Peter Tino
School of Computer Science, University of Birmingham, the United Kingdom
Discriminative Subspace Emersion from learning feature relevances across different populations
Apr 02, 2025Abstract:In a given classification task, the accuracy of the learner is often hampered by finiteness of the training set, high-dimensionality of the feature space and severe overlap between classes. In the context of interpretable learners, with (piecewise) linear separation boundaries, these issues can be mitigated by careful construction of optimization procedures and/or estimation of relevant features for the task. However, when the task is shared across two disjoint populations the main interest is shifted towards estimating a set of features that discriminate the most between the two, when performing classification. We propose a new Discriminative Subspace Emersion (DSE) method to extend subspace learning toward a general relevance learning framework. DSE allows us to identify the most relevant features in distinguishing the classification task across two populations, even in cases of high overlap between classes. The proposed methodology is designed to work with multiple sets of labels and is derived in principle without being tied to a specific choice of base learner. Theoretical and empirical investigations over synthetic and real-world datasets indicate that DSE accurately identifies a common subspace for the classification across different populations. This is shown to be true for a surprisingly high degree of overlap between classes.
Whole-Genome Phenotype Prediction with Machine Learning: Open Problems in Bacterial Genomics
Feb 11, 2025Abstract:How can we identify causal genetic mechanisms that govern bacterial traits? Initial efforts entrusting machine learning models to handle the task of predicting phenotype from genotype return high accuracy scores. However, attempts to extract any meaning from the predictive models are found to be corrupted by falsely identified "causal" features. Relying solely on pattern recognition and correlations is unreliable, significantly so in bacterial genomics settings where high-dimensionality and spurious associations are the norm. Though it is not yet clear whether we can overcome this hurdle, significant efforts are being made towards discovering potential high-risk bacterial genetic variants. In view of this, we set up open problems surrounding phenotype prediction from bacterial whole-genome datasets and extending those to learning causal effects, and discuss challenges that impact the reliability of a machine's decision-making when faced with datasets of this nature.
On the importance of structural identifiability for machine learning with partially observed dynamical systems
Feb 06, 2025Abstract:The successful application of modern machine learning for time series classification is often hampered by limitations in quality and quantity of available training data. To overcome these limitations, available domain expert knowledge in the form of parametrised mechanistic dynamical models can be used whenever it is available and time series observations may be represented as an element from a given class of parametrised dynamical models. This makes the learning process interpretable and allows the modeller to deal with sparsely and irregularly sampled data in a natural way. However, the internal processes of a dynamical model are often only partially observed. This can lead to ambiguity regarding which particular model realization best explains a given time series observation. This problem is well-known in the literature, and a dynamical model with this issue is referred to as structurally unidentifiable. Training a classifier that incorporates knowledge about a structurally unidentifiable dynamical model can negatively influence classification performance. To address this issue, we employ structural identifiability analysis to explicitly relate parameter configurations that are associated with identical system outputs. Using the derived relations in classifier training, we demonstrate that this method significantly improves the classifier's ability to generalize to unseen data on a number of example models from the biomedical domain. This effect is especially pronounced when the number of training instances is limited. Our results demonstrate the importance of accounting for structural identifiability, a topic that has received relatively little attention from the machine learning community.
Linear Simple Cycle Reservoirs at the edge of stability perform Fourier decomposition of the input driving signals
Nov 30, 2024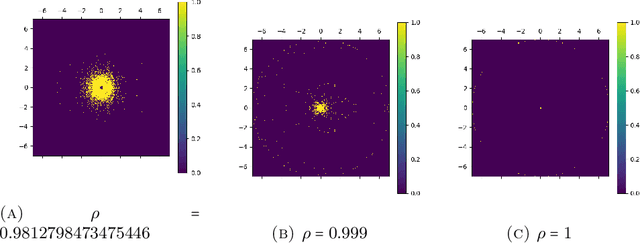
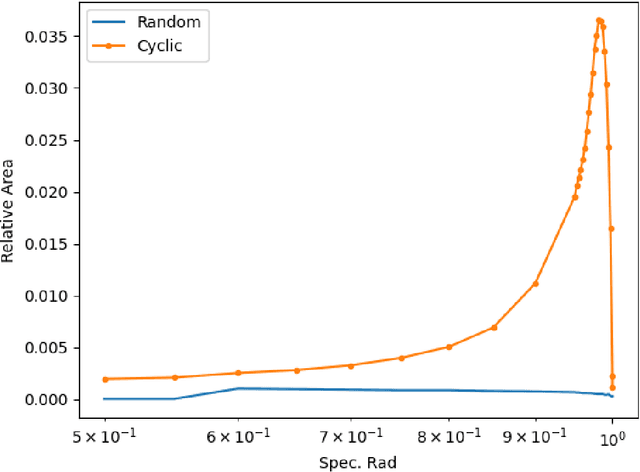
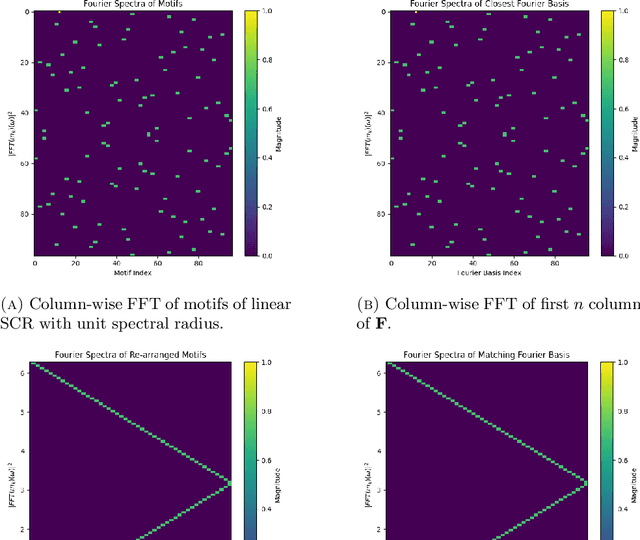
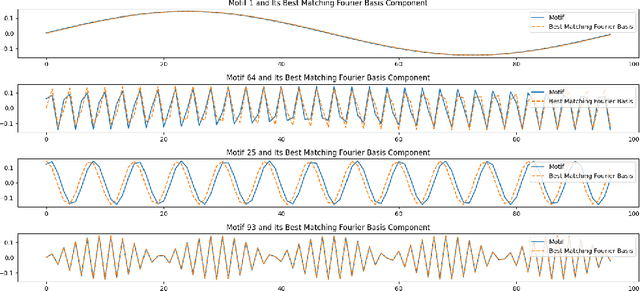
Abstract:This paper explores the representational structure of linear Simple Cycle Reservoirs (SCR) operating at the edge of stability. We view SCR as providing in their state space feature representations of the input-driving time series. By endowing the state space with the canonical dot-product, we ``reverse engineer" the corresponding kernel (inner product) operating in the original time series space. The action of this time-series kernel is fully characterized by the eigenspace of the corresponding metric tensor. We demonstrate that when linear SCRs are constructed at the edge of stability, the eigenvectors of the time-series kernel align with the Fourier basis. This theoretical insight is supported by numerical experiments.
A distance function for stochastic matrices
Oct 16, 2024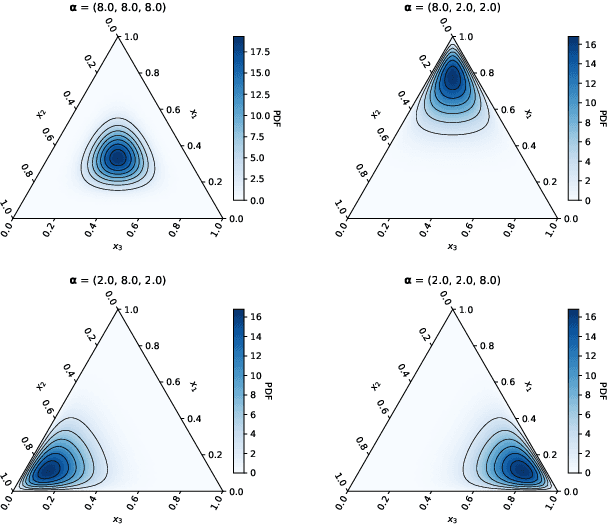
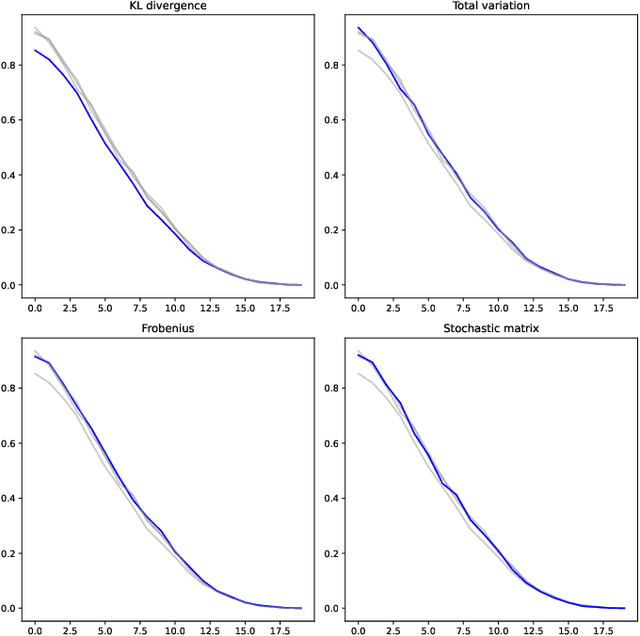
Abstract:Motivated by information geometry, a distance function on the space of stochastic matrices is advocated. Starting with sequences of Markov chains the Bhattacharyya angle is advocated as the natural tool for comparing both short and long term Markov chain runs. Bounds on the convergence of the distance and mixing times are derived. Guided by the desire to compare different Markov chain models, especially in the setting of healthcare processes, a new distance function on the space of stochastic matrices is presented. It is a true distance measure which has a closed form and is efficient to implement for numerical evaluation. In the case of ergodic Markov chains, it is shown that considering either the Bhattacharyya angle on Markov sequences or the new stochastic matrix distance leads to the same distance between models.
An Interpretable Alternative to Neural Representation Learning for Rating Prediction -- Transparent Latent Class Modeling of User Reviews
Jul 02, 2024



Abstract:Nowadays, neural network (NN) and deep learning (DL) techniques are widely adopted in many applications, including recommender systems. Given the sparse and stochastic nature of collaborative filtering (CF) data, recent works have critically analyzed the effective improvement of neural-based approaches compared to simpler and often transparent algorithms for recommendation. Previous results showed that NN and DL models can be outperformed by traditional algorithms in many tasks. Moreover, given the largely black-box nature of neural-based methods, interpretable results are not naturally obtained. Following on this debate, we first present a transparent probabilistic model that topologically organizes user and product latent classes based on the review information. In contrast to popular neural techniques for representation learning, we readily obtain a statistical, visualization-friendly tool that can be easily inspected to understand user and product characteristics from a textual-based perspective. Then, given the limitations of common embedding techniques, we investigate the possibility of using the estimated interpretable quantities as model input for a rating prediction task. To contribute to the recent debates, we evaluate our results in terms of both capacity for interpretability and predictive performances in comparison with popular text-based neural approaches. The results demonstrate that the proposed latent class representations can yield competitive predictive performances, compared to popular, but difficult-to-interpret approaches.
Predictive Modeling in the Reservoir Kernel Motif Space
May 11, 2024



Abstract:This work proposes a time series prediction method based on the kernel view of linear reservoirs. In particular, the time series motifs of the reservoir kernel are used as representational basis on which general readouts are constructed. We provide a geometric interpretation of our approach shedding light on how our approach is related to the core reservoir models and in what way the two approaches differ. Empirical experiments then compare predictive performances of our suggested model with those of recent state-of-art transformer based models, as well as the established recurrent network model - LSTM. The experiments are performed on both univariate and multivariate time series and with a variety of prediction horizons. Rather surprisingly we show that even when linear readout is employed, our method has the capacity to outperform transformer models on univariate time series and attain competitive results on multivariate benchmark datasets. We conclude that simple models with easily controllable capacity but capturing enough memory and subsequence structure can outperform potentially over-complicated deep learning models. This does not mean that reservoir motif based models are preferable to other more complex alternatives - rather, when introducing a new complex time series model one should employ as a sanity check simple, but potentially powerful alternatives/baselines such as reservoir models or the models introduced here.
Interpretable Models Capable of Handling Systematic Missingness in Imbalanced Classes and Heterogeneous Datasets
Jun 04, 2022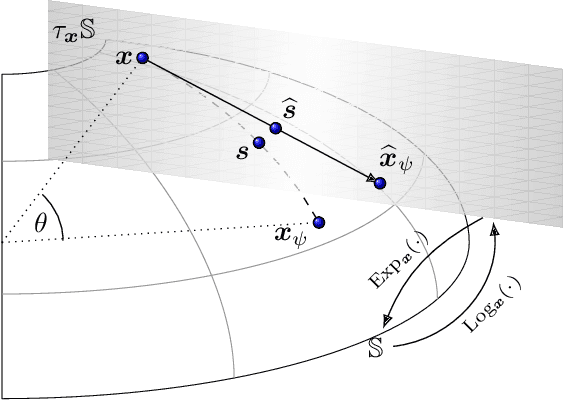
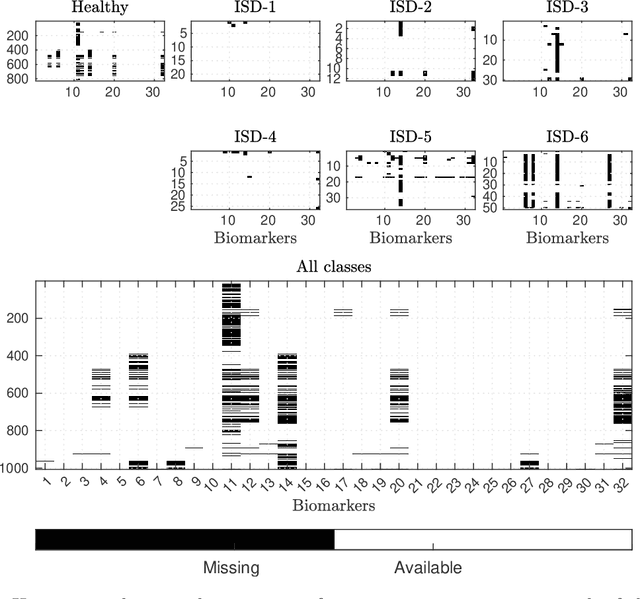
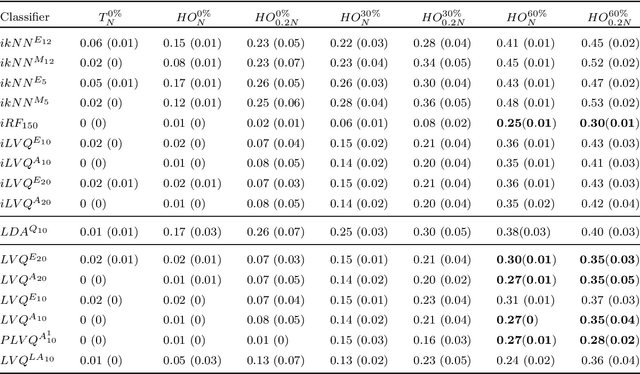

Abstract:Application of interpretable machine learning techniques on medical datasets facilitate early and fast diagnoses, along with getting deeper insight into the data. Furthermore, the transparency of these models increase trust among application domain experts. Medical datasets face common issues such as heterogeneous measurements, imbalanced classes with limited sample size, and missing data, which hinder the straightforward application of machine learning techniques. In this paper we present a family of prototype-based (PB) interpretable models which are capable of handling these issues. The models introduced in this contribution show comparable or superior performance to alternative techniques applicable in such situations. However, unlike ensemble based models, which have to compromise on easy interpretation, the PB models here do not. Moreover we propose a strategy of harnessing the power of ensembles while maintaining the intrinsic interpretability of the PB models, by averaging the model parameter manifolds. All the models were evaluated on a synthetic (publicly available dataset) in addition to detailed analyses of two real-world medical datasets (one publicly available). Results indicated that the models and strategies we introduced addressed the challenges of real-world medical data, while remaining computationally inexpensive and transparent, as well as similar or superior in performance compared to their alternatives.
Probabilistic Learning Vector Quantization on Manifold of Symmetric Positive Definite Matrices
Feb 01, 2021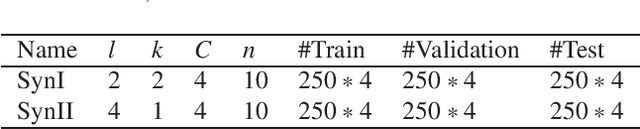
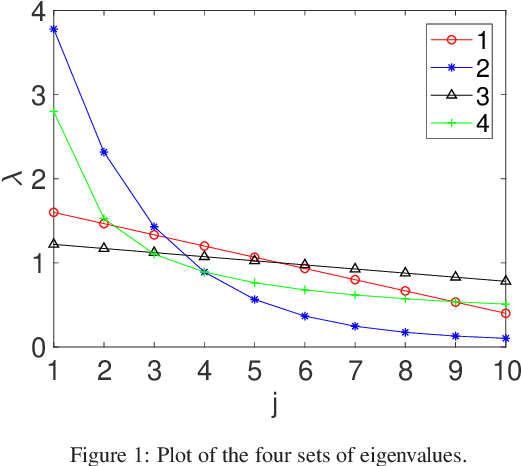
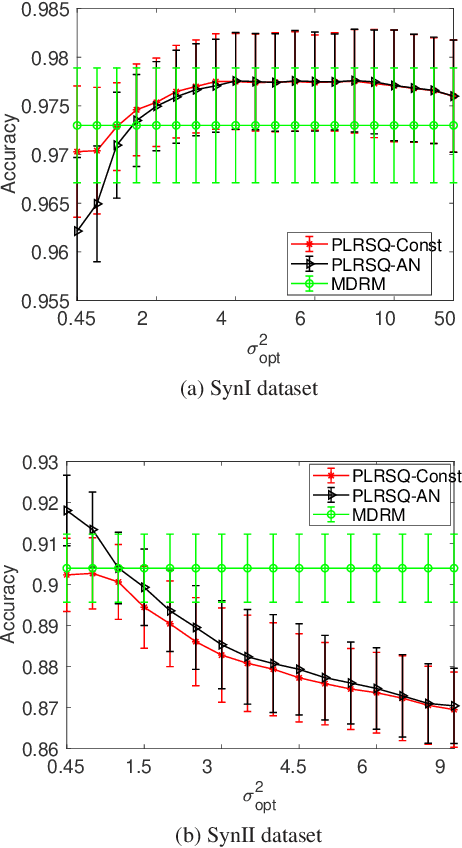
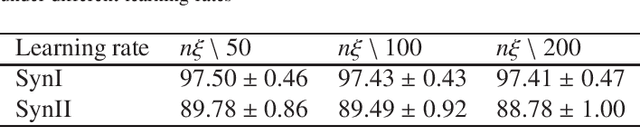
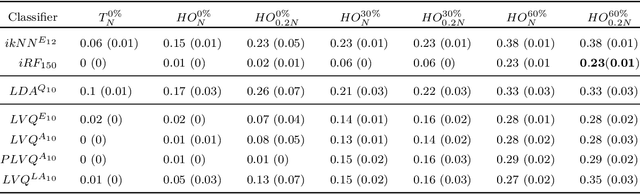
Abstract:In this paper, we develop a new classification method for manifold-valued data in the framework of probabilistic learning vector quantization. In many classification scenarios, the data can be naturally represented by symmetric positive definite matrices, which are inherently points that live on a curved Riemannian manifold. Due to the non-Euclidean geometry of Riemannian manifolds, traditional Euclidean machine learning algorithms yield poor results on such data. In this paper, we generalize the probabilistic learning vector quantization algorithm for data points living on the manifold of symmetric positive definite matrices equipped with Riemannian natural metric (affine-invariant metric). By exploiting the induced Riemannian distance, we derive the probabilistic learning Riemannian space quantization algorithm, obtaining the learning rule through Riemannian gradient descent. Empirical investigations on synthetic data, image data , and motor imagery EEG data demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method.
LAAT: Locally Aligned Ant Technique for detecting manifolds of varying density
Sep 17, 2020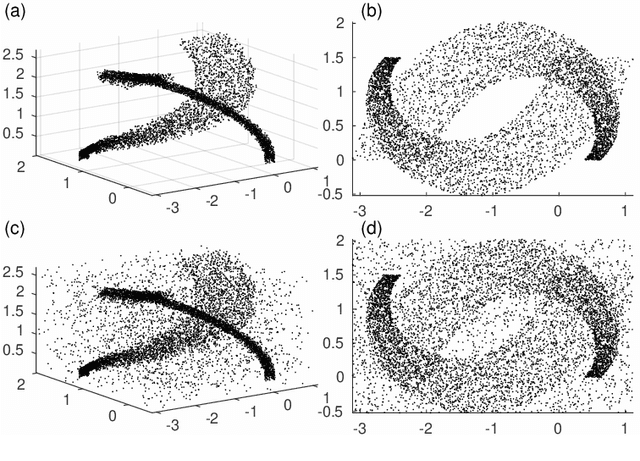



Abstract:Dimensionality reduction and clustering are often used as preliminary steps for many complex machine learning tasks. The presence of noise and outliers can deteriorate the performance of such preprocessing and therefore impair the subsequent analysis tremendously. In manifold learning, several studies indicate solutions for removing background noise or noise close to the structure when the density is substantially higher than that exhibited by the noise. However, in many applications, including astronomical datasets, the density varies alongside manifolds that are buried in a noisy background. We propose a novel method to extract manifolds in the presence of noise based on the idea of Ant colony optimization. In contrast to the existing random walk solutions, our technique captures points which are locally aligned with major directions of the manifold. Moreover, we empirically show that the biologically inspired formulation of ant pheromone reinforces this behavior enabling it to recover multiple manifolds embedded in extremely noisy data clouds. The algorithm's performance is demonstrated in comparison to the state-of-the-art approaches, such as Markov Chain, LLPD, and Disperse, on several synthetic and real astronomical datasets stemming from an N-body simulation of a cosmological volume.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge