Muyan Weng
Bursting Filter Bubble: Enhancing Serendipity Recommendations with Aligned Large Language Models
Feb 19, 2025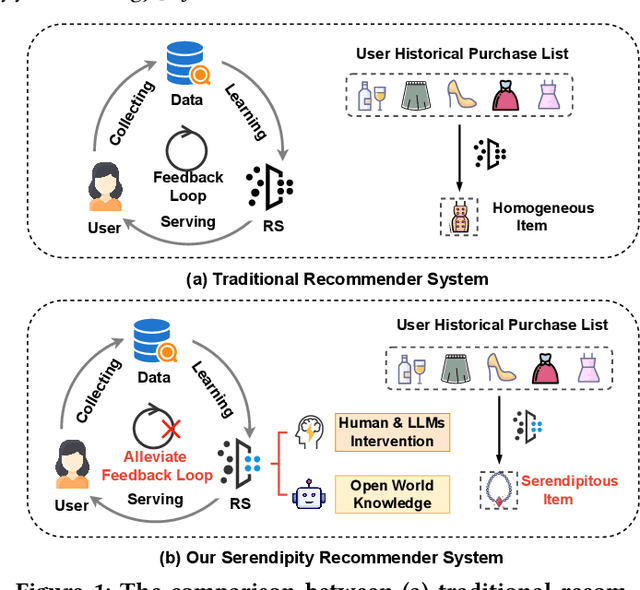
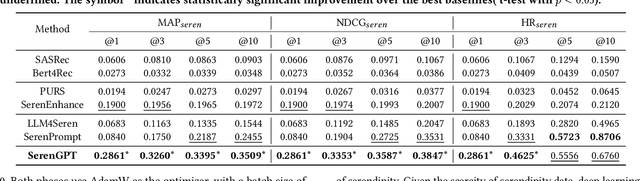
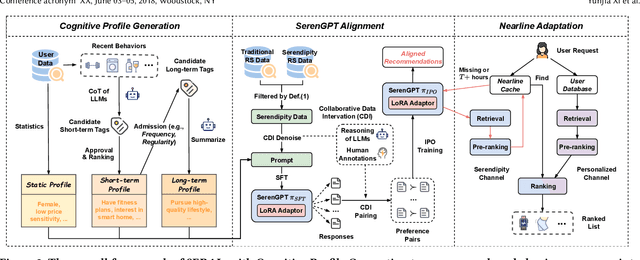
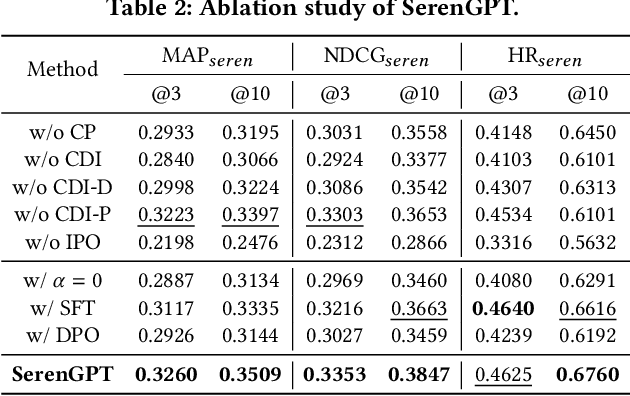
Abstract:Recommender systems (RSs) often suffer from the feedback loop phenomenon, e.g., RSs are trained on data biased by their recommendations. This leads to the filter bubble effect that reinforces homogeneous content and reduces user satisfaction. To this end, serendipity recommendations, which offer unexpected yet relevant items, are proposed. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown potential in serendipity prediction due to their extensive world knowledge and reasoning capabilities. However, they still face challenges in aligning serendipity judgments with human assessments, handling long user behavior sequences, and meeting the latency requirements of industrial RSs. To address these issues, we propose SERAL (Serendipity Recommendations with Aligned Large Language Models), a framework comprising three stages: (1) Cognition Profile Generation to compress user behavior into multi-level profiles; (2) SerenGPT Alignment to align serendipity judgments with human preferences using enriched training data; and (3) Nearline Adaptation to integrate SerenGPT into industrial RSs pipelines efficiently. Online experiments demonstrate that SERAL improves exposure ratio (PVR), clicks, and transactions of serendipitous items by 5.7%, 29.56%, and 27.6%, enhancing user experience without much impact on overall revenue. Now, it has been fully deployed in the "Guess What You Like" of the Taobao App homepage.
Beyond Positive History: Re-ranking with List-level Hybrid Feedback
Oct 28, 2024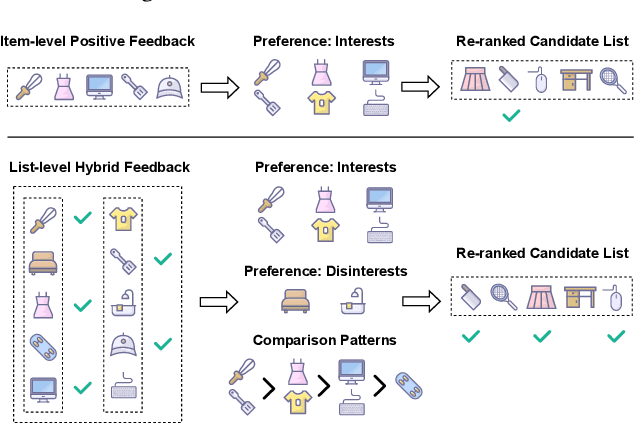
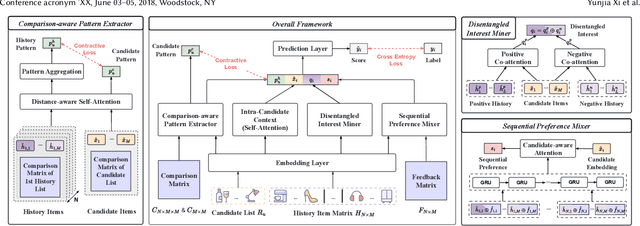
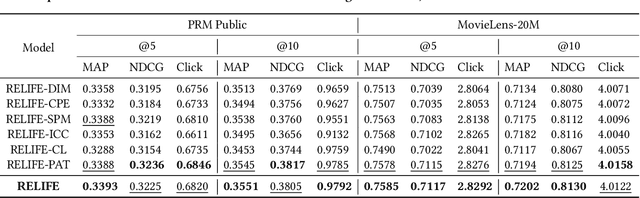
Abstract:As the last stage of recommender systems, re-ranking generates a re-ordered list that aligns with the user's preference. However, previous works generally focus on item-level positive feedback as history (e.g., only clicked items) and ignore that users provide positive or negative feedback on items in the entire list. This list-level hybrid feedback can reveal users' holistic preferences and reflect users' comparison behavior patterns manifesting within a list. Such patterns could predict user behaviors on candidate lists, thus aiding better re-ranking. Despite appealing benefits, extracting and integrating preferences and behavior patterns from list-level hybrid feedback into re-ranking multiple items remains challenging. To this end, we propose Re-ranking with List-level Hybrid Feedback (dubbed RELIFE). It captures user's preferences and behavior patterns with three modules: a Disentangled Interest Miner to disentangle the user's preferences into interests and disinterests, a Sequential Preference Mixer to learn users' entangled preferences considering the context of feedback, and a Comparison-aware Pattern Extractor to capture user's behavior patterns within each list. Moreover, for better integration of patterns, contrastive learning is adopted to align the behavior patterns of candidate and historical lists. Extensive experiments show that RELIFE significantly outperforms SOTA re-ranking baselines.
Efficient and Deployable Knowledge Infusion for Open-World Recommendations via Large Language Models
Aug 20, 2024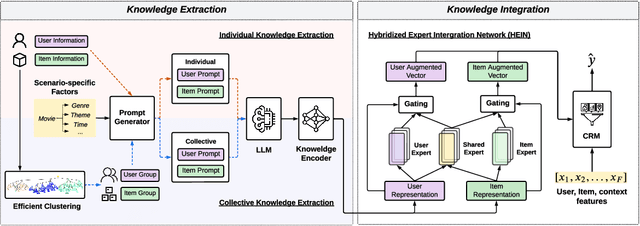
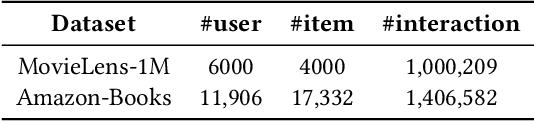
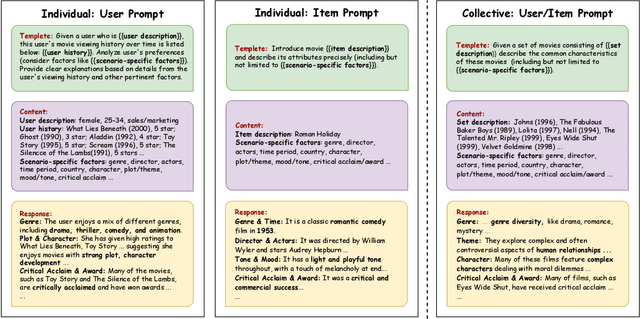
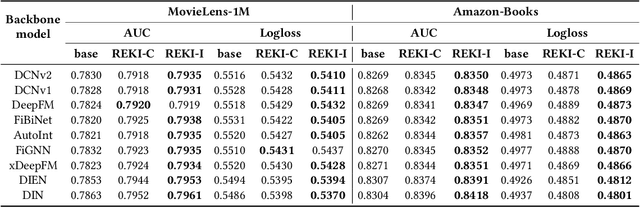
Abstract:Recommender systems (RSs) play a pervasive role in today's online services, yet their closed-loop nature constrains their access to open-world knowledge. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in bridging this gap. However, previous attempts to directly implement LLMs as recommenders fall short in meeting the requirements of industrial RSs, particularly in terms of online inference latency and offline resource efficiency. Thus, we propose REKI to acquire two types of external knowledge about users and items from LLMs. Specifically, we introduce factorization prompting to elicit accurate knowledge reasoning on user preferences and items. We develop individual knowledge extraction and collective knowledge extraction tailored for different scales of scenarios, effectively reducing offline resource consumption. Subsequently, generated knowledge undergoes efficient transformation and condensation into augmented vectors through a hybridized expert-integrated network, ensuring compatibility. The obtained vectors can then be used to enhance any conventional recommendation model. We also ensure efficient inference by preprocessing and prestoring the knowledge from LLMs. Experiments demonstrate that REKI outperforms state-of-the-art baselines and is compatible with lots of recommendation algorithms and tasks. Now, REKI has been deployed to Huawei's news and music recommendation platforms and gained a 7% and 1.99% improvement during the online A/B test.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge