Chuanbiao Song
Veritas: Generalizable Deepfake Detection via Pattern-Aware Reasoning
Aug 28, 2025



Abstract:Deepfake detection remains a formidable challenge due to the complex and evolving nature of fake content in real-world scenarios. However, existing academic benchmarks suffer from severe discrepancies from industrial practice, typically featuring homogeneous training sources and low-quality testing images, which hinder the practical deployments of current detectors. To mitigate this gap, we introduce HydraFake, a dataset that simulates real-world challenges with hierarchical generalization testing. Specifically, HydraFake involves diversified deepfake techniques and in-the-wild forgeries, along with rigorous training and evaluation protocol, covering unseen model architectures, emerging forgery techniques and novel data domains. Building on this resource, we propose Veritas, a multi-modal large language model (MLLM) based deepfake detector. Different from vanilla chain-of-thought (CoT), we introduce pattern-aware reasoning that involves critical reasoning patterns such as "planning" and "self-reflection" to emulate human forensic process. We further propose a two-stage training pipeline to seamlessly internalize such deepfake reasoning capacities into current MLLMs. Experiments on HydraFake dataset reveal that although previous detectors show great generalization on cross-model scenarios, they fall short on unseen forgeries and data domains. Our Veritas achieves significant gains across different OOD scenarios, and is capable of delivering transparent and faithful detection outputs.
NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image Generation Model Quality Assessment
May 22, 2025Abstract:This paper reports on the NTIRE 2025 challenge on Text to Image (T2I) generation model quality assessment, which will be held in conjunction with the New Trends in Image Restoration and Enhancement Workshop (NTIRE) at CVPR 2025. The aim of this challenge is to address the fine-grained quality assessment of text-to-image generation models. This challenge evaluates text-to-image models from two aspects: image-text alignment and image structural distortion detection, and is divided into the alignment track and the structural track. The alignment track uses the EvalMuse-40K, which contains around 40K AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) generated by 20 popular generative models. The alignment track has a total of 371 registered participants. A total of 1,883 submissions are received in the development phase, and 507 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 12 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. The structure track uses the EvalMuse-Structure, which contains 10,000 AI-Generated Images (AIGIs) with corresponding structural distortion mask. A total of 211 participants have registered in the structure track. A total of 1155 submissions are received in the development phase, and 487 submissions are received in the test phase. Finally, 8 participating teams submitted their models and fact sheets. Almost all methods have achieved better results than baseline methods, and the winning methods in both tracks have demonstrated superior prediction performance on T2I model quality assessment.
Benchmarking Unified Face Attack Detection via Hierarchical Prompt Tuning
May 19, 2025Abstract:Presentation Attack Detection and Face Forgery Detection are designed to protect face data from physical media-based Presentation Attacks and digital editing-based DeepFakes respectively. But separate training of these two models makes them vulnerable to unknown attacks and burdens deployment environments. The lack of a Unified Face Attack Detection model to handle both types of attacks is mainly due to two factors. First, there's a lack of adequate benchmarks for models to explore. Existing UAD datasets have limited attack types and samples, restricting the model's ability to address advanced threats. To address this, we propose UniAttackDataPlus (UniAttackData+), the most extensive and sophisticated collection of forgery techniques to date. It includes 2,875 identities and their 54 kinds of falsified samples, totaling 697,347 videos. Second, there's a lack of a reliable classification criterion. Current methods try to find an arbitrary criterion within the same semantic space, which fails when encountering diverse attacks. So, we present a novel Visual-Language Model-based Hierarchical Prompt Tuning Framework (HiPTune) that adaptively explores multiple classification criteria from different semantic spaces. We build a Visual Prompt Tree to explore various classification rules hierarchically. Then, by adaptively pruning the prompts, the model can select the most suitable prompts to guide the encoder to extract discriminative features at different levels in a coarse-to-fine way. Finally, to help the model understand the classification criteria in visual space, we propose a Dynamically Prompt Integration module to project the visual prompts to the text encoder for more accurate semantics. Experiments on 12 datasets have shown the potential to inspire further innovations in the UAD field.
InterAnimate: Taming Region-aware Diffusion Model for Realistic Human Interaction Animation
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Recent video generation research has focused heavily on isolated actions, leaving interactive motions-such as hand-face interactions-largely unexamined. These interactions are essential for emerging biometric authentication systems, which rely on interactive motion-based anti-spoofing approaches. From a security perspective, there is a growing need for large-scale, high-quality interactive videos to train and strengthen authentication models. In this work, we introduce a novel paradigm for animating realistic hand-face interactions. Our approach simultaneously learns spatio-temporal contact dynamics and biomechanically plausible deformation effects, enabling natural interactions where hand movements induce anatomically accurate facial deformations while maintaining collision-free contact. To facilitate this research, we present InterHF, a large-scale hand-face interaction dataset featuring 18 interaction patterns and 90,000 annotated videos. Additionally, we propose InterAnimate, a region-aware diffusion model designed specifically for interaction animation. InterAnimate leverages learnable spatial and temporal latents to effectively capture dynamic interaction priors and integrates a region-aware interaction mechanism that injects these priors into the denoising process. To the best of our knowledge, this work represents the first large-scale effort to systematically study human hand-face interactions. Qualitative and quantitative results show InterAnimate produces highly realistic animations, setting a new benchmark. Code and data will be made public to advance research.
Supervised Contrastive Learning for Snapshot Spectral Imaging Face Anti-Spoofing
May 29, 2024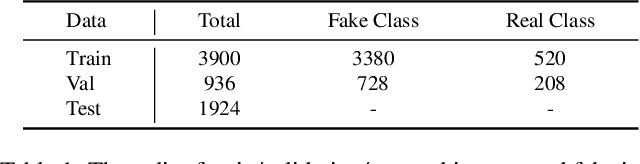

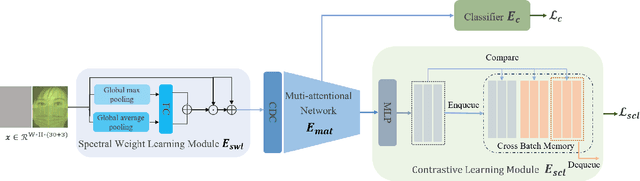
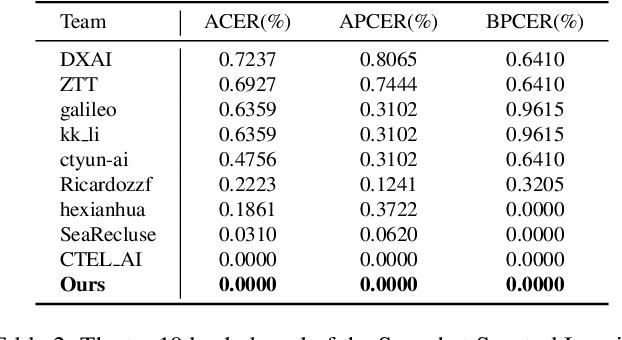
Abstract:This study reveals a cutting-edge re-balanced contrastive learning strategy aimed at strengthening face anti-spoofing capabilities within facial recognition systems, with a focus on countering the challenges posed by printed photos, and highly realistic silicone or latex masks. Leveraging the HySpeFAS dataset, which benefits from Snapshot Spectral Imaging technology to provide hyperspectral images, our approach harmonizes class-level contrastive learning with data resampling and an innovative real-face oriented reweighting technique. This method effectively mitigates dataset imbalances and reduces identity-related biases. Notably, our strategy achieved an unprecedented 0.0000\% Average Classification Error Rate (ACER) on the HySpeFAS dataset, ranking first at the Chalearn Snapshot Spectral Imaging Face Anti-spoofing Challenge on CVPR 2024.
Adversarial Attacks on ML Defense Models Competition
Oct 15, 2021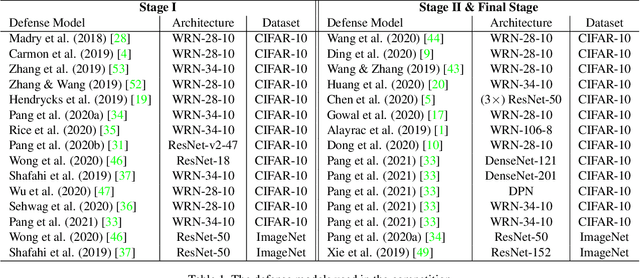
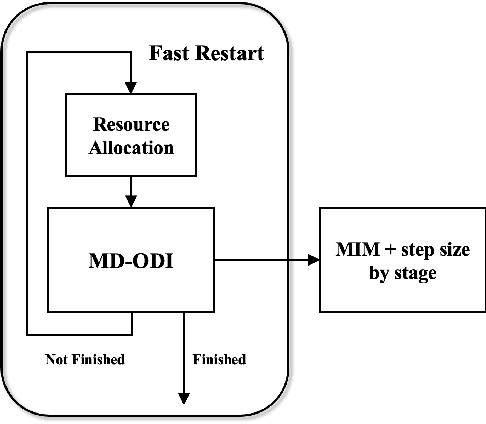
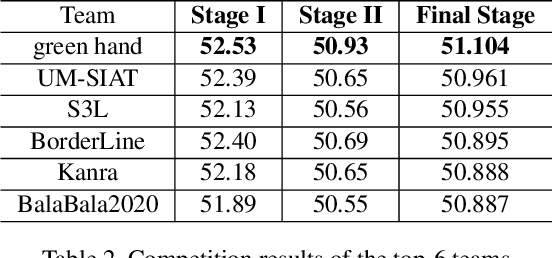
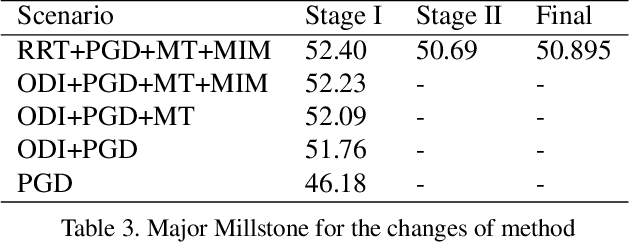
Abstract:Due to the vulnerability of deep neural networks (DNNs) to adversarial examples, a large number of defense techniques have been proposed to alleviate this problem in recent years. However, the progress of building more robust models is usually hampered by the incomplete or incorrect robustness evaluation. To accelerate the research on reliable evaluation of adversarial robustness of the current defense models in image classification, the TSAIL group at Tsinghua University and the Alibaba Security group organized this competition along with a CVPR 2021 workshop on adversarial machine learning (https://aisecure-workshop.github.io/amlcvpr2021/). The purpose of this competition is to motivate novel attack algorithms to evaluate adversarial robustness more effectively and reliably. The participants were encouraged to develop stronger white-box attack algorithms to find the worst-case robustness of different defenses. This competition was conducted on an adversarial robustness evaluation platform -- ARES (https://github.com/thu-ml/ares), and is held on the TianChi platform (https://tianchi.aliyun.com/competition/entrance/531847/introduction) as one of the series of AI Security Challengers Program. After the competition, we summarized the results and established a new adversarial robustness benchmark at https://ml.cs.tsinghua.edu.cn/ares-bench/, which allows users to upload adversarial attack algorithms and defense models for evaluation.
Regional Adversarial Training for Better Robust Generalization
Sep 04, 2021
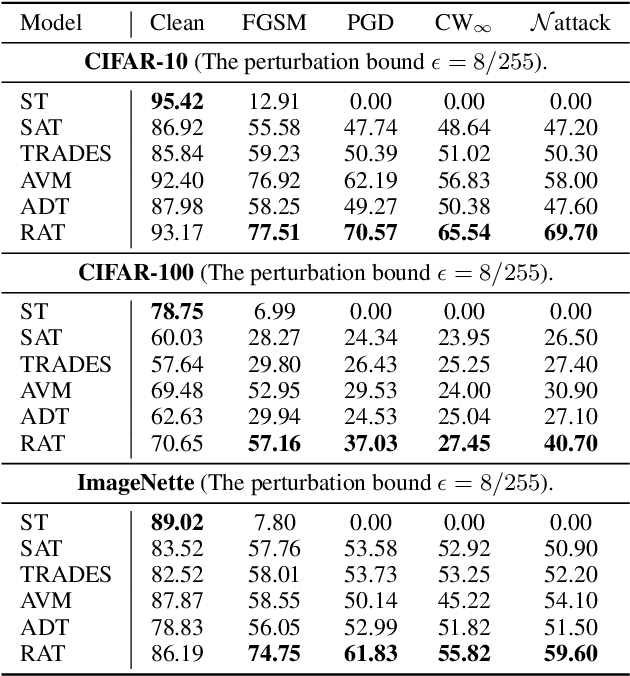
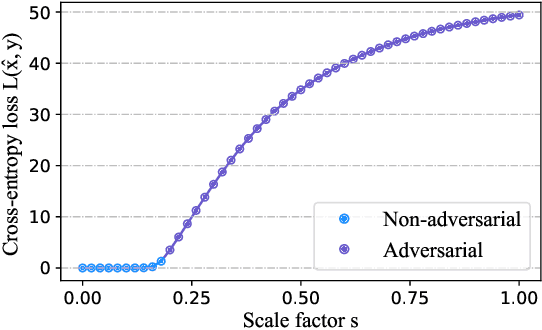
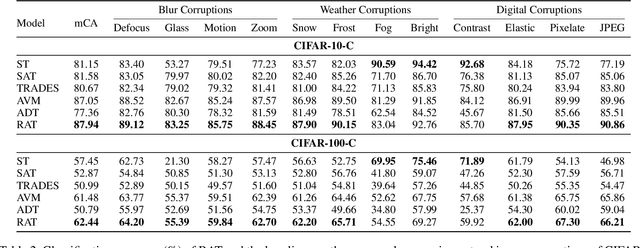
Abstract:Adversarial training (AT) has been demonstrated as one of the most promising defense methods against various adversarial attacks. To our knowledge, existing AT-based methods usually train with the locally most adversarial perturbed points and treat all the perturbed points equally, which may lead to considerably weaker adversarial robust generalization on test data. In this work, we introduce a new adversarial training framework that considers the diversity as well as characteristics of the perturbed points in the vicinity of benign samples. To realize the framework, we propose a Regional Adversarial Training (RAT) defense method that first utilizes the attack path generated by the typical iterative attack method of projected gradient descent (PGD), and constructs an adversarial region based on the attack path. Then, RAT samples diverse perturbed training points efficiently inside this region, and utilizes a distance-aware label smoothing mechanism to capture our intuition that perturbed points at different locations should have different impact on the model performance. Extensive experiments on several benchmark datasets show that RAT consistently makes significant improvement on standard adversarial training (SAT), and exhibits better robust generalization.
Multi-stage Optimization based Adversarial Training
Jun 26, 2021



Abstract:In the field of adversarial robustness, there is a common practice that adopts the single-step adversarial training for quickly developing adversarially robust models. However, the single-step adversarial training is most likely to cause catastrophic overfitting, as after a few training epochs it will be hard to generate strong adversarial examples to continuously boost the adversarial robustness. In this work, we aim to avoid the catastrophic overfitting by introducing multi-step adversarial examples during the single-step adversarial training. Then, to balance the large training overhead of generating multi-step adversarial examples, we propose a Multi-stage Optimization based Adversarial Training (MOAT) method that periodically trains the model on mixed benign examples, single-step adversarial examples, and multi-step adversarial examples stage by stage. In this way, the overall training overhead is reduced significantly, meanwhile, the model could avoid catastrophic overfitting. Extensive experiments on CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 datasets demonstrate that under similar amount of training overhead, the proposed MOAT exhibits better robustness than either single-step or multi-step adversarial training methods.
Nesterov Accelerated Gradient and Scale Invariance for Improving Transferability of Adversarial Examples
Aug 17, 2019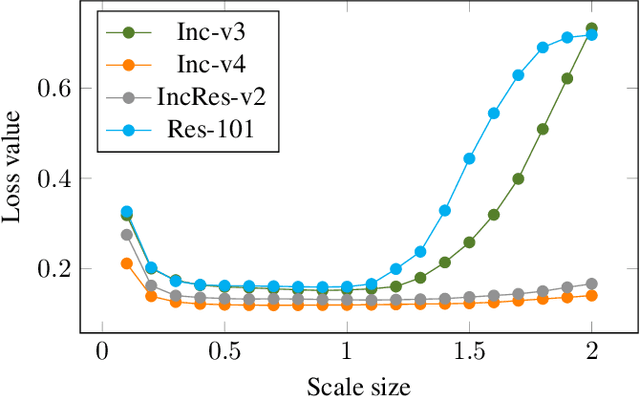

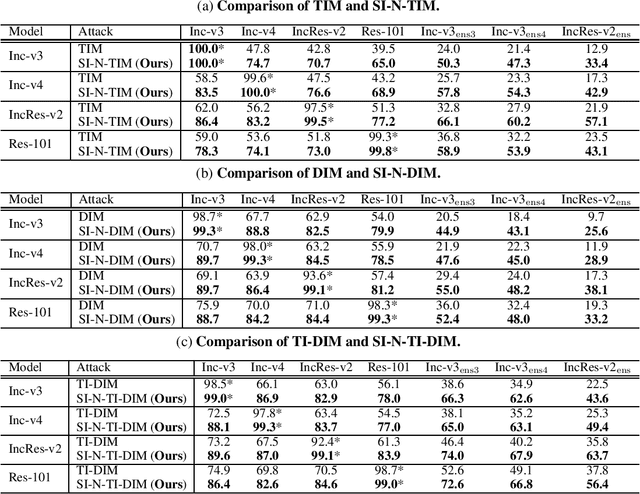
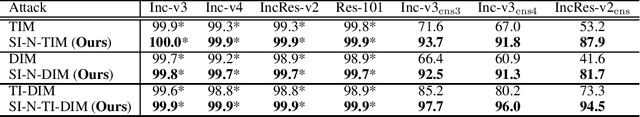
Abstract:Recent evidence suggests that deep neural networks (DNNs) are vulnerable to adversarial examples, which are crafted by adding human-imperceptible perturbations to legitimate examples. However, most of the existing adversarial attacks generate adversarial examples with weak transferability, making it difficult to evaluate the robustness of DNNs under the challenging black-box setting. To address this issue, we propose two methods: Nesterov momentum iterative fast gradient sign method (N-MI-FGSM) and scale-invariant attack method (SIM), to improve the transferability of adversarial examples. N-MI-FGSM tries a better optimizer by applying the idea of Nesterov accelerated gradient to gradient-based attack method. SIM leverages the scale-invariant property of DNNs and optimizes the generated adversarial example by a set of scaled images as the inputs. Further, the two methods can be naturally combined to form a strong attack and enhance existing gradient attack methods. Empirical results on ImageNet and NIPS 2017 adversarial competition show that the proposed methods can generate adversarial examples with higher transferability than existing competing baselines.
Improving the Generalization of Adversarial Training with Domain Adaptation
Oct 24, 2018



Abstract:By injecting adversarial examples into training data, the adversarial training method is promising for improving the robustness of deep learning models. However, most existing adversarial training approaches are based on a specific type of adversarial attack. It may not provide sufficiently representative samples from the adversarial domain, leading to a weak generalization ability on adversarial examples from other attacks. To scale to large datasets, perturbations on inputs to generate adversarial examples are usually crafted using fast single-step attacks. This work is mainly focused on the adversarial training with the single-step yet efficient FGSM adversary. In this scenario, it is difficult to train a model with great generalization due to the lack of representative adversarial samples, aka the samples are unable to accurately reflect the adversarial domain. To alleviate this problem, we propose a novel Adversarial Training with Domain Adaptation (ATDA) method. Our intuition is regarding adversarial training on FGSM adversary as a domain adaption task with limited number of target domain samples. The main idea is to learn a representation that is semantically meaningful and domain invariant on the clean domain as well as the adversarial domain. Empirical evaluations on Fashion-MNIST, SVHN, CIFAR-10 and CIFAR-100 demonstrate that ATDA can greatly improve the generalization of adversarial training and outperforms state-of-the-art methods on standard benchmark datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge