Dongdong Chen
VISTA: Enhancing Visual Conditioning via Track-Following Preference Optimization in Vision-Language-Action Models
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated strong performance across a wide range of robotic manipulation tasks. Despite the success, extending large pretrained Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to the action space can induce vision-action misalignment, where action predictions exhibit weak dependence on the current visual state, leading to unreliable action outputs. In this work, we study VLA models through the lens of visual conditioning and empirically show that successful rollouts consistently exhibit stronger visual dependence than failed ones. Motivated by this observation, we propose a training framework that explicitly strengthens visual conditioning in VLA models. Our approach first aligns action prediction with visual input via preference optimization on a track-following surrogate task, and then transfers the enhanced alignment to instruction-following task through latent-space distillation during supervised finetuning. Without introducing architectural modifications or additional data collection, our method improves both visual conditioning and task performance for discrete OpenVLA, and further yields consistent gains when extended to the continuous OpenVLA-OFT setting. Project website: https://vista-vla.github.io/ .
Bridging Online and Offline RL: Contextual Bandit Learning for Multi-Turn Code Generation
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Recently, there have been significant research interests in training large language models (LLMs) with reinforcement learning (RL) on real-world tasks, such as multi-turn code generation. While online RL tends to perform better than offline RL, its higher training cost and instability hinders wide adoption. In this paper, we build on the observation that multi-turn code generation can be formulated as a one-step recoverable Markov decision process and propose contextual bandit learning with offline trajectories (Cobalt), a new method that combines the benefits of online and offline RL. Cobalt first collects code generation trajectories using a reference LLM and divides them into partial trajectories as contextual prompts. Then, during online bandit learning, the LLM is trained to complete each partial trajectory prompt through single-step code generation. Cobalt outperforms two multi-turn online RL baselines based on GRPO and VeRPO, and substantially improves R1-Distill 8B and Qwen3 8B by up to 9.0 and 6.2 absolute Pass@1 scores on LiveCodeBench. Also, we analyze LLMs' in-context reward hacking behaviors and augment Cobalt training with perturbed trajectories to mitigate this issue. Overall, our results demonstrate Cobalt as a promising solution for iterative decision-making tasks like multi-turn code generation. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/OSU-NLP-Group/cobalt.
SHARE: A Fully Unsupervised Framework for Single Hyperspectral Image Restoration
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Hyperspectral image (HSI) restoration is a fundamental challenge in computational imaging and computer vision. It involves ill-posed inverse problems, such as inpainting and super-resolution. Although deep learning methods have transformed the field through data-driven learning, their effectiveness hinges on access to meticulously curated ground-truth datasets. This fundamentally restricts their applicability in real-world scenarios where such data is unavailable. This paper presents SHARE (Single Hyperspectral Image Restoration with Equivariance), a fully unsupervised framework that unifies geometric equivariance principles with low-rank spectral modelling to eliminate the need for ground truth. SHARE's core concept is to exploit the intrinsic invariance of hyperspectral structures under differentiable geometric transformations (e.g. rotations and scaling) to derive self-supervision signals through equivariance consistency constraints. Our novel Dynamic Adaptive Spectral Attention (DASA) module further enhances this paradigm shift by explicitly encoding the global low-rank property of HSI and adaptively refining local spectral-spatial correlations through learnable attention mechanisms. Extensive experiments on HSI inpainting and super-resolution tasks demonstrate the effectiveness of SHARE. Our method outperforms many state-of-the-art unsupervised approaches and achieves performance comparable to that of supervised methods. We hope that our approach will shed new light on HSI restoration and broader scientific imaging scenarios. The code will be released at https://github.com/xuwayyy/SHARE.
Equivariant Learning for Unsupervised Image Dehazing
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Image Dehazing (ID) aims to produce a clear image from an observation contaminated by haze. Current ID methods typically rely on carefully crafted priors or extensive haze-free ground truth, both of which are expensive or impractical to acquire, particularly in the context of scientific imaging. We propose a new unsupervised learning framework called Equivariant Image Dehazing (EID) that exploits the symmetry of image signals to restore clarity to hazy observations. By enforcing haze consistency and systematic equivariance, EID can recover clear patterns directly from raw, hazy images. Additionally, we propose an adversarial learning strategy to model unknown haze physics and facilitate EID learning. Experiments on two scientific image dehazing benchmarks (including cell microscopy and medical endoscopy) and on natural image dehazing have demonstrated that EID significantly outperforms state-of-the-art approaches. By unifying equivariant learning with modelling haze physics, we hope that EID will enable more versatile and effective haze removal in scientific imaging. Code and datasets will be published.
ReasonGen-R1: CoT for Autoregressive Image generation models through SFT and RL
May 30, 2025Abstract:Although chain-of-thought reasoning and reinforcement learning (RL) have driven breakthroughs in NLP, their integration into generative vision models remains underexplored. We introduce ReasonGen-R1, a two-stage framework that first imbues an autoregressive image generator with explicit text-based "thinking" skills via supervised fine-tuning on a newly generated reasoning dataset of written rationales, and then refines its outputs using Group Relative Policy Optimization. To enable the model to reason through text before generating images, We automatically generate and release a corpus of model crafted rationales paired with visual prompts, enabling controlled planning of object layouts, styles, and scene compositions. Our GRPO algorithm uses reward signals from a pretrained vision language model to assess overall visual quality, optimizing the policy in each update. Evaluations on GenEval, DPG, and the T2I benchmark demonstrate that ReasonGen-R1 consistently outperforms strong baselines and prior state-of-the-art models. More: aka.ms/reasongen.
DeepInverse: A Python package for solving imaging inverse problems with deep learning
May 26, 2025Abstract:DeepInverse is an open-source PyTorch-based library for solving imaging inverse problems. The library covers all crucial steps in image reconstruction from the efficient implementation of forward operators (e.g., optics, MRI, tomography), to the definition and resolution of variational problems and the design and training of advanced neural network architectures. In this paper, we describe the main functionality of the library and discuss the main design choices.
Phi-4-Mini-Reasoning: Exploring the Limits of Small Reasoning Language Models in Math
Apr 30, 2025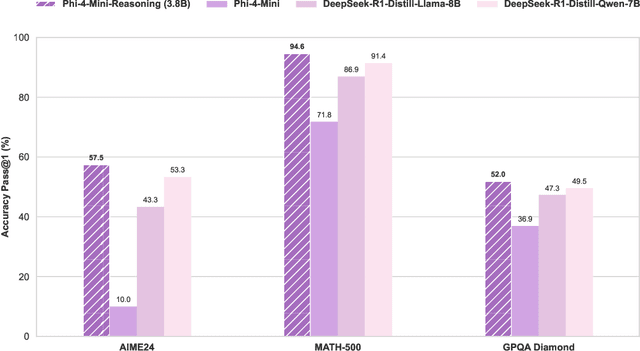
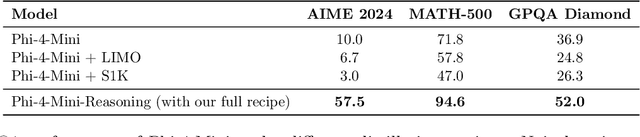

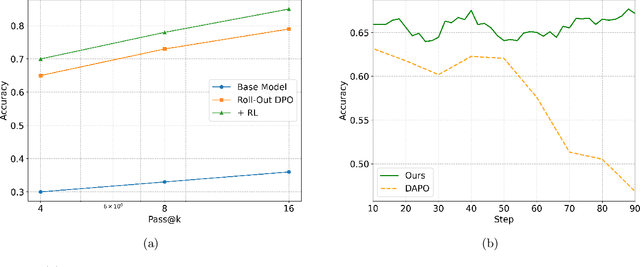
Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) significantly enhances formal reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs) by training them to explicitly generate intermediate reasoning steps. While LLMs readily benefit from such techniques, improving reasoning in Small Language Models (SLMs) remains challenging due to their limited model capacity. Recent work by Deepseek-R1 demonstrates that distillation from LLM-generated synthetic data can substantially improve the reasoning ability of SLM. However, the detailed modeling recipe is not disclosed. In this work, we present a systematic training recipe for SLMs that consists of four steps: (1) large-scale mid-training on diverse distilled long-CoT data, (2) supervised fine-tuning on high-quality long-CoT data, (3) Rollout DPO leveraging a carefully curated preference dataset, and (4) Reinforcement Learning (RL) with Verifiable Reward. We apply our method on Phi-4-Mini, a compact 3.8B-parameter model. The resulting Phi-4-Mini-Reasoning model exceeds, on math reasoning tasks, much larger reasoning models, e.g., outperforming DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Qwen-7B by 3.2 points and DeepSeek-R1-Distill-Llama-8B by 7.7 points on Math-500. Our results validate that a carefully designed training recipe, with large-scale high-quality CoT data, is effective to unlock strong reasoning capabilities even in resource-constrained small models.
Show and Segment: Universal Medical Image Segmentation via In-Context Learning
Mar 25, 2025Abstract:Medical image segmentation remains challenging due to the vast diversity of anatomical structures, imaging modalities, and segmentation tasks. While deep learning has made significant advances, current approaches struggle to generalize as they require task-specific training or fine-tuning on unseen classes. We present Iris, a novel In-context Reference Image guided Segmentation framework that enables flexible adaptation to novel tasks through the use of reference examples without fine-tuning. At its core, Iris features a lightweight context task encoding module that distills task-specific information from reference context image-label pairs. This rich context embedding information is used to guide the segmentation of target objects. By decoupling task encoding from inference, Iris supports diverse strategies from one-shot inference and context example ensemble to object-level context example retrieval and in-context tuning. Through comprehensive evaluation across twelve datasets, we demonstrate that Iris performs strongly compared to task-specific models on in-distribution tasks. On seven held-out datasets, Iris shows superior generalization to out-of-distribution data and unseen classes. Further, Iris's task encoding module can automatically discover anatomical relationships across datasets and modalities, offering insights into medical objects without explicit anatomical supervision.
FreeFlux: Understanding and Exploiting Layer-Specific Roles in RoPE-Based MMDiT for Versatile Image Editing
Mar 20, 2025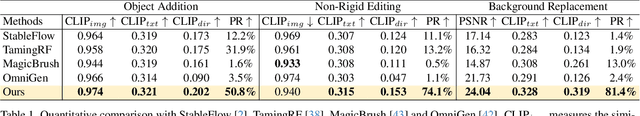
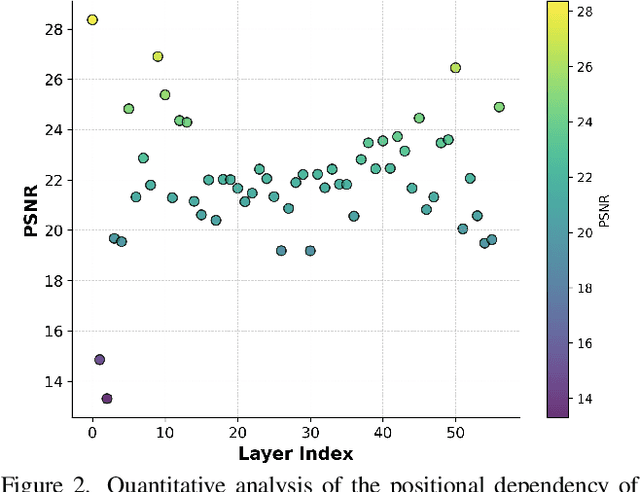
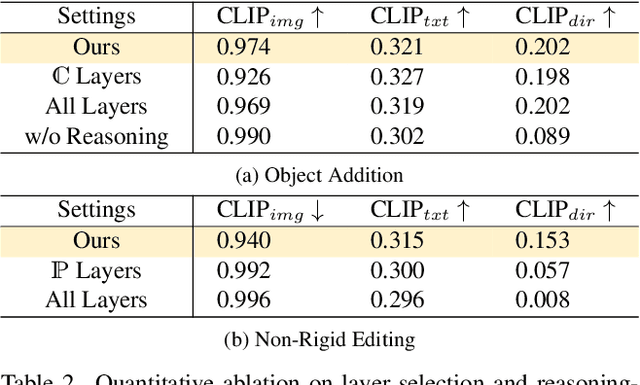
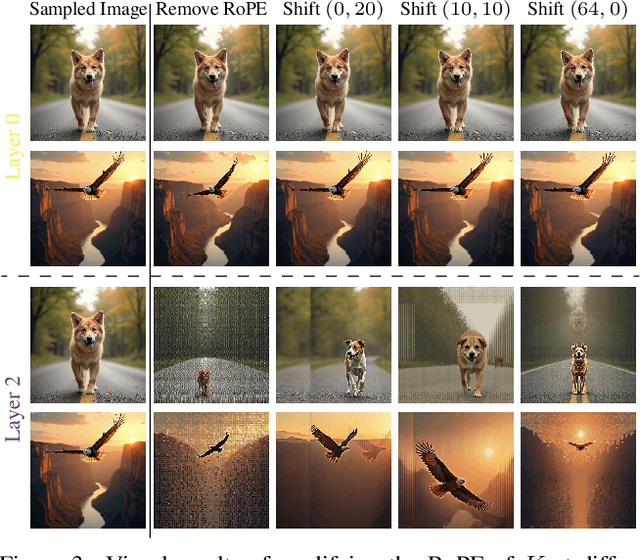
Abstract:The integration of Rotary Position Embedding (RoPE) in Multimodal Diffusion Transformer (MMDiT) has significantly enhanced text-to-image generation quality. However, the fundamental reliance of self-attention layers on positional embedding versus query-key similarity during generation remains an intriguing question. We present the first mechanistic analysis of RoPE-based MMDiT models (e.g., FLUX), introducing an automated probing strategy that disentangles positional information versus content dependencies by strategically manipulating RoPE during generation. Our analysis reveals distinct dependency patterns that do not straightforwardly correlate with depth, offering new insights into the layer-specific roles in RoPE-based MMDiT. Based on these findings, we propose a training-free, task-specific image editing framework that categorizes editing tasks into three types: position-dependent editing (e.g., object addition), content similarity-dependent editing (e.g., non-rigid editing), and region-preserved editing (e.g., background replacement). For each type, we design tailored key-value injection strategies based on the characteristics of the editing task. Extensive qualitative and quantitative evaluations demonstrate that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches, particularly in preserving original semantic content and achieving seamless modifications.
I2V3D: Controllable image-to-video generation with 3D guidance
Mar 12, 2025



Abstract:We present I2V3D, a novel framework for animating static images into dynamic videos with precise 3D control, leveraging the strengths of both 3D geometry guidance and advanced generative models. Our approach combines the precision of a computer graphics pipeline, enabling accurate control over elements such as camera movement, object rotation, and character animation, with the visual fidelity of generative AI to produce high-quality videos from coarsely rendered inputs. To support animations with any initial start point and extended sequences, we adopt a two-stage generation process guided by 3D geometry: 1) 3D-Guided Keyframe Generation, where a customized image diffusion model refines rendered keyframes to ensure consistency and quality, and 2) 3D-Guided Video Interpolation, a training-free approach that generates smooth, high-quality video frames between keyframes using bidirectional guidance. Experimental results highlight the effectiveness of our framework in producing controllable, high-quality animations from single input images by harmonizing 3D geometry with generative models. The code for our framework will be publicly released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge