Yongjun Bao
TempMe: Video Temporal Token Merging for Efficient Text-Video Retrieval
Sep 02, 2024Abstract:Most text-video retrieval methods utilize the text-image pre-trained CLIP as a backbone, incorporating complex modules that result in high computational overhead. As a result, many studies focus on efficient fine-tuning. The primary challenge in efficient adaption arises from the inherent differences between image and video modalities. Each sampled video frame must be processed by the image encoder independently, which increases complexity and complicates practical deployment. Although existing efficient methods fine-tune with small trainable parameters, they still incur high inference costs due to the large token number. In this work, we argue that temporal redundancy significantly contributes to the model's high complexity due to the repeated information in consecutive frames. Existing token compression methods for image models fail to solve the unique challenges, as they overlook temporal redundancy across frames. To tackle these problems, we propose Temporal Token Merging (TempMe) to reduce temporal redundancy. Specifically, we introduce a progressive multi-granularity framework. By gradually combining neighboring clips, we merge temporal tokens across different frames and learn video-level features, leading to lower complexity and better performance. Extensive experiments validate the superiority of our TempMe. Compared to previous efficient text-video retrieval methods, TempMe significantly reduces output tokens by 95% and GFLOPs by 51%, while achieving a 1.8X speedup and a 4.4% R-Sum improvement. Additionally, TempMe exhibits robust generalization capabilities by integrating effectively with both efficient and full fine-tuning methods. With full fine-tuning, TempMe achieves a significant 7.9% R-Sum improvement, trains 1.57X faster, and utilizes 75.2% GPU memory usage. Our code will be released.
PYRA: Parallel Yielding Re-Activation for Training-Inference Efficient Task Adaptation
Mar 14, 2024



Abstract:Recently, the scale of transformers has grown rapidly, which introduces considerable challenges in terms of training overhead and inference efficiency in the scope of task adaptation. Existing works, namely Parameter-Efficient Fine-Tuning (PEFT) and model compression, have separately investigated the challenges. However, PEFT cannot guarantee the inference efficiency of the original backbone, especially for large-scale models. Model compression requires significant training costs for structure searching and re-training. Consequently, a simple combination of them cannot guarantee accomplishing both training efficiency and inference efficiency with minimal costs. In this paper, we propose a novel Parallel Yielding Re-Activation (PYRA) method for such a challenge of training-inference efficient task adaptation. PYRA first utilizes parallel yielding adaptive weights to comprehensively perceive the data distribution in downstream tasks. A re-activation strategy for token modulation is then applied for tokens to be merged, leading to calibrated token features. Extensive experiments demonstrate that PYRA outperforms all competing methods under both low compression rate and high compression rate, demonstrating its effectiveness and superiority in maintaining both training efficiency and inference efficiency for large-scale foundation models. Our code will be released to the public.
Exploring Structured Semantic Prior for Multi Label Recognition with Incomplete Labels
Mar 24, 2023



Abstract:Multi-label recognition (MLR) with incomplete labels is very challenging. Recent works strive to explore the image-to-label correspondence in the vision-language model, \ie, CLIP, to compensate for insufficient annotations. In spite of promising performance, they generally overlook the valuable prior about the label-to-label correspondence. In this paper, we advocate remedying the deficiency of label supervision for the MLR with incomplete labels by deriving a structured semantic prior about the label-to-label correspondence via a semantic prior prompter. We then present a novel Semantic Correspondence Prompt Network (SCPNet), which can thoroughly explore the structured semantic prior. A Prior-Enhanced Self-Supervised Learning method is further introduced to enhance the use of the prior. Comprehensive experiments and analyses on several widely used benchmark datasets show that our method significantly outperforms existing methods on all datasets, well demonstrating the effectiveness and the superiority of our method. Our code will be available at https://github.com/jameslahm/SCPNet.
* Accepted by IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR) 2023
Adaptive Experimentation with Delayed Binary Feedback
Feb 02, 2022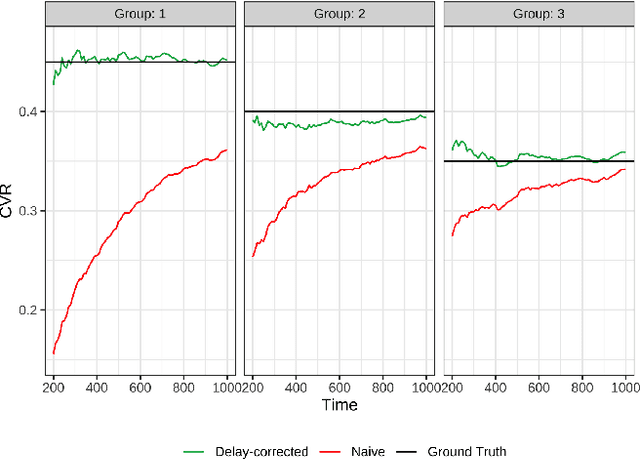
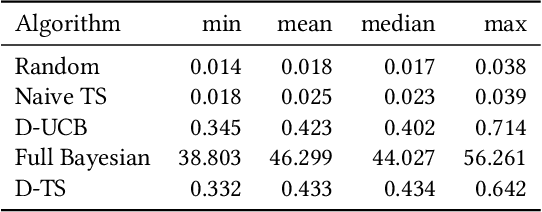
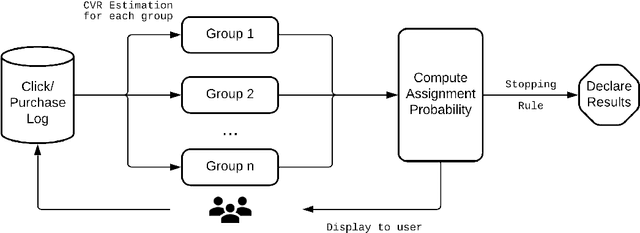
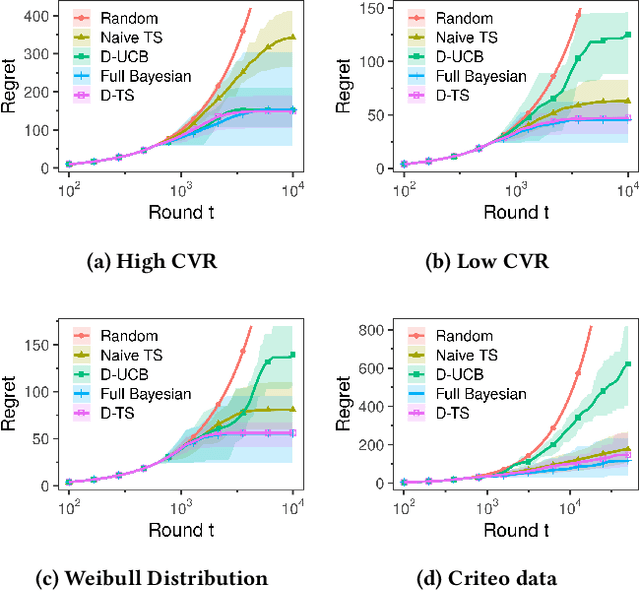
Abstract:Conducting experiments with objectives that take significant delays to materialize (e.g. conversions, add-to-cart events, etc.) is challenging. Although the classical "split sample testing" is still valid for the delayed feedback, the experiment will take longer to complete, which also means spending more resources on worse-performing strategies due to their fixed allocation schedules. Alternatively, adaptive approaches such as "multi-armed bandits" are able to effectively reduce the cost of experimentation. But these methods generally cannot handle delayed objectives directly out of the box. This paper presents an adaptive experimentation solution tailored for delayed binary feedback objectives by estimating the real underlying objectives before they materialize and dynamically allocating variants based on the estimates. Experiments show that the proposed method is more efficient for delayed feedback compared to various other approaches and is robust in different settings. In addition, we describe an experimentation product powered by this algorithm. This product is currently deployed in the online experimentation platform of JD.com, a large e-commerce company and a publisher of digital ads.
Blending Advertising with Organic Content in E-Commerce: A Virtual Bids Optimization Approach
May 28, 2021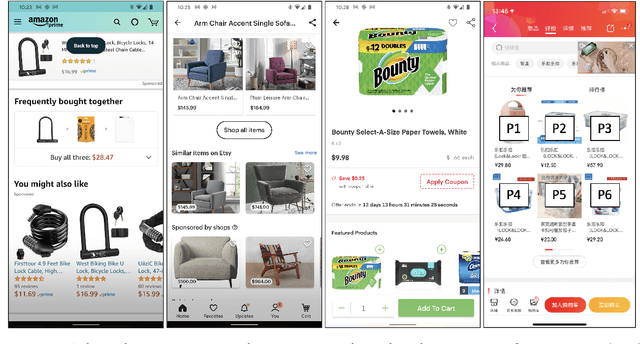
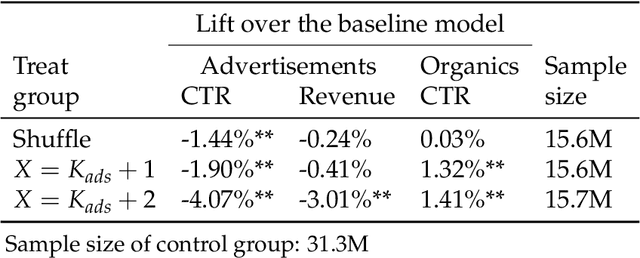
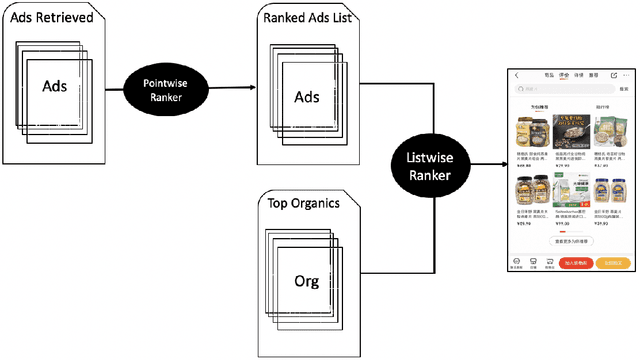
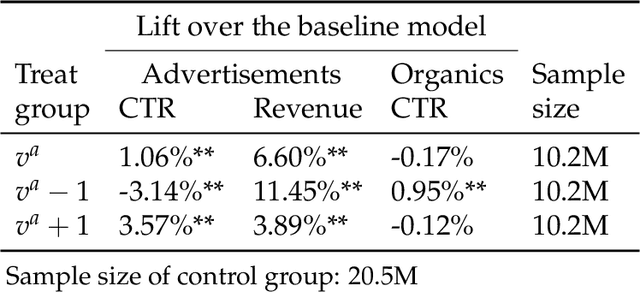
Abstract:In e-commerce platforms, sponsored and non-sponsored content are jointly displayed to users and both may interactively influence their engagement behavior. The former content helps advertisers achieve their marketing goals and provides a stream of ad revenue to the platform. The latter content contributes to users' engagement with the platform, which is key to its long-term health. A burning issue for e-commerce platform design is how to blend advertising with content in a way that respects these interactions and balances these multiple business objectives. This paper describes a system developed for this purpose in the context of blending personalized sponsored content with non-sponsored content on the product detail pages of JD.COM, an e-commerce company. This system has three key features: (1) Optimization of multiple competing business objectives through a new virtual bids approach and the expressiveness of the latent, implicit valuation of the platform for the multiple objectives via these virtual bids. (2) Modeling of users' click behavior as a function of their characteristics, the individual characteristics of each sponsored content and the influence exerted by other sponsored and non-sponsored content displayed alongside through a deep learning approach; (3) Consideration of externalities in the allocation of ads, thereby making it directly compatible with a Vickrey-Clarke-Groves (VCG) auction scheme for the computation of payments in the presence of these externalities. The system is currently deployed and serving all traffic through JD.COM's mobile application. Experiments demonstrating the performance and advantages of the system are presented.
Probing Product Description Generation via Posterior Distillation
Mar 02, 2021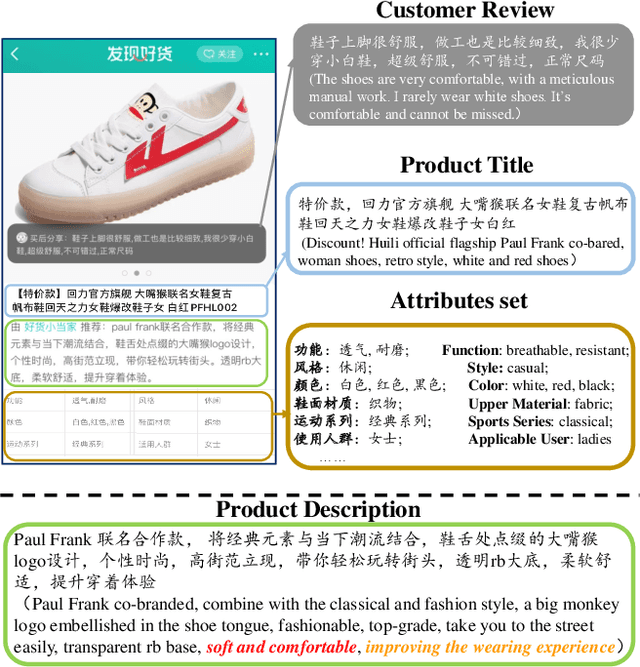

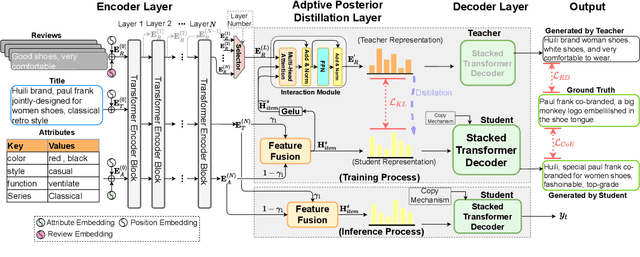

Abstract:In product description generation (PDG), the user-cared aspect is critical for the recommendation system, which can not only improve user's experiences but also obtain more clicks. High-quality customer reviews can be considered as an ideal source to mine user-cared aspects. However, in reality, a large number of new products (known as long-tailed commodities) cannot gather sufficient amount of customer reviews, which brings a big challenge in the product description generation task. Existing works tend to generate the product description solely based on item information, i.e., product attributes or title words, which leads to tedious contents and cannot attract customers effectively. To tackle this problem, we propose an adaptive posterior network based on Transformer architecture that can utilize user-cared information from customer reviews. Specifically, we first extend the self-attentive Transformer encoder to encode product titles and attributes. Then, we apply an adaptive posterior distillation module to utilize useful review information, which integrates user-cared aspects to the generation process. Finally, we apply a Transformer-based decoding phase with copy mechanism to automatically generate the product description. Besides, we also collect a large-scare Chinese product description dataset to support our work and further research in this field. Experimental results show that our model is superior to traditional generative models in both automatic indicators and human evaluation.
DADNN: Multi-Scene CTR Prediction via Domain-Aware Deep Neural Network
Nov 24, 2020
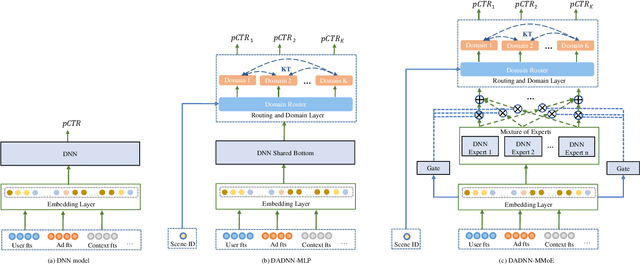
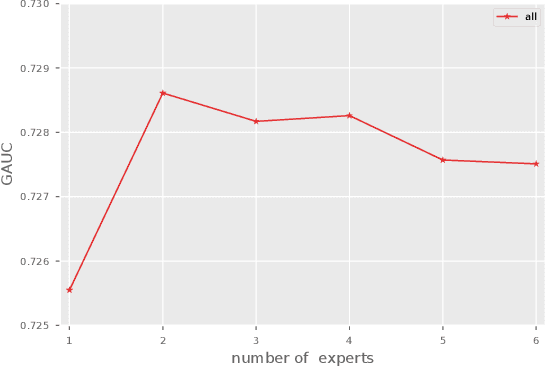
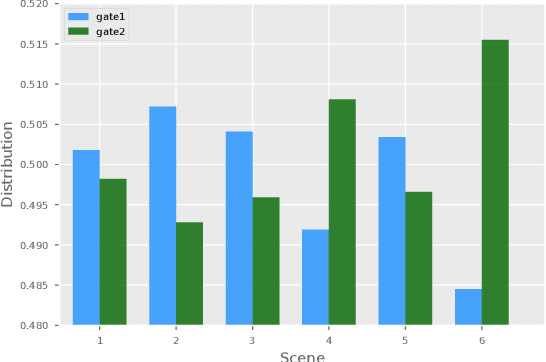
Abstract:Click through rate(CTR) prediction is a core task in advertising systems. The booming e-commerce business in our company, results in a growing number of scenes. Most of them are so-called long-tail scenes, which means that the traffic of a single scene is limited, but the overall traffic is considerable. Typical studies mainly focus on serving a single scene with a well designed model. However, this method brings excessive resource consumption both on offline training and online serving. Besides, simply training a single model with data from multiple scenes ignores the characteristics of their own. To address these challenges, we propose a novel but practical model named Domain-Aware Deep Neural Network(DADNN) by serving multiple scenes with only one model. Specifically, shared bottom block among all scenes is applied to learn a common representation, while domain-specific heads maintain the characteristics of every scene. Besides, knowledge transfer is introduced to enhance the opportunity of knowledge sharing among different scenes. In this paper, we study two instances of DADNN where its shared bottom block is multilayer perceptron(MLP) and Multi-gate Mixture-of-Experts(MMoE) respectively, for which we denote as DADNN-MLP and DADNN-MMoE.Comprehensive offline experiments on a real production dataset from our company show that DADNN outperforms several state-of-the-art methods for multi-scene CTR prediction. Extensive online A/B tests reveal that DADNN-MLP contributes up to 6.7% CTR and 3.0% CPM(Cost Per Mille) promotion compared with a well-engineered DCN model. Furthermore, DADNN-MMoE outperforms DADNN-MLP with a relative improvement of 2.2% and 2.7% on CTR and CPM respectively. More importantly, DADNN utilizes a single model for multiple scenes which saves a lot of offline training and online serving resources.
Kalman Filtering Attention for User Behavior Modeling in CTR Prediction
Oct 20, 2020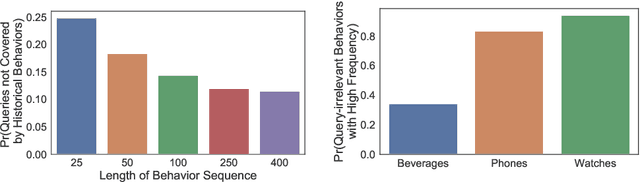
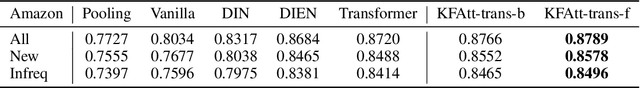
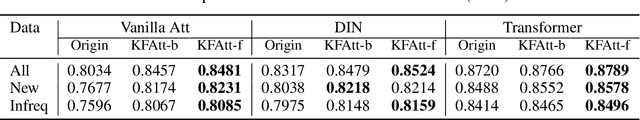
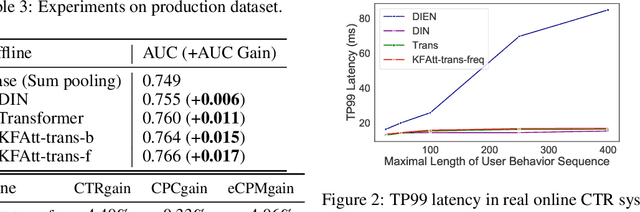
Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is one of the fundamental tasks for e-commerce search engines. As search becomes more personalized, it is necessary to capture the user interest from rich behavior data. Existing user behavior modeling algorithms develop different attention mechanisms to emphasize query-relevant behaviors and suppress irrelevant ones. Despite being extensively studied, these attentions still suffer from two limitations. First, conventional attentions mostly limit the attention field only to a single user's behaviors, which is not suitable in e-commerce where users often hunt for new demands that are irrelevant to any historical behaviors. Second, these attentions are usually biased towards frequent behaviors, which is unreasonable since high frequency does not necessarily indicate great importance. To tackle the two limitations, we propose a novel attention mechanism, termed Kalman Filtering Attention (KFAtt), that considers the weighted pooling in attention as a maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation. By incorporating a priori, KFAtt resorts to global statistics when few user behaviors are relevant. Moreover, a frequency capping mechanism is incorporated to correct the bias towards frequent behaviors. Offline experiments on both benchmark and a 10 billion scale real production dataset, together with an Online A/B test, show that KFAtt outperforms all compared state-of-the-arts. KFAtt has been deployed in the ranking system of a leading e commerce website, serving the main traffic of hundreds of millions of active users everyday.
Group-wise Contrastive Learning for Neural Dialogue Generation
Oct 13, 2020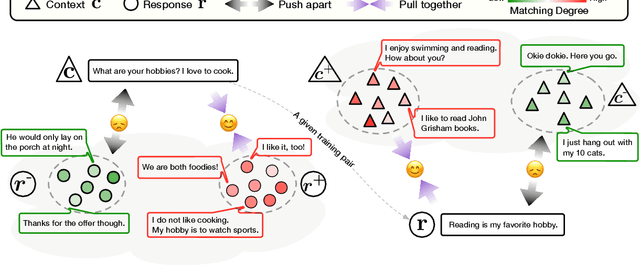
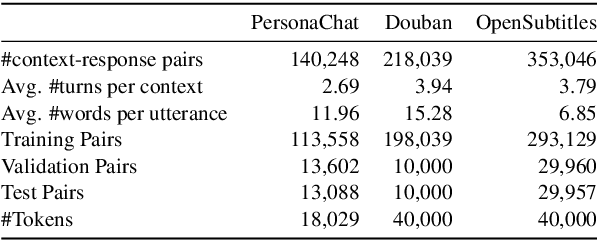
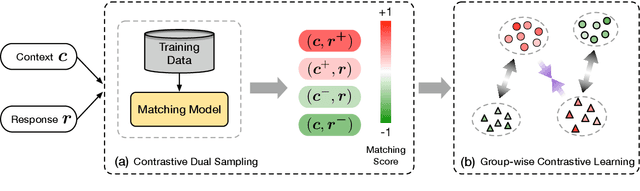
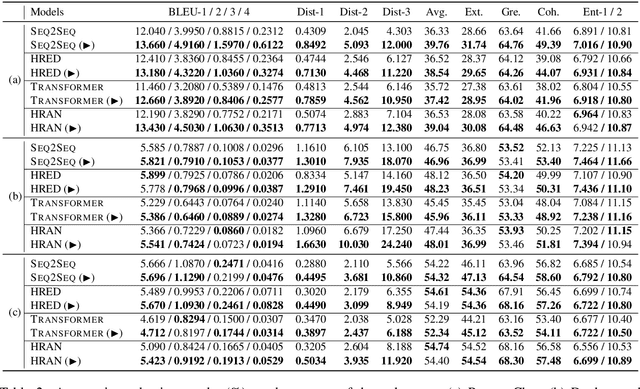
Abstract:Neural dialogue response generation has gained much popularity in recent years. Maximum Likelihood Estimation (MLE) objective is widely adopted in existing dialogue model learning. However, models trained with MLE objective function are plagued by the low-diversity issue when it comes to the open-domain conversational setting. Inspired by the observation that humans not only learn from the positive signals but also benefit from correcting behaviors of undesirable actions, in this work, we introduce contrastive learning into dialogue generation, where the model explicitly perceives the difference between the well-chosen positive and negative utterances. Specifically, we employ a pretrained baseline model as a reference. During contrastive learning, the target dialogue model is trained to give higher conditional probabilities for the positive samples, and lower conditional probabilities for those negative samples, compared to the reference model. To manage the multi-mapping relations prevailed in human conversation, we augment contrastive dialogue learning with group-wise dual sampling. Extensive experimental results show that the proposed group-wise contrastive learning framework is suited for training a wide range of neural dialogue generation models with very favorable performance over the baseline training approaches.
Category-Specific CNN for Visual-aware CTR Prediction at JD.com
Jun 19, 2020



Abstract:As one of the largest B2C e-commerce platforms in China, JD com also powers a leading advertising system, serving millions of advertisers with fingertip connection to hundreds of millions of customers. In our system, as well as most e-commerce scenarios, ads are displayed with images.This makes visual-aware Click Through Rate (CTR) prediction of crucial importance to both business effectiveness and user experience. Existing algorithms usually extract visual features using off-the-shelf Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and late fuse the visual and non-visual features for the finally predicted CTR. Despite being extensively studied, this field still face two key challenges. First, although encouraging progress has been made in offline studies, applying CNNs in real systems remains non-trivial, due to the strict requirements for efficient end-to-end training and low-latency online serving. Second, the off-the-shelf CNNs and late fusion architectures are suboptimal. Specifically, off-the-shelf CNNs were designed for classification thus never take categories as input features. While in e-commerce, categories are precisely labeled and contain abundant visual priors that will help the visual modeling. Unaware of the ad category, these CNNs may extract some unnecessary category-unrelated features, wasting CNN's limited expression ability. To overcome the two challenges, we propose Category-specific CNN (CSCNN) specially for CTR prediction. CSCNN early incorporates the category knowledge with a light-weighted attention-module on each convolutional layer. This enables CSCNN to extract expressive category-specific visual patterns that benefit the CTR prediction. Offline experiments on benchmark and a 10 billion scale real production dataset from JD, together with an Online A/B test show that CSCNN outperforms all compared state-of-the-art algorithms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge