Dian Chen
Expert Knowledge-Guided Decision Calibration for Accurate Fine-Grained Tree Species Classification
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Accurate fine-grained tree species classification is critical for forest inventory and biodiversity monitoring. Existing methods predominantly focus on designing complex architectures to fit local data distributions. However, they often overlook the long-tailed distributions and high inter-class similarity inherent in limited data, thereby struggling to distinguish between few-shot or confusing categories. In the process of knowledge dissemination in the human world, individuals will actively seek expert assistance to transcend the limitations of local thinking. Inspired by this, we introduce an external "Domain Expert" and propose an Expert Knowledge-Guided Classification Decision Calibration Network (EKDC-Net) to overcome these challenges. Our framework addresses two core issues: expert knowledge extraction and utilization. Specifically, we first develop a Local Prior Guided Knowledge Extraction Module (LPKEM). By leveraging Class Activation Map (CAM) analysis, LPKEM guides the domain expert to focus exclusively on discriminative features essential for classification. Subsequently, to effectively integrate this knowledge, we design an Uncertainty-Guided Decision Calibration Module (UDCM). This module dynamically corrects the local model's decisions by considering both overall category uncertainty and instance-level prediction uncertainty. Furthermore, we present a large-scale classification dataset covering 102 tree species, named CU-Tree102 to address the issue of scarce diversity in current benchmarks. Experiments on three benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance. Crucially, as a lightweight plug-and-play module, EKDC-Net improves backbone accuracy by 6.42% and precision by 11.46% using only 0.08M additional learnable parameters. The dataset, code, and pre-trained models are available at https://github.com/WHU-USI3DV/TreeCLS.
AnyView: Synthesizing Any Novel View in Dynamic Scenes
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Modern generative video models excel at producing convincing, high-quality outputs, but struggle to maintain multi-view and spatiotemporal consistency in highly dynamic real-world environments. In this work, we introduce \textbf{AnyView}, a diffusion-based video generation framework for \emph{dynamic view synthesis} with minimal inductive biases or geometric assumptions. We leverage multiple data sources with various levels of supervision, including monocular (2D), multi-view static (3D) and multi-view dynamic (4D) datasets, to train a generalist spatiotemporal implicit representation capable of producing zero-shot novel videos from arbitrary camera locations and trajectories. We evaluate AnyView on standard benchmarks, showing competitive results with the current state of the art, and propose \textbf{AnyViewBench}, a challenging new benchmark tailored towards \emph{extreme} dynamic view synthesis in diverse real-world scenarios. In this more dramatic setting, we find that most baselines drastically degrade in performance, as they require significant overlap between viewpoints, while AnyView maintains the ability to produce realistic, plausible, and spatiotemporally consistent videos when prompted from \emph{any} viewpoint. Results, data, code, and models can be viewed at: https://tri-ml.github.io/AnyView/
RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
Dec 16, 2025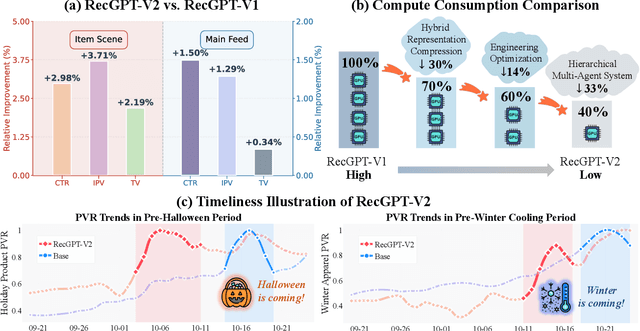
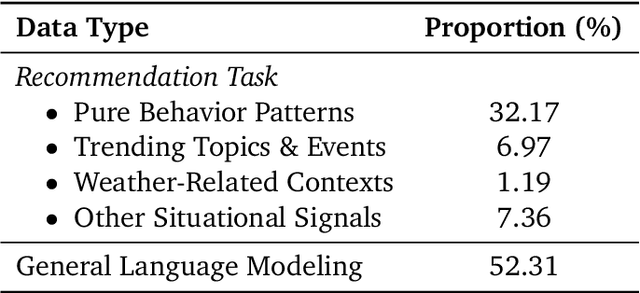
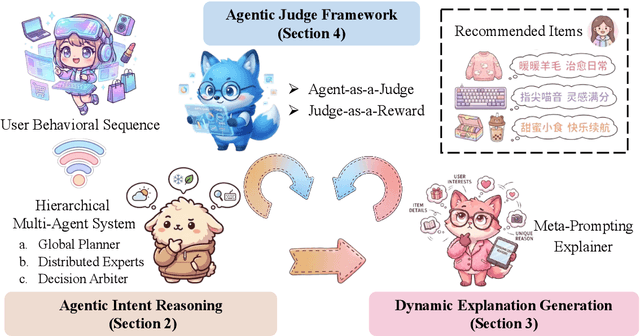
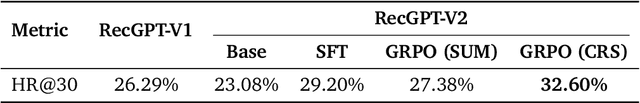
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in transforming recommender systems from implicit behavioral pattern matching to explicit intent reasoning. While RecGPT-V1 successfully pioneered this paradigm by integrating LLM-based reasoning into user interest mining and item tag prediction, it suffers from four fundamental limitations: (1) computational inefficiency and cognitive redundancy across multiple reasoning routes; (2) insufficient explanation diversity in fixed-template generation; (3) limited generalization under supervised learning paradigms; and (4) simplistic outcome-focused evaluation that fails to match human standards. To address these challenges, we present RecGPT-V2 with four key innovations. First, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System restructures intent reasoning through coordinated collaboration, eliminating cognitive duplication while enabling diverse intent coverage. Combined with Hybrid Representation Inference that compresses user-behavior contexts, our framework reduces GPU consumption by 60% and improves exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%. Second, a Meta-Prompting framework dynamically generates contextually adaptive prompts, improving explanation diversity by +7.3%. Third, constrained reinforcement learning mitigates multi-reward conflicts, achieving +24.1% improvement in tag prediction and +13.0% in explanation acceptance. Fourth, an Agent-as-a-Judge framework decomposes assessment into multi-step reasoning, improving human preference alignment. Online A/B tests on Taobao demonstrate significant improvements: +2.98% CTR, +3.71% IPV, +2.19% TV, and +11.46% NER. RecGPT-V2 establishes both the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying LLM-powered intent reasoning at scale, bridging the gap between cognitive exploration and industrial utility.
GeoPep: A geometry-aware masked language model for protein-peptide binding site prediction
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Multimodal approaches that integrate protein structure and sequence have achieved remarkable success in protein-protein interface prediction. However, extending these methods to protein-peptide interactions remains challenging due to the inherent conformational flexibility of peptides and the limited availability of structural data that hinder direct training of structure-aware models. To address these limitations, we introduce GeoPep, a novel framework for peptide binding site prediction that leverages transfer learning from ESM3, a multimodal protein foundation model. GeoPep fine-tunes ESM3's rich pre-learned representations from protein-protein binding to address the limited availability of protein-peptide binding data. The fine-tuned model is further integrated with a parameter-efficient neural network architecture capable of learning complex patterns from sparse data. Furthermore, the model is trained using distance-based loss functions that exploit 3D structural information to enhance binding site prediction. Comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that GeoPep significantly outperforms existing methods in protein-peptide binding site prediction by effectively capturing sparse and heterogeneous binding patterns.
UniLDiff: Unlocking the Power of Diffusion Priors for All-in-One Image Restoration
Jul 31, 2025



Abstract:All-in-One Image Restoration (AiOIR) has emerged as a promising yet challenging research direction. To address its core challenges, we propose a novel unified image restoration framework based on latent diffusion models (LDMs). Our approach structurally integrates low-quality visual priors into the diffusion process, unlocking the powerful generative capacity of diffusion models for diverse degradations. Specifically, we design a Degradation-Aware Feature Fusion (DAFF) module to enable adaptive handling of diverse degradation types. Furthermore, to mitigate detail loss caused by the high compression and iterative sampling of LDMs, we design a Detail-Aware Expert Module (DAEM) in the decoder to enhance texture and fine-structure recovery. Extensive experiments across multi-task and mixed degradation settings demonstrate that our method consistently achieves state-of-the-art performance, highlighting the practical potential of diffusion priors for unified image restoration. Our code will be released.
XSpecMesh: Quality-Preserving Auto-Regressive Mesh Generation Acceleration via Multi-Head Speculative Decoding
Jul 31, 2025Abstract:Current auto-regressive models can generate high-quality, topologically precise meshes; however, they necessitate thousands-or even tens of thousands-of next-token predictions during inference, resulting in substantial latency. We introduce XSpecMesh, a quality-preserving acceleration method for auto-regressive mesh generation models. XSpecMesh employs a lightweight, multi-head speculative decoding scheme to predict multiple tokens in parallel within a single forward pass, thereby accelerating inference. We further propose a verification and resampling strategy: the backbone model verifies each predicted token and resamples any tokens that do not meet the quality criteria. In addition, we propose a distillation strategy that trains the lightweight decoding heads by distilling from the backbone model, encouraging their prediction distributions to align and improving the success rate of speculative predictions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves a 1.7x speedup without sacrificing generation quality. Our code will be released.
RecGPT Technical Report
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems are among the most impactful applications of artificial intelligence, serving as critical infrastructure connecting users, merchants, and platforms. However, most current industrial systems remain heavily reliant on historical co-occurrence patterns and log-fitting objectives, i.e., optimizing for past user interactions without explicitly modeling user intent. This log-fitting approach often leads to overfitting to narrow historical preferences, failing to capture users' evolving and latent interests. As a result, it reinforces filter bubbles and long-tail phenomena, ultimately harming user experience and threatening the sustainability of the whole recommendation ecosystem. To address these challenges, we rethink the overall design paradigm of recommender systems and propose RecGPT, a next-generation framework that places user intent at the center of the recommendation pipeline. By integrating large language models (LLMs) into key stages of user interest mining, item retrieval, and explanation generation, RecGPT transforms log-fitting recommendation into an intent-centric process. To effectively align general-purpose LLMs to the above domain-specific recommendation tasks at scale, RecGPT incorporates a multi-stage training paradigm, which integrates reasoning-enhanced pre-alignment and self-training evolution, guided by a Human-LLM cooperative judge system. Currently, RecGPT has been fully deployed on the Taobao App. Online experiments demonstrate that RecGPT achieves consistent performance gains across stakeholders: users benefit from increased content diversity and satisfaction, merchants and the platform gain greater exposure and conversions. These comprehensive improvement results across all stakeholders validates that LLM-driven, intent-centric design can foster a more sustainable and mutually beneficial recommendation ecosystem.
GTR: Gaussian Splatting Tracking and Reconstruction of Unknown Objects Based on Appearance and Geometric Complexity
May 17, 2025Abstract:We present a novel method for 6-DoF object tracking and high-quality 3D reconstruction from monocular RGBD video. Existing methods, while achieving impressive results, often struggle with complex objects, particularly those exhibiting symmetry, intricate geometry or complex appearance. To bridge these gaps, we introduce an adaptive method that combines 3D Gaussian Splatting, hybrid geometry/appearance tracking, and key frame selection to achieve robust tracking and accurate reconstructions across a diverse range of objects. Additionally, we present a benchmark covering these challenging object classes, providing high-quality annotations for evaluating both tracking and reconstruction performance. Our approach demonstrates strong capabilities in recovering high-fidelity object meshes, setting a new standard for single-sensor 3D reconstruction in open-world environments.
Sustainable Smart Farm Networks: Enhancing Resilience and Efficiency with Decision Theory-Guided Deep Reinforcement Learning
May 06, 2025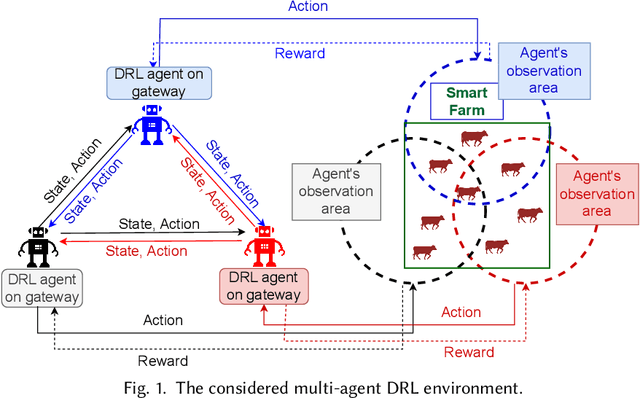
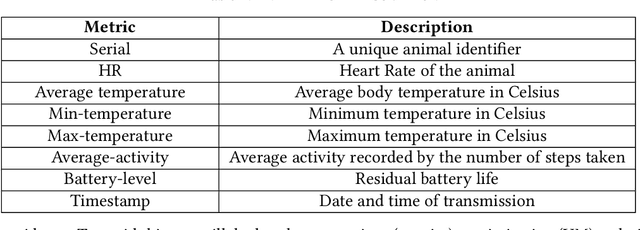
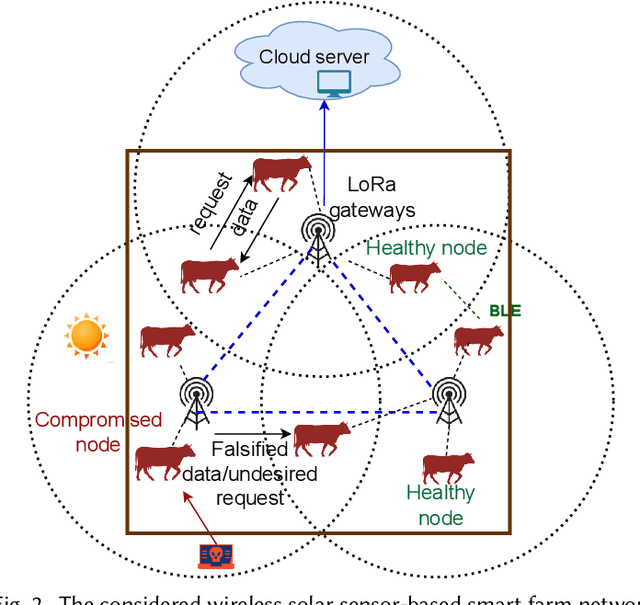
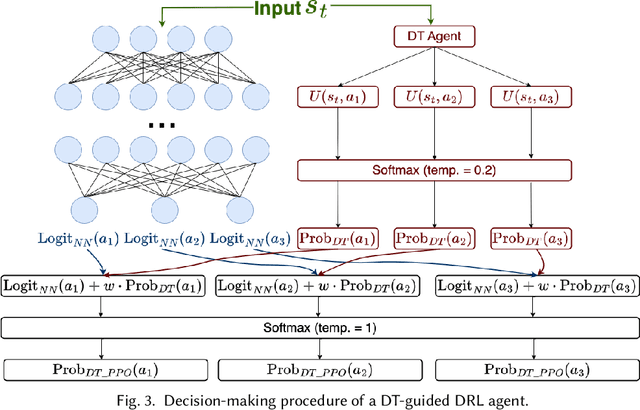
Abstract:Solar sensor-based monitoring systems have become a crucial agricultural innovation, advancing farm management and animal welfare through integrating sensor technology, Internet-of-Things, and edge and cloud computing. However, the resilience of these systems to cyber-attacks and their adaptability to dynamic and constrained energy supplies remain largely unexplored. To address these challenges, we propose a sustainable smart farm network designed to maintain high-quality animal monitoring under various cyber and adversarial threats, as well as fluctuating energy conditions. Our approach utilizes deep reinforcement learning (DRL) to devise optimal policies that maximize both monitoring effectiveness and energy efficiency. To overcome DRL's inherent challenge of slow convergence, we integrate transfer learning (TL) and decision theory (DT) to accelerate the learning process. By incorporating DT-guided strategies, we optimize monitoring quality and energy sustainability, significantly reducing training time while achieving comparable performance rewards. Our experimental results prove that DT-guided DRL outperforms TL-enhanced DRL models, improving system performance and reducing training runtime by 47.5%.
Empirical Analysis of Privacy-Fairness-Accuracy Trade-offs in Federated Learning: A Step Towards Responsible AI
Mar 20, 2025Abstract:Federated Learning (FL) enables collaborative machine learning while preserving data privacy but struggles to balance privacy preservation (PP) and fairness. Techniques like Differential Privacy (DP), Homomorphic Encryption (HE), and Secure Multi-Party Computation (SMC) protect sensitive data but introduce trade-offs. DP enhances privacy but can disproportionately impact underrepresented groups, while HE and SMC mitigate fairness concerns at the cost of computational overhead. This work explores the privacy-fairness trade-offs in FL under IID (Independent and Identically Distributed) and non-IID data distributions, benchmarking q-FedAvg, q-MAML, and Ditto on diverse datasets. Our findings highlight context-dependent trade-offs and offer guidelines for designing FL systems that uphold responsible AI principles, ensuring fairness, privacy, and equitable real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge