Hu Liu
BAPS: A Fine-Grained Low-Precision Scheme for Softmax in Attention via Block-Aware Precision reScaling
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:As the performance gains from accelerating quantized matrix multiplication plateau, the softmax operation becomes the critical bottleneck in Transformer inference. This bottleneck stems from two hardware limitations: (1) limited data bandwidth between matrix and vector compute cores, and (2) the significant area cost of high-precision (FP32/16) exponentiation units (EXP2). To address these issues, we introduce a novel low-precision workflow that employs a specific 8-bit floating-point format (HiF8) and block-aware precision rescaling for softmax. Crucially, our algorithmic innovations make low-precision softmax feasible without the significant model accuracy loss that hampers direct low-precision approaches. Specifically, our design (i) halves the required data movement bandwidth by enabling matrix multiplication outputs constrained to 8-bit, and (ii) substantially reduces the EXP2 unit area by computing exponentiations in low (8-bit) precision. Extensive evaluation on language models and multi-modal models confirms the validity of our method. By alleviating the vector computation bottleneck, our work paves the way for doubling end-to-end inference throughput without increasing chip area, and offers a concrete co-design path for future low-precision hardware and software.
Serving Large Language Models on Huawei CloudMatrix384
Jun 15, 2025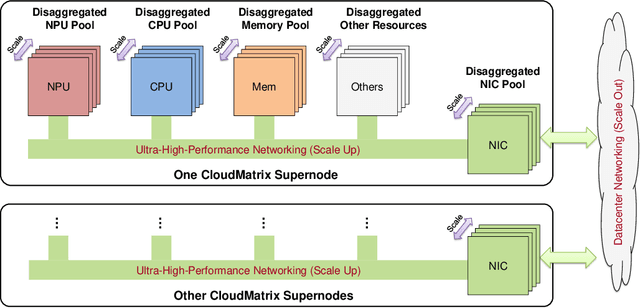
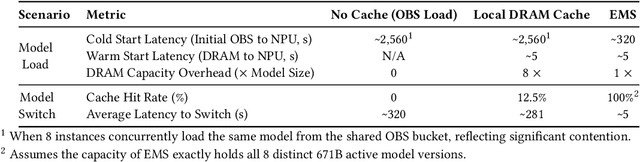
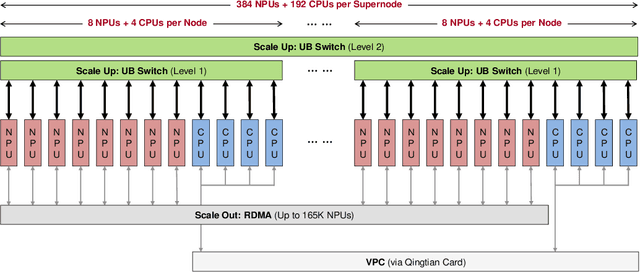
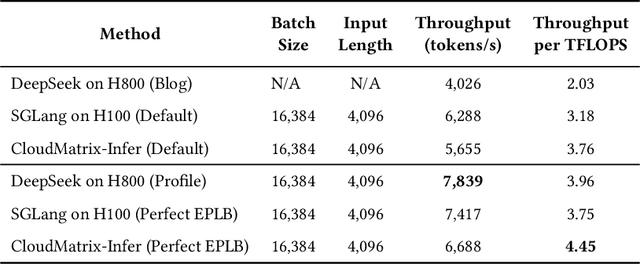
Abstract:The rapid evolution of large language models (LLMs), driven by growing parameter scales, adoption of mixture-of-experts (MoE) architectures, and expanding context lengths, imposes unprecedented demands on AI infrastructure. Traditional AI clusters face limitations in compute intensity, memory bandwidth, inter-chip communication, and latency, compounded by variable workloads and strict service-level objectives. Addressing these issues requires fundamentally redesigned hardware-software integration. This paper introduces Huawei CloudMatrix, a next-generation AI datacenter architecture, realized in the production-grade CloudMatrix384 supernode. It integrates 384 Ascend 910C NPUs and 192 Kunpeng CPUs interconnected via an ultra-high-bandwidth Unified Bus (UB) network, enabling direct all-to-all communication and dynamic pooling of resources. These features optimize performance for communication-intensive operations, such as large-scale MoE expert parallelism and distributed key-value cache access. To fully leverage CloudMatrix384, we propose CloudMatrix-Infer, an advanced LLM serving solution incorporating three core innovations: a peer-to-peer serving architecture that independently scales prefill, decode, and caching; a large-scale expert parallelism strategy supporting EP320 via efficient UB-based token dispatch; and hardware-aware optimizations including specialized operators, microbatch-based pipelining, and INT8 quantization. Evaluation with the DeepSeek-R1 model shows CloudMatrix-Infer achieves state-of-the-art efficiency: prefill throughput of 6,688 tokens/s per NPU and decode throughput of 1,943 tokens/s per NPU (<50 ms TPOT). It effectively balances throughput and latency, sustaining 538 tokens/s even under stringent 15 ms latency constraints, while INT8 quantization maintains model accuracy across benchmarks.
Unconstrained Monotonic Calibration of Predictions in Deep Ranking Systems
Apr 19, 2025Abstract:Ranking models primarily focus on modeling the relative order of predictions while often neglecting the significance of the accuracy of their absolute values. However, accurate absolute values are essential for certain downstream tasks, necessitating the calibration of the original predictions. To address this, existing calibration approaches typically employ predefined transformation functions with order-preserving properties to adjust the original predictions. Unfortunately, these functions often adhere to fixed forms, such as piece-wise linear functions, which exhibit limited expressiveness and flexibility, thereby constraining their effectiveness in complex calibration scenarios. To mitigate this issue, we propose implementing a calibrator using an Unconstrained Monotonic Neural Network (UMNN), which can learn arbitrary monotonic functions with great modeling power. This approach significantly relaxes the constraints on the calibrator, improving its flexibility and expressiveness while avoiding excessively distorting the original predictions by requiring monotonicity. Furthermore, to optimize this highly flexible network for calibration, we introduce a novel additional loss function termed Smooth Calibration Loss (SCLoss), which aims to fulfill a necessary condition for achieving the ideal calibration state. Extensive offline experiments confirm the effectiveness of our method in achieving superior calibration performance. Moreover, deployment in Kuaishou's large-scale online video ranking system demonstrates that the method's calibration improvements translate into enhanced business metrics. The source code is available at https://github.com/baiyimeng/UMC.
Ascend HiFloat8 Format for Deep Learning
Sep 26, 2024



Abstract:This preliminary white paper proposes a novel 8-bit floating-point data format HiFloat8 (abbreviated as HiF8) for deep learning. HiF8 features tapered precision. For normal value encoding, it provides 7 exponent values with 3-bit mantissa, 8 exponent values with 2-bit mantissa, and 16 exponent values with 1-bit mantissa. For denormal value encoding, it extends the dynamic range by 7 extra powers of 2, from 31 to 38 binades (notice that FP16 covers 40 binades). Meanwhile, HiF8 encodes all the special values except that positive zero and negative zero are represented by only one bit-pattern. Thanks to the better balance between precision and dynamic range, HiF8 can be simultaneously used in both forward and backward passes of AI training. In this paper, we will describe the definition and rounding methods of HiF8, as well as the tentative training and inference solutions. To demonstrate the efficacy of HiF8, massive simulation results on various neural networks, including traditional neural networks and large language models (LLMs), will also be presented.
Beyond Relevance: Improving User Engagement by Personalization for Short-Video Search
Sep 17, 2024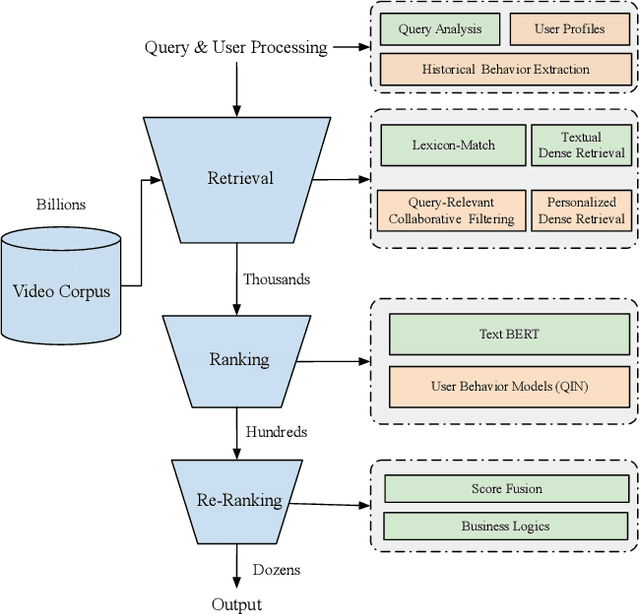
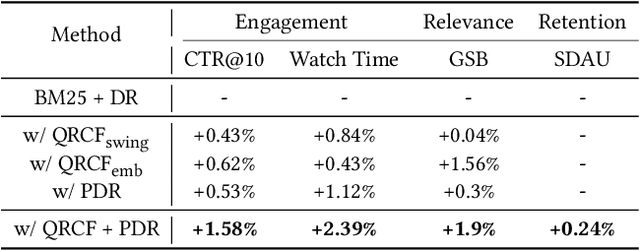
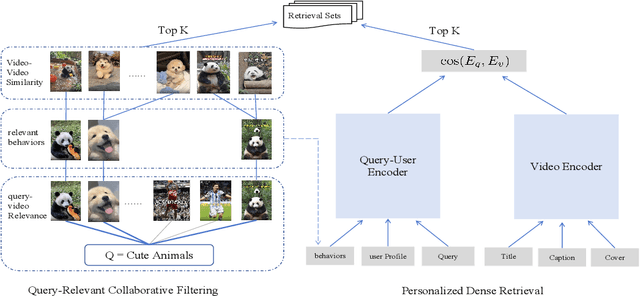
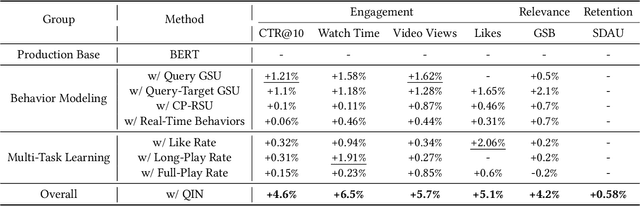
Abstract:Personalized search has been extensively studied in various applications, including web search, e-commerce, social networks, etc. With the soaring popularity of short-video platforms, exemplified by TikTok and Kuaishou, the question arises: can personalization elevate the realm of short-video search, and if so, which techniques hold the key? In this work, we introduce $\text{PR}^2$, a novel and comprehensive solution for personalizing short-video search, where $\text{PR}^2$ stands for the Personalized Retrieval and Ranking augmented search system. Specifically, $\text{PR}^2$ leverages query-relevant collaborative filtering and personalized dense retrieval to extract relevant and individually tailored content from a large-scale video corpus. Furthermore, it utilizes the QIN (Query-Dominate User Interest Network) ranking model, to effectively harness user long-term preferences and real-time behaviors, and efficiently learn from user various implicit feedback through a multi-task learning framework. By deploying the $\text{PR}^2$ in production system, we have achieved the most remarkable user engagement improvements in recent years: a 10.2% increase in CTR@10, a notable 20% surge in video watch time, and a 1.6% uplift of search DAU. We believe the practical insights presented in this work are valuable especially for building and improving personalized search systems for the short video platforms.
A Self-boosted Framework for Calibrated Ranking
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:Scale-calibrated ranking systems are ubiquitous in real-world applications nowadays, which pursue accurate ranking quality and calibrated probabilistic predictions simultaneously. For instance, in the advertising ranking system, the predicted click-through rate (CTR) is utilized for ranking and required to be calibrated for the downstream cost-per-click ads bidding. Recently, multi-objective based methods have been wildly adopted as a standard approach for Calibrated Ranking, which incorporates the combination of two loss functions: a pointwise loss that focuses on calibrated absolute values and a ranking loss that emphasizes relative orderings. However, when applied to industrial online applications, existing multi-objective CR approaches still suffer from two crucial limitations. First, previous methods need to aggregate the full candidate list within a single mini-batch to compute the ranking loss. Such aggregation strategy violates extensive data shuffling which has long been proven beneficial for preventing overfitting, and thus degrades the training effectiveness. Second, existing multi-objective methods apply the two inherently conflicting loss functions on a single probabilistic prediction, which results in a sub-optimal trade-off between calibration and ranking. To tackle the two limitations, we propose a Self-Boosted framework for Calibrated Ranking (SBCR).
Two New Stenosis Detection Methods of Coronary Angiograms
Dec 14, 2021



Abstract:Coronary angiography is the "gold standard" for diagnosing coronary artery disease (CAD). At present, the methods for detecting and evaluating coronary artery stenosis cannot satisfy the clinical needs, e.g., there is no prior study of detecting stenoses in prespecified vessel segments, which is necessary in clinical practice. Two vascular stenosis detection methods are proposed to assist the diagnosis. The first one is an automatic method, which can automatically extract the entire coronary artery tree and mark all the possible stenoses. The second one is an interactive method. With this method, the user can choose any vessel segment to do further analysis of its stenoses. Experiments show that the proposed methods are robust for angiograms with various vessel structures. The precision, sensitivity, and $F_1$ score of the automatic stenosis detection method are 0.821, 0.757, and 0.788, respectively. Further investigation proves that the interactive method can provide a more precise outcome of stenosis detection, and our quantitative analysis is closer to reality. The proposed automatic method and interactive method are effective and can complement each other in clinical practice. The first method can be used for preliminary screening, and the second method can be used for further quantitative analysis. We believe the proposed solution is more suitable for the clinical diagnosis of CAD.
Two New Stenoses Detection Methods of Coronary Angiograms
Aug 03, 2021



Abstract:Coronary angiography is the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of coronary heart disease. At present, the methods for detecting coronary artery stenoses and evaluating the degree of it in coronary angiograms are either subjective or not efficient enough. Two vascular stenoses detection methods in coronary angiograms are proposed to assist the diagnosis. The first one is an automatic method, which can automatically segment the entire coronary vessels and mark the stenoses. The second one is an interactive method. With this method, the user only needs to give a start point and an end point to detect the stenoses of a certain vascular segment. We have shown that the proposed tracking methods are robust for angiograms with various vessel structure. The automatic detection method can effectively measure the diameter of the vessel and mark the stenoses in different angiograms. Further investigation proves that the results of interactive detection method can accurately reflect the true stenoses situation. The proposed automatic method and interactive method are effective in various angiograms and can complement each other in clinical practice. The first method can be used for preliminary screening and the second method can be used for further quantitative analysis. It has the potential to improve the level of clinical diagnosis of coronary heart disease.
Kalman Filtering Attention for User Behavior Modeling in CTR Prediction
Oct 20, 2020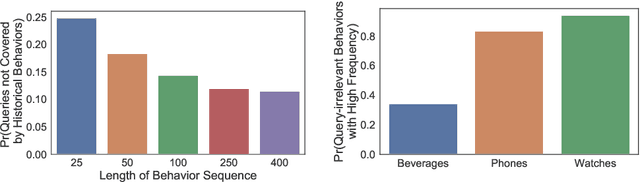
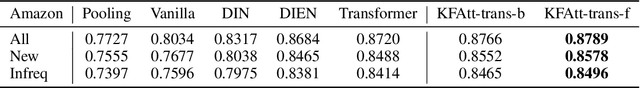
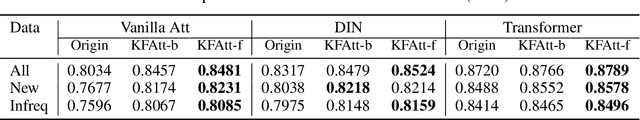
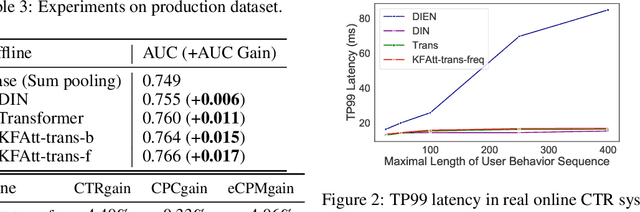
Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is one of the fundamental tasks for e-commerce search engines. As search becomes more personalized, it is necessary to capture the user interest from rich behavior data. Existing user behavior modeling algorithms develop different attention mechanisms to emphasize query-relevant behaviors and suppress irrelevant ones. Despite being extensively studied, these attentions still suffer from two limitations. First, conventional attentions mostly limit the attention field only to a single user's behaviors, which is not suitable in e-commerce where users often hunt for new demands that are irrelevant to any historical behaviors. Second, these attentions are usually biased towards frequent behaviors, which is unreasonable since high frequency does not necessarily indicate great importance. To tackle the two limitations, we propose a novel attention mechanism, termed Kalman Filtering Attention (KFAtt), that considers the weighted pooling in attention as a maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation. By incorporating a priori, KFAtt resorts to global statistics when few user behaviors are relevant. Moreover, a frequency capping mechanism is incorporated to correct the bias towards frequent behaviors. Offline experiments on both benchmark and a 10 billion scale real production dataset, together with an Online A/B test, show that KFAtt outperforms all compared state-of-the-arts. KFAtt has been deployed in the ranking system of a leading e commerce website, serving the main traffic of hundreds of millions of active users everyday.
Category-Specific CNN for Visual-aware CTR Prediction at JD.com
Jun 19, 2020



Abstract:As one of the largest B2C e-commerce platforms in China, JD com also powers a leading advertising system, serving millions of advertisers with fingertip connection to hundreds of millions of customers. In our system, as well as most e-commerce scenarios, ads are displayed with images.This makes visual-aware Click Through Rate (CTR) prediction of crucial importance to both business effectiveness and user experience. Existing algorithms usually extract visual features using off-the-shelf Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and late fuse the visual and non-visual features for the finally predicted CTR. Despite being extensively studied, this field still face two key challenges. First, although encouraging progress has been made in offline studies, applying CNNs in real systems remains non-trivial, due to the strict requirements for efficient end-to-end training and low-latency online serving. Second, the off-the-shelf CNNs and late fusion architectures are suboptimal. Specifically, off-the-shelf CNNs were designed for classification thus never take categories as input features. While in e-commerce, categories are precisely labeled and contain abundant visual priors that will help the visual modeling. Unaware of the ad category, these CNNs may extract some unnecessary category-unrelated features, wasting CNN's limited expression ability. To overcome the two challenges, we propose Category-specific CNN (CSCNN) specially for CTR prediction. CSCNN early incorporates the category knowledge with a light-weighted attention-module on each convolutional layer. This enables CSCNN to extract expressive category-specific visual patterns that benefit the CTR prediction. Offline experiments on benchmark and a 10 billion scale real production dataset from JD, together with an Online A/B test show that CSCNN outperforms all compared state-of-the-art algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge