Risheng Liu
Every SAM Drop Counts: Embracing Semantic Priors for Multi-Modality Image Fusion and Beyond
Mar 03, 2025
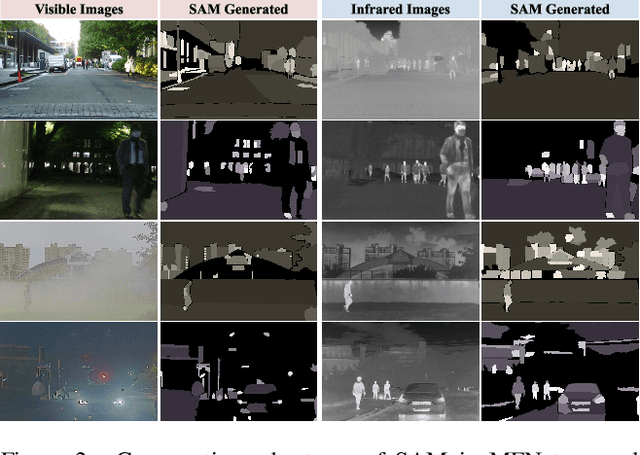
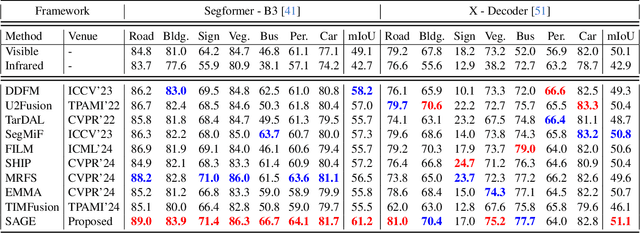

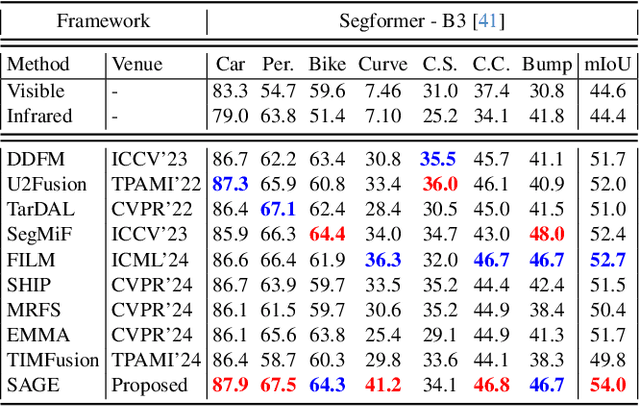
Abstract:Multi-modality image fusion, particularly infrared and visible image fusion, plays a crucial role in integrating diverse modalities to enhance scene understanding. Early research primarily focused on visual quality, yet challenges remain in preserving fine details, making it difficult to adapt to subsequent tasks. Recent approaches have shifted towards task-specific design, but struggle to achieve the ``The Best of Both Worlds'' due to inconsistent optimization goals. To address these issues, we propose a novel method that leverages the semantic knowledge from the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to Grow the quality of fusion results and Establish downstream task adaptability, namely SAGE. Specifically, we design a Semantic Persistent Attention (SPA) Module that efficiently maintains source information via the persistent repository while extracting high-level semantic priors from SAM. More importantly, to eliminate the impractical dependence on SAM during inference, we introduce a bi-level optimization-driven distillation mechanism with triplet losses, which allow the student network to effectively extract knowledge at the feature, pixel, and contrastive semantic levels, thereby removing reliance on the cumbersome SAM model. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves a balance between high-quality visual results and downstream task adaptability while maintaining practical deployment efficiency.
DEAL: Data-Efficient Adversarial Learning for High-Quality Infrared Imaging
Mar 02, 2025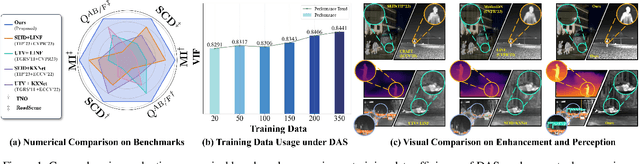
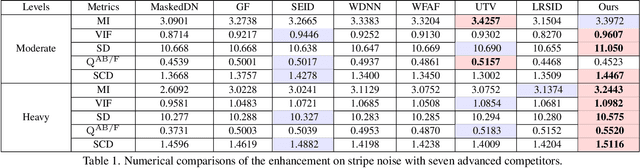
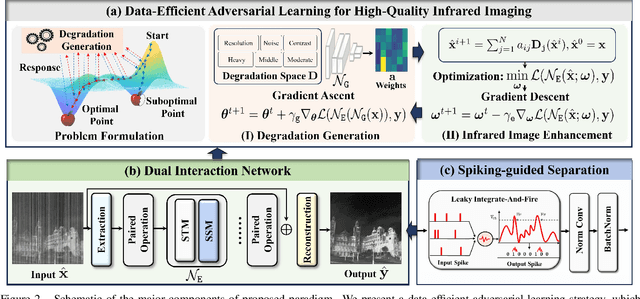
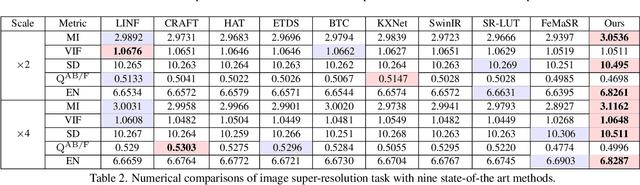
Abstract:Thermal imaging is often compromised by dynamic, complex degradations caused by hardware limitations and unpredictable environmental factors. The scarcity of high-quality infrared data, coupled with the challenges of dynamic, intricate degradations, makes it difficult to recover details using existing methods. In this paper, we introduce thermal degradation simulation integrated into the training process via a mini-max optimization, by modeling these degraded factors as adversarial attacks on thermal images. The simulation is dynamic to maximize objective functions, thus capturing a broad spectrum of degraded data distributions. This approach enables training with limited data, thereby improving model performance.Additionally, we introduce a dual-interaction network that combines the benefits of spiking neural networks with scale transformation to capture degraded features with sharp spike signal intensities. This architecture ensures compact model parameters while preserving efficient feature representation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method not only achieves superior visual quality under diverse single and composited degradation, but also delivers a significant reduction in processing when trained on only fifty clear images, outperforming existing techniques in efficiency and accuracy. The source code will be available at https://github.com/LiuZhu-CV/DEAL.
Infrared and Visible Image Fusion: From Data Compatibility to Task Adaption
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:Infrared-visible image fusion (IVIF) is a critical task in computer vision, aimed at integrating the unique features of both infrared and visible spectra into a unified representation. Since 2018, the field has entered the deep learning era, with an increasing variety of approaches introducing a range of networks and loss functions to enhance visual performance. However, challenges such as data compatibility, perception accuracy, and efficiency remain. Unfortunately, there is a lack of recent comprehensive surveys that address this rapidly expanding domain. This paper fills that gap by providing a thorough survey covering a broad range of topics. We introduce a multi-dimensional framework to elucidate common learning-based IVIF methods, from visual enhancement strategies to data compatibility and task adaptability. We also present a detailed analysis of these approaches, accompanied by a lookup table clarifying their core ideas. Furthermore, we summarize performance comparisons, both quantitatively and qualitatively, focusing on registration, fusion, and subsequent high-level tasks. Beyond technical analysis, we discuss potential future directions and open issues in this area. For further details, visit our GitHub repository: https://github.com/RollingPlain/IVIF_ZOO.
HUPE: Heuristic Underwater Perceptual Enhancement with Semantic Collaborative Learning
Nov 29, 2024Abstract:Underwater images are often affected by light refraction and absorption, reducing visibility and interfering with subsequent applications. Existing underwater image enhancement methods primarily focus on improving visual quality while overlooking practical implications. To strike a balance between visual quality and application, we propose a heuristic invertible network for underwater perception enhancement, dubbed HUPE, which enhances visual quality and demonstrates flexibility in handling other downstream tasks. Specifically, we introduced an information-preserving reversible transformation with embedded Fourier transform to establish a bidirectional mapping between underwater images and their clear images. Additionally, a heuristic prior is incorporated into the enhancement process to better capture scene information. To further bridge the feature gap between vision-based enhancement images and application-oriented images, a semantic collaborative learning module is applied in the joint optimization process of the visual enhancement task and the downstream task, which guides the proposed enhancement model to extract more task-oriented semantic features while obtaining visually pleasing images. Extensive experiments, both quantitative and qualitative, demonstrate the superiority of our HUPE over state-of-the-art methods. The source code is available at https://github.com/ZengxiZhang/HUPE.
Advancing Generalized Transfer Attack with Initialization Derived Bilevel Optimization and Dynamic Sequence Truncation
Jun 04, 2024



Abstract:Transfer attacks generate significant interest for real-world black-box applications by crafting transferable adversarial examples through surrogate models. Whereas, existing works essentially directly optimize the single-level objective w.r.t. the surrogate model, which always leads to poor interpretability of attack mechanism and limited generalization performance over unknown victim models. In this work, we propose the \textbf{B}il\textbf{E}vel \textbf{T}ransfer \textbf{A}ttac\textbf{K} (BETAK) framework by establishing an initialization derived bilevel optimization paradigm, which explicitly reformulates the nested constraint relationship between the Upper-Level (UL) pseudo-victim attacker and the Lower-Level (LL) surrogate attacker. Algorithmically, we introduce the Hyper Gradient Response (HGR) estimation as an effective feedback for the transferability over pseudo-victim attackers, and propose the Dynamic Sequence Truncation (DST) technique to dynamically adjust the back-propagation path for HGR and reduce computational overhead simultaneously. Meanwhile, we conduct detailed algorithmic analysis and provide convergence guarantee to support non-convexity of the LL surrogate attacker. Extensive evaluations demonstrate substantial improvement of BETAK (e.g., $\mathbf{53.41}$\% increase of attack success rates against IncRes-v$2_{ens}$) against different victims and defense methods in targeted and untargeted attack scenarios. The source code is available at https://github.com/callous-youth/BETAK.
Moreau Envelope for Nonconvex Bi-Level Optimization: A Single-loop and Hessian-free Solution Strategy
May 16, 2024


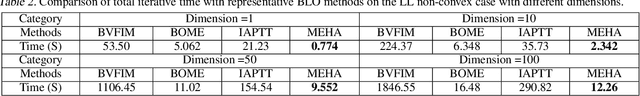
Abstract:This work focuses on addressing two major challenges in the context of large-scale nonconvex Bi-Level Optimization (BLO) problems, which are increasingly applied in machine learning due to their ability to model nested structures. These challenges involve ensuring computational efficiency and providing theoretical guarantees. While recent advances in scalable BLO algorithms have primarily relied on lower-level convexity simplification, our work specifically tackles large-scale BLO problems involving nonconvexity in both the upper and lower levels. We simultaneously address computational and theoretical challenges by introducing an innovative single-loop gradient-based algorithm, utilizing the Moreau envelope-based reformulation, and providing non-asymptotic convergence analysis for general nonconvex BLO problems. Notably, our algorithm relies solely on first-order gradient information, enhancing its practicality and efficiency, especially for large-scale BLO learning tasks. We validate our approach's effectiveness through experiments on various synthetic problems, two typical hyper-parameter learning tasks, and a real-world neural architecture search application, collectively demonstrating its superior performance.
Towards Robust Image Stitching: An Adaptive Resistance Learning against Compatible Attacks
Feb 25, 2024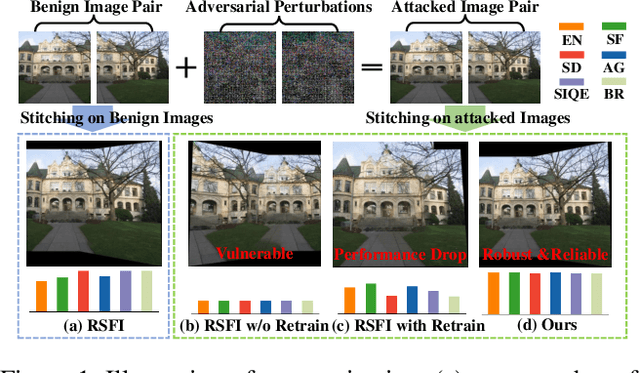
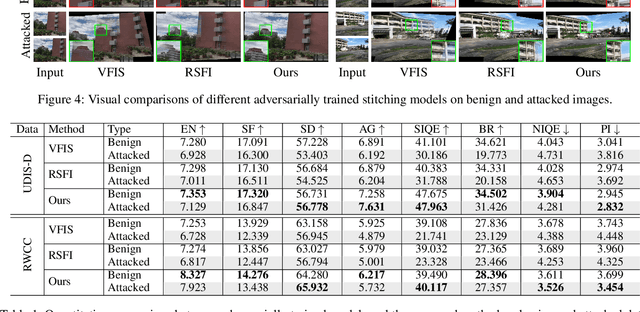
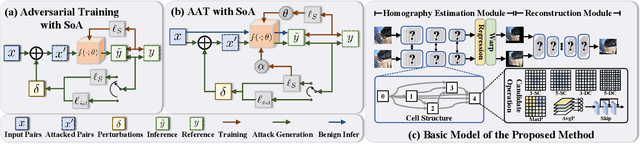
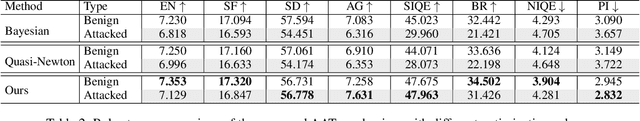
Abstract:Image stitching seamlessly integrates images captured from varying perspectives into a single wide field-of-view image. Such integration not only broadens the captured scene but also augments holistic perception in computer vision applications. Given a pair of captured images, subtle perturbations and distortions which go unnoticed by the human visual system tend to attack the correspondence matching, impairing the performance of image stitching algorithms. In light of this challenge, this paper presents the first attempt to improve the robustness of image stitching against adversarial attacks. Specifically, we introduce a stitching-oriented attack~(SoA), tailored to amplify the alignment loss within overlapping regions, thereby targeting the feature matching procedure. To establish an attack resistant model, we delve into the robustness of stitching architecture and develop an adaptive adversarial training~(AAT) to balance attack resistance with stitching precision. In this way, we relieve the gap between the routine adversarial training and benign models, ensuring resilience without quality compromise. Comprehensive evaluation across real-world and synthetic datasets validate the deterioration of SoA on stitching performance. Furthermore, AAT emerges as a more robust solution against adversarial perturbations, delivering superior stitching results. Code is available at:https://github.com/Jzy2017/TRIS.
From Text to Pixels: A Context-Aware Semantic Synergy Solution for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Dec 31, 2023



Abstract:With the rapid progression of deep learning technologies, multi-modality image fusion has become increasingly prevalent in object detection tasks. Despite its popularity, the inherent disparities in how different sources depict scene content make fusion a challenging problem. Current fusion methodologies identify shared characteristics between the two modalities and integrate them within this shared domain using either iterative optimization or deep learning architectures, which often neglect the intricate semantic relationships between modalities, resulting in a superficial understanding of inter-modal connections and, consequently, suboptimal fusion outcomes. To address this, we introduce a text-guided multi-modality image fusion method that leverages the high-level semantics from textual descriptions to integrate semantics from infrared and visible images. This method capitalizes on the complementary characteristics of diverse modalities, bolstering both the accuracy and robustness of object detection. The codebook is utilized to enhance a streamlined and concise depiction of the fused intra- and inter-domain dynamics, fine-tuned for optimal performance in detection tasks. We present a bilevel optimization strategy that establishes a nexus between the joint problem of fusion and detection, optimizing both processes concurrently. Furthermore, we introduce the first dataset of paired infrared and visible images accompanied by text prompts, paving the way for future research. Extensive experiments on several datasets demonstrate that our method not only produces visually superior fusion results but also achieves a higher detection mAP over existing methods, achieving state-of-the-art results.
Learn from the Past: A Proxy based Adversarial Defense Framework to Boost Robustness
Oct 19, 2023



Abstract:In light of the vulnerability of deep learning models to adversarial samples and the ensuing security issues, a range of methods, including Adversarial Training (AT) as a prominent representative, aimed at enhancing model robustness against various adversarial attacks, have seen rapid development. However, existing methods essentially assist the current state of target model to defend against parameter-oriented adversarial attacks with explicit or implicit computation burdens, which also suffers from unstable convergence behavior due to inconsistency of optimization trajectories. Diverging from previous work, this paper reconsiders the update rule of target model and corresponding deficiency to defend based on its current state. By introducing the historical state of the target model as a proxy, which is endowed with much prior information for defense, we formulate a two-stage update rule, resulting in a general adversarial defense framework, which we refer to as `LAST' ({\bf L}earn from the P{\bf ast}). Besides, we devise a Self Distillation (SD) based defense objective to constrain the update process of the proxy model without the introduction of larger teacher models. Experimentally, we demonstrate consistent and significant performance enhancements by refining a series of single-step and multi-step AT methods (e.g., up to $\bf 9.2\%$ and $\bf 20.5\%$ improvement of Robust Accuracy (RA) on CIFAR10 and CIFAR100 datasets, respectively) across various datasets, backbones and attack modalities, and validate its ability to enhance training stability and ameliorate catastrophic overfitting issues meanwhile.
Diving into Darkness: A Dual-Modulated Framework for High-Fidelity Super-Resolution in Ultra-Dark Environments
Sep 11, 2023



Abstract:Super-resolution tasks oriented to images captured in ultra-dark environments is a practical yet challenging problem that has received little attention. Due to uneven illumination and low signal-to-noise ratio in dark environments, a multitude of problems such as lack of detail and color distortion may be magnified in the super-resolution process compared to normal-lighting environments. Consequently, conventional low-light enhancement or super-resolution methods, whether applied individually or in a cascaded manner for such problem, often encounter limitations in recovering luminance, color fidelity, and intricate details. To conquer these issues, this paper proposes a specialized dual-modulated learning framework that, for the first time, attempts to deeply dissect the nature of the low-light super-resolution task. Leveraging natural image color characteristics, we introduce a self-regularized luminance constraint as a prior for addressing uneven lighting. Expanding on this, we develop Illuminance-Semantic Dual Modulation (ISDM) components to enhance feature-level preservation of illumination and color details. Besides, instead of deploying naive up-sampling strategies, we design the Resolution-Sensitive Merging Up-sampler (RSMU) module that brings together different sampling modalities as substrates, effectively mitigating the presence of artifacts and halos. Comprehensive experiments showcases the applicability and generalizability of our approach to diverse and challenging ultra-low-light conditions, outperforming state-of-the-art methods with a notable improvement (i.e., $\uparrow$5\% in PSNR, and $\uparrow$43\% in LPIPS). Especially noteworthy is the 19-fold increase in the RMSE score, underscoring our method's exceptional generalization across different darkness levels. The code will be available online upon publication of the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge