Qi Chu
Machine Failure Detection Based on Projected Quantum Models
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Detecting machine failures promptly is of utmost importance in industry for maintaining efficiency and minimizing downtime. This paper introduces a failure detection algorithm based on quantum computing and a statistical change-point detection approach. Our method leverages the potential of projected quantum feature maps to enhance the precision of anomaly detection in machine monitoring systems. We empirically validate our approach on benchmark multi-dimensional time series datasets as well as on a real-world dataset comprising IoT sensor readings from operational machines, ensuring the practical relevance of our study. The algorithm was executed on IBM's 133-qubit Heron quantum processor, demonstrating the feasibility of integrating quantum computing into industrial maintenance procedures. The presented results underscore the effectiveness of our quantum-based failure detection system, showcasing its capability to accurately identify anomalies in noisy time series data. This work not only highlights the potential of quantum computing in industrial diagnostics but also paves the way for more sophisticated quantum algorithms in the realm of predictive maintenance.
SAPL: Semantic-Agnostic Prompt Learning in CLIP for Weakly Supervised Image Manipulation Localization
Jan 09, 2026Abstract:Malicious image manipulation threatens public safety and requires efficient localization methods. Existing approaches depend on costly pixel-level annotations which make training expensive. Existing weakly supervised methods rely only on image-level binary labels and focus on global classification, often overlooking local edge cues that are critical for precise localization. We observe that feature variations at manipulated boundaries are substantially larger than in interior regions. To address this gap, we propose Semantic-Agnostic Prompt Learning (SAPL) in CLIP, which learns text prompts that intentionally encode non-semantic, boundary-centric cues so that CLIPs multimodal similarity highlights manipulation edges rather than high-level object semantics. SAPL combines two complementary modules Edge-aware Contextual Prompt Learning (ECPL) and Hierarchical Edge Contrastive Learning (HECL) to exploit edge information in both textual and visual spaces. The proposed ECPL leverages edge-enhanced image features to generate learnable textual prompts via an attention mechanism, embedding semantic-irrelevant information into text features, to guide CLIP focusing on manipulation edges. The proposed HECL extract genuine and manipulated edge patches, and utilize contrastive learning to boost the discrimination between genuine edge patches and manipulated edge patches. Finally, we predict the manipulated regions from the similarity map after processing. Extensive experiments on multiple public benchmarks demonstrate that SAPL significantly outperforms existing approaches, achieving state-of-the-art localization performance.
LAKAN: Landmark-assisted Adaptive Kolmogorov-Arnold Network for Face Forgery Detection
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:The rapid development of deepfake generation techniques necessitates robust face forgery detection algorithms. While methods based on Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers are effective, there is still room for improvement in modeling the highly complex and non-linear nature of forgery artifacts. To address this issue, we propose a novel detection method based on the Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (KAN). By replacing fixed activation functions with learnable splines, our KAN-based approach is better suited to this challenge. Furthermore, to guide the network's focus towards critical facial areas, we introduce a Landmark-assisted Adaptive Kolmogorov-Arnold Network (LAKAN) module. This module uses facial landmarks as a structural prior to dynamically generate the internal parameters of the KAN, creating an instance-specific signal that steers a general-purpose image encoder towards the most informative facial regions with artifacts. This core innovation creates a powerful combination between geometric priors and the network's learning process. Extensive experiments on multiple public datasets show that our proposed method achieves superior performance.
MARS-Bench: A Multi-turn Athletic Real-world Scenario Benchmark for Dialogue Evaluation
May 27, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (\textbf{LLMs}), e.g. ChatGPT, have been widely adopted in real-world dialogue applications. However, LLMs' robustness, especially in handling long complex dialogue sessions, including frequent motivation transfer, sophisticated cross-turn dependency, is criticized all along. Nevertheless, no existing benchmarks can fully reflect these weaknesses. We present \textbf{MARS-Bench}, a \textbf{M}ulti-turn \textbf{A}thletic \textbf{R}eal-world \textbf{S}cenario Dialogue \textbf{Bench}mark, designed to remedy the gap. MARS-Bench is constructed from play-by-play text commentary so to feature realistic dialogues specifically designed to evaluate three critical aspects of multi-turn conversations: Ultra Multi-turn, Interactive Multi-turn, and Cross-turn Tasks. Extensive experiments on MARS-Bench also reveal that closed-source LLMs significantly outperform open-source alternatives, explicit reasoning significantly boosts LLMs' robustness on handling long complex dialogue sessions, and LLMs indeed face significant challenges when handling motivation transfer and sophisticated cross-turn dependency. Moreover, we provide mechanistic interpretability on how attention sinks due to special tokens lead to LLMs' performance degradation when handling long complex dialogue sessions based on attention visualization experiment in Qwen2.5-7B-Instruction.
Your Classifier Can Do More: Towards Bridging the Gaps in Classification, Robustness, and Generation
May 26, 2025Abstract:Joint Energy-based Models (JEMs), a class of hybrid generative-discriminative models, are well known for their ability to achieve both high classification accuracy and generative capability within a single model. However, their robustness still lags significantly behind the classifiers based adversarial training (AT). Conversely, while AT is currently the most effective approach to improving the classifier's robustness, it typically sacrifices accuracy on clean data and lacks generative capability. The triple trade-off between classification accuracy, generative capability and robustness, raises a natural question: Can a single model simultaneously achieve high classification accuracy, adversarial robustness, and generative performance? -- a goal that has been rarely explored. To address this question, we systematically analyze the energy distribution differences of clean, adversarial, and generated samples across various JEM variants and adversarially trained models. We observe that AT tends to reduce the energy gap between clean and adversarial samples, while JEMs reduce the gap between clean and synthetic ones. This observation suggests a key insight: if the energy distributions of all three data types can be aligned, we might unify the strengths of AT and JEMs, resolving their inherent trade-offs. Building on this idea, we propose Energy-based Joint Distribution Adversarial Training (EB-JDAT), to jointly model the clean data distribution, the adversarial distribution, and the classifier by maximizing their joint probability. EB-JDAT is a general and flexible optimization method, compatible with various JEM variants. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that EB-JDAT not only maintains near original accuracy and generative capability of JEMs, but also significantly enhances robustness, even surpassing state-of-the-art ATs.
Benchmarking Unified Face Attack Detection via Hierarchical Prompt Tuning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Presentation Attack Detection and Face Forgery Detection are designed to protect face data from physical media-based Presentation Attacks and digital editing-based DeepFakes respectively. But separate training of these two models makes them vulnerable to unknown attacks and burdens deployment environments. The lack of a Unified Face Attack Detection model to handle both types of attacks is mainly due to two factors. First, there's a lack of adequate benchmarks for models to explore. Existing UAD datasets have limited attack types and samples, restricting the model's ability to address advanced threats. To address this, we propose UniAttackDataPlus (UniAttackData+), the most extensive and sophisticated collection of forgery techniques to date. It includes 2,875 identities and their 54 kinds of falsified samples, totaling 697,347 videos. Second, there's a lack of a reliable classification criterion. Current methods try to find an arbitrary criterion within the same semantic space, which fails when encountering diverse attacks. So, we present a novel Visual-Language Model-based Hierarchical Prompt Tuning Framework (HiPTune) that adaptively explores multiple classification criteria from different semantic spaces. We build a Visual Prompt Tree to explore various classification rules hierarchically. Then, by adaptively pruning the prompts, the model can select the most suitable prompts to guide the encoder to extract discriminative features at different levels in a coarse-to-fine way. Finally, to help the model understand the classification criteria in visual space, we propose a Dynamically Prompt Integration module to project the visual prompts to the text encoder for more accurate semantics. Experiments on 12 datasets have shown the potential to inspire further innovations in the UAD field.
Context-Aware Weakly Supervised Image Manipulation Localization with SAM Refinement
Mar 26, 2025Abstract:Malicious image manipulation poses societal risks, increasing the importance of effective image manipulation detection methods. Recent approaches in image manipulation detection have largely been driven by fully supervised approaches, which require labor-intensive pixel-level annotations. Thus, it is essential to explore weakly supervised image manipulation localization methods that only require image-level binary labels for training. However, existing weakly supervised image manipulation methods overlook the importance of edge information for accurate localization, leading to suboptimal localization performance. To address this, we propose a Context-Aware Boundary Localization (CABL) module to aggregate boundary features and learn context-inconsistency for localizing manipulated areas. Furthermore, by leveraging Class Activation Mapping (CAM) and Segment Anything Model (SAM), we introduce the CAM-Guided SAM Refinement (CGSR) module to generate more accurate manipulation localization maps. By integrating two modules, we present a novel weakly supervised framework based on a dual-branch Transformer-CNN architecture. Our method achieves outstanding localization performance across multiple datasets.
Inclusion 2024 Global Multimedia Deepfake Detection: Towards Multi-dimensional Facial Forgery Detection
Dec 30, 2024
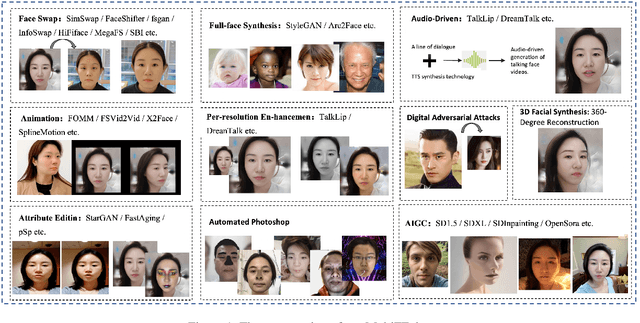


Abstract:In this paper, we present the Global Multimedia Deepfake Detection held concurrently with the Inclusion 2024. Our Multimedia Deepfake Detection aims to detect automatic image and audio-video manipulations including but not limited to editing, synthesis, generation, Photoshop,etc. Our challenge has attracted 1500 teams from all over the world, with about 5000 valid result submission counts. We invite the top 20 teams to present their solutions to the challenge, from which the top 3 teams are awarded prizes in the grand finale. In this paper, we present the solutions from the top 3 teams of the two tracks, to boost the research work in the field of image and audio-video forgery detection. The methodologies developed through the challenge will contribute to the development of next-generation deepfake detection systems and we encourage participants to open source their methods.
Llama SLayer 8B: Shallow Layers Hold the Key to Knowledge Injection
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:As a manner to augment pre-trained large language models (LLM), knowledge injection is critical to develop vertical domain large models and has been widely studied. Although most current approaches, including parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) and block expansion methods, uniformly apply knowledge across all LLM layers, it raises the question: are all layers equally crucial for knowledge injection? We begin by evaluating the importance of each layer in finding the optimal layer range for knowledge injection. Intuitively, the more important layers should play a more critical role in knowledge injection and deserve a denser injection. We observe performance dips in question-answering benchmarks after the removal or expansion of the shallow layers, and the degradation shrinks as the layer gets deeper, indicating that the shallow layers hold the key to knowledge injection. This insight leads us to propose the S strategy, a post-pretraining strategy of selectively enhancing shallow layers while pruning the less effective deep ones. Based on this strategy, we introduce Llama Slayer-8B and Llama Slayer-8B-Instruct. We experimented on the corpus of code $\&$ math and demonstrated the effectiveness of our strategy. Further experiments across different LLM, Mistral-7B, and a legal corpus confirmed the general applicability of the approach, underscoring its wide-ranging efficacy. Our code is available at: \https://github.com/txchen-USTC/Llama-Slayer
Mixture-of-Noises Enhanced Forgery-Aware Predictor for Multi-Face Manipulation Detection and Localization
Aug 05, 2024



Abstract:With the advancement of face manipulation technology, forgery images in multi-face scenarios are gradually becoming a more complex and realistic challenge. Despite this, detection and localization methods for such multi-face manipulations remain underdeveloped. Traditional manipulation localization methods either indirectly derive detection results from localization masks, resulting in limited detection performance, or employ a naive two-branch structure to simultaneously obtain detection and localization results, which cannot effectively benefit the localization capability due to limited interaction between two tasks. This paper proposes a new framework, namely MoNFAP, specifically tailored for multi-face manipulation detection and localization. The MoNFAP primarily introduces two novel modules: the Forgery-aware Unified Predictor (FUP) Module and the Mixture-of-Noises Module (MNM). The FUP integrates detection and localization tasks using a token learning strategy and multiple forgery-aware transformers, which facilitates the use of classification information to enhance localization capability. Besides, motivated by the crucial role of noise information in forgery detection, the MNM leverages multiple noise extractors based on the concept of the mixture of experts to enhance the general RGB features, further boosting the performance of our framework. Finally, we establish a comprehensive benchmark for multi-face detection and localization and the proposed \textit{MoNFAP} achieves significant performance. The codes will be made available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge