Greg Shakhnarovich
FastMap: Revisiting Dense and Scalable Structure from Motion
May 07, 2025Abstract:We propose FastMap, a new global structure from motion method focused on speed and simplicity. Previous methods like COLMAP and GLOMAP are able to estimate high-precision camera poses, but suffer from poor scalability when the number of matched keypoint pairs becomes large. We identify two key factors leading to this problem: poor parallelization and computationally expensive optimization steps. To overcome these issues, we design an SfM framework that relies entirely on GPU-friendly operations, making it easily parallelizable. Moreover, each optimization step runs in time linear to the number of image pairs, independent of keypoint pairs or 3D points. Through extensive experiments, we show that FastMap is one to two orders of magnitude faster than COLMAP and GLOMAP on large-scale scenes with comparable pose accuracy.
Zero-Shot Novel View and Depth Synthesis with Multi-View Geometric Diffusion
Jan 30, 2025



Abstract:Current methods for 3D scene reconstruction from sparse posed images employ intermediate 3D representations such as neural fields, voxel grids, or 3D Gaussians, to achieve multi-view consistent scene appearance and geometry. In this paper we introduce MVGD, a diffusion-based architecture capable of direct pixel-level generation of images and depth maps from novel viewpoints, given an arbitrary number of input views. Our method uses raymap conditioning to both augment visual features with spatial information from different viewpoints, as well as to guide the generation of images and depth maps from novel views. A key aspect of our approach is the multi-task generation of images and depth maps, using learnable task embeddings to guide the diffusion process towards specific modalities. We train this model on a collection of more than 60 million multi-view samples from publicly available datasets, and propose techniques to enable efficient and consistent learning in such diverse conditions. We also propose a novel strategy that enables the efficient training of larger models by incrementally fine-tuning smaller ones, with promising scaling behavior. Through extensive experiments, we report state-of-the-art results in multiple novel view synthesis benchmarks, as well as multi-view stereo and video depth estimation.
SHuBERT: Self-Supervised Sign Language Representation Learning via Multi-Stream Cluster Prediction
Nov 25, 2024
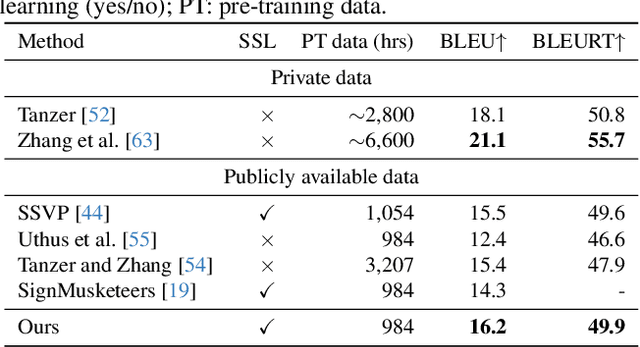

Abstract:Sign language processing has traditionally relied on task-specific models,limiting the potential for transfer learning across tasks. We introduce SHuBERT (Sign Hidden-Unit BERT), a self-supervised transformer encoder that learns strong representations from approximately 1,000 hours of American Sign Language (ASL) video content. Inspired by the success of the HuBERT speech representation model, SHuBERT adapts masked prediction for multi-stream visual sign language input, learning to predict multiple targets for corresponding to clustered hand, face, and body pose streams. SHuBERT achieves state-of-the-art performance across multiple benchmarks. On sign language translation, it outperforms prior methods trained on publicly available data on the How2Sign (+0.7 BLEU), OpenASL (+10.0 BLEU), and FLEURS-ASL (+0.3 BLEU) benchmarks. Similarly for isolated sign language recognition, SHuBERT's accuracy surpasses that of specialized models on ASL-Citizen (+5\%) and SEM-LEX (+20.6\%), while coming close to them on WLASL2000 (-3\%). Ablation studies confirm the contribution of each component of the approach.
SignMusketeers: An Efficient Multi-Stream Approach for Sign Language Translation at Scale
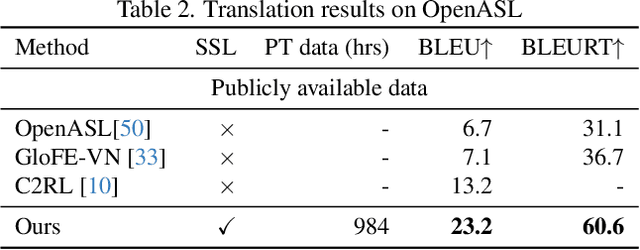
Jun 11, 2024Abstract:A persistent challenge in sign language video processing, including the task of sign language to written language translation, is how we learn representations of sign language in an effective and efficient way that can preserve the important attributes of these languages, while remaining invariant to irrelevant visual differences. Informed by the nature and linguistics of signed languages, our proposed method focuses on just the most relevant parts in a signing video: the face, hands and body posture of the signer. However, instead of using pose estimation coordinates from off-the-shelf pose tracking models, which have inconsistent performance for hands and faces, we propose to learn the complex handshapes and rich facial expressions of sign languages in a self-supervised fashion. Our approach is based on learning from individual frames (rather than video sequences) and is therefore much more efficient than prior work on sign language pre-training. Compared to a recent model that established a new state of the art in sign language translation on the How2Sign dataset, our approach yields similar translation performance, using less than 3\% of the compute.
Alpha Invariance: On Inverse Scaling Between Distance and Volume Density in Neural Radiance Fields
Apr 02, 2024
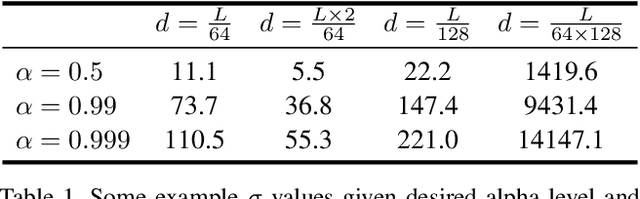
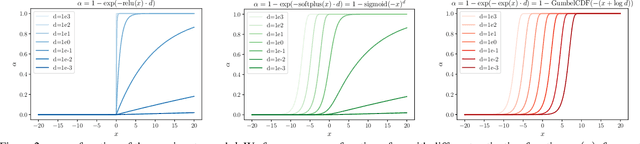
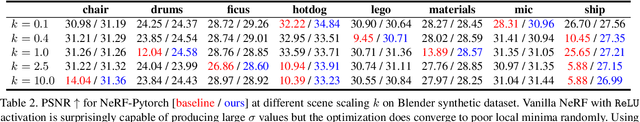
Abstract:Scale-ambiguity in 3D scene dimensions leads to magnitude-ambiguity of volumetric densities in neural radiance fields, i.e., the densities double when scene size is halved, and vice versa. We call this property alpha invariance. For NeRFs to better maintain alpha invariance, we recommend 1) parameterizing both distance and volume densities in log space, and 2) a discretization-agnostic initialization strategy to guarantee high ray transmittance. We revisit a few popular radiance field models and find that these systems use various heuristics to deal with issues arising from scene scaling. We test their behaviors and show our recipe to be more robust.
Generative Models: What do they know? Do they know things? Let's find out!
Nov 28, 2023Abstract:Generative models have been shown to be capable of synthesizing highly detailed and realistic images. It is natural to suspect that they implicitly learn to model some image intrinsics such as surface normals, depth, or shadows. In this paper, we present compelling evidence that generative models indeed internally produce high-quality scene intrinsic maps. We introduce Intrinsic LoRA (I LoRA), a universal, plug-and-play approach that transforms any generative model into a scene intrinsic predictor, capable of extracting intrinsic scene maps directly from the original generator network without needing additional decoders or fully fine-tuning the original network. Our method employs a Low-Rank Adaptation (LoRA) of key feature maps, with newly learned parameters that make up less than 0.6% of the total parameters in the generative model. Optimized with a small set of labeled images, our model-agnostic approach adapts to various generative architectures, including Diffusion models, GANs, and Autoregressive models. We show that the scene intrinsic maps produced by our method compare well with, and in some cases surpass those generated by leading supervised techniques.
Instant3D: Fast Text-to-3D with Sparse-View Generation and Large Reconstruction Model
Nov 23, 2023

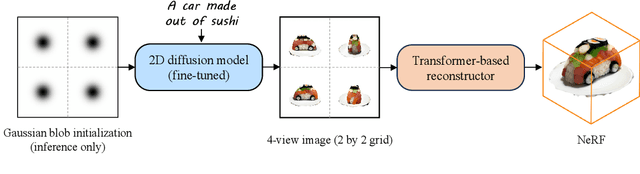
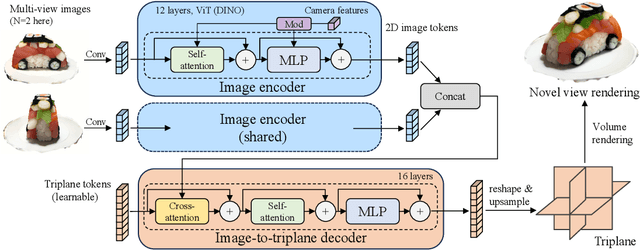
Abstract:Text-to-3D with diffusion models has achieved remarkable progress in recent years. However, existing methods either rely on score distillation-based optimization which suffer from slow inference, low diversity and Janus problems, or are feed-forward methods that generate low-quality results due to the scarcity of 3D training data. In this paper, we propose Instant3D, a novel method that generates high-quality and diverse 3D assets from text prompts in a feed-forward manner. We adopt a two-stage paradigm, which first generates a sparse set of four structured and consistent views from text in one shot with a fine-tuned 2D text-to-image diffusion model, and then directly regresses the NeRF from the generated images with a novel transformer-based sparse-view reconstructor. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our method can generate diverse 3D assets of high visual quality within 20 seconds, which is two orders of magnitude faster than previous optimization-based methods that can take 1 to 10 hours. Our project webpage: https://jiahao.ai/instant3d/.
HyperFields: Towards Zero-Shot Generation of NeRFs from Text
Oct 27, 2023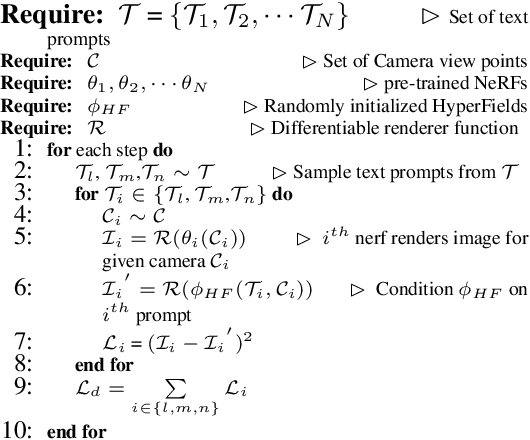
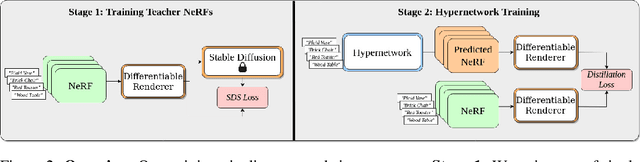
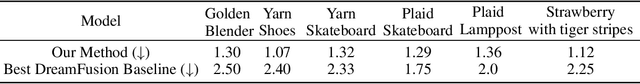
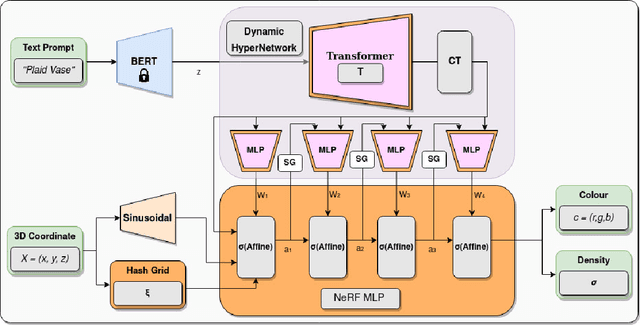
Abstract:We introduce HyperFields, a method for generating text-conditioned Neural Radiance Fields (NeRFs) with a single forward pass and (optionally) some fine-tuning. Key to our approach are: (i) a dynamic hypernetwork, which learns a smooth mapping from text token embeddings to the space of NeRFs; (ii) NeRF distillation training, which distills scenes encoded in individual NeRFs into one dynamic hypernetwork. These techniques enable a single network to fit over a hundred unique scenes. We further demonstrate that HyperFields learns a more general map between text and NeRFs, and consequently is capable of predicting novel in-distribution and out-of-distribution scenes -- either zero-shot or with a few finetuning steps. Finetuning HyperFields benefits from accelerated convergence thanks to the learned general map, and is capable of synthesizing novel scenes 5 to 10 times faster than existing neural optimization-based methods. Our ablation experiments show that both the dynamic architecture and NeRF distillation are critical to the expressivity of HyperFields.
LoopDraw: a Loop-Based Autoregressive Model for Shape Synthesis and Editing
Dec 09, 2022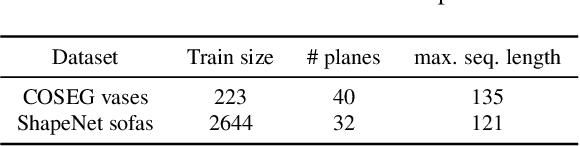
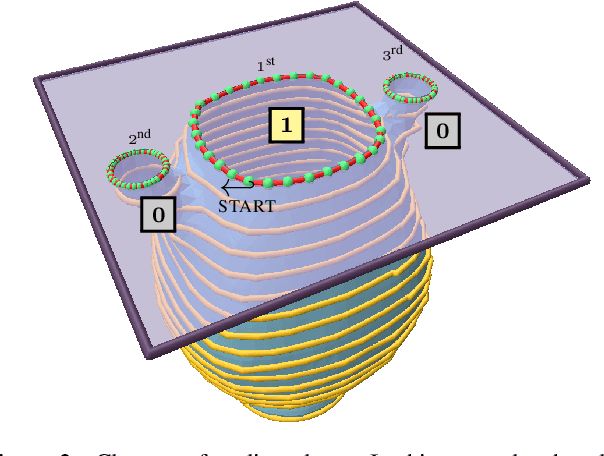
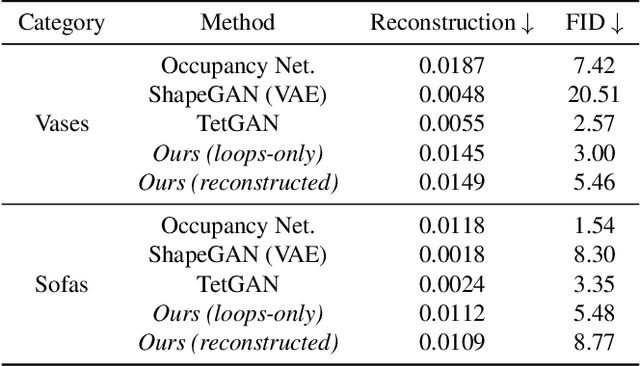
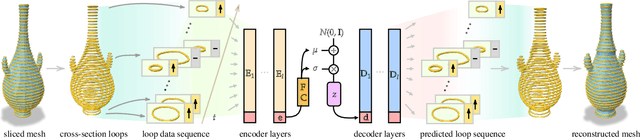
Abstract:There is no settled universal 3D representation for geometry with many alternatives such as point clouds, meshes, implicit functions, and voxels to name a few. In this work, we present a new, compelling alternative for representing shapes using a sequence of cross-sectional closed loops. The loops across all planes form an organizational hierarchy which we leverage for autoregressive shape synthesis and editing. Loops are a non-local description of the underlying shape, as simple loop manipulations (such as shifts) result in significant structural changes to the geometry. This is in contrast to manipulating local primitives such as points in a point cloud or a triangle in a triangle mesh. We further demonstrate that loops are intuitive and natural primitive for analyzing and editing shapes, both computationally and for users.
Score Jacobian Chaining: Lifting Pretrained 2D Diffusion Models for 3D Generation
Dec 01, 2022
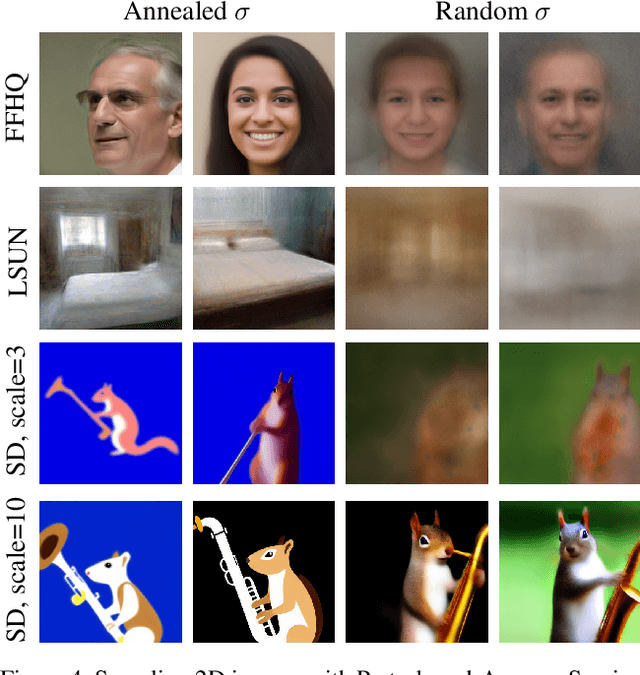
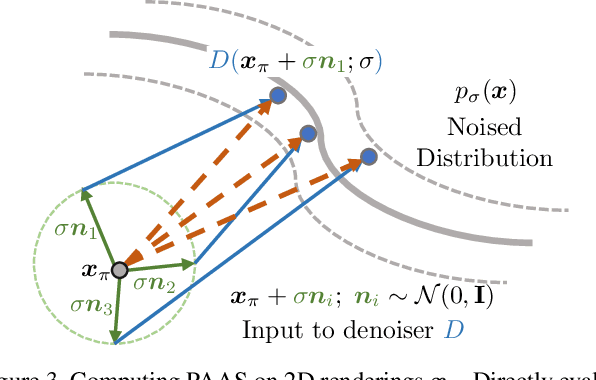

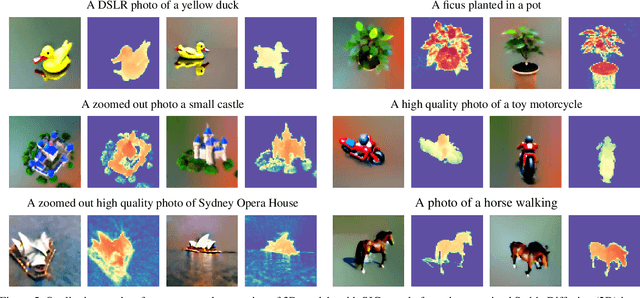
Abstract:A diffusion model learns to predict a vector field of gradients. We propose to apply chain rule on the learned gradients, and back-propagate the score of a diffusion model through the Jacobian of a differentiable renderer, which we instantiate to be a voxel radiance field. This setup aggregates 2D scores at multiple camera viewpoints into a 3D score, and repurposes a pretrained 2D model for 3D data generation. We identify a technical challenge of distribution mismatch that arises in this application, and propose a novel estimation mechanism to resolve it. We run our algorithm on several off-the-shelf diffusion image generative models, including the recently released Stable Diffusion trained on the large-scale LAION dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge