Pengwei Wang
Reshaping Action Error Distributions for Reliable Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In robotic manipulation, vision-language-action (VLA) models have emerged as a promising paradigm for learning generalizable and scalable robot policies. Most existing VLA frameworks rely on standard supervised objectives, typically cross-entropy for discrete actions and mean squared error (MSE) for continuous action regression, which impose strong pointwise constraints on individual predictions. In this work, we focus on continuous-action VLA models and move beyond conventional MSE-based regression by reshaping action error distributions during training. Drawing on information-theoretic principles, we introduce Minimum Error Entropy (MEE) into modern VLA architectures and propose a trajectory-level MEE objective, together with two weighted variants, combined with MSE for continuous-action VLA training. We evaluate our approaches across standard, few-shot, and noisy settings on multiple representative VLA architectures, using simulation benchmarks such as LIBERO and SimplerEnv as well as real-world robotic manipulation tasks. Experimental results demonstrate consistent improvements in success rates and robustness across these settings. Under imbalanced data regimes, the gains persist within a well-characterized operating range, while incurring negligible additional training cost and no impact on inference efficiency. We further provide theoretical analyses that explain why MEE-based supervision is effective and characterize its practical range. Project Page: https://cognition2actionlab.github.io/VLA-TMEE.github.io/
Latent Reasoning VLA: Latent Thinking and Prediction for Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models benefit from chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning, but existing approaches incur high inference overhead and rely on discrete reasoning representations that mismatch continuous perception and control. We propose Latent Reasoning VLA (\textbf{LaRA-VLA}), a unified VLA framework that internalizes multi-modal CoT reasoning into continuous latent representations for embodied action. LaRA-VLA performs unified reasoning and prediction in latent space, eliminating explicit CoT generation at inference time and enabling efficient, action-oriented control. To realize latent embodied reasoning, we introduce a curriculum-based training paradigm that progressively transitions from explicit textual and visual CoT supervision to latent reasoning, and finally adapts latent reasoning dynamics to condition action generation. We construct two structured CoT datasets and evaluate LaRA-VLA on both simulation benchmarks and long-horizon real-robot manipulation tasks. Experimental results show that LaRA-VLA consistently outperforms state-of-the-art VLA methods while reducing inference latency by up to 90\% compared to explicit CoT-based approaches, demonstrating latent reasoning as an effective and efficient paradigm for real-time embodied control. Project Page: \href{https://loveju1y.github.io/Latent-Reasoning-VLA/}{LaRA-VLA Website}.
RoboBrain 2.5: Depth in Sight, Time in Mind
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We introduce RoboBrain 2.5, a next-generation embodied AI foundation model that advances general perception, spatial reasoning, and temporal modeling through extensive training on high-quality spatiotemporal supervision. Building upon its predecessor, RoboBrain 2.5 introduces two major capability upgrades. Specifically, it unlocks Precise 3D Spatial Reasoning by shifting from 2D pixel-relative grounding to depth-aware coordinate prediction and absolute metric constraint comprehension, generating complete 3D manipulation traces as ordered keypoint sequences under physical constraints. Complementing this spatial precision, the model establishes Dense Temporal Value Estimation that provides dense, step-aware progress prediction and execution state understanding across varying viewpoints, producing stable feedback signals for downstream learning. Together, these upgrades extend the framework toward more physically grounded and execution-aware embodied intelligence for complex, fine-grained manipulation. The code and checkpoints are available at project website: https://superrobobrain.github.io
Action-Sketcher: From Reasoning to Action via Visual Sketches for Long-Horizon Robotic Manipulation
Jan 04, 2026Abstract:Long-horizon robotic manipulation is increasingly important for real-world deployment, requiring spatial disambiguation in complex layouts and temporal resilience under dynamic interaction. However, existing end-to-end and hierarchical Vision-Language-Action (VLA) policies often rely on text-only cues while keeping plan intent latent, which undermines referential grounding in cluttered or underspecified scenes, impedes effective task decomposition of long-horizon goals with close-loop interaction, and limits causal explanation by obscuring the rationale behind action choices. To address these issues, we first introduce Visual Sketch, an implausible visual intermediate that renders points, boxes, arrows, and typed relations in the robot's current views to externalize spatial intent, connect language to scene geometry. Building on Visual Sketch, we present Action-Sketcher, a VLA framework that operates in a cyclic See-Think-Sketch-Act workflow coordinated by adaptive token-gated strategy for reasoning triggers, sketch revision, and action issuance, thereby supporting reactive corrections and human interaction while preserving real-time action prediction. To enable scalable training and evaluation, we curate diverse corpus with interleaved images, text, Visual Sketch supervision, and action sequences, and train Action-Sketcher with a multi-stage curriculum recipe that combines interleaved sequence alignment for modality unification, language-to-sketch consistency for precise linguistic grounding, and imitation learning augmented with sketch-to-action reinforcement for robustness. Extensive experiments on cluttered scenes and multi-object tasks, in simulation and on real-world tasks, show improved long-horizon success, stronger robustness to dynamic scene changes, and enhanced interpretability via editable sketches and step-wise plans. Project website: https://action-sketcher.github.io
RoboMirror: Understand Before You Imitate for Video to Humanoid Locomotion
Dec 30, 2025Abstract:Humans learn locomotion through visual observation, interpreting visual content first before imitating actions. However, state-of-the-art humanoid locomotion systems rely on either curated motion capture trajectories or sparse text commands, leaving a critical gap between visual understanding and control. Text-to-motion methods suffer from semantic sparsity and staged pipeline errors, while video-based approaches only perform mechanical pose mimicry without genuine visual understanding. We propose RoboMirror, the first retargeting-free video-to-locomotion framework embodying "understand before you imitate". Leveraging VLMs, it distills raw egocentric/third-person videos into visual motion intents, which directly condition a diffusion-based policy to generate physically plausible, semantically aligned locomotion without explicit pose reconstruction or retargeting. Extensive experiments validate the effectiveness of RoboMirror, it enables telepresence via egocentric videos, drastically reduces third-person control latency by 80%, and achieves a 3.7% higher task success rate than baselines. By reframing humanoid control around video understanding, we bridge the visual understanding and action gap.
Robo-Dopamine: General Process Reward Modeling for High-Precision Robotic Manipulation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:The primary obstacle for applying reinforcement learning (RL) to real-world robotics is the design of effective reward functions. While recently learning-based Process Reward Models (PRMs) are a promising direction, they are often hindered by two fundamental limitations: their reward models lack step-aware understanding and rely on single-view perception, leading to unreliable assessments of fine-grained manipulation progress; and their reward shaping procedures are theoretically unsound, often inducing a semantic trap that misguides policy optimization. To address these, we introduce Dopamine-Reward, a novel reward modeling method for learning a general-purpose, step-aware process reward model from multi-view inputs. At its core is our General Reward Model (GRM), trained on a vast 3,400+ hour dataset, which leverages Step-wise Reward Discretization for structural understanding and Multi-Perspective Reward Fusion to overcome perceptual limitations. Building upon Dopamine-Reward, we propose Dopamine-RL, a robust policy learning framework that employs a theoretically-sound Policy-Invariant Reward Shaping method, which enables the agent to leverage dense rewards for efficient self-improvement without altering the optimal policy, thereby fundamentally avoiding the semantic trap. Extensive experiments across diverse simulated and real-world tasks validate our approach. GRM achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in reward assessment, and Dopamine-RL built on GRM significantly improves policy learning efficiency. For instance, after GRM is adapted to a new task in a one-shot manner from a single expert trajectory, the resulting reward model enables Dopamine-RL to improve the policy from near-zero to 95% success with only 150 online rollouts (approximately 1 hour of real robot interaction), while retaining strong generalization across tasks. Project website: https://robo-dopamine.github.io
Do You Have Freestyle? Expressive Humanoid Locomotion via Audio Control
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:Humans intuitively move to sound, but current humanoid robots lack expressive improvisational capabilities, confined to predefined motions or sparse commands. Generating motion from audio and then retargeting it to robots relies on explicit motion reconstruction, leading to cascaded errors, high latency, and disjointed acoustic-actuation mapping. We propose RoboPerform, the first unified audio-to-locomotion framework that can directly generate music-driven dance and speech-driven co-speech gestures from audio. Guided by the core principle of "motion = content + style", the framework treats audio as implicit style signals and eliminates the need for explicit motion reconstruction. RoboPerform integrates a ResMoE teacher policy for adapting to diverse motion patterns and a diffusion-based student policy for audio style injection. This retargeting-free design ensures low latency and high fidelity. Experimental validation shows that RoboPerform achieves promising results in physical plausibility and audio alignment, successfully transforming robots into responsive performers capable of reacting to audio.
RoboTracer: Mastering Spatial Trace with Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Spatial tracing, as a fundamental embodied interaction ability for robots, is inherently challenging as it requires multi-step metric-grounded reasoning compounded with complex spatial referring and real-world metric measurement. However, existing methods struggle with this compositional task. To this end, we propose RoboTracer, a 3D-aware VLM that first achieves both 3D spatial referring and measuring via a universal spatial encoder and a regression-supervised decoder to enhance scale awareness during supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Moreover, RoboTracer advances multi-step metric-grounded reasoning via reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) with metric-sensitive process rewards, supervising key intermediate perceptual cues to accurately generate spatial traces. To support SFT and RFT training, we introduce TraceSpatial, a large-scale dataset of 30M QA pairs, spanning outdoor/indoor/tabletop scenes and supporting complex reasoning processes (up to 9 steps). We further present TraceSpatial-Bench, a challenging benchmark filling the gap to evaluate spatial tracing. Experimental results show that RoboTracer surpasses baselines in spatial understanding, measuring, and referring, with an average success rate of 79.1%, and also achieves SOTA performance on TraceSpatial-Bench by a large margin, exceeding Gemini-2.5-Pro by 36% accuracy. Notably, RoboTracer can be integrated with various control policies to execute long-horizon, dynamic tasks across diverse robots (UR5, G1 humanoid) in cluttered real-world scenes.
PIGEON: VLM-Driven Object Navigation via Points of Interest Selection
Nov 17, 2025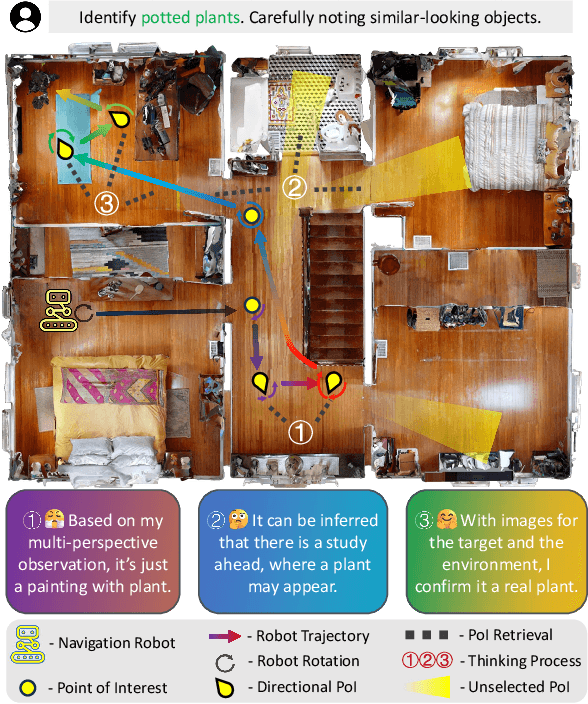
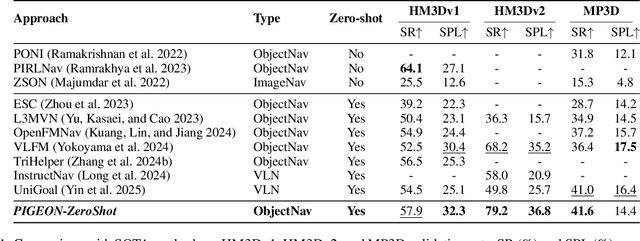

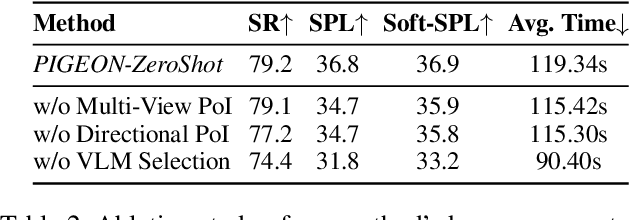
Abstract:Navigating to a specified object in an unknown environment is a fundamental yet challenging capability of embodied intelligence. However, current methods struggle to balance decision frequency with intelligence, resulting in decisions lacking foresight or discontinuous actions. In this work, we propose PIGEON: Point of Interest Guided Exploration for Object Navigation with VLM, maintaining a lightweight and semantically aligned snapshot memory during exploration as semantic input for the exploration strategy. We use a large Visual-Language Model (VLM), named PIGEON-VL, to select Points of Interest (PoI) formed during exploration and then employ a lower-level planner for action output, increasing the decision frequency. Additionally, this PoI-based decision-making enables the generation of Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Reward (RLVR) data suitable for simulators. Experiments on classic object navigation benchmarks demonstrate that our zero-shot transfer method achieves state-of-the-art performance, while RLVR further enhances the model's semantic guidance capabilities, enabling deep reasoning during real-time navigation.
GridPrune: From "Where to Look" to "What to Select" in Visual Token Pruning for MLLMs
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in a wide range of vision-language tasks. However, the large number of visual tokens introduces significant computational overhead. To address this issue, visual token pruning has emerged as a key technique for enhancing the efficiency of MLLMs. In cognitive science, humans tend to first determine which regions of a scene to attend to ("where to look") before deciding which specific elements within those regions to process in detail ("what to select"). This two-stage strategy enables the visual system to efficiently allocate attention at a coarse spatial level before performing fine-grained selection. However, existing pruning methods primarily focus on directly optimizing "what to select", typically using attention scores or similarity metrics. They rarely consider "where to look", which has been shown to lead to inefficient spatial allocation, positional bias, and the retention of irrelevant or redundant tokens. In this paper, we propose GridPrune, a method that replaces the global Top-K mechanism with a "guide-globally, select-locally" zonal selection system. GridPrune splits the pruning process into two steps: first, it uses text-conditional guidance to dynamically allocate a token budget across spatial zones; and then, it performs local selection within each budgeted zone. Experimental results demonstrate that GridPrune achieves superior performance across various MLLM architectures. On LLaVA-NeXT-7B, GridPrune retains 96.98% of the full performance while using 11.1% of the tokens, outperforming the best-performing baseline by 2.34% at the same pruning rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge