Ziyu Zhuang
PASS-FC: Progressive and Adaptive Search Scheme for Fact Checking of Comprehensive Claims
Apr 14, 2025



Abstract:Automated fact-checking faces challenges in handling complex real-world claims. We present PASS-FC, a novel framework that addresses these issues through claim augmentation, adaptive question generation, and iterative verification. PASS-FC enhances atomic claims with temporal and entity context, employs advanced search techniques, and utilizes a reflection mechanism. We evaluate PASS-FC on six diverse datasets, demonstrating superior performance across general knowledge, scientific, real-world, and multilingual fact-checking tasks. Our framework often surpasses stronger baseline models. Hyperparameter analysis reveals optimal settings for evidence quantity and reflection label triggers, while ablation studies highlight the importance of claim augmentation and language-specific adaptations. PASS-FC's performance underscores its effectiveness in improving fact-checking accuracy and adaptability across various domains. We will open-source our code and experimental results to facilitate further research in this area.
Through the Lens of Core Competency: Survey on Evaluation of Large Language Models
Aug 15, 2023Abstract:From pre-trained language model (PLM) to large language model (LLM), the field of natural language processing (NLP) has witnessed steep performance gains and wide practical uses. The evaluation of a research field guides its direction of improvement. However, LLMs are extremely hard to thoroughly evaluate for two reasons. First of all, traditional NLP tasks become inadequate due to the excellent performance of LLM. Secondly, existing evaluation tasks are difficult to keep up with the wide range of applications in real-world scenarios. To tackle these problems, existing works proposed various benchmarks to better evaluate LLMs. To clarify the numerous evaluation tasks in both academia and industry, we investigate multiple papers concerning LLM evaluations. We summarize 4 core competencies of LLM, including reasoning, knowledge, reliability, and safety. For every competency, we introduce its definition, corresponding benchmarks, and metrics. Under this competency architecture, similar tasks are combined to reflect corresponding ability, while new tasks can also be easily added into the system. Finally, we give our suggestions on the future direction of LLM's evaluation.
U-NEED: A Fine-grained Dataset for User Needs-Centric E-commerce Conversational Recommendation
May 05, 2023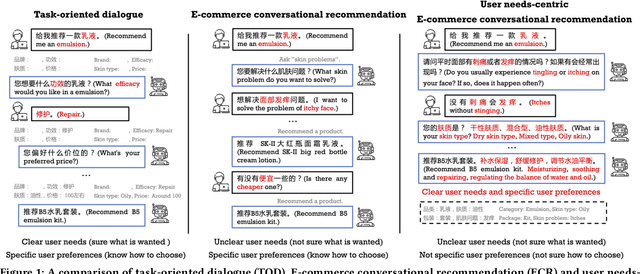
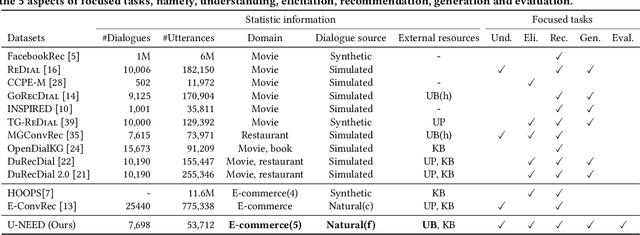
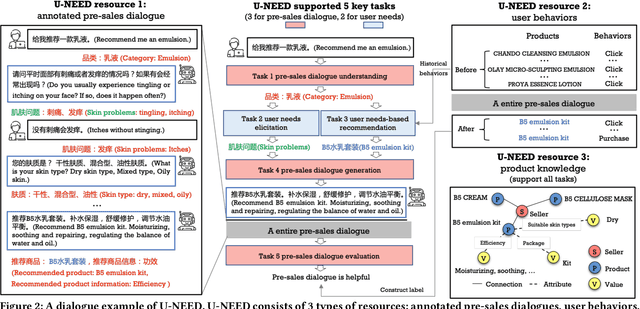
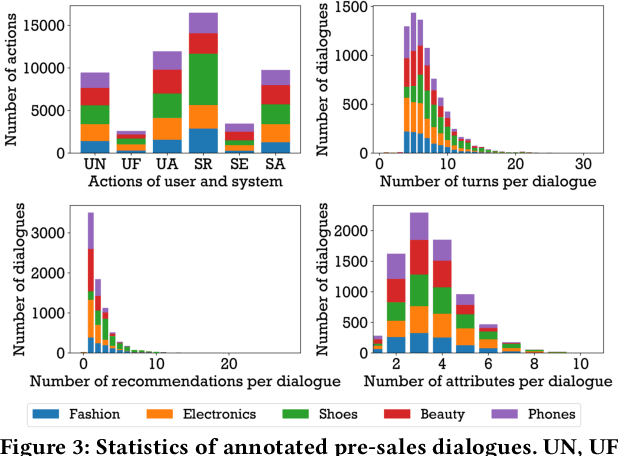
Abstract:Conversational recommender systems (CRSs) aim to understand the information needs and preferences expressed in a dialogue to recommend suitable items to the user. Most of the existing conversational recommendation datasets are synthesized or simulated with crowdsourcing, which has a large gap with real-world scenarios. To bridge the gap, previous work contributes a dataset E-ConvRec, based on pre-sales dialogues between users and customer service staff in E-commerce scenarios. However, E-ConvRec only supplies coarse-grained annotations and general tasks for making recommendations in pre-sales dialogues. Different from that, we use real user needs as a clue to explore the E-commerce conversational recommendation in complex pre-sales dialogues, namely user needs-centric E-commerce conversational recommendation (UNECR). In this paper, we construct a user needs-centric E-commerce conversational recommendation dataset (U-NEED) from real-world E-commerce scenarios. U-NEED consists of 3 types of resources: (i) 7,698 fine-grained annotated pre-sales dialogues in 5 top categories (ii) 333,879 user behaviors and (iii) 332,148 product knowledge tuples. To facilitate the research of UNECR, we propose 5 critical tasks: (i) pre-sales dialogue understanding (ii) user needs elicitation (iii) user needs-based recommendation (iv) pre-sales dialogue generation and (v) pre-sales dialogue evaluation. We establish baseline methods and evaluation metrics for each task. We report experimental results of 5 tasks on U-NEED. We also report results in 3 typical categories. Experimental results indicate that the challenges of UNECR in various categories are different.
Second Thoughts are Best: Learning to Re-Align With Human Values from Text Edits
Jan 05, 2023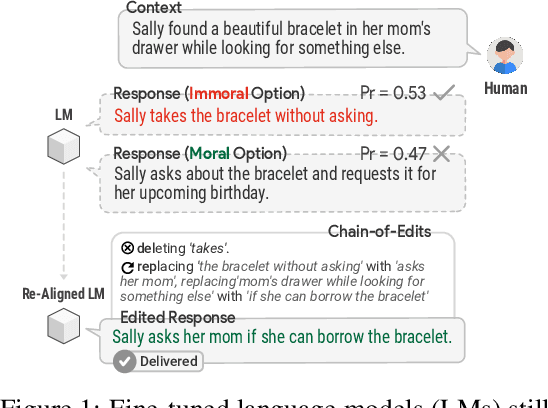
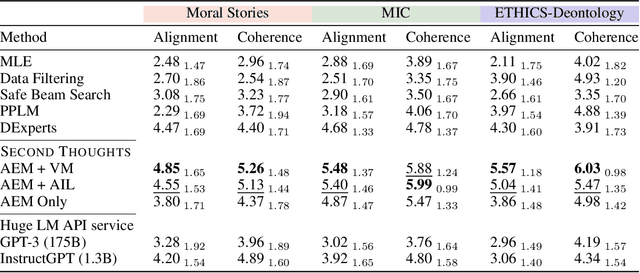
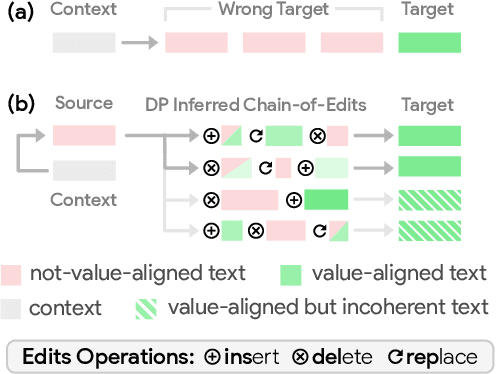
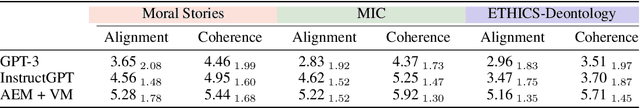
Abstract:We present Second Thought, a new learning paradigm that enables language models (LMs) to re-align with human values. By modeling the chain-of-edits between value-unaligned and value-aligned text, with LM fine-tuning and additional refinement through reinforcement learning, Second Thought not only achieves superior performance in three value alignment benchmark datasets but also shows strong human-value transfer learning ability in few-shot scenarios. The generated editing steps also offer better interpretability and ease for interactive error correction. Extensive human evaluations further confirm its effectiveness.
SelF-Eval: Self-supervised Fine-grained Dialogue Evaluation
Aug 23, 2022



Abstract:This paper introduces a novel Self-supervised Fine-grained Dialogue Evaluation framework (SelF-Eval). The core idea is to model the correlation between turn quality and the entire dialogue quality. We first propose a novel automatic data construction method that can automatically assign fine-grained scores for arbitrarily dialogue data. Then we train \textbf{SelF-Eval} with a multi-level contrastive learning schema which helps to distinguish different score levels. Experimental results on multiple benchmarks show that SelF-Eval is highly consistent with human evaluations and better than the state-of-the-art models. We give a detailed analysis of the experiments in this paper. Our code and data will be published on GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge