Lingfei Qian
Ebisu: Benchmarking Large Language Models in Japanese Finance
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Japanese finance combines agglutinative, head-final linguistic structure, mixed writing systems, and high-context communication norms that rely on indirect expression and implicit commitment, posing a substantial challenge for LLMs. We introduce Ebisu, a benchmark for native Japanese financial language understanding, comprising two linguistically and culturally grounded, expert-annotated tasks: JF-ICR, which evaluates implicit commitment and refusal recognition in investor-facing Q&A, and JF-TE, which assesses hierarchical extraction and ranking of nested financial terminology from professional disclosures. We evaluate a diverse set of open-source and proprietary LLMs spanning general-purpose, Japanese-adapted, and financial models. Results show that even state-of-the-art systems struggle on both tasks. While increased model scale yields limited improvements, language- and domain-specific adaptation does not reliably improve performance, leaving substantial gaps unresolved. Ebisu provides a focused benchmark for advancing linguistically and culturally grounded financial NLP. All datasets and evaluation scripts are publicly released.
MedViz: An Agent-based, Visual-guided Research Assistant for Navigating Biomedical Literature
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Biomedical researchers face increasing challenges in navigating millions of publications in diverse domains. Traditional search engines typically return articles as ranked text lists, offering little support for global exploration or in-depth analysis. Although recent advances in generative AI and large language models have shown promise in tasks such as summarization, extraction, and question answering, their dialog-based implementations are poorly integrated with literature search workflows. To address this gap, we introduce MedViz, a visual analytics system that integrates multiple AI agents with interactive visualization to support the exploration of the large-scale biomedical literature. MedViz combines a semantic map of millions of articles with agent-driven functions for querying, summarizing, and hypothesis generation, allowing researchers to iteratively refine questions, identify trends, and uncover hidden connections. By bridging intelligent agents with interactive visualization, MedViz transforms biomedical literature search into a dynamic, exploratory process that accelerates knowledge discovery.
EHRNavigator: A Multi-Agent System for Patient-Level Clinical Question Answering over Heterogeneous Electronic Health Records
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Clinical decision-making increasingly relies on timely and context-aware access to patient information within Electronic Health Records (EHRs), yet most existing natural language question-answering (QA) systems are evaluated solely on benchmark datasets, limiting their practical relevance. To overcome this limitation, we introduce EHRNavigator, a multi-agent framework that harnesses AI agents to perform patient-level question answering across heterogeneous and multimodal EHR data. We assessed its performance using both public benchmark and institutional datasets under realistic hospital conditions characterized by diverse schemas, temporal reasoning demands, and multimodal evidence integration. Through quantitative evaluation and clinician-validated chart review, EHRNavigator demonstrated strong generalization, achieving 86% accuracy on real-world cases while maintaining clinically acceptable response times. Overall, these findings confirm that EHRNavigator effectively bridges the gap between benchmark evaluation and clinical deployment, offering a robust, adaptive, and efficient solution for real-world EHR question answering.
FinCriticalED: A Visual Benchmark for Financial Fact-Level OCR Evaluation
Nov 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce FinCriticalED (Financial Critical Error Detection), a visual benchmark for evaluating OCR and vision language models on financial documents at the fact level. Financial documents contain visually dense and table heavy layouts where numerical and temporal information is tightly coupled with structure. In high stakes settings, small OCR mistakes such as sign inversion or shifted dates can lead to materially different interpretations, while traditional OCR metrics like ROUGE and edit distance capture only surface level text similarity. \ficriticaled provides 500 image-HTML pairs with expert annotated financial facts covering over seven hundred numerical and temporal facts. It introduces three key contributions. First, it establishes the first fact level evaluation benchmark for financial document understanding, shifting evaluation from lexical overlap to domain critical factual correctness. Second, all annotations are created and verified by financial experts with strict quality control over signs, magnitudes, and temporal expressions. Third, we develop an LLM-as-Judge evaluation pipeline that performs structured fact extraction and contextual verification for visually complex financial documents. We benchmark OCR systems, open source vision language models, and proprietary models on FinCriticalED. Results show that although the strongest proprietary models achieve the highest factual accuracy, substantial errors remain in visually intricate numerical and temporal contexts. Through quantitative evaluation and expert case studies, FinCriticalED provides a rigorous foundation for advancing visual factual precision in financial and other precision critical domains.
Memorization in Large Language Models in Medicine: Prevalence, Characteristics, and Implications
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated significant potential in medicine. To date, LLMs have been widely applied to tasks such as diagnostic assistance, medical question answering, and clinical information synthesis. However, a key open question remains: to what extent do LLMs memorize medical training data. In this study, we present the first comprehensive evaluation of memorization of LLMs in medicine, assessing its prevalence (how frequently it occurs), characteristics (what is memorized), volume (how much content is memorized), and potential downstream impacts (how memorization may affect medical applications). We systematically analyze common adaptation scenarios: (1) continued pretraining on medical corpora, (2) fine-tuning on standard medical benchmarks, and (3) fine-tuning on real-world clinical data, including over 13,000 unique inpatient records from Yale New Haven Health System. The results demonstrate that memorization is prevalent across all adaptation scenarios and significantly higher than reported in the general domain. Memorization affects both the development and adoption of LLMs in medicine and can be categorized into three types: beneficial (e.g., accurate recall of clinical guidelines and biomedical references), uninformative (e.g., repeated disclaimers or templated medical document language), and harmful (e.g., regeneration of dataset-specific or sensitive clinical content). Based on these findings, we offer practical recommendations to facilitate beneficial memorization that enhances domain-specific reasoning and factual accuracy, minimize uninformative memorization to promote deeper learning beyond surface-level patterns, and mitigate harmful memorization to prevent the leakage of sensitive or identifiable patient information.
MMAFFBen: A Multilingual and Multimodal Affective Analysis Benchmark for Evaluating LLMs and VLMs
May 30, 2025



Abstract:Large language models and vision-language models (which we jointly call LMs) have transformed NLP and CV, demonstrating remarkable potential across various fields. However, their capabilities in affective analysis (i.e. sentiment analysis and emotion detection) remain underexplored. This gap is largely due to the absence of comprehensive evaluation benchmarks, and the inherent complexity of affective analysis tasks. In this paper, we introduce MMAFFBen, the first extensive open-source benchmark for multilingual multimodal affective analysis. MMAFFBen encompasses text, image, and video modalities across 35 languages, covering four key affective analysis tasks: sentiment polarity, sentiment intensity, emotion classification, and emotion intensity. Moreover, we construct the MMAFFIn dataset for fine-tuning LMs on affective analysis tasks, and further develop MMAFFLM-3b and MMAFFLM-7b based on it. We evaluate various representative LMs, including GPT-4o-mini, providing a systematic comparison of their affective understanding capabilities. This project is available at https://github.com/lzw108/MMAFFBen.
FinTagging: An LLM-ready Benchmark for Extracting and Structuring Financial Information
May 27, 2025Abstract:We introduce FinTagging, the first full-scope, table-aware XBRL benchmark designed to evaluate the structured information extraction and semantic alignment capabilities of large language models (LLMs) in the context of XBRL-based financial reporting. Unlike prior benchmarks that oversimplify XBRL tagging as flat multi-class classification and focus solely on narrative text, FinTagging decomposes the XBRL tagging problem into two subtasks: FinNI for financial entity extraction and FinCL for taxonomy-driven concept alignment. It requires models to jointly extract facts and align them with the full 10k+ US-GAAP taxonomy across both unstructured text and structured tables, enabling realistic, fine-grained evaluation. We assess a diverse set of LLMs under zero-shot settings, systematically analyzing their performance on both subtasks and overall tagging accuracy. Our results reveal that, while LLMs demonstrate strong generalization in information extraction, they struggle with fine-grained concept alignment, particularly in disambiguating closely related taxonomy entries. These findings highlight the limitations of existing LLMs in fully automating XBRL tagging and underscore the need for improved semantic reasoning and schema-aware modeling to meet the demands of accurate financial disclosure. Code is available at our GitHub repository and data is at our Hugging Face repository.
Plutus: Benchmarking Large Language Models in Low-Resource Greek Finance
Feb 26, 2025Abstract:Despite Greece's pivotal role in the global economy, large language models (LLMs) remain underexplored for Greek financial context due to the linguistic complexity of Greek and the scarcity of domain-specific datasets. Previous efforts in multilingual financial natural language processing (NLP) have exposed considerable performance disparities, yet no dedicated Greek financial benchmarks or Greek-specific financial LLMs have been developed until now. To bridge this gap, we introduce Plutus-ben, the first Greek Financial Evaluation Benchmark, and Plutus-8B, the pioneering Greek Financial LLM, fine-tuned with Greek domain-specific data. Plutus-ben addresses five core financial NLP tasks in Greek: numeric and textual named entity recognition, question answering, abstractive summarization, and topic classification, thereby facilitating systematic and reproducible LLM assessments. To underpin these tasks, we present three novel, high-quality Greek financial datasets, thoroughly annotated by expert native Greek speakers, augmented by two existing resources. Our comprehensive evaluation of 22 LLMs on Plutus-ben reveals that Greek financial NLP remains challenging due to linguistic complexity, domain-specific terminology, and financial reasoning gaps. These findings underscore the limitations of cross-lingual transfer, the necessity for financial expertise in Greek-trained models, and the challenges of adapting financial LLMs to Greek text. We release Plutus-ben, Plutus-8B, and all associated datasets publicly to promote reproducible research and advance Greek financial NLP, fostering broader multilingual inclusivity in finance.
Fino1: On the Transferability of Reasoning Enhanced LLMs to Finance
Feb 12, 2025Abstract:Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have shown strong general reasoning abilities, yet their effectiveness in financial reasoning remains underexplored. In this study, we comprehensively evaluate 16 powerful reasoning and general LLMs on three complex financial tasks involving financial text, tabular data, and equations, assessing numerical reasoning, tabular interpretation, financial terminology comprehension, long-context processing, and equation-based problem solving. Our results show that while better datasets and pretraining improve financial reasoning, general enhancements like CoT fine-tuning do not always yield consistent gains. Moreover, all reasoning strategies face challenges in improving performance on long-context and multi-table tasks. To address these limitations, we develop a financial reasoning-enhanced model based on Llama-3.1-8B-Instruct, by CoT fine-tuning and reinforcement learning with domain-specific reasoning paths. Even with simple fine-tuning with one financial dataset, our model achieves a consistent 10% performance improvement across tasks, surpassing all 8B models and even Llama3-70B-Instruct and Llama3.1-70B-Instruct on average. Our results highlight the need for domain-specific adaptations in financial tasks, emphasizing future directions such as multi-table reasoning, long-context processing, and financial terminology comprehension. All our datasets, models, and codes are publicly available. Furthermore, we introduce a leaderboard for benchmarking future datasets and models.
Enhancing Financial Time-Series Forecasting with Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Feb 11, 2025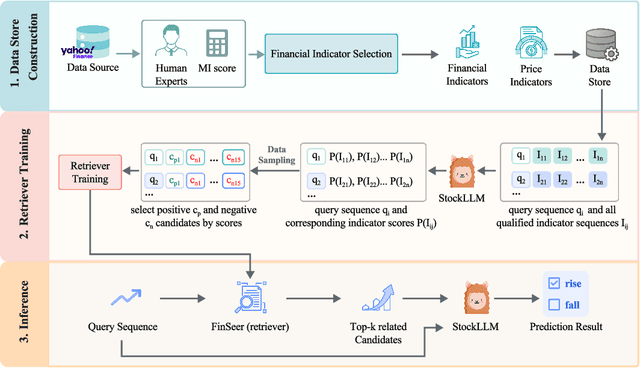
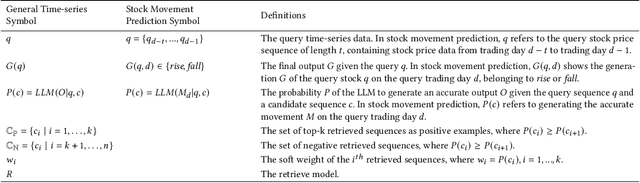
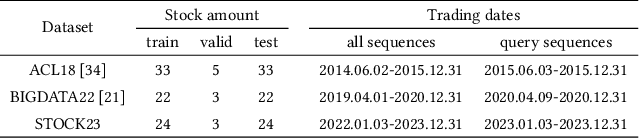
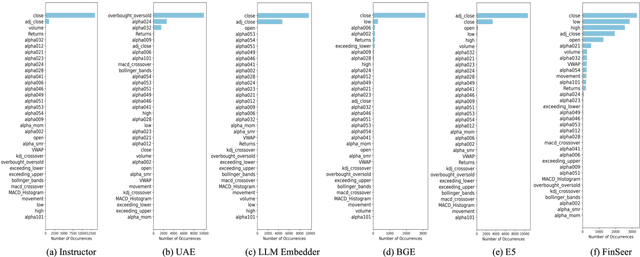
Abstract:Stock movement prediction, a critical task in financial time-series forecasting, relies on identifying and retrieving key influencing factors from vast and complex datasets. However, traditional text-trained or numeric similarity-based retrieval methods often struggle to handle the intricacies of financial data. To address this, we propose the first retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework specifically designed for financial time-series forecasting. Our framework incorporates three key innovations: a fine-tuned 1B large language model (StockLLM) as its backbone, a novel candidate selection method enhanced by LLM feedback, and a training objective that maximizes the similarity between queries and historically significant sequences. These advancements enable our retriever, FinSeer, to uncover meaningful patterns while effectively minimizing noise in complex financial datasets. To support robust evaluation, we also construct new datasets that integrate financial indicators and historical stock prices. Experimental results demonstrate that our RAG framework outperforms both the baseline StockLLM and random retrieval methods, showcasing its effectiveness. FinSeer, as the retriever, achieves an 8% higher accuracy on the BIGDATA22 benchmark and retrieves more impactful sequences compared to existing retrieval methods. This work highlights the importance of tailored retrieval models in financial forecasting and provides a novel, scalable framework for future research in the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge