Chao Yi
RecGPT-V2 Technical Report
Dec 16, 2025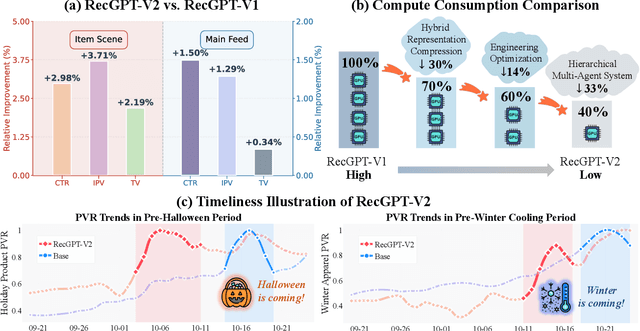
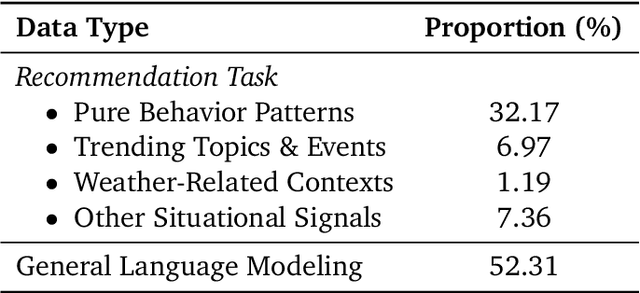
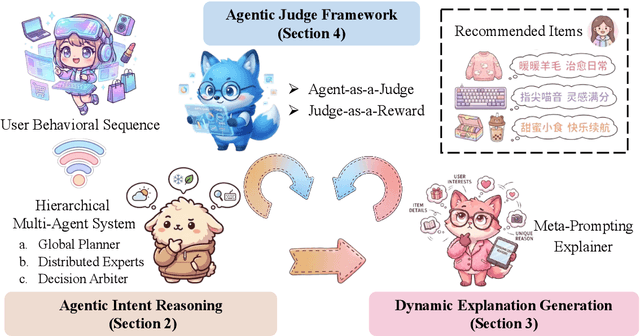
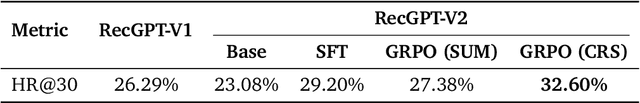
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable potential in transforming recommender systems from implicit behavioral pattern matching to explicit intent reasoning. While RecGPT-V1 successfully pioneered this paradigm by integrating LLM-based reasoning into user interest mining and item tag prediction, it suffers from four fundamental limitations: (1) computational inefficiency and cognitive redundancy across multiple reasoning routes; (2) insufficient explanation diversity in fixed-template generation; (3) limited generalization under supervised learning paradigms; and (4) simplistic outcome-focused evaluation that fails to match human standards. To address these challenges, we present RecGPT-V2 with four key innovations. First, a Hierarchical Multi-Agent System restructures intent reasoning through coordinated collaboration, eliminating cognitive duplication while enabling diverse intent coverage. Combined with Hybrid Representation Inference that compresses user-behavior contexts, our framework reduces GPU consumption by 60% and improves exclusive recall from 9.39% to 10.99%. Second, a Meta-Prompting framework dynamically generates contextually adaptive prompts, improving explanation diversity by +7.3%. Third, constrained reinforcement learning mitigates multi-reward conflicts, achieving +24.1% improvement in tag prediction and +13.0% in explanation acceptance. Fourth, an Agent-as-a-Judge framework decomposes assessment into multi-step reasoning, improving human preference alignment. Online A/B tests on Taobao demonstrate significant improvements: +2.98% CTR, +3.71% IPV, +2.19% TV, and +11.46% NER. RecGPT-V2 establishes both the technical feasibility and commercial viability of deploying LLM-powered intent reasoning at scale, bridging the gap between cognitive exploration and industrial utility.
MUSE: A Simple Yet Effective Multimodal Search-Based Framework for Lifelong User Interest Modeling
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Lifelong user interest modeling is crucial for industrial recommender systems, yet existing approaches rely predominantly on ID-based features, suffering from poor generalization on long-tail items and limited semantic expressiveness. While recent work explores multimodal representations for behavior retrieval in the General Search Unit (GSU), they often neglect multimodal integration in the fine-grained modeling stage -- the Exact Search Unit (ESU). In this work, we present a systematic analysis of how to effectively leverage multimodal signals across both stages of the two-stage lifelong modeling framework. Our key insight is that simplicity suffices in the GSU: lightweight cosine similarity with high-quality multimodal embeddings outperforms complex retrieval mechanisms. In contrast, the ESU demands richer multimodal sequence modeling and effective ID-multimodal fusion to unlock its full potential. Guided by these principles, we propose MUSE, a simple yet effective multimodal search-based framework. MUSE has been deployed in Taobao display advertising system, enabling 100K-length user behavior sequence modeling and delivering significant gains in top-line metrics with negligible online latency overhead. To foster community research, we share industrial deployment practices and open-source the first large-scale dataset featuring ultra-long behavior sequences paired with high-quality multimodal embeddings. Our code and data is available at https://taobao-mm.github.io.
RecGPT Technical Report
Jul 30, 2025



Abstract:Recommender systems are among the most impactful applications of artificial intelligence, serving as critical infrastructure connecting users, merchants, and platforms. However, most current industrial systems remain heavily reliant on historical co-occurrence patterns and log-fitting objectives, i.e., optimizing for past user interactions without explicitly modeling user intent. This log-fitting approach often leads to overfitting to narrow historical preferences, failing to capture users' evolving and latent interests. As a result, it reinforces filter bubbles and long-tail phenomena, ultimately harming user experience and threatening the sustainability of the whole recommendation ecosystem. To address these challenges, we rethink the overall design paradigm of recommender systems and propose RecGPT, a next-generation framework that places user intent at the center of the recommendation pipeline. By integrating large language models (LLMs) into key stages of user interest mining, item retrieval, and explanation generation, RecGPT transforms log-fitting recommendation into an intent-centric process. To effectively align general-purpose LLMs to the above domain-specific recommendation tasks at scale, RecGPT incorporates a multi-stage training paradigm, which integrates reasoning-enhanced pre-alignment and self-training evolution, guided by a Human-LLM cooperative judge system. Currently, RecGPT has been fully deployed on the Taobao App. Online experiments demonstrate that RecGPT achieves consistent performance gains across stakeholders: users benefit from increased content diversity and satisfaction, merchants and the platform gain greater exposure and conversions. These comprehensive improvement results across all stakeholders validates that LLM-driven, intent-centric design can foster a more sustainable and mutually beneficial recommendation ecosystem.
Bursting Filter Bubble: Enhancing Serendipity Recommendations with Aligned Large Language Models
Feb 19, 2025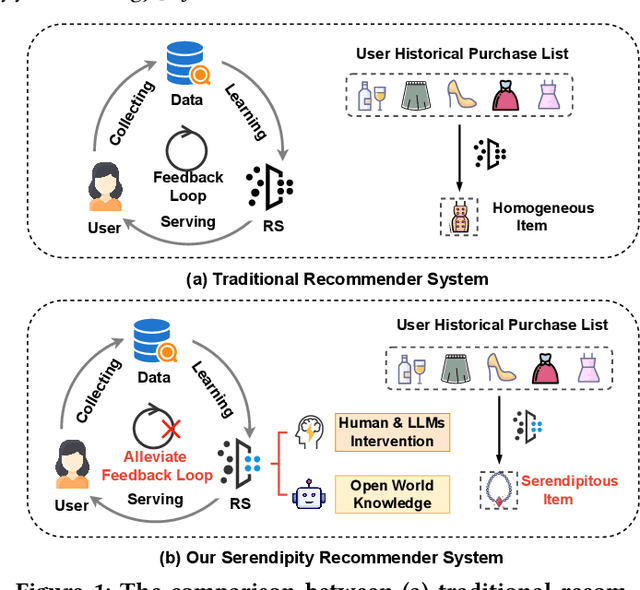
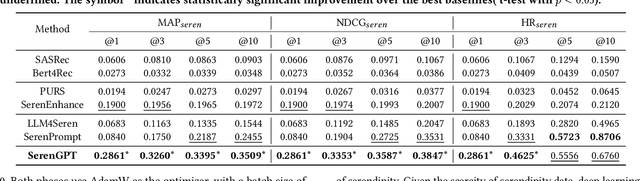
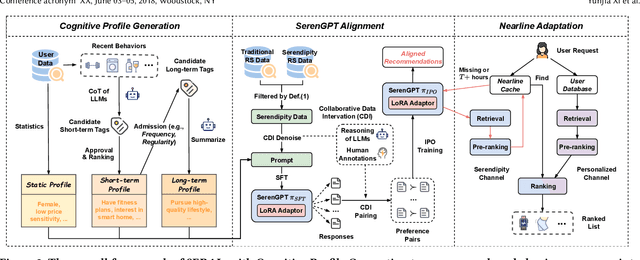
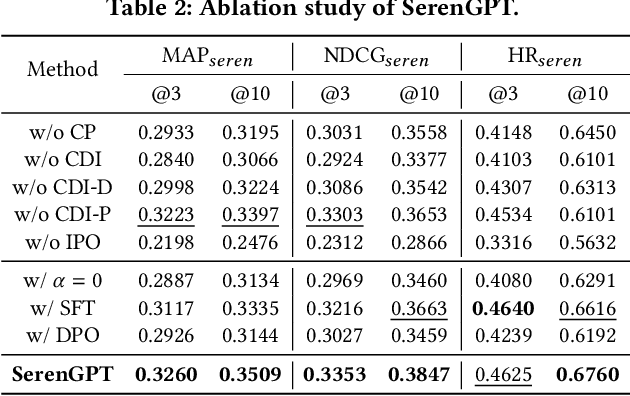
Abstract:Recommender systems (RSs) often suffer from the feedback loop phenomenon, e.g., RSs are trained on data biased by their recommendations. This leads to the filter bubble effect that reinforces homogeneous content and reduces user satisfaction. To this end, serendipity recommendations, which offer unexpected yet relevant items, are proposed. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have shown potential in serendipity prediction due to their extensive world knowledge and reasoning capabilities. However, they still face challenges in aligning serendipity judgments with human assessments, handling long user behavior sequences, and meeting the latency requirements of industrial RSs. To address these issues, we propose SERAL (Serendipity Recommendations with Aligned Large Language Models), a framework comprising three stages: (1) Cognition Profile Generation to compress user behavior into multi-level profiles; (2) SerenGPT Alignment to align serendipity judgments with human preferences using enriched training data; and (3) Nearline Adaptation to integrate SerenGPT into industrial RSs pipelines efficiently. Online experiments demonstrate that SERAL improves exposure ratio (PVR), clicks, and transactions of serendipitous items by 5.7%, 29.56%, and 27.6%, enhancing user experience without much impact on overall revenue. Now, it has been fully deployed in the "Guess What You Like" of the Taobao App homepage.
Parrot: Multilingual Visual Instruction Tuning
Jun 04, 2024

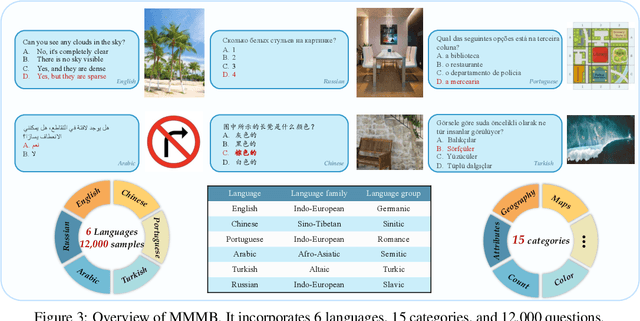
Abstract:The rapid development of Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) like GPT-4V has marked a significant step towards artificial general intelligence. Existing methods mainly focus on aligning vision encoders with LLMs through supervised fine-tuning (SFT) to endow LLMs with multimodal abilities, making MLLMs' inherent ability to react to multiple languages progressively deteriorate as the training process evolves. We empirically find that the imbalanced SFT datasets, primarily composed of English-centric image-text pairs, lead to significantly reduced performance in non-English languages. This is due to the failure of aligning the vision encoder and LLM with multilingual tokens during the SFT process. In this paper, we introduce Parrot, a novel method that utilizes textual guidance to drive visual token alignment at the language level. Parrot makes the visual tokens condition on diverse language inputs and uses Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) to promote the alignment of multilingual tokens. Specifically, to enhance non-English visual tokens alignment, we compute the cross-attention using the initial visual features and textual embeddings, the result of which is then fed into the MoE router to select the most relevant experts. The selected experts subsequently convert the initial visual tokens into language-specific visual tokens. Moreover, considering the current lack of benchmarks for evaluating multilingual capabilities within the field, we collect and make available a Massive Multilingual Multimodal Benchmark which includes 6 languages, 15 categories, and 12,000 questions, named as MMMB. Our method not only demonstrates state-of-the-art performance on multilingual MMBench and MMMB, but also excels across a broad range of multimodal tasks. Both the source code and the training dataset of Parrot will be made publicly available.
Leveraging Cross-Modal Neighbor Representation for Improved CLIP Classification
Apr 27, 2024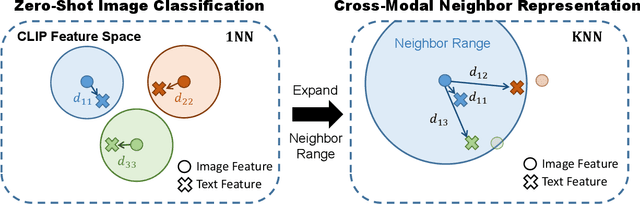
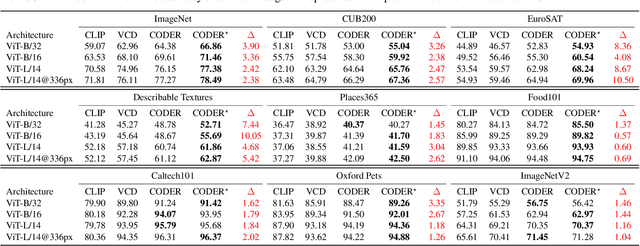
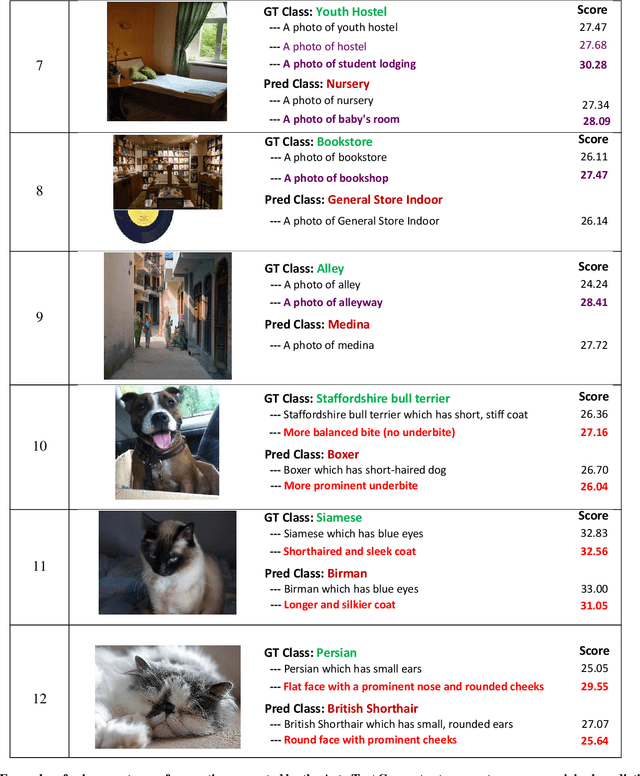
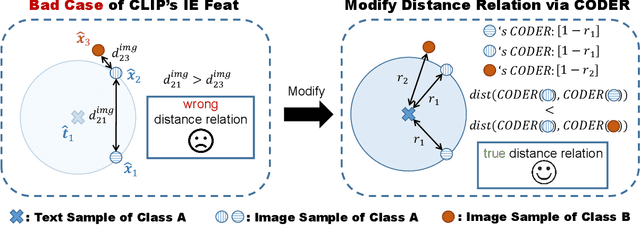
Abstract:CLIP showcases exceptional cross-modal matching capabilities due to its training on image-text contrastive learning tasks. However, without specific optimization for unimodal scenarios, its performance in single-modality feature extraction might be suboptimal. Despite this, some studies have directly used CLIP's image encoder for tasks like few-shot classification, introducing a misalignment between its pre-training objectives and feature extraction methods. This inconsistency can diminish the quality of the image's feature representation, adversely affecting CLIP's effectiveness in target tasks. In this paper, we view text features as precise neighbors of image features in CLIP's space and present a novel CrOss-moDal nEighbor Representation(CODER) based on the distance structure between images and their neighbor texts. This feature extraction method aligns better with CLIP's pre-training objectives, thereby fully leveraging CLIP's robust cross-modal capabilities. The key to construct a high-quality CODER lies in how to create a vast amount of high-quality and diverse texts to match with images. We introduce the Auto Text Generator(ATG) to automatically generate the required texts in a data-free and training-free manner. We apply CODER to CLIP's zero-shot and few-shot image classification tasks. Experiment results across various datasets and models confirm CODER's effectiveness. Code is available at:https://github.com/YCaigogogo/CVPR24-CODER.
Bridge the Modality and Capacity Gaps in Vision-Language Model Selection
Mar 20, 2024

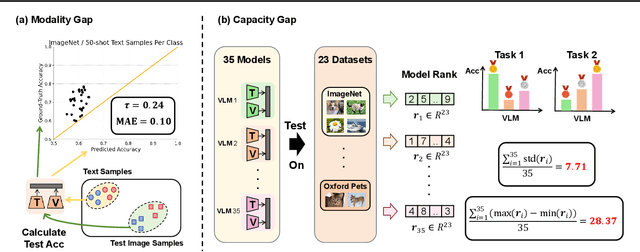

Abstract:Vision Language Models (VLMs) excel in zero-shot image classification by pairing images with textual category names. The expanding variety of Pre-Trained VLMs enhances the likelihood of identifying a suitable VLM for specific tasks. Thus, a promising zero-shot image classification strategy is selecting the most appropriate Pre-Trained VLM from the VLM Zoo, relying solely on the text data of the target dataset without access to the dataset's images. In this paper, we analyze two inherent challenges in assessing the ability of a VLM in this Language-Only VLM selection: the "Modality Gap" -- the disparity in VLM's embeddings across two different modalities, making text a less reliable substitute for images; and the "Capability Gap" -- the discrepancy between the VLM's overall ranking and its ranking for target dataset, hindering direct prediction of a model's dataset-specific performance from its general performance. We propose VLM Selection With gAp Bridging (SWAB) to mitigate the negative impact of these two gaps. SWAB first adopts optimal transport to capture the relevance between open-source datasets and target dataset with a transportation matrix. It then uses this matrix to transfer useful statistics of VLMs from open-source datasets to the target dataset for bridging those two gaps and enhancing the VLM's capacity estimation for VLM selection. Experiments across various VLMs and image classification datasets validate SWAB's effectiveness.
ZhiJian: A Unifying and Rapidly Deployable Toolbox for Pre-trained Model Reuse
Aug 17, 2023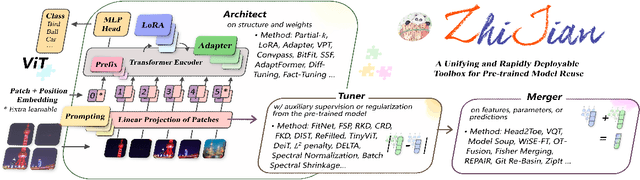
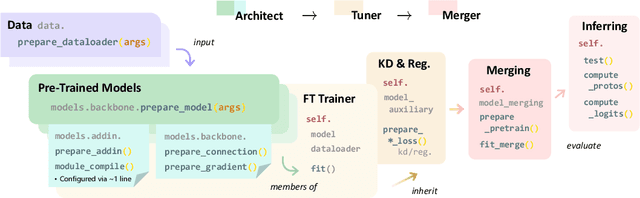
Abstract:The rapid expansion of foundation pre-trained models and their fine-tuned counterparts has significantly contributed to the advancement of machine learning. Leveraging pre-trained models to extract knowledge and expedite learning in real-world tasks, known as "Model Reuse", has become crucial in various applications. Previous research focuses on reusing models within a certain aspect, including reusing model weights, structures, and hypothesis spaces. This paper introduces ZhiJian, a comprehensive and user-friendly toolbox for model reuse, utilizing the PyTorch backend. ZhiJian presents a novel paradigm that unifies diverse perspectives on model reuse, encompassing target architecture construction with PTM, tuning target model with PTM, and PTM-based inference. This empowers deep learning practitioners to explore downstream tasks and identify the complementary advantages among different methods. ZhiJian is readily accessible at https://github.com/zhangyikaii/lamda-zhijian facilitating seamless utilization of pre-trained models and streamlining the model reuse process for researchers and developers.
Finding Similar Exercises in Retrieval Manner
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:When students make a mistake in an exercise, they can consolidate it by ``similar exercises'' which have the same concepts, purposes and methods. Commonly, for a certain subject and study stage, the size of the exercise bank is in the range of millions to even tens of millions, how to find similar exercises for a given exercise becomes a crucial technical problem. Generally, we can assign a variety of explicit labels to the exercise, and then query through the labels, but the label annotation is time-consuming, laborious and costly, with limited precision and granularity, so it is not feasible. In practice, we define ``similar exercises'' as a retrieval process of finding a set of similar exercises based on recall, ranking and re-rank procedures, called the \textbf{FSE} problem (Finding similar exercises). Furthermore, comprehensive representation of the semantic information of exercises was obtained through representation learning. In addition to the reasonable architecture, we also explore what kind of tasks are more conducive to the learning of exercise semantic information from pre-training and supervised learning. It is difficult to annotate similar exercises and the annotation consistency among experts is low. Therefore this paper also provides solutions to solve the problem of low-quality annotated data. Compared with other methods, this paper has obvious advantages in both architecture rationality and algorithm precision, which now serves the daily teaching of hundreds of schools.
* 37th Conference on AAAI 2023 Artificial Intelligence for Education(AI4Edu)
Underwater Image Enhancement based on Deep Learning and Image Formation Model
Jan 07, 2021



Abstract:Underwater robots play an important role in oceanic geological exploration, resource exploitation, ecological research, and other fields. However, the visual perception of underwater robots is affected by various environmental factors. The main challenge now is that images captured by underwater robots are color-distorted. The hue of underwater images tends to be close to green and blue. In addition, the contrast is low and the details are fuzzy. In this paper, a new underwater image enhancement algorithm based on deep learning and image formation model is proposed. Experimental results show that the advantages of the proposed method are that it eliminates the influence of underwater environmental factors, enriches the color, enhances details, achieves higher scores in PSNR and SSIM metrics, and helps feature key-point point matching get better results. Another significant advantage is that its computation speed is much faster than other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge