Yanyan Lan
S$^2$Drug: Bridging Protein Sequence and 3D Structure in Contrastive Representation Learning for Virtual Screening
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:Virtual screening (VS) is an essential task in drug discovery, focusing on the identification of small-molecule ligands that bind to specific protein pockets. Existing deep learning methods, from early regression models to recent contrastive learning approaches, primarily rely on structural data while overlooking protein sequences, which are more accessible and can enhance generalizability. However, directly integrating protein sequences poses challenges due to the redundancy and noise in large-scale protein-ligand datasets. To address these limitations, we propose \textbf{S$^2$Drug}, a two-stage framework that explicitly incorporates protein \textbf{S}equence information and 3D \textbf{S}tructure context in protein-ligand contrastive representation learning. In the first stage, we perform protein sequence pretraining on ChemBL using an ESM2-based backbone, combined with a tailored data sampling strategy to reduce redundancy and noise on both protein and ligand sides. In the second stage, we fine-tune on PDBBind by fusing sequence and structure information through a residue-level gating module, while introducing an auxiliary binding site prediction task. This auxiliary task guides the model to accurately localize binding residues within the protein sequence and capture their 3D spatial arrangement, thereby refining protein-ligand matching. Across multiple benchmarks, S$^2$Drug consistently improves virtual screening performance and achieves strong results on binding site prediction, demonstrating the value of bridging sequence and structure in contrastive learning.
Coder as Editor: Code-driven Interpretable Molecular Optimization
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Molecular optimization is a central task in drug discovery that requires precise structural reasoning and domain knowledge. While large language models (LLMs) have shown promise in generating high-level editing intentions in natural language, they often struggle to faithfully execute these modifications-particularly when operating on non-intuitive representations like SMILES. We introduce MECo, a framework that bridges reasoning and execution by translating editing actions into executable code. MECo reformulates molecular optimization for LLMs as a cascaded framework: generating human-interpretable editing intentions from a molecule and property goal, followed by translating those intentions into executable structural edits via code generation. Our approach achieves over 98% accuracy in reproducing held-out realistic edits derived from chemical reactions and target-specific compound pairs. On downstream optimization benchmarks spanning physicochemical properties and target activities, MECo substantially improves consistency by 38-86 percentage points to 90%+ and achieves higher success rates over SMILES-based baselines while preserving structural similarity. By aligning intention with execution, MECo enables consistent, controllable and interpretable molecular design, laying the foundation for high-fidelity feedback loops and collaborative human-AI workflows in drug discovery.
AANet: Virtual Screening under Structural Uncertainty via Alignment and Aggregation
Jun 06, 2025Abstract:Virtual screening (VS) is a critical component of modern drug discovery, yet most existing methods--whether physics-based or deep learning-based--are developed around holo protein structures with known ligand-bound pockets. Consequently, their performance degrades significantly on apo or predicted structures such as those from AlphaFold2, which are more representative of real-world early-stage drug discovery, where pocket information is often missing. In this paper, we introduce an alignment-and-aggregation framework to enable accurate virtual screening under structural uncertainty. Our method comprises two core components: (1) a tri-modal contrastive learning module that aligns representations of the ligand, the holo pocket, and cavities detected from structures, thereby enhancing robustness to pocket localization error; and (2) a cross-attention based adapter for dynamically aggregating candidate binding sites, enabling the model to learn from activity data even without precise pocket annotations. We evaluated our method on a newly curated benchmark of apo structures, where it significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods in blind apo setting, improving the early enrichment factor (EF1%) from 11.75 to 37.19. Notably, it also maintains strong performance on holo structures. These results demonstrate the promise of our approach in advancing first-in-class drug discovery, particularly in scenarios lacking experimentally resolved protein-ligand complexes.
PharmAgents: Building a Virtual Pharma with Large Language Model Agents
Mar 31, 2025Abstract:The discovery of novel small molecule drugs remains a critical scientific challenge with far-reaching implications for treating diseases and advancing human health. Traditional drug development--especially for small molecule therapeutics--is a highly complex, resource-intensive, and time-consuming process that requires multidisciplinary collaboration. Recent breakthroughs in artificial intelligence (AI), particularly the rise of large language models (LLMs), present a transformative opportunity to streamline and accelerate this process. In this paper, we introduce PharmAgents, a virtual pharmaceutical ecosystem driven by LLM-based multi-agent collaboration. PharmAgents simulates the full drug discovery workflow--from target discovery to preclinical evaluation--by integrating explainable, LLM-driven agents equipped with specialized machine learning models and computational tools. Through structured knowledge exchange and automated optimization, PharmAgents identifies potential therapeutic targets, discovers promising lead compounds, enhances binding affinity and key molecular properties, and performs in silico analyses of toxicity and synthetic feasibility. Additionally, the system supports interpretability, agent interaction, and self-evolvement, enabling it to refine future drug designs based on prior experience. By showcasing the potential of LLM-powered multi-agent systems in drug discovery, this work establishes a new paradigm for autonomous, explainable, and scalable pharmaceutical research, with future extensions toward comprehensive drug lifecycle management.
Straight-Line Diffusion Model for Efficient 3D Molecular Generation
Mar 04, 2025Abstract:Diffusion-based models have shown great promise in molecular generation but often require a large number of sampling steps to generate valid samples. In this paper, we introduce a novel Straight-Line Diffusion Model (SLDM) to tackle this problem, by formulating the diffusion process to follow a linear trajectory. The proposed process aligns well with the noise sensitivity characteristic of molecular structures and uniformly distributes reconstruction effort across the generative process, thus enhancing learning efficiency and efficacy. Consequently, SLDM achieves state-of-the-art performance on 3D molecule generation benchmarks, delivering a 100-fold improvement in sampling efficiency. Furthermore, experiments on toy data and image generation tasks validate the generality and robustness of SLDM, showcasing its potential across diverse generative modeling domains.
UniGEM: A Unified Approach to Generation and Property Prediction for Molecules
Oct 14, 2024



Abstract:Molecular generation and molecular property prediction are both crucial for drug discovery, but they are often developed independently. Inspired by recent studies, which demonstrate that diffusion model, a prominent generative approach, can learn meaningful data representations that enhance predictive tasks, we explore the potential for developing a unified generative model in the molecular domain that effectively addresses both molecular generation and property prediction tasks. However, the integration of these tasks is challenging due to inherent inconsistencies, making simple multi-task learning ineffective. To address this, we propose UniGEM, the first unified model to successfully integrate molecular generation and property prediction, delivering superior performance in both tasks. Our key innovation lies in a novel two-phase generative process, where predictive tasks are activated in the later stages, after the molecular scaffold is formed. We further enhance task balance through innovative training strategies. Rigorous theoretical analysis and comprehensive experiments demonstrate our significant improvements in both tasks. The principles behind UniGEM hold promise for broader applications, including natural language processing and computer vision.
Pre-training with Fractional Denoising to Enhance Molecular Property Prediction
Jul 14, 2024Abstract:Deep learning methods have been considered promising for accelerating molecular screening in drug discovery and material design. Due to the limited availability of labelled data, various self-supervised molecular pre-training methods have been presented. While many existing methods utilize common pre-training tasks in computer vision (CV) and natural language processing (NLP), they often overlook the fundamental physical principles governing molecules. In contrast, applying denoising in pre-training can be interpreted as an equivalent force learning, but the limited noise distribution introduces bias into the molecular distribution. To address this issue, we introduce a molecular pre-training framework called fractional denoising (Frad), which decouples noise design from the constraints imposed by force learning equivalence. In this way, the noise becomes customizable, allowing for incorporating chemical priors to significantly improve molecular distribution modeling. Experiments demonstrate that our framework consistently outperforms existing methods, establishing state-of-the-art results across force prediction, quantum chemical properties, and binding affinity tasks. The refined noise design enhances force accuracy and sampling coverage, which contribute to the creation of physically consistent molecular representations, ultimately leading to superior predictive performance.
SIU: A Million-Scale Structural Small Molecule-Protein Interaction Dataset for Unbiased Bioactivity Prediction
Jun 13, 2024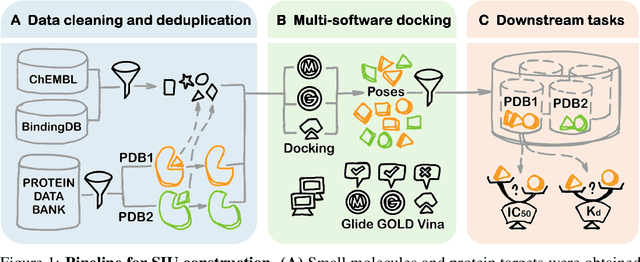

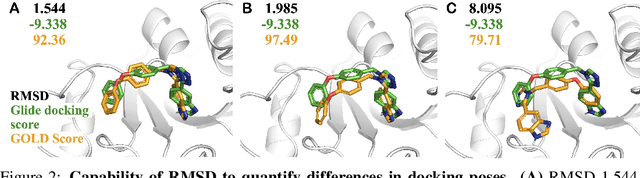
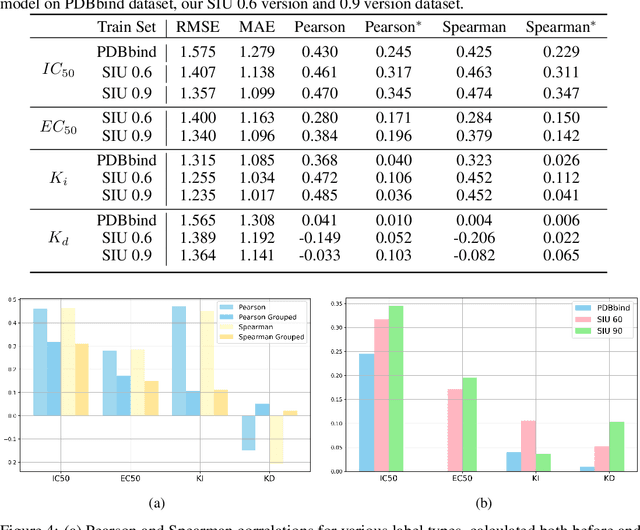
Abstract:Small molecules play a pivotal role in modern medicine, and scrutinizing their interactions with protein targets is essential for the discovery and development of novel, life-saving therapeutics. The term "bioactivity" encompasses various biological effects resulting from these interactions, including both binding and functional responses. The magnitude of bioactivity dictates the therapeutic or toxic pharmacological outcomes of small molecules, rendering accurate bioactivity prediction crucial for the development of safe and effective drugs. However, existing structural datasets of small molecule-protein interactions are often limited in scale and lack systematically organized bioactivity labels, thereby impeding our understanding of these interactions and precise bioactivity prediction. In this study, we introduce a comprehensive dataset of small molecule-protein interactions, consisting of over a million binding structures, each annotated with real biological activity labels. This dataset is designed to facilitate unbiased bioactivity prediction. We evaluated several classical models on this dataset, and the results demonstrate that the task of unbiased bioactivity prediction is challenging yet essential.
From Theory to Therapy: Reframing SBDD Model Evaluation via Practical Metrics
Jun 13, 2024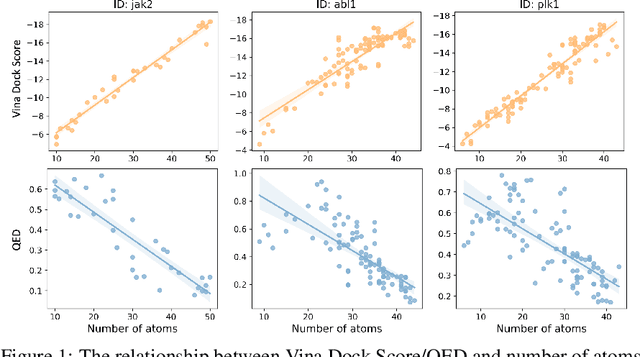
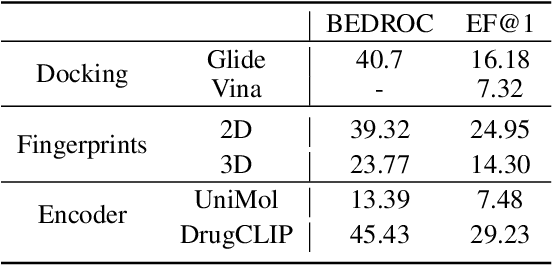
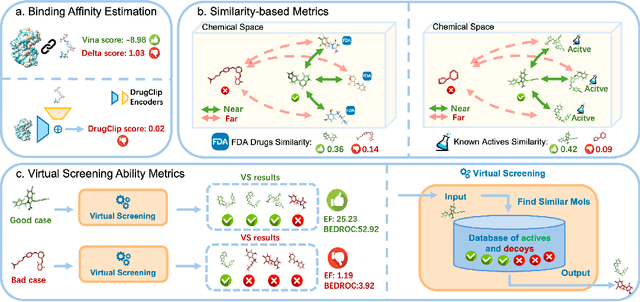
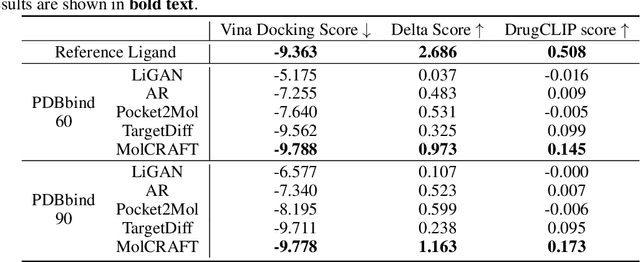
Abstract:Recent advancements in structure-based drug design (SBDD) have significantly enhanced the efficiency and precision of drug discovery by generating molecules tailored to bind specific protein pockets. Despite these technological strides, their practical application in real-world drug development remains challenging due to the complexities of synthesizing and testing these molecules. The reliability of the Vina docking score, the current standard for assessing binding abilities, is increasingly questioned due to its susceptibility to overfitting. To address these limitations, we propose a comprehensive evaluation framework that includes assessing the similarity of generated molecules to known active compounds, introducing a virtual screening-based metric for practical deployment capabilities, and re-evaluating binding affinity more rigorously. Our experiments reveal that while current SBDD models achieve high Vina scores, they fall short in practical usability metrics, highlighting a significant gap between theoretical predictions and real-world applicability. Our proposed metrics and dataset aim to bridge this gap, enhancing the practical applicability of future SBDD models and aligning them more closely with the needs of pharmaceutical research and development.
Multi-level Interaction Modeling for Protein Mutational Effect Prediction
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Protein-protein interactions are central mediators in many biological processes. Accurately predicting the effects of mutations on interactions is crucial for guiding the modulation of these interactions, thereby playing a significant role in therapeutic development and drug discovery. Mutations generally affect interactions hierarchically across three levels: mutated residues exhibit different sidechain conformations, which lead to changes in the backbone conformation, eventually affecting the binding affinity between proteins. However, existing methods typically focus only on sidechain-level interaction modeling, resulting in suboptimal predictions. In this work, we propose a self-supervised multi-level pre-training framework, ProMIM, to fully capture all three levels of interactions with well-designed pretraining objectives. Experiments show ProMIM outperforms all the baselines on the standard benchmark, especially on mutations where significant changes in backbone conformations may occur. In addition, leading results from zero-shot evaluations for SARS-CoV-2 mutational effect prediction and antibody optimization underscore the potential of ProMIM as a powerful next-generation tool for developing novel therapeutic approaches and new drugs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge