Wenlong Wan
Action Dubber: Timing Audible Actions via Inflectional Flow
Jun 16, 2025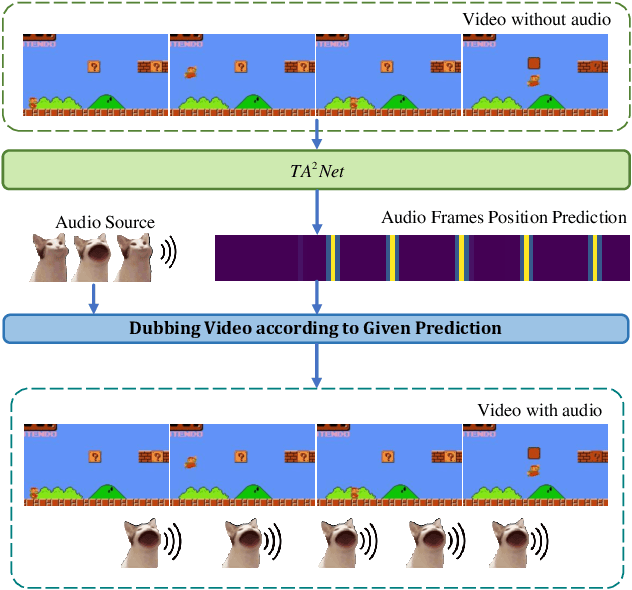
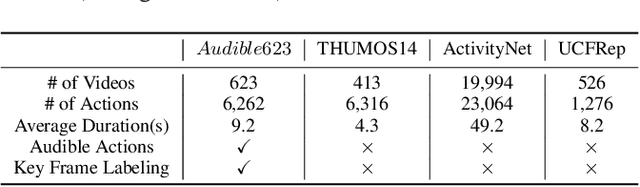

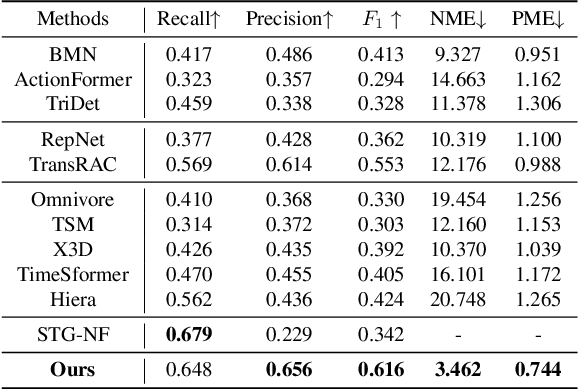
Abstract:We introduce the task of Audible Action Temporal Localization, which aims to identify the spatio-temporal coordinates of audible movements. Unlike conventional tasks such as action recognition and temporal action localization, which broadly analyze video content, our task focuses on the distinct kinematic dynamics of audible actions. It is based on the premise that key actions are driven by inflectional movements; for example, collisions that produce sound often involve abrupt changes in motion. To capture this, we propose $TA^{2}Net$, a novel architecture that estimates inflectional flow using the second derivative of motion to determine collision timings without relying on audio input. $TA^{2}Net$ also integrates a self-supervised spatial localization strategy during training, combining contrastive learning with spatial analysis. This dual design improves temporal localization accuracy and simultaneously identifies sound sources within video frames. To support this task, we introduce a new benchmark dataset, $Audible623$, derived from Kinetics and UCF101 by removing non-essential vocalization subsets. Extensive experiments confirm the effectiveness of our approach on $Audible623$ and show strong generalizability to other domains, such as repetitive counting and sound source localization. Code and dataset are available at https://github.com/WenlongWan/Audible623.
Revisit Input Perturbation Problems for LLMs: A Unified Robustness Evaluation Framework for Noisy Slot Filling Task
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:With the increasing capabilities of large language models (LLMs), these high-performance models have achieved state-of-the-art results on a wide range of natural language processing (NLP) tasks. However, the models' performance on commonly-used benchmark datasets often fails to accurately reflect their reliability and robustness when applied to real-world noisy data. To address these challenges, we propose a unified robustness evaluation framework based on the slot-filling task to systematically evaluate the dialogue understanding capability of LLMs in diverse input perturbation scenarios. Specifically, we construct a input perturbation evaluation dataset, Noise-LLM, which contains five types of single perturbation and four types of mixed perturbation data. Furthermore, we utilize a multi-level data augmentation method (character, word, and sentence levels) to construct a candidate data pool, and carefully design two ways of automatic task demonstration construction strategies (instance-level and entity-level) with various prompt templates. Our aim is to assess how well various robustness methods of LLMs perform in real-world noisy scenarios. The experiments have demonstrated that the current open-source LLMs generally achieve limited perturbation robustness performance. Based on these experimental observations, we make some forward-looking suggestions to fuel the research in this direction.
Two New Stenosis Detection Methods of Coronary Angiograms
Dec 14, 2021



Abstract:Coronary angiography is the "gold standard" for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD). At present, the methods for detecting and evaluating coronary artery stenosis cannot satisfy the clinical needs, e.g., there is no prior study of detecting stenoses in prespecified vessel segments, which is necessary in clinical practice. Two vascular stenosis detection methods are proposed to assist the diagnosis. The first one is an automatic method, which can automatically extract the entire coronary artery tree and mark all the possible stenoses. The second one is an interactive method. With this method, the user can choose any vessel segment to do further analysis of its stenoses. Experiments show that the proposed methods are robust for angiograms with various vessel structures. The precision, sensitivity, and $F_1$ score of the automatic stenosis detection method are 0.821, 0.757, and 0.788, respectively. Further investigation proves that the interactive method can provide a more precise outcome of stenosis detection, and our quantitative analysis is closer to reality. The proposed automatic method and interactive method are effective and can complement each other in clinical practice. The first method can be used for preliminary screening, and the second method can be used for further quantitative analysis. We believe the proposed solution is more suitable for the clinical diagnosis of CAD.
Two New Stenoses Detection Methods of Coronary Angiograms
Aug 03, 2021



Abstract:Coronary angiography is the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. At present, the methods for detecting coronary artery stenoses and evaluating the degree of it in coronary angiograms are either subjective or not efficient enough. Two vascular stenoses detection methods in coronary angiograms are proposed to assist the diagnosis. The first one is an automatic method, which can automatically segment the entire coronary vessels and mark the stenoses. The second one is an interactive method. With this method, the user only needs to give a start point and an end point to detect the stenoses of a certain vascular segment. We have shown that the proposed tracking methods are robust for angiograms with various vessel structure. The automatic detection method can effectively measure the diameter of the vessel and mark the stenoses in different angiograms. Further investigation proves that the results of interactive detection method can accurately reflect the true stenoses situation. The proposed automatic method and interactive method are effective in various angiograms and can complement each other in clinical practice. The first method can be used for preliminary screening and the second method can be used for further quantitative analysis. It has the potential to improve the level of clinical diagnosis of coronary heart disease.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge