Zhao Xu
Text is All You Need for Vision-Language Model Jailbreaking
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) are increasingly equipped with robust safety safeguards to prevent responses to harmful or disallowed prompts. However, these defenses often focus on analyzing explicit textual inputs or relevant visual scenes. In this work, we introduce Text-DJ, a novel jailbreak attack that bypasses these safeguards by exploiting the model's Optical Character Recognition (OCR) capability. Our methodology consists of three stages. First, we decompose a single harmful query into multiple and semantically related but more benign sub-queries. Second, we pick a set of distraction queries that are maximally irrelevant to the harmful query. Third, we present all decomposed sub-queries and distraction queries to the LVLM simultaneously as a grid of images, with the position of the sub-queries being middle within the grid. We demonstrate that this method successfully circumvents the safety alignment of state-of-the-art LVLMs. We argue this attack succeeds by (1) converting text-based prompts into images, bypassing standard text-based filters, and (2) inducing distractions, where the model's safety protocols fail to link the scattered sub-queries within a high number of irrelevant queries. Overall, our findings expose a critical vulnerability in LVLMs' OCR capabilities that are not robust to dispersed, multi-image adversarial inputs, highlighting the need for defenses for fragmented multimodal inputs.
Triplets Better Than Pairs: Towards Stable and Effective Self-Play Fine-Tuning for LLMs
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Recently, self-play fine-tuning (SPIN) has been proposed to adapt large language models to downstream applications with scarce expert-annotated data, by iteratively generating synthetic responses from the model itself. However, SPIN is designed to optimize the current reward advantages of annotated responses over synthetic responses at hand, which may gradually vanish during iterations, leading to unstable optimization. Moreover, the utilization of reference policy induces a misalignment issue between the reward formulation for training and the metric for generation. To address these limitations, we propose a novel Triplet-based Self-Play fIne-tuNing (T-SPIN) method that integrates two key designs. First, beyond current advantages, T-SPIN additionally incorporates historical advantages between iteratively generated responses and proto-synthetic responses produced by the initial policy. Even if the current advantages diminish, historical advantages remain effective, stabilizing the overall optimization. Second, T-SPIN introduces the entropy constraint into the self-play framework, which is theoretically justified to support reference-free fine-tuning, eliminating the training-generation discrepancy. Empirical results on various tasks demonstrate not only the superior performance of T-SPIN over SPIN, but also its stable evolution during iterations. Remarkably, compared to supervised fine-tuning, T-SPIN achieves comparable or even better performance with only 25% samples, highlighting its effectiveness when faced with scarce annotated data.
Deep But Reliable: Advancing Multi-turn Reasoning for Thinking with Images
Dec 19, 2025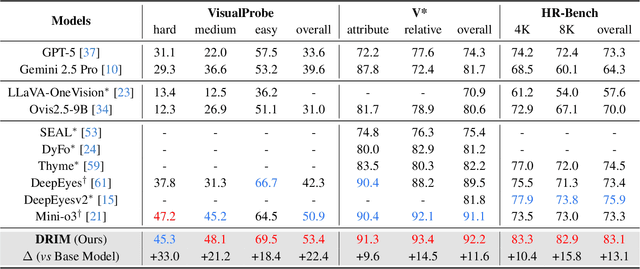
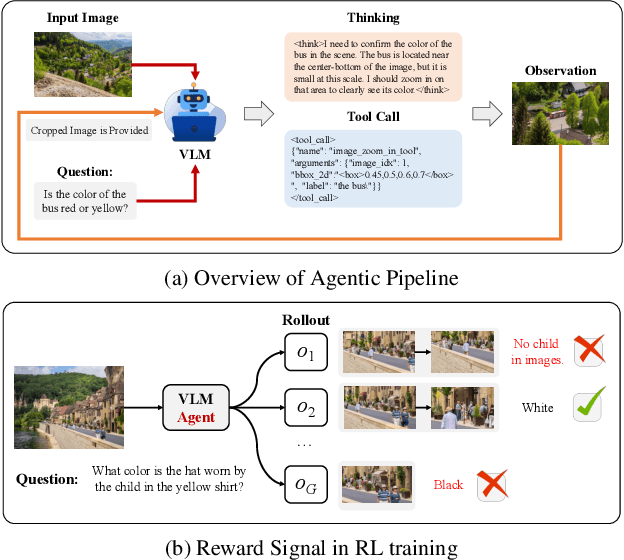
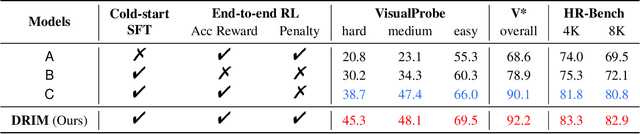
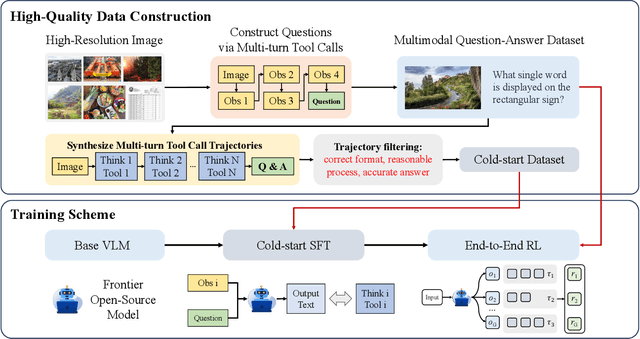
Abstract:Recent advances in large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have exhibited strong reasoning capabilities on complex visual tasks by thinking with images in their Chain-of-Thought (CoT), which is achieved by actively invoking tools to analyze visual inputs rather than merely perceiving them. However, existing models often struggle to reflect on and correct themselves when attempting incorrect reasoning trajectories. To address this limitation, we propose DRIM, a model that enables deep but reliable multi-turn reasoning when thinking with images in its multimodal CoT. Our pipeline comprises three stages: data construction, cold-start SFT and RL. Based on a high-resolution image dataset, we construct high-difficulty and verifiable visual question-answer pairs, where solving each task requires multi-turn tool calls to reach the correct answer. In the SFT stage, we collect tool trajectories as cold-start data, guiding a multi-turn reasoning pattern. In the RL stage, we introduce redundancy-penalized policy optimization, which incentivizes the model to develop a self-reflective reasoning pattern. The basic idea is to impose judgment on reasoning trajectories and penalize those that produce incorrect answers without sufficient multi-scale exploration. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DRIM achieves superior performance on visual understanding benchmarks.
Omni-View: Unlocking How Generation Facilitates Understanding in Unified 3D Model based on Multiview images
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:This paper presents Omni-View, which extends the unified multimodal understanding and generation to 3D scenes based on multiview images, exploring the principle that "generation facilitates understanding". Consisting of understanding model, texture module, and geometry module, Omni-View jointly models scene understanding, novel view synthesis, and geometry estimation, enabling synergistic interaction between 3D scene understanding and generation tasks. By design, it leverages the spatiotemporal modeling capabilities of its texture module responsible for appearance synthesis, alongside the explicit geometric constraints provided by its dedicated geometry module, thereby enriching the model's holistic understanding of 3D scenes. Trained with a two-stage strategy, Omni-View achieves a state-of-the-art score of 55.4 on the VSI-Bench benchmark, outperforming existing specialized 3D understanding models, while simultaneously delivering strong performance in both novel view synthesis and 3D scene generation.
TransBench: Benchmarking Machine Translation for Industrial-Scale Applications
May 20, 2025Abstract:Machine translation (MT) has become indispensable for cross-border communication in globalized industries like e-commerce, finance, and legal services, with recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) significantly enhancing translation quality. However, applying general-purpose MT models to industrial scenarios reveals critical limitations due to domain-specific terminology, cultural nuances, and stylistic conventions absent in generic benchmarks. Existing evaluation frameworks inadequately assess performance in specialized contexts, creating a gap between academic benchmarks and real-world efficacy. To address this, we propose a three-level translation capability framework: (1) Basic Linguistic Competence, (2) Domain-Specific Proficiency, and (3) Cultural Adaptation, emphasizing the need for holistic evaluation across these dimensions. We introduce TransBench, a benchmark tailored for industrial MT, initially targeting international e-commerce with 17,000 professionally translated sentences spanning 4 main scenarios and 33 language pairs. TransBench integrates traditional metrics (BLEU, TER) with Marco-MOS, a domain-specific evaluation model, and provides guidelines for reproducible benchmark construction. Our contributions include: (1) a structured framework for industrial MT evaluation, (2) the first publicly available benchmark for e-commerce translation, (3) novel metrics probing multi-level translation quality, and (4) open-sourced evaluation tools. This work bridges the evaluation gap, enabling researchers and practitioners to systematically assess and enhance MT systems for industry-specific needs.
Unified Multimodal Understanding and Generation Models: Advances, Challenges, and Opportunities
May 05, 2025Abstract:Recent years have seen remarkable progress in both multimodal understanding models and image generation models. Despite their respective successes, these two domains have evolved independently, leading to distinct architectural paradigms: While autoregressive-based architectures have dominated multimodal understanding, diffusion-based models have become the cornerstone of image generation. Recently, there has been growing interest in developing unified frameworks that integrate these tasks. The emergence of GPT-4o's new capabilities exemplifies this trend, highlighting the potential for unification. However, the architectural differences between the two domains pose significant challenges. To provide a clear overview of current efforts toward unification, we present a comprehensive survey aimed at guiding future research. First, we introduce the foundational concepts and recent advancements in multimodal understanding and text-to-image generation models. Next, we review existing unified models, categorizing them into three main architectural paradigms: diffusion-based, autoregressive-based, and hybrid approaches that fuse autoregressive and diffusion mechanisms. For each category, we analyze the structural designs and innovations introduced by related works. Additionally, we compile datasets and benchmarks tailored for unified models, offering resources for future exploration. Finally, we discuss the key challenges facing this nascent field, including tokenization strategy, cross-modal attention, and data. As this area is still in its early stages, we anticipate rapid advancements and will regularly update this survey. Our goal is to inspire further research and provide a valuable reference for the community. The references associated with this survey will be available on GitHub soon.
CHATS: Combining Human-Aligned Optimization and Test-Time Sampling for Text-to-Image Generation
Feb 18, 2025



Abstract:Diffusion models have emerged as a dominant approach for text-to-image generation. Key components such as the human preference alignment and classifier-free guidance play a crucial role in ensuring generation quality. However, their independent application in current text-to-image models continues to face significant challenges in achieving strong text-image alignment, high generation quality, and consistency with human aesthetic standards. In this work, we for the first time, explore facilitating the collaboration of human performance alignment and test-time sampling to unlock the potential of text-to-image models. Consequently, we introduce CHATS (Combining Human-Aligned optimization and Test-time Sampling), a novel generative framework that separately models the preferred and dispreferred distributions and employs a proxy-prompt-based sampling strategy to utilize the useful information contained in both distributions. We observe that CHATS exhibits exceptional data efficiency, achieving strong performance with only a small, high-quality funetuning dataset. Extensive experiments demonstrate that CHATS surpasses traditional preference alignment methods, setting new state-of-the-art across various standard benchmarks.
Evaluating Image Caption via Cycle-consistent Text-to-Image Generation
Jan 08, 2025



Abstract:Evaluating image captions typically relies on reference captions, which are costly to obtain and exhibit significant diversity and subjectivity. While reference-free evaluation metrics have been proposed, most focus on cross-modal evaluation between captions and images. Recent research has revealed that the modality gap generally exists in the representation of contrastive learning-based multi-modal systems, undermining the reliability of cross-modality metrics like CLIPScore. In this paper, we propose CAMScore, a cyclic reference-free automatic evaluation metric for image captioning models. To circumvent the aforementioned modality gap, CAMScore utilizes a text-to-image model to generate images from captions and subsequently evaluates these generated images against the original images. Furthermore, to provide fine-grained information for a more comprehensive evaluation, we design a three-level evaluation framework for CAMScore that encompasses pixel-level, semantic-level, and objective-level perspectives. Extensive experiment results across multiple benchmark datasets show that CAMScore achieves a superior correlation with human judgments compared to existing reference-based and reference-free metrics, demonstrating the effectiveness of the framework.
MDP3: A Training-free Approach for List-wise Frame Selection in Video-LLMs
Jan 06, 2025Abstract:Video large language models (Video-LLMs) have made significant progress in understanding videos. However, processing multiple frames leads to lengthy visual token sequences, presenting challenges such as the limited context length cannot accommodate the entire video, and the inclusion of irrelevant frames hinders visual perception. Hence, effective frame selection is crucial. This paper emphasizes that frame selection should follow three key principles: query relevance, list-wise diversity, and sequentiality. Existing methods, such as uniform frame sampling and query-frame matching, do not capture all of these principles. Thus, we propose Markov decision determinantal point process with dynamic programming (MDP3) for frame selection, a training-free and model-agnostic method that can be seamlessly integrated into existing Video-LLMs. Our method first estimates frame similarities conditioned on the query using a conditional Gaussian kernel within the reproducing kernel Hilbert space~(RKHS). We then apply the determinantal point process~(DPP) to the similarity matrix to capture both query relevance and list-wise diversity. To incorporate sequentiality, we segment the video and apply DPP within each segment, conditioned on the preceding segment selection, modeled as a Markov decision process~(MDP) for allocating selection sizes across segments. Theoretically, MDP3 provides a \((1 - 1/e)\)-approximate solution to the NP-hard list-wise frame selection problem with pseudo-polynomial time complexity, demonstrating its efficiency. Empirically, MDP3 significantly outperforms existing methods, verifying its effectiveness and robustness.
UNIC-Adapter: Unified Image-instruction Adapter with Multi-modal Transformer for Image Generation
Dec 25, 2024



Abstract:Recently, text-to-image generation models have achieved remarkable advancements, particularly with diffusion models facilitating high-quality image synthesis from textual descriptions. However, these models often struggle with achieving precise control over pixel-level layouts, object appearances, and global styles when using text prompts alone. To mitigate this issue, previous works introduce conditional images as auxiliary inputs for image generation, enhancing control but typically necessitating specialized models tailored to different types of reference inputs. In this paper, we explore a new approach to unify controllable generation within a single framework. Specifically, we propose the unified image-instruction adapter (UNIC-Adapter) built on the Multi-Modal-Diffusion Transformer architecture, to enable flexible and controllable generation across diverse conditions without the need for multiple specialized models. Our UNIC-Adapter effectively extracts multi-modal instruction information by incorporating both conditional images and task instructions, injecting this information into the image generation process through a cross-attention mechanism enhanced by Rotary Position Embedding. Experimental results across a variety of tasks, including pixel-level spatial control, subject-driven image generation, and style-image-based image synthesis, demonstrate the effectiveness of our UNIC-Adapter in unified controllable image generation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge