Haozhi Cao
An Efficient Scene Coordinate Encoding and Relocalization Method
Dec 09, 2024



Abstract:Scene Coordinate Regression (SCR) is a visual localization technique that utilizes deep neural networks (DNN) to directly regress 2D-3D correspondences for camera pose estimation. However, current SCR methods often face challenges in handling repetitive textures and meaningless areas due to their reliance on implicit triangulation. In this paper, we propose an efficient scene coordinate encoding and relocalization method. Compared with the existing SCR methods, we design a unified architecture for both scene encoding and salient keypoint detection, enabling our system to focus on encoding informative regions, thereby significantly enhancing efficiency. Additionally, we introduce a mechanism that leverages sequential information during both map encoding and relocalization, which strengthens implicit triangulation, particularly in repetitive texture environments. Comprehensive experiments conducted across indoor and outdoor datasets demonstrate that the proposed system outperforms other state-of-the-art (SOTA) SCR methods. Our single-frame relocalization mode improves the recall rate of our baseline by 6.4% and increases the running speed from 56Hz to 90Hz. Furthermore, our sequence-based mode increases the recall rate by 11% while maintaining the original efficiency.
UniRiT: Towards Few-Shot Non-Rigid Point Cloud Registration
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:Non-rigid point cloud registration is a critical challenge in 3D scene understanding, particularly in surgical navigation. Although existing methods achieve excellent performance when trained on large-scale, high-quality datasets, these datasets are prohibitively expensive to collect and annotate, e.g., organ data in authentic medical scenarios. With insufficient training samples and data noise, existing methods degrade significantly since non-rigid patterns are more flexible and complicated than rigid ones, and the distributions across samples are more distinct, leading to higher difficulty in representation learning with few data. In this work, we aim to deal with this challenging few-shot non-rigid point cloud registration problem. Based on the observation that complex non-rigid transformation patterns can be decomposed into rigid and small non-rigid transformations, we propose a novel and effective framework, UniRiT. UniRiT adopts a two-step registration strategy that first aligns the centroids of the source and target point clouds and then refines the registration with non-rigid transformations, thereby significantly reducing the problem complexity. To validate the performance of UniRiT on real-world datasets, we introduce a new dataset, MedMatch3D, which consists of real human organs and exhibits high variability in sample distribution. We further establish a new challenging benchmark for few-shot non-rigid registration. Extensive empirical results demonstrate that UniRiT achieves state-of-the-art performance on MedMatch3D, improving the existing best approach by 94.22%.
Enhancing Dataset Distillation via Label Inconsistency Elimination and Learning Pattern Refinement
Oct 17, 2024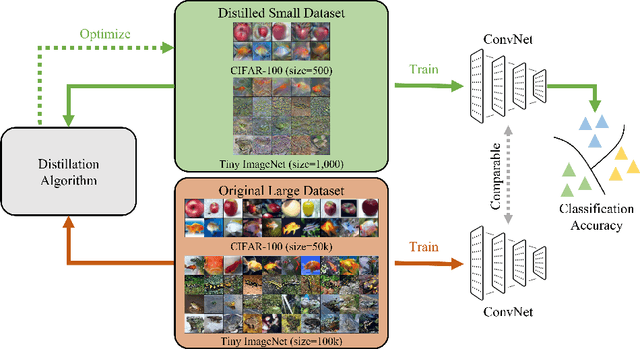
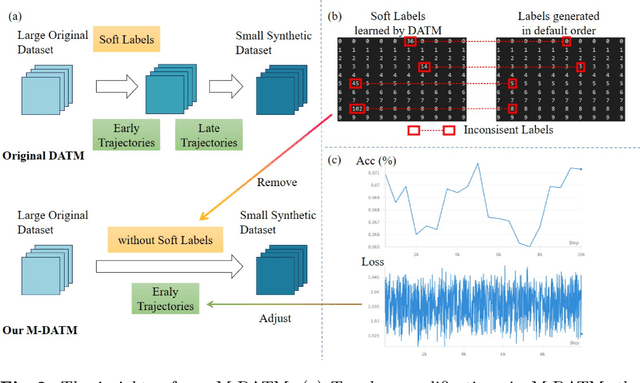
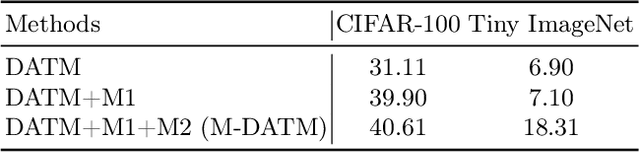
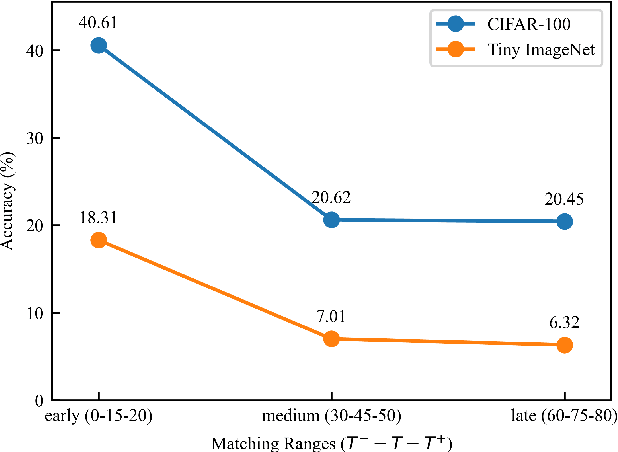
Abstract:Dataset Distillation (DD) seeks to create a condensed dataset that, when used to train a model, enables the model to achieve performance similar to that of a model trained on the entire original dataset. It relieves the model training from processing massive data and thus reduces the computation resources, storage, and time costs. This paper illustrates our solution that ranks 1st in the ECCV-2024 Data Distillation Challenge (track 1). Our solution, Modified Difficulty-Aligned Trajectory Matching (M-DATM), introduces two key modifications to the original state-of-the-art method DATM: (1) the soft labels learned by DATM do not achieve one-to-one correspondence with the counterparts generated by the official evaluation script, so we remove the soft labels technique to alleviate such inconsistency; (2) since the removal of soft labels makes it harder for the synthetic dataset to learn late trajectory information, particularly on Tiny ImageNet, we reduce the matching range, allowing the synthetic data to concentrate more on the easier patterns. In the final evaluation, our M-DATM achieved accuracies of 0.4061 and 0.1831 on the CIFAR-100 and Tiny ImageNet datasets, ranking 1st in the Fixed Images Per Class (IPC) Track.
SGBA: Semantic Gaussian Mixture Model-Based LiDAR Bundle Adjustment
Oct 02, 2024Abstract:LiDAR bundle adjustment (BA) is an effective approach to reduce the drifts in pose estimation from the front-end. Existing works on LiDAR BA usually rely on predefined geometric features for landmark representation. This reliance restricts generalizability, as the system will inevitably deteriorate in environments where these specific features are absent. To address this issue, we propose SGBA, a LiDAR BA scheme that models the environment as a semantic Gaussian mixture model (GMM) without predefined feature types. This approach encodes both geometric and semantic information, offering a comprehensive and general representation adaptable to various environments. Additionally, to limit computational complexity while ensuring generalizability, we propose an adaptive semantic selection framework that selects the most informative semantic clusters for optimization by evaluating the condition number of the cost function. Lastly, we introduce a probabilistic feature association scheme that considers the entire probability density of assignments, which can manage uncertainties in measurement and initial pose estimation. We have conducted various experiments and the results demonstrate that SGBA can achieve accurate and robust pose refinement even in challenging scenarios with low-quality initial pose estimation and limited geometric features. We plan to open-source the work for the benefit of the community https://github.com/Ji1Xinyu/SGBA.
GERA: Geometric Embedding for Efficient Point Registration Analysis
Oct 01, 2024Abstract:Point cloud registration aims to provide estimated transformations to align point clouds, which plays a crucial role in pose estimation of various navigation systems, such as surgical guidance systems and autonomous vehicles. Despite the impressive performance of recent models on benchmark datasets, many rely on complex modules like KPConv and Transformers, which impose significant computational and memory demands. These requirements hinder their practical application, particularly in resource-constrained environments such as mobile robotics. In this paper, we propose a novel point cloud registration network that leverages a pure MLP architecture, constructing geometric information offline. This approach eliminates the computational and memory burdens associated with traditional complex feature extractors and significantly reduces inference time and resource consumption. Our method is the first to replace 3D coordinate inputs with offline-constructed geometric encoding, improving generalization and stability, as demonstrated by Maximum Mean Discrepancy (MMD) comparisons. This efficient and accurate geometric representation marks a significant advancement in point cloud analysis, particularly for applications requiring fast and reliability.
AIR-Embodied: An Efficient Active 3DGS-based Interaction and Reconstruction Framework with Embodied Large Language Model
Sep 24, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in 3D reconstruction and neural rendering have enhanced the creation of high-quality digital assets, yet existing methods struggle to generalize across varying object shapes, textures, and occlusions. While Next Best View (NBV) planning and Learning-based approaches offer solutions, they are often limited by predefined criteria and fail to manage occlusions with human-like common sense. To address these problems, we present AIR-Embodied, a novel framework that integrates embodied AI agents with large-scale pretrained multi-modal language models to improve active 3DGS reconstruction. AIR-Embodied utilizes a three-stage process: understanding the current reconstruction state via multi-modal prompts, planning tasks with viewpoint selection and interactive actions, and employing closed-loop reasoning to ensure accurate execution. The agent dynamically refines its actions based on discrepancies between the planned and actual outcomes. Experimental evaluations across virtual and real-world environments demonstrate that AIR-Embodied significantly enhances reconstruction efficiency and quality, providing a robust solution to challenges in active 3D reconstruction.
MCD: Diverse Large-Scale Multi-Campus Dataset for Robot Perception
Mar 18, 2024Abstract:Perception plays a crucial role in various robot applications. However, existing well-annotated datasets are biased towards autonomous driving scenarios, while unlabelled SLAM datasets are quickly over-fitted, and often lack environment and domain variations. To expand the frontier of these fields, we introduce a comprehensive dataset named MCD (Multi-Campus Dataset), featuring a wide range of sensing modalities, high-accuracy ground truth, and diverse challenging environments across three Eurasian university campuses. MCD comprises both CCS (Classical Cylindrical Spinning) and NRE (Non-Repetitive Epicyclic) lidars, high-quality IMUs (Inertial Measurement Units), cameras, and UWB (Ultra-WideBand) sensors. Furthermore, in a pioneering effort, we introduce semantic annotations of 29 classes over 59k sparse NRE lidar scans across three domains, thus providing a novel challenge to existing semantic segmentation research upon this largely unexplored lidar modality. Finally, we propose, for the first time to the best of our knowledge, continuous-time ground truth based on optimization-based registration of lidar-inertial data on large survey-grade prior maps, which are also publicly released, each several times the size of existing ones. We conduct a rigorous evaluation of numerous state-of-the-art algorithms on MCD, report their performance, and highlight the challenges awaiting solutions from the research community.
Reliable Spatial-Temporal Voxels For Multi-Modal Test-Time Adaptation
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Multi-modal test-time adaptation (MM-TTA) is proposed to adapt models to an unlabeled target domain by leveraging the complementary multi-modal inputs in an online manner. Previous MM-TTA methods rely on predictions of cross-modal information in each input frame, while they ignore the fact that predictions of geometric neighborhoods within consecutive frames are highly correlated, leading to unstable predictions across time. To fulfill this gap, we propose ReLiable Spatial-temporal Voxels (Latte), an MM-TTA method that leverages reliable cross-modal spatial-temporal correspondences for multi-modal 3D segmentation. Motivated by the fact that reliable predictions should be consistent with their spatial-temporal correspondences, Latte aggregates consecutive frames in a slide window manner and constructs ST voxel to capture temporally local prediction consistency for each modality. After filtering out ST voxels with high ST entropy, Latte conducts cross-modal learning for each point and pixel by attending to those with reliable and consistent predictions among both spatial and temporal neighborhoods. Experimental results show that Latte achieves state-of-the-art performance on three different MM-TTA benchmarks compared to previous MM-TTA or TTA methods.
MoPA: Multi-Modal Prior Aided Domain Adaptation for 3D Semantic Segmentation
Sep 21, 2023Abstract:Multi-modal unsupervised domain adaptation (MM-UDA) for 3D semantic segmentation is a practical solution to embed semantic understanding in autonomous systems without expensive point-wise annotations. While previous MM-UDA methods can achieve overall improvement, they suffer from significant class-imbalanced performance, restricting their adoption in real applications. This imbalanced performance is mainly caused by: 1) self-training with imbalanced data and 2) the lack of pixel-wise 2D supervision signals. In this work, we propose Multi-modal Prior Aided (MoPA) domain adaptation to improve the performance of rare objects. Specifically, we develop Valid Ground-based Insertion (VGI) to rectify the imbalance supervision signals by inserting prior rare objects collected from the wild while avoiding introducing artificial artifacts that lead to trivial solutions. Meanwhile, our SAM consistency loss leverages the 2D prior semantic masks from SAM as pixel-wise supervision signals to encourage consistent predictions for each object in the semantic mask. The knowledge learned from modal-specific prior is then shared across modalities to achieve better rare object segmentation. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on the challenging MM-UDA benchmark. Code will be available at https://github.com/AronCao49/MoPA.
Outram: One-shot Global Localization via Triangulated Scene Graph and Global Outlier Pruning
Sep 16, 2023



Abstract:One-shot LiDAR localization refers to the ability to estimate the robot pose from one single point cloud, which yields significant advantages in initialization and relocalization processes. In the point cloud domain, the topic has been extensively studied as a global descriptor retrieval (i.e., loop closure detection) and pose refinement (i.e., point cloud registration) problem both in isolation or combined. However, few have explicitly considered the relationship between candidate retrieval and correspondence generation in pose estimation, leaving them brittle to substructure ambiguities. To this end, we propose a hierarchical one-shot localization algorithm called Outram that leverages substructures of 3D scene graphs for locally consistent correspondence searching and global substructure-wise outlier pruning. Such a hierarchical process couples the feature retrieval and the correspondence extraction to resolve the substructure ambiguities by conducting a local-to-global consistency refinement. We demonstrate the capability of Outram in a variety of scenarios in multiple large-scale outdoor datasets. Our implementation is open-sourced: https://github.com/Pamphlett/Outram.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge