining the efficiency frontier, Step 3.5 Flash provides a high-density foundation for deploying sophisticated agents in real-world industrial environments.
PALUM: Part-based Attention Learning for Unified Motion Retargeting
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Retargeting motion between characters with different skeleton structures is a fundamental challenge in computer animation. When source and target characters have vastly different bone arrangements, maintaining the original motion's semantics and quality becomes increasingly difficult. We present PALUM, a novel approach that learns common motion representations across diverse skeleton topologies by partitioning joints into semantic body parts and applying attention mechanisms to capture spatio-temporal relationships. Our method transfers motion to target skeletons by leveraging these skeleton-agnostic representations alongside target-specific structural information. To ensure robust learning and preserve motion fidelity, we introduce a cycle consistency mechanism that maintains semantic coherence throughout the retargeting process. Extensive experiments demonstrate superior performance in handling diverse skeletal structures while maintaining motion realism and semantic fidelity, even when generalizing to previously unseen skeleton-motion combinations. We will make our implementation publicly available to support future research.
GraphMMP: A Graph Neural Network Model with Mutual Information and Global Fusion for Multimodal Medical Prognosis
Aug 24, 2025Abstract:In the field of multimodal medical data analysis, leveraging diverse types of data and understanding their hidden relationships continues to be a research focus. The main challenges lie in effectively modeling the complex interactions between heterogeneous data modalities with distinct characteristics while capturing both local and global dependencies across modalities. To address these challenges, this paper presents a two-stage multimodal prognosis model, GraphMMP, which is based on graph neural networks. The proposed model constructs feature graphs using mutual information and features a global fusion module built on Mamba, which significantly boosts prognosis performance. Empirical results show that GraphMMP surpasses existing methods on datasets related to liver prognosis and the METABRIC study, demonstrating its effectiveness in multimodal medical prognosis tasks.
Rethinking 1-bit Optimization Leveraging Pre-trained Large Language Models
Aug 09, 2025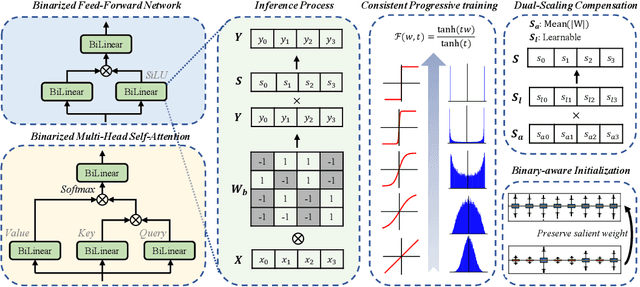
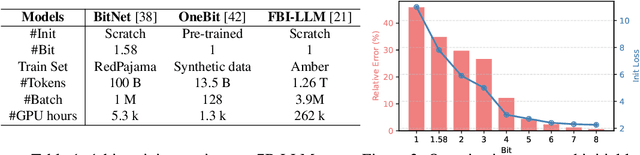
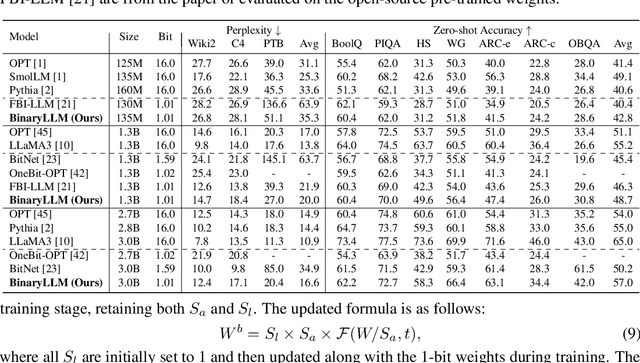
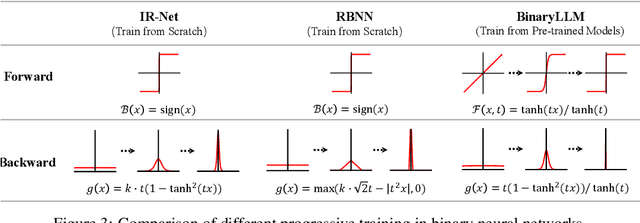
Abstract:1-bit LLM quantization offers significant advantages in reducing storage and computational costs. However, existing methods typically train 1-bit LLMs from scratch, failing to fully leverage pre-trained models. This results in high training costs and notable accuracy degradation. We identify that the large gap between full precision and 1-bit representations makes direct adaptation difficult. In this paper, we introduce a consistent progressive training for both forward and backward, smoothly converting the floating-point weights into the binarized ones. Additionally, we incorporate binary-aware initialization and dual-scaling compensation to reduce the difficulty of progressive training and improve the performance. Experimental results on LLMs of various sizes demonstrate that our method outperforms existing approaches. Our results show that high-performance 1-bit LLMs can be achieved using pre-trained models, eliminating the need for expensive training from scratch.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025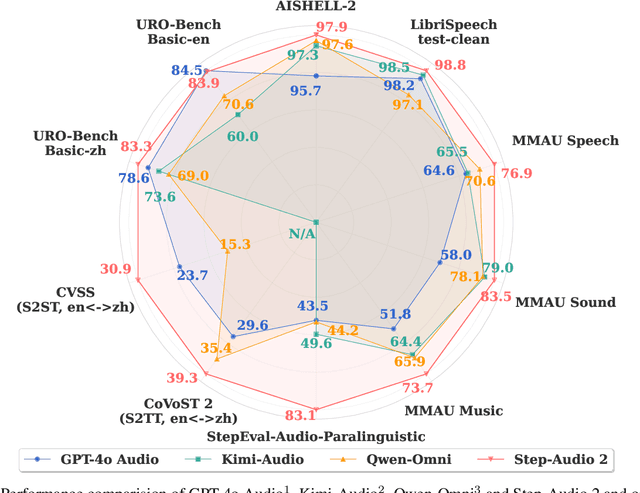

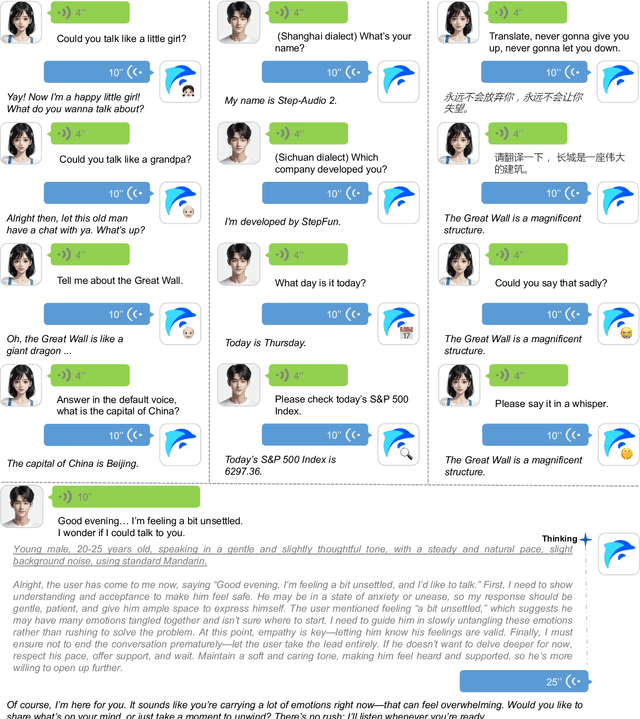

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
Introducing Quality Estimation to Machine Translation Post-editing Workflow: An Empirical Study on Its Usefulness
Jul 22, 2025Abstract:This preliminary study investigates the usefulness of sentence-level Quality Estimation (QE) in English-Chinese Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE), focusing on its impact on post-editing speed and student translators' perceptions. It also explores the interaction effects between QE and MT quality, as well as between QE and translation expertise. The findings reveal that QE significantly reduces post-editing time. The examined interaction effects were not significant, suggesting that QE consistently improves MTPE efficiency across medium- and high-quality MT outputs and among student translators with varying levels of expertise. In addition to indicating potentially problematic segments, QE serves multiple functions in MTPE, such as validating translators' evaluations of MT quality and enabling them to double-check translation outputs. However, interview data suggest that inaccurate QE may hinder post-editing processes. This research provides new insights into the strengths and limitations of QE, facilitating its more effective integration into MTPE workflows to enhance translators' productivity.
From Black Boxes to Transparent Minds: Evaluating and Enhancing the Theory of Mind in Multimodal Large Language Models
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:As large language models evolve, there is growing anticipation that they will emulate human-like Theory of Mind (ToM) to assist with routine tasks. However, existing methods for evaluating machine ToM focus primarily on unimodal models and largely treat these models as black boxes, lacking an interpretative exploration of their internal mechanisms. In response, this study adopts an approach based on internal mechanisms to provide an interpretability-driven assessment of ToM in multimodal large language models (MLLMs). Specifically, we first construct a multimodal ToM test dataset, GridToM, which incorporates diverse belief testing tasks and perceptual information from multiple perspectives. Next, our analysis shows that attention heads in multimodal large models can distinguish cognitive information across perspectives, providing evidence of ToM capabilities. Furthermore, we present a lightweight, training-free approach that significantly enhances the model's exhibited ToM by adjusting in the direction of the attention head.
PRISM2: Unlocking Multi-Modal General Pathology AI with Clinical Dialogue
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Recent pathology foundation models can provide rich tile-level representations but fall short of delivering general-purpose clinical utility without further extensive model development. These models lack whole-slide image (WSI) understanding and are not trained with large-scale diagnostic data, limiting their performance on diverse downstream tasks. We introduce PRISM2, a multi-modal slide-level foundation model trained via clinical dialogue to enable scalable, generalizable pathology AI. PRISM2 is trained on nearly 700,000 specimens (2.3 million WSIs) paired with real-world clinical diagnostic reports in a two-stage process. In Stage 1, a vision-language model is trained using contrastive and captioning objectives to align whole slide embeddings with textual clinical diagnosis. In Stage 2, the language model is unfrozen to enable diagnostic conversation and extract more clinically meaningful representations from hidden states. PRISM2 achieves strong performance on diagnostic and biomarker prediction tasks, outperforming prior slide-level models including PRISM and TITAN. It also introduces a zero-shot yes/no classification approach that surpasses CLIP-style methods without prompt tuning or class enumeration. By aligning visual features with clinical reasoning, PRISM2 improves generalization on both data-rich and low-sample tasks, offering a scalable path forward for building general pathology AI agents capable of assisting diagnostic and prognostic decisions.
Step-Audio-AQAA: a Fully End-to-End Expressive Large Audio Language Model
Jun 10, 2025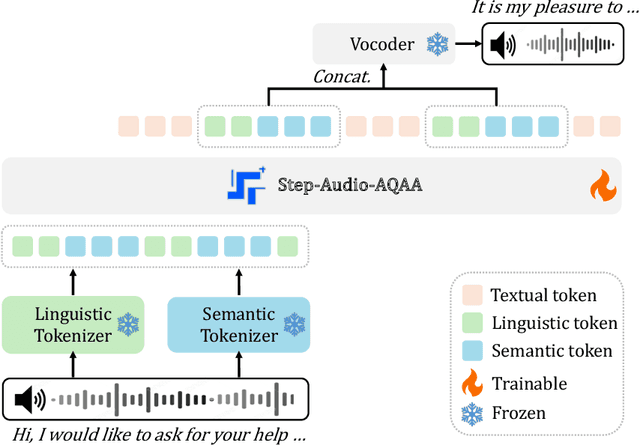
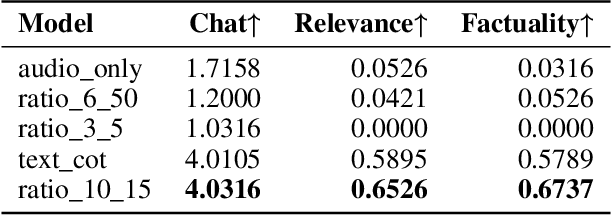
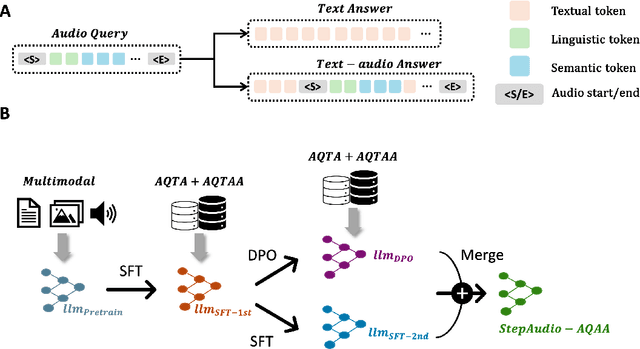
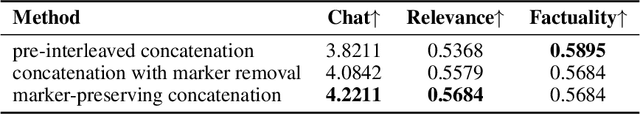
Abstract:Large Audio-Language Models (LALMs) have significantly advanced intelligent human-computer interaction, yet their reliance on text-based outputs limits their ability to generate natural speech responses directly, hindering seamless audio interactions. To address this, we introduce Step-Audio-AQAA, a fully end-to-end LALM designed for Audio Query-Audio Answer (AQAA) tasks. The model integrates a dual-codebook audio tokenizer for linguistic and semantic feature extraction, a 130-billion-parameter backbone LLM and a neural vocoder for high-fidelity speech synthesis. Our post-training approach employs interleaved token-output of text and audio to enhance semantic coherence and combines Direct Preference Optimization (DPO) with model merge to improve performance. Evaluations on the StepEval-Audio-360 benchmark demonstrate that Step-Audio-AQAA excels especially in speech control, outperforming the state-of-art LALMs in key areas. This work contributes a promising solution for end-to-end LALMs and highlights the critical role of token-based vocoder in enhancing overall performance for AQAA tasks.
Re-evaluating Open-ended Evaluation of Large Language Models
Feb 27, 2025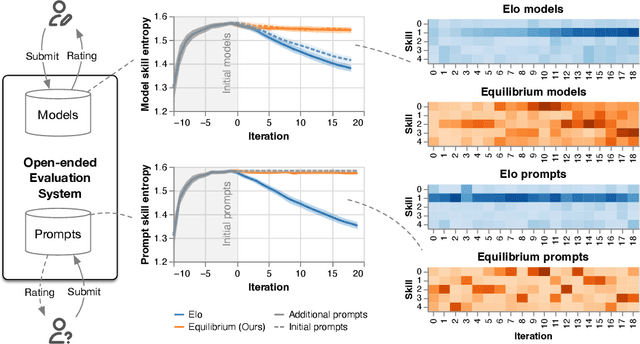
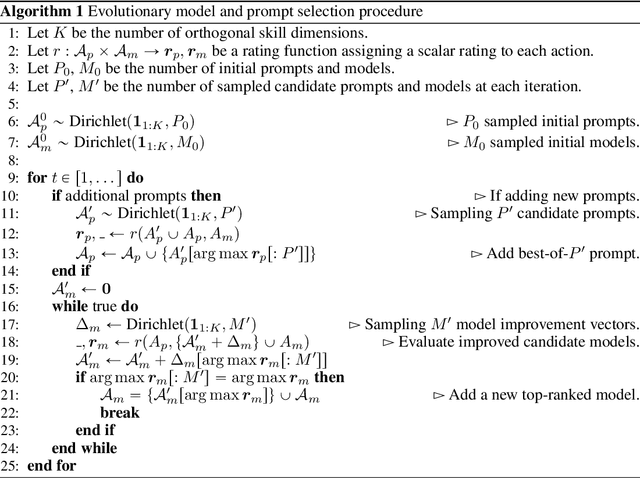
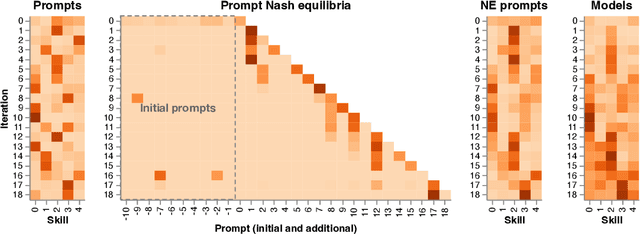
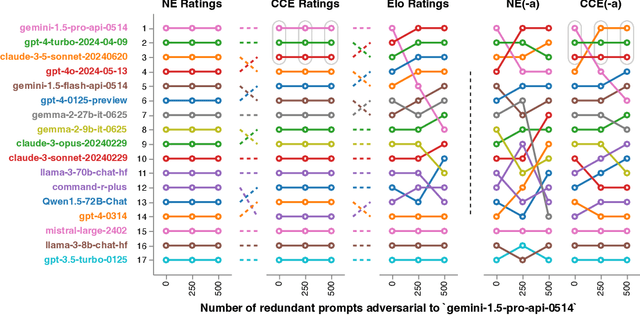
Abstract:Evaluation has traditionally focused on ranking candidates for a specific skill. Modern generalist models, such as Large Language Models (LLMs), decidedly outpace this paradigm. Open-ended evaluation systems, where candidate models are compared on user-submitted prompts, have emerged as a popular solution. Despite their many advantages, we show that the current Elo-based rating systems can be susceptible to and even reinforce biases in data, intentional or accidental, due to their sensitivity to redundancies. To address this issue, we propose evaluation as a 3-player game, and introduce novel game-theoretic solution concepts to ensure robustness to redundancy. We show that our method leads to intuitive ratings and provide insights into the competitive landscape of LLM development.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge