Guanyao Wu
Every SAM Drop Counts: Embracing Semantic Priors for Multi-Modality Image Fusion and Beyond
Mar 03, 2025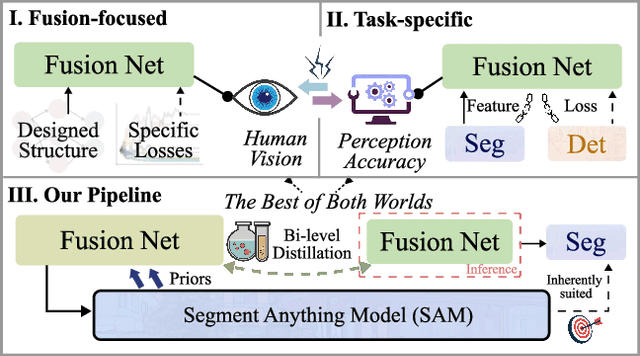
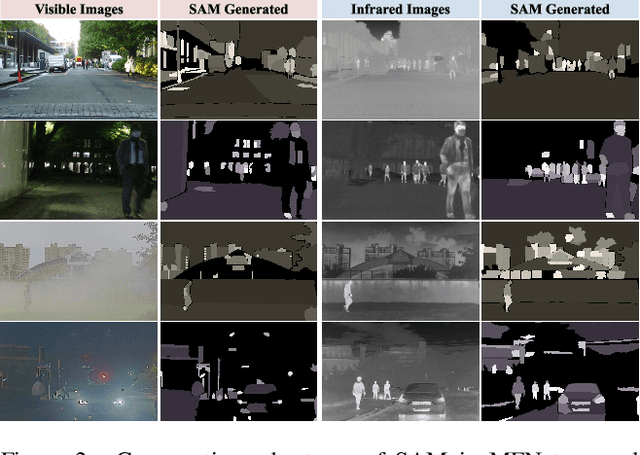
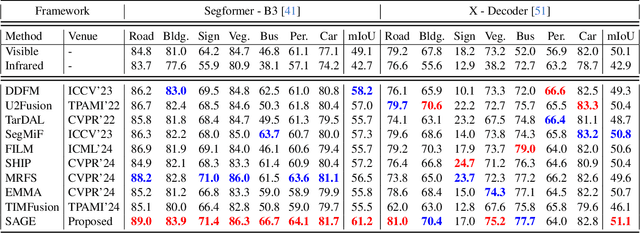

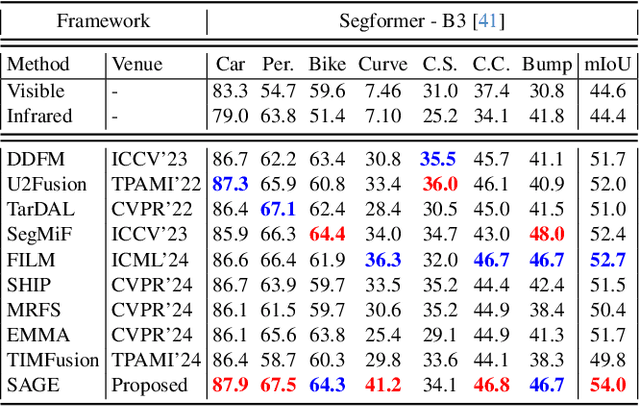
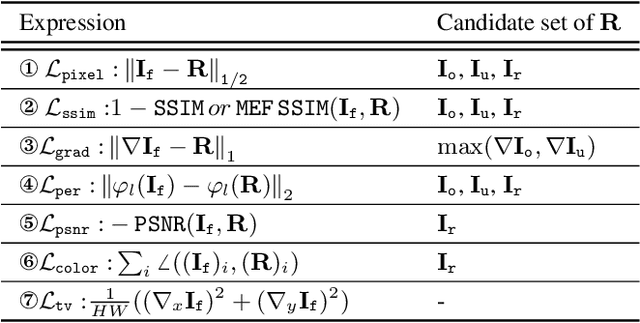
Abstract:Multi-modality image fusion, particularly infrared and visible image fusion, plays a crucial role in integrating diverse modalities to enhance scene understanding. Early research primarily focused on visual quality, yet challenges remain in preserving fine details, making it difficult to adapt to subsequent tasks. Recent approaches have shifted towards task-specific design, but struggle to achieve the ``The Best of Both Worlds'' due to inconsistent optimization goals. To address these issues, we propose a novel method that leverages the semantic knowledge from the Segment Anything Model (SAM) to Grow the quality of fusion results and Establish downstream task adaptability, namely SAGE. Specifically, we design a Semantic Persistent Attention (SPA) Module that efficiently maintains source information via the persistent repository while extracting high-level semantic priors from SAM. More importantly, to eliminate the impractical dependence on SAM during inference, we introduce a bi-level optimization-driven distillation mechanism with triplet losses, which allow the student network to effectively extract knowledge at the feature, pixel, and contrastive semantic levels, thereby removing reliance on the cumbersome SAM model. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves a balance between high-quality visual results and downstream task adaptability while maintaining practical deployment efficiency.
Infrared and Visible Image Fusion: From Data Compatibility to Task Adaption
Jan 18, 2025Abstract:Infrared-visible image fusion (IVIF) is a critical task in computer vision, aimed at integrating the unique features of both infrared and visible spectra into a unified representation. Since 2018, the field has entered the deep learning era, with an increasing variety of approaches introducing a range of networks and loss functions to enhance visual performance. However, challenges such as data compatibility, perception accuracy, and efficiency remain. Unfortunately, there is a lack of recent comprehensive surveys that address this rapidly expanding domain. This paper fills that gap by providing a thorough survey covering a broad range of topics. We introduce a multi-dimensional framework to elucidate common learning-based IVIF methods, from visual enhancement strategies to data compatibility and task adaptability. We also present a detailed analysis of these approaches, accompanied by a lookup table clarifying their core ideas. Furthermore, we summarize performance comparisons, both quantitatively and qualitatively, focusing on registration, fusion, and subsequent high-level tasks. Beyond technical analysis, we discuss potential future directions and open issues in this area. For further details, visit our GitHub repository: https://github.com/RollingPlain/IVIF_ZOO.
Hybrid-Supervised Dual-Search: Leveraging Automatic Learning for Loss-free Multi-Exposure Image Fusion
Sep 03, 2023
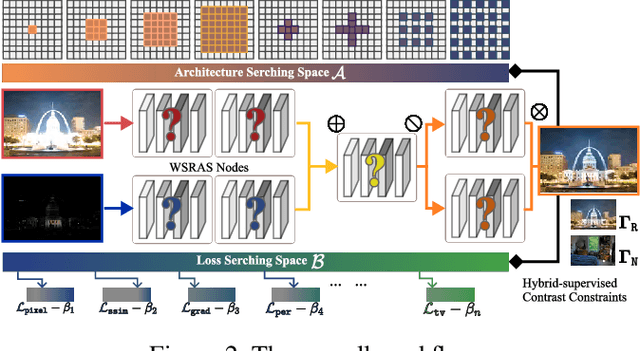
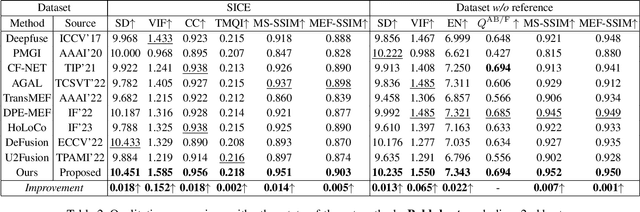
Abstract:Multi-exposure image fusion (MEF) has emerged as a prominent solution to address the limitations of digital imaging in representing varied exposure levels. Despite its advancements, the field grapples with challenges, notably the reliance on manual designs for network structures and loss functions, and the constraints of utilizing simulated reference images as ground truths. Consequently, current methodologies often suffer from color distortions and exposure artifacts, further complicating the quest for authentic image representation. In addressing these challenges, this paper presents a Hybrid-Supervised Dual-Search approach for MEF, dubbed HSDS-MEF, which introduces a bi-level optimization search scheme for automatic design of both network structures and loss functions. More specifically, we harnesses a unique dual research mechanism rooted in a novel weighted structure refinement architecture search. Besides, a hybrid supervised contrast constraint seamlessly guides and integrates with searching process, facilitating a more adaptive and comprehensive search for optimal loss functions. We realize the state-of-the-art performance in comparison to various competitive schemes, yielding a 10.61% and 4.38% improvement in Visual Information Fidelity (VIF) for general and no-reference scenarios, respectively, while providing results with high contrast, rich details and colors.
Multi-interactive Feature Learning and a Full-time Multi-modality Benchmark for Image Fusion and Segmentation
Aug 04, 2023Abstract:Multi-modality image fusion and segmentation play a vital role in autonomous driving and robotic operation. Early efforts focus on boosting the performance for only one task, \emph{e.g.,} fusion or segmentation, making it hard to reach~`Best of Both Worlds'. To overcome this issue, in this paper, we propose a \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{i}nteractive \textbf{F}eature learning architecture for image fusion and \textbf{Seg}mentation, namely SegMiF, and exploit dual-task correlation to promote the performance of both tasks. The SegMiF is of a cascade structure, containing a fusion sub-network and a commonly used segmentation sub-network. By slickly bridging intermediate features between two components, the knowledge learned from the segmentation task can effectively assist the fusion task. Also, the benefited fusion network supports the segmentation one to perform more pretentiously. Besides, a hierarchical interactive attention block is established to ensure fine-grained mapping of all the vital information between two tasks, so that the modality/semantic features can be fully mutual-interactive. In addition, a dynamic weight factor is introduced to automatically adjust the corresponding weights of each task, which can balance the interactive feature correspondence and break through the limitation of laborious tuning. Furthermore, we construct a smart multi-wave binocular imaging system and collect a full-time multi-modality benchmark with 15 annotated pixel-level categories for image fusion and segmentation. Extensive experiments on several public datasets and our benchmark demonstrate that the proposed method outputs visually appealing fused images and perform averagely $7.66\%$ higher segmentation mIoU in the real-world scene than the state-of-the-art approaches. The source code and benchmark are available at \url{https://github.com/JinyuanLiu-CV/SegMiF}.
Embracing Compact and Robust Architectures for Multi-Exposure Image Fusion
May 20, 2023Abstract:In recent years, deep learning-based methods have achieved remarkable progress in multi-exposure image fusion. However, existing methods rely on aligned image pairs, inevitably generating artifacts when faced with device shaking in real-world scenarios. Moreover, these learning-based methods are built on handcrafted architectures and operations by increasing network depth or width, neglecting different exposure characteristics. As a result, these direct cascaded architectures with redundant parameters fail to achieve highly effective inference time and lead to massive computation. To alleviate these issues, in this paper, we propose a search-based paradigm, involving self-alignment and detail repletion modules for robust multi-exposure image fusion. By utilizing scene relighting and deformable convolutions, the self-alignment module can accurately align images despite camera movement. Furthermore, by imposing a hardware-sensitive constraint, we introduce neural architecture search to discover compact and efficient networks, investigating effective feature representation for fusion. We realize the state-of-the-art performance in comparison to various competitive schemes, yielding a 4.02% and 29.34% improvement in PSNR for general and misaligned scenarios, respectively, while reducing inference time by 68.1%. The source code will be available at https://github.com/LiuZhu-CV/CRMEF.
Bi-level Dynamic Learning for Jointly Multi-modality Image Fusion and Beyond
May 11, 2023Abstract:Recently, multi-modality scene perception tasks, e.g., image fusion and scene understanding, have attracted widespread attention for intelligent vision systems. However, early efforts always consider boosting a single task unilaterally and neglecting others, seldom investigating their underlying connections for joint promotion. To overcome these limitations, we establish the hierarchical dual tasks-driven deep model to bridge these tasks. Concretely, we firstly construct an image fusion module to fuse complementary characteristics and cascade dual task-related modules, including a discriminator for visual effects and a semantic network for feature measurement. We provide a bi-level perspective to formulate image fusion and follow-up downstream tasks. To incorporate distinct task-related responses for image fusion, we consider image fusion as a primary goal and dual modules as learnable constraints. Furthermore, we develop an efficient first-order approximation to compute corresponding gradients and present dynamic weighted aggregation to balance the gradients for fusion learning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method, which not only produces visually pleasant fused results but also realizes significant promotion for detection and segmentation than the state-of-the-art approaches.
CoCoNet: Coupled Contrastive Learning Network with Multi-level Feature Ensemble for Multi-modality Image Fusion
Nov 20, 2022Abstract:Infrared and visible image fusion targets to provide an informative image by combining complementary information from different sensors. Existing learning-based fusion approaches attempt to construct various loss functions to preserve complementary features from both modalities, while neglecting to discover the inter-relationship between the two modalities, leading to redundant or even invalid information on the fusion results. To alleviate these issues, we propose a coupled contrastive learning network, dubbed CoCoNet, to realize infrared and visible image fusion in an end-to-end manner. Concretely, to simultaneously retain typical features from both modalities and remove unwanted information emerging on the fused result, we develop a coupled contrastive constraint in our loss function.In a fused imge, its foreground target/background detail part is pulled close to the infrared/visible source and pushed far away from the visible/infrared source in the representation space. We further exploit image characteristics to provide data-sensitive weights, which allows our loss function to build a more reliable relationship with source images. Furthermore, to learn rich hierarchical feature representation and comprehensively transfer features in the fusion process, a multi-level attention module is established. In addition, we also apply the proposed CoCoNet on medical image fusion of different types, e.g., magnetic resonance image and positron emission tomography image, magnetic resonance image and single photon emission computed tomography image. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves the state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance under both subjective and objective evaluation, especially in preserving prominent targets and recovering vital textural details.
Target-aware Dual Adversarial Learning and a Multi-scenario Multi-Modality Benchmark to Fuse Infrared and Visible for Object Detection
Mar 30, 2022
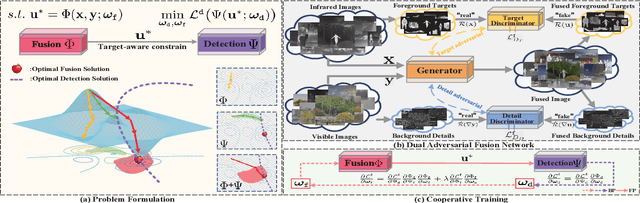
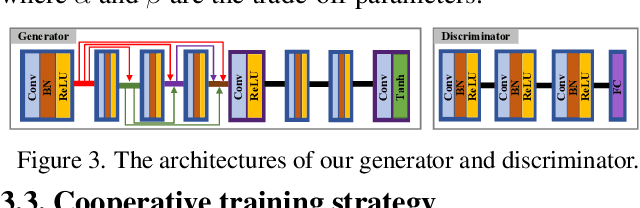
Abstract:This study addresses the issue of fusing infrared and visible images that appear differently for object detection. Aiming at generating an image of high visual quality, previous approaches discover commons underlying the two modalities and fuse upon the common space either by iterative optimization or deep networks. These approaches neglect that modality differences implying the complementary information are extremely important for both fusion and subsequent detection task. This paper proposes a bilevel optimization formulation for the joint problem of fusion and detection, and then unrolls to a target-aware Dual Adversarial Learning (TarDAL) network for fusion and a commonly used detection network. The fusion network with one generator and dual discriminators seeks commons while learning from differences, which preserves structural information of targets from the infrared and textural details from the visible. Furthermore, we build a synchronized imaging system with calibrated infrared and optical sensors, and collect currently the most comprehensive benchmark covering a wide range of scenarios. Extensive experiments on several public datasets and our benchmark demonstrate that our method outputs not only visually appealing fusion but also higher detection mAP than the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge