Xiaoshuai Hao
DriveWorld-VLA: Unified Latent-Space World Modeling with Vision-Language-Action for Autonomous Driving
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:End-to-end (E2E) autonomous driving has recently attracted increasing interest in unifying Vision-Language-Action (VLA) with World Models to enhance decision-making and forward-looking imagination. However, existing methods fail to effectively unify future scene evolution and action planning within a single architecture due to inadequate sharing of latent states, limiting the impact of visual imagination on action decisions. To address this limitation, we propose DriveWorld-VLA, a novel framework that unifies world modeling and planning within a latent space by tightly integrating VLA and world models at the representation level, which enables the VLA planner to benefit directly from holistic scene-evolution modeling and reducing reliance on dense annotated supervision. Additionally, DriveWorld-VLA incorporates the latent states of the world model as core decision-making states for the VLA planner, facilitating the planner to assess how candidate actions impact future scene evolution. By conducting world modeling entirely in the latent space, DriveWorld-VLA supports controllable, action-conditioned imagination at the feature level, avoiding expensive pixel-level rollouts. Extensive open-loop and closed-loop evaluations demonstrate the effectiveness of DriveWorld-VLA, which achieves state-of-the-art performance with 91.3 PDMS on NAVSIMv1, 86.8 EPDMS on NAVSIMv2, and 0.16 3-second average collision rate on nuScenes. Code and models will be released in https://github.com/liulin815/DriveWorld-VLA.git.
EXaMCaP: Subset Selection with Entropy Gain Maximization for Probing Capability Gains of Large Chart Understanding Training Sets
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Recent works focus on synthesizing Chart Understanding (ChartU) training sets to inject advanced chart knowledge into Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), where the sufficiency of the knowledge is typically verified by quantifying capability gains via the fine-tune-then-evaluate paradigm. However, full-set fine-tuning MLLMs to assess such gains incurs significant time costs, hindering the iterative refinement cycles of the ChartU dataset. Reviewing the ChartU dataset synthesis and data selection domains, we find that subsets can potentially probe the MLLMs' capability gains from full-set fine-tuning. Given that data diversity is vital for boosting MLLMs' performance and entropy reflects this feature, we propose EXaMCaP, which uses entropy gain maximization to select a subset. To obtain a high-diversity subset, EXaMCaP chooses the maximum-entropy subset from the large ChartU dataset. As enumerating all possible subsets is impractical, EXaMCaP iteratively selects samples to maximize the gain in set entropy relative to the current set, approximating the maximum-entropy subset of the full dataset. Experiments show that EXaMCaP outperforms baselines in probing the capability gains of the ChartU training set, along with its strong effectiveness across diverse subset sizes and compatibility with various MLLM architectures.
The RoboSense Challenge: Sense Anything, Navigate Anywhere, Adapt Across Platforms
Jan 08, 2026Abstract:Autonomous systems are increasingly deployed in open and dynamic environments -- from city streets to aerial and indoor spaces -- where perception models must remain reliable under sensor noise, environmental variation, and platform shifts. However, even state-of-the-art methods often degrade under unseen conditions, highlighting the need for robust and generalizable robot sensing. The RoboSense 2025 Challenge is designed to advance robustness and adaptability in robot perception across diverse sensing scenarios. It unifies five complementary research tracks spanning language-grounded decision making, socially compliant navigation, sensor configuration generalization, cross-view and cross-modal correspondence, and cross-platform 3D perception. Together, these tasks form a comprehensive benchmark for evaluating real-world sensing reliability under domain shifts, sensor failures, and platform discrepancies. RoboSense 2025 provides standardized datasets, baseline models, and unified evaluation protocols, enabling large-scale and reproducible comparison of robust perception methods. The challenge attracted 143 teams from 85 institutions across 16 countries, reflecting broad community engagement. By consolidating insights from 23 winning solutions, this report highlights emerging methodological trends, shared design principles, and open challenges across all tracks, marking a step toward building robots that can sense reliably, act robustly, and adapt across platforms in real-world environments.
Vision-Language-Action Models for Autonomous Driving: Past, Present, and Future
Dec 18, 2025Abstract:Autonomous driving has long relied on modular "Perception-Decision-Action" pipelines, where hand-crafted interfaces and rule-based components often break down in complex or long-tailed scenarios. Their cascaded design further propagates perception errors, degrading downstream planning and control. Vision-Action (VA) models address some limitations by learning direct mappings from visual inputs to actions, but they remain opaque, sensitive to distribution shifts, and lack structured reasoning or instruction-following capabilities. Recent progress in Large Language Models (LLMs) and multimodal learning has motivated the emergence of Vision-Language-Action (VLA) frameworks, which integrate perception with language-grounded decision making. By unifying visual understanding, linguistic reasoning, and actionable outputs, VLAs offer a pathway toward more interpretable, generalizable, and human-aligned driving policies. This work provides a structured characterization of the emerging VLA landscape for autonomous driving. We trace the evolution from early VA approaches to modern VLA frameworks and organize existing methods into two principal paradigms: End-to-End VLA, which integrates perception, reasoning, and planning within a single model, and Dual-System VLA, which separates slow deliberation (via VLMs) from fast, safety-critical execution (via planners). Within these paradigms, we further distinguish subclasses such as textual vs. numerical action generators and explicit vs. implicit guidance mechanisms. We also summarize representative datasets and benchmarks for evaluating VLA-based driving systems and highlight key challenges and open directions, including robustness, interpretability, and instruction fidelity. Overall, this work aims to establish a coherent foundation for advancing human-compatible autonomous driving systems.
Is Your VLM for Autonomous Driving Safety-Ready? A Comprehensive Benchmark for Evaluating External and In-Cabin Risks
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) show great promise for autonomous driving, but their suitability for safety-critical scenarios is largely unexplored, raising safety concerns. This issue arises from the lack of comprehensive benchmarks that assess both external environmental risks and in-cabin driving behavior safety simultaneously. To bridge this critical gap, we introduce DSBench, the first comprehensive Driving Safety Benchmark designed to assess a VLM's awareness of various safety risks in a unified manner. DSBench encompasses two major categories: external environmental risks and in-cabin driving behavior safety, divided into 10 key categories and a total of 28 sub-categories. This comprehensive evaluation covers a wide range of scenarios, ensuring a thorough assessment of VLMs' performance in safety-critical contexts. Extensive evaluations across various mainstream open-source and closed-source VLMs reveal significant performance degradation under complex safety-critical situations, highlighting urgent safety concerns. To address this, we constructed a large dataset of 98K instances focused on in-cabin and external safety scenarios, showing that fine-tuning on this dataset significantly enhances the safety performance of existing VLMs and paves the way for advancing autonomous driving technology. The benchmark toolkit, code, and model checkpoints will be publicly accessible.
SocialNav-Map: Dynamic Mapping with Human Trajectory Prediction for Zero-Shot Social Navigation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:Social navigation in densely populated dynamic environments poses a significant challenge for autonomous mobile robots, requiring advanced strategies for safe interaction. Existing reinforcement learning (RL)-based methods require over 2000+ hours of extensive training and often struggle to generalize to unfamiliar environments without additional fine-tuning, limiting their practical application in real-world scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose SocialNav-Map, a novel zero-shot social navigation framework that combines dynamic human trajectory prediction with occupancy mapping, enabling safe and efficient navigation without the need for environment-specific training. Specifically, SocialNav-Map first transforms the task goal position into the constructed map coordinate system. Subsequently, it creates a dynamic occupancy map that incorporates predicted human movements as dynamic obstacles. The framework employs two complementary methods for human trajectory prediction: history prediction and orientation prediction. By integrating these predicted trajectories into the occupancy map, the robot can proactively avoid potential collisions with humans while efficiently navigating to its destination. Extensive experiments on the Social-HM3D and Social-MP3D datasets demonstrate that SocialNav-Map significantly outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) RL-based methods, which require 2,396 GPU hours of training. Notably, it reduces human collision rates by over 10% without necessitating any training in novel environments. By eliminating the need for environment-specific training, SocialNav-Map achieves superior navigation performance, paving the way for the deployment of social navigation systems in real-world environments characterized by diverse human behaviors. The code is available at: https://github.com/linglingxiansen/SocialNav-Map.
Is your VLM Sky-Ready? A Comprehensive Spatial Intelligence Benchmark for UAV Navigation
Nov 17, 2025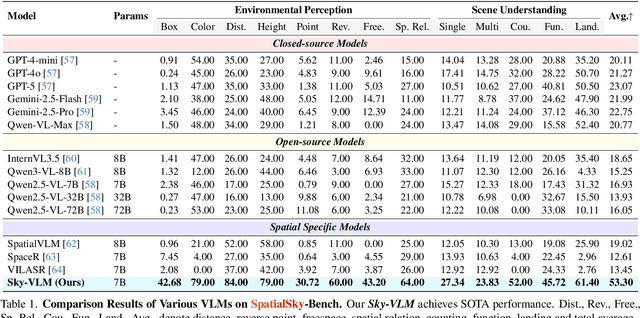
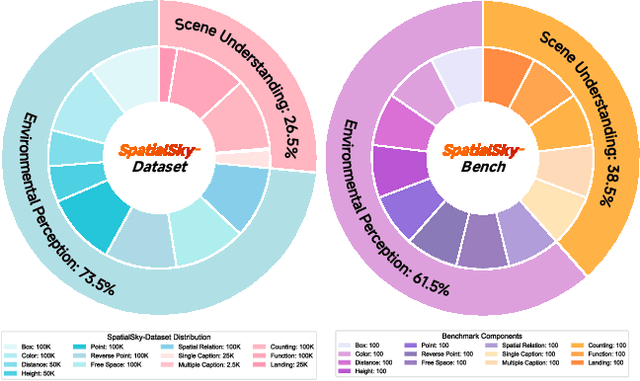
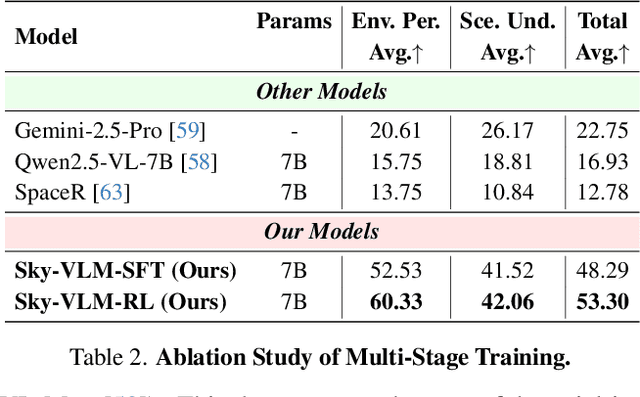
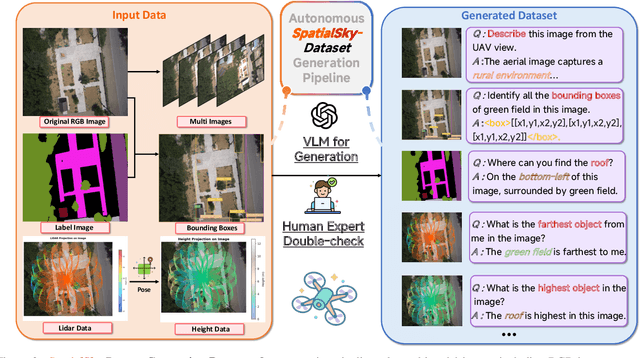
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs), leveraging their powerful visual perception and reasoning capabilities, have been widely applied in Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) tasks. However, the spatial intelligence capabilities of existing VLMs in UAV scenarios remain largely unexplored, raising concerns about their effectiveness in navigating and interpreting dynamic environments. To bridge this gap, we introduce SpatialSky-Bench, a comprehensive benchmark specifically designed to evaluate the spatial intelligence capabilities of VLMs in UAV navigation. Our benchmark comprises two categories-Environmental Perception and Scene Understanding-divided into 13 subcategories, including bounding boxes, color, distance, height, and landing safety analysis, among others. Extensive evaluations of various mainstream open-source and closed-source VLMs reveal unsatisfactory performance in complex UAV navigation scenarios, highlighting significant gaps in their spatial capabilities. To address this challenge, we developed the SpatialSky-Dataset, a comprehensive dataset containing 1M samples with diverse annotations across various scenarios. Leveraging this dataset, we introduce Sky-VLM, a specialized VLM designed for UAV spatial reasoning across multiple granularities and contexts. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that Sky-VLM achieves state-of-the-art performance across all benchmark tasks, paving the way for the development of VLMs suitable for UAV scenarios. The source code is available at https://github.com/linglingxiansen/SpatialSKy.
RoboAfford++: A Generative AI-Enhanced Dataset for Multimodal Affordance Learning in Robotic Manipulation and Navigation
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Robotic manipulation and navigation are fundamental capabilities of embodied intelligence, enabling effective robot interactions with the physical world. Achieving these capabilities requires a cohesive understanding of the environment, including object recognition to localize target objects, object affordances to identify potential interaction areas and spatial affordances to discern optimal areas for both object placement and robot movement. While Vision-Language Models (VLMs) excel at high-level task planning and scene understanding, they often struggle to infer actionable positions for physical interaction, such as functional grasping points and permissible placement regions. This limitation stems from the lack of fine-grained annotations for object and spatial affordances in their training datasets. To tackle this challenge, we introduce RoboAfford++, a generative AI-enhanced dataset for multimodal affordance learning for both robotic manipulation and navigation. Our dataset comprises 869,987 images paired with 2.0 million question answering (QA) annotations, covering three critical tasks: object affordance recognition to identify target objects based on attributes and spatial relationships, object affordance prediction to pinpoint functional parts for manipulation, and spatial affordance localization to identify free space for object placement and robot navigation. Complementing this dataset, we propose RoboAfford-Eval, a comprehensive benchmark for assessing affordance-aware prediction in real-world scenarios, featuring 338 meticulously annotated samples across the same three tasks. Extensive experimental results reveal the deficiencies of existing VLMs in affordance learning, while fine-tuning on the RoboAfford++ dataset significantly enhances their ability to reason about object and spatial affordances, validating the dataset's effectiveness.
RoboOS-NeXT: A Unified Memory-based Framework for Lifelong, Scalable, and Robust Multi-Robot Collaboration
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:The proliferation of collaborative robots across diverse tasks and embodiments presents a central challenge: achieving lifelong adaptability, scalable coordination, and robust scheduling in multi-agent systems. Existing approaches, from vision-language-action (VLA) models to hierarchical frameworks, fall short due to their reliance on limited or dividual-agent memory. This fundamentally constrains their ability to learn over long horizons, scale to heterogeneous teams, or recover from failures, highlighting the need for a unified memory representation. To address these limitations, we introduce RoboOS-NeXT, a unified memory-based framework for lifelong, scalable, and robust multi-robot collaboration. At the core of RoboOS-NeXT is the novel Spatio-Temporal-Embodiment Memory (STEM), which integrates spatial scene geometry, temporal event history, and embodiment profiles into a shared representation. This memory-centric design is integrated into a brain-cerebellum framework, where a high-level brain model performs global planning by retrieving and updating STEM, while low-level controllers execute actions locally. This closed loop between cognition, memory, and execution enables dynamic task allocation, fault-tolerant collaboration, and consistent state synchronization. We conduct extensive experiments spanning complex coordination tasks in restaurants, supermarkets, and households. Our results demonstrate that RoboOS-NeXT achieves superior performance across heterogeneous embodiments, validating its effectiveness in enabling lifelong, scalable, and robust multi-robot collaboration. Project website: https://flagopen.github.io/RoboOS/
Team Xiaomi EV-AD VLA: Learning to Navigate Socially Through Proactive Risk Perception - Technical Report for IROS 2025 RoboSense Challenge Social Navigation Track
Oct 09, 2025Abstract:In this report, we describe the technical details of our submission to the IROS 2025 RoboSense Challenge Social Navigation Track. This track focuses on developing RGBD-based perception and navigation systems that enable autonomous agents to navigate safely, efficiently, and socially compliantly in dynamic human-populated indoor environments. The challenge requires agents to operate from an egocentric perspective using only onboard sensors including RGB-D observations and odometry, without access to global maps or privileged information, while maintaining social norm compliance such as safe distances and collision avoidance. Building upon the Falcon model, we introduce a Proactive Risk Perception Module to enhance social navigation performance. Our approach augments Falcon with collision risk understanding that learns to predict distance-based collision risk scores for surrounding humans, which enables the agent to develop more robust spatial awareness and proactive collision avoidance behaviors. The evaluation on the Social-HM3D benchmark demonstrates that our method improves the agent's ability to maintain personal space compliance while navigating toward goals in crowded indoor scenes with dynamic human agents, achieving 2nd place among 16 participating teams in the challenge.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge