Yi Han
Independent Researcher, Australia
MIRROR: Manifold Ideal Reference ReconstructOR for Generalizable AI-Generated Image Detection
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:High-fidelity generative models have narrowed the perceptual gap between synthetic and real images, posing serious threats to media security. Most existing AI-generated image (AIGI) detectors rely on artifact-based classification and struggle to generalize to evolving generative traces. In contrast, human judgment relies on stable real-world regularities, with deviations from the human cognitive manifold serving as a more generalizable signal of forgery. Motivated by this insight, we reformulate AIGI detection as a Reference-Comparison problem that verifies consistency with the real-image manifold rather than fitting specific forgery cues. We propose MIRROR (Manifold Ideal Reference ReconstructOR), a framework that explicitly encodes reality priors using a learnable discrete memory bank. MIRROR projects an input into a manifold-consistent ideal reference via sparse linear combination, and uses the resulting residuals as robust detection signals. To evaluate whether detectors reach the "superhuman crossover" required to replace human experts, we introduce the Human-AIGI benchmark, featuring a psychophysically curated human-imperceptible subset. Across 14 benchmarks, MIRROR consistently outperforms prior methods, achieving gains of 2.1% on six standard benchmarks and 8.1% on seven in-the-wild benchmarks. On Human-AIGI, MIRROR reaches 89.6% accuracy across 27 generators, surpassing both lay users and visual experts, and further approaching the human perceptual limit as pretrained backbones scale. The code is publicly available at: https://github.com/349793927/MIRROR
RoboBrain 2.5: Depth in Sight, Time in Mind
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:We introduce RoboBrain 2.5, a next-generation embodied AI foundation model that advances general perception, spatial reasoning, and temporal modeling through extensive training on high-quality spatiotemporal supervision. Building upon its predecessor, RoboBrain 2.5 introduces two major capability upgrades. Specifically, it unlocks Precise 3D Spatial Reasoning by shifting from 2D pixel-relative grounding to depth-aware coordinate prediction and absolute metric constraint comprehension, generating complete 3D manipulation traces as ordered keypoint sequences under physical constraints. Complementing this spatial precision, the model establishes Dense Temporal Value Estimation that provides dense, step-aware progress prediction and execution state understanding across varying viewpoints, producing stable feedback signals for downstream learning. Together, these upgrades extend the framework toward more physically grounded and execution-aware embodied intelligence for complex, fine-grained manipulation. The code and checkpoints are available at project website: https://superrobobrain.github.io
CARLA-Round: A Multi-Factor Simulation Dataset for Roundabout Trajectory Prediction
Jan 17, 2026Abstract:Accurate trajectory prediction of vehicles at roundabouts is critical for reducing traffic accidents, yet it remains highly challenging due to their circular road geometry, continuous merging and yielding interactions, and absence of traffic signals. Developing accurate prediction algorithms relies on reliable, multimodal, and realistic datasets; however, such datasets for roundabout scenarios are scarce, as real-world data collection is often limited by incomplete observations and entangled factors that are difficult to isolate. We present CARLA-Round, a systematically designed simulation dataset for roundabout trajectory prediction. The dataset varies weather conditions (five types) and traffic density levels (spanning Level-of-Service A-E) in a structured manner, resulting in 25 controlled scenarios. Each scenario incorporates realistic mixtures of driving behaviors and provides explicit annotations that are largely absent from existing datasets. Unlike randomly sampled simulation data, this structured design enables precise analysis of how different conditions influence trajectory prediction performance. Validation experiments using standard baselines (LSTM, GCN, GRU+GCN) reveal traffic density dominates prediction difficulty with strong monotonic effects, while weather shows non-linear impacts. The best model achieves 0.312m ADE on real-world rounD dataset, demonstrating effective sim-to-real transfer. This systematic approach quantifies factor impacts impossible to isolate in confounded real-world datasets. Our CARLA-Round dataset is available at https://github.com/Rebecca689/CARLA-Round.
Adaptive Causal Coordination Detection for Social Media: A Memory-Guided Framework with Semi-Supervised Learning
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Detecting coordinated inauthentic behavior on social media remains a critical and persistent challenge, as most existing approaches rely on superficial correlation analysis, employ static parameter settings, and demand extensive and labor-intensive manual annotation. To address these limitations systematically, we propose the Adaptive Causal Coordination Detection (ACCD) framework. ACCD adopts a three-stage, progressive architecture that leverages a memory-guided adaptive mechanism to dynamically learn and retain optimal detection configurations for diverse coordination scenarios. Specifically, in the first stage, ACCD introduces an adaptive Convergent Cross Mapping (CCM) technique to deeply identify genuine causal relationships between accounts. The second stage integrates active learning with uncertainty sampling within a semi-supervised classification scheme, significantly reducing the burden of manual labeling. The third stage deploys an automated validation module driven by historical detection experience, enabling self-verification and optimization of the detection outcomes. We conduct a comprehensive evaluation using real-world datasets, including the Twitter IRA dataset, Reddit coordination traces, and several widely-adopted bot detection benchmarks. Experimental results demonstrate that ACCD achieves an F1-score of 87.3\% in coordinated attack detection, representing a 15.2\% improvement over the strongest existing baseline. Furthermore, the system reduces manual annotation requirements by 68\% and achieves a 2.8x speedup in processing through hierarchical clustering optimization. In summary, ACCD provides a more accurate, efficient, and highly automated end-to-end solution for identifying coordinated behavior on social platforms, offering substantial practical value and promising potential for broad application.
Beyond Artifacts: Real-Centric Envelope Modeling for Reliable AI-Generated Image Detection
Dec 24, 2025Abstract:The rapid progress of generative models has intensified the need for reliable and robust detection under real-world conditions. However, existing detectors often overfit to generator-specific artifacts and remain highly sensitive to real-world degradations. As generative architectures evolve and images undergo multi-round cross-platform sharing and post-processing (chain degradations), these artifact cues become obsolete and harder to detect. To address this, we propose Real-centric Envelope Modeling (REM), a new paradigm that shifts detection from learning generator artifacts to modeling the robust distribution of real images. REM introduces feature-level perturbations in self-reconstruction to generate near-real samples, and employs an envelope estimator with cross-domain consistency to learn a boundary enclosing the real image manifold. We further build RealChain, a comprehensive benchmark covering both open-source and commercial generators with simulated real-world degradation. Across eight benchmark evaluations, REM achieves an average improvement of 7.5% over state-of-the-art methods, and notably maintains exceptional generalization on the severely degraded RealChain benchmark, establishing a solid foundation for synthetic image detection under real-world conditions. The code and the RealChain benchmark will be made publicly available upon acceptance of the paper.
RoboTracer: Mastering Spatial Trace with Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
Dec 15, 2025Abstract:Spatial tracing, as a fundamental embodied interaction ability for robots, is inherently challenging as it requires multi-step metric-grounded reasoning compounded with complex spatial referring and real-world metric measurement. However, existing methods struggle with this compositional task. To this end, we propose RoboTracer, a 3D-aware VLM that first achieves both 3D spatial referring and measuring via a universal spatial encoder and a regression-supervised decoder to enhance scale awareness during supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Moreover, RoboTracer advances multi-step metric-grounded reasoning via reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) with metric-sensitive process rewards, supervising key intermediate perceptual cues to accurately generate spatial traces. To support SFT and RFT training, we introduce TraceSpatial, a large-scale dataset of 30M QA pairs, spanning outdoor/indoor/tabletop scenes and supporting complex reasoning processes (up to 9 steps). We further present TraceSpatial-Bench, a challenging benchmark filling the gap to evaluate spatial tracing. Experimental results show that RoboTracer surpasses baselines in spatial understanding, measuring, and referring, with an average success rate of 79.1%, and also achieves SOTA performance on TraceSpatial-Bench by a large margin, exceeding Gemini-2.5-Pro by 36% accuracy. Notably, RoboTracer can be integrated with various control policies to execute long-horizon, dynamic tasks across diverse robots (UR5, G1 humanoid) in cluttered real-world scenes.
FinCriticalED: A Visual Benchmark for Financial Fact-Level OCR Evaluation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce FinCriticalED (Financial Critical Error Detection), a visual benchmark for evaluating OCR and vision language models on financial documents at the fact level. Financial documents contain visually dense and table heavy layouts where numerical and temporal information is tightly coupled with structure. In high stakes settings, small OCR mistakes such as sign inversion or shifted dates can lead to materially different interpretations, while traditional OCR metrics like ROUGE and edit distance capture only surface level text similarity. \ficriticaled provides 500 image-HTML pairs with expert annotated financial facts covering over seven hundred numerical and temporal facts. It introduces three key contributions. First, it establishes the first fact level evaluation benchmark for financial document understanding, shifting evaluation from lexical overlap to domain critical factual correctness. Second, all annotations are created and verified by financial experts with strict quality control over signs, magnitudes, and temporal expressions. Third, we develop an LLM-as-Judge evaluation pipeline that performs structured fact extraction and contextual verification for visually complex financial documents. We benchmark OCR systems, open source vision language models, and proprietary models on FinCriticalED. Results show that although the strongest proprietary models achieve the highest factual accuracy, substantial errors remain in visually intricate numerical and temporal contexts. Through quantitative evaluation and expert case studies, FinCriticalED provides a rigorous foundation for advancing visual factual precision in financial and other precision critical domains.
TIGeR: Tool-Integrated Geometric Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
Oct 08, 2025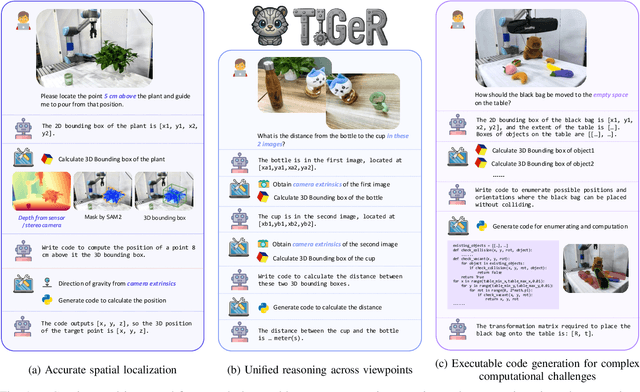
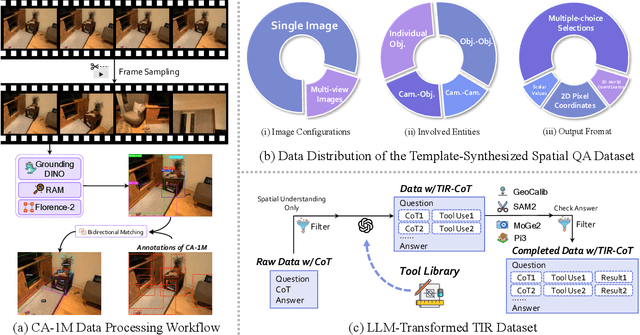
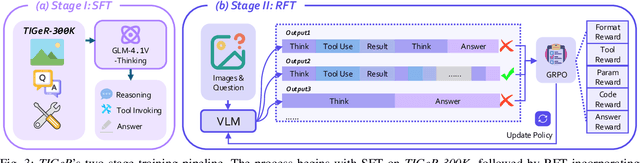
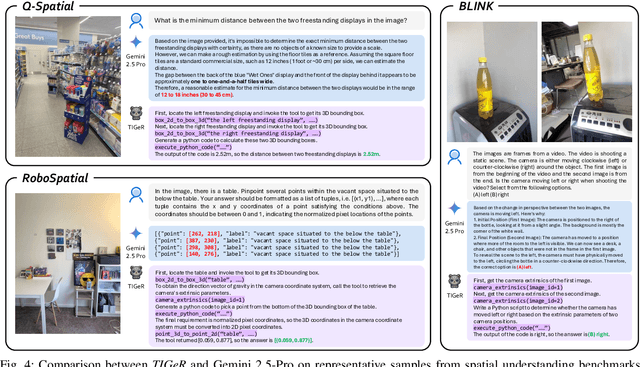
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have shown remarkable capabilities in spatial reasoning, yet they remain fundamentally limited to qualitative precision and lack the computational precision required for real-world robotics. Current approaches fail to leverage metric cues from depth sensors and camera calibration, instead reducing geometric problems to pattern recognition tasks that cannot deliver the centimeter-level accuracy essential for robotic manipulation. We present TIGeR (Tool-Integrated Geometric Reasoning), a novel framework that transforms VLMs from perceptual estimators to geometric computers by enabling them to generate and execute precise geometric computations through external tools. Rather than attempting to internalize complex geometric operations within neural networks, TIGeR empowers models to recognize geometric reasoning requirements, synthesize appropriate computational code, and invoke specialized libraries for exact calculations. To support this paradigm, we introduce TIGeR-300K, a comprehensive tool-invocation-oriented dataset covering point transformations, pose estimation, trajectory generation, and spatial compatibility verification, complete with tool invocation sequences and intermediate computations. Through a two-stage training pipeline combining supervised fine-tuning (SFT) and reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT) with our proposed hierarchical reward design, TIGeR achieves SOTA performance on geometric reasoning benchmarks while demonstrating centimeter-level precision in real-world robotic manipulation tasks.
RoboBrain 2.0 Technical Report
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:We introduce RoboBrain 2.0, our latest generation of embodied vision-language foundation models, designed to unify perception, reasoning, and planning for complex embodied tasks in physical environments. It comes in two variants: a lightweight 7B model and a full-scale 32B model, featuring a heterogeneous architecture with a vision encoder and a language model. Despite its compact size, RoboBrain 2.0 achieves strong performance across a wide spectrum of embodied reasoning tasks. On both spatial and temporal benchmarks, the 32B variant achieves leading results, surpassing prior open-source and proprietary models. In particular, it supports key real-world embodied AI capabilities, including spatial understanding (e.g., affordance prediction, spatial referring, trajectory forecasting) and temporal decision-making (e.g., closed-loop interaction, multi-agent long-horizon planning, and scene graph updating). This report details the model architecture, data construction, multi-stage training strategies, infrastructure and practical applications. We hope RoboBrain 2.0 advances embodied AI research and serves as a practical step toward building generalist embodied agents. The code, checkpoint and benchmark are available at https://superrobobrain.github.io.
RoboRefer: Towards Spatial Referring with Reasoning in Vision-Language Models for Robotics
Jun 04, 2025Abstract:Spatial referring is a fundamental capability of embodied robots to interact with the 3D physical world. However, even with the powerful pretrained vision language models (VLMs), recent approaches are still not qualified to accurately understand the complex 3D scenes and dynamically reason about the instruction-indicated locations for interaction. To this end, we propose RoboRefer, a 3D-aware VLM that can first achieve precise spatial understanding by integrating a disentangled but dedicated depth encoder via supervised fine-tuning (SFT). Moreover, RoboRefer advances generalized multi-step spatial reasoning via reinforcement fine-tuning (RFT), with metric-sensitive process reward functions tailored for spatial referring tasks. To support SFT and RFT training, we introduce RefSpatial, a large-scale dataset of 20M QA pairs (2x prior), covering 31 spatial relations (vs. 15 prior) and supporting complex reasoning processes (up to 5 steps). In addition, we introduce RefSpatial-Bench, a challenging benchmark filling the gap in evaluating spatial referring with multi-step reasoning. Experiments show that SFT-trained RoboRefer achieves state-of-the-art spatial understanding, with an average success rate of 89.6%. RFT-trained RoboRefer further outperforms all other baselines by a large margin, even surpassing Gemini-2.5-Pro by 17.4% in average accuracy on RefSpatial-Bench. Notably, RoboRefer can be integrated with various control policies to execute long-horizon, dynamic tasks across diverse robots (e,g., UR5, G1 humanoid) in cluttered real-world scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge