Yijing Xu
Enhancing Financial Time-Series Forecasting with Retrieval-Augmented Large Language Models
Feb 11, 2025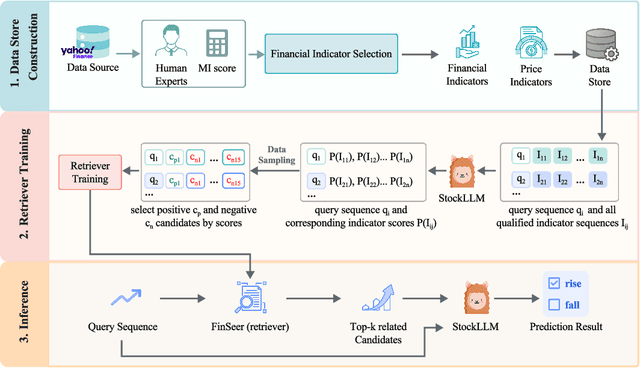
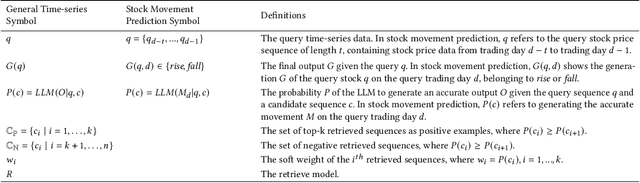
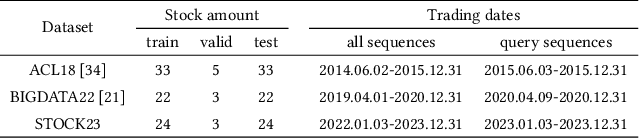
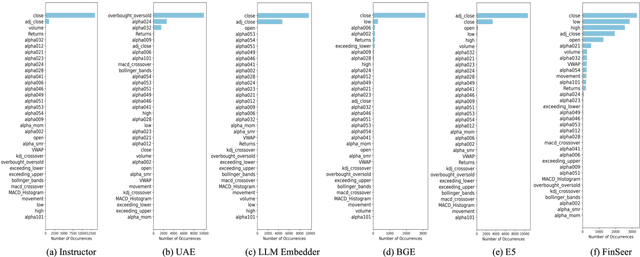
Abstract:Stock movement prediction, a critical task in financial time-series forecasting, relies on identifying and retrieving key influencing factors from vast and complex datasets. However, traditional text-trained or numeric similarity-based retrieval methods often struggle to handle the intricacies of financial data. To address this, we propose the first retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework specifically designed for financial time-series forecasting. Our framework incorporates three key innovations: a fine-tuned 1B large language model (StockLLM) as its backbone, a novel candidate selection method enhanced by LLM feedback, and a training objective that maximizes the similarity between queries and historically significant sequences. These advancements enable our retriever, FinSeer, to uncover meaningful patterns while effectively minimizing noise in complex financial datasets. To support robust evaluation, we also construct new datasets that integrate financial indicators and historical stock prices. Experimental results demonstrate that our RAG framework outperforms both the baseline StockLLM and random retrieval methods, showcasing its effectiveness. FinSeer, as the retriever, achieves an 8% higher accuracy on the BIGDATA22 benchmark and retrieves more impactful sequences compared to existing retrieval methods. This work highlights the importance of tailored retrieval models in financial forecasting and provides a novel, scalable framework for future research in the field.
Retrieval-augmented Large Language Models for Financial Time Series Forecasting
Feb 09, 2025



Abstract:Stock movement prediction, a fundamental task in financial time-series forecasting, requires identifying and retrieving critical influencing factors from vast amounts of time-series data. However, existing text-trained or numeric similarity-based retrieval methods fall short in handling complex financial analysis. To address this, we propose the first retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) framework for financial time-series forecasting, featuring three key innovations: a fine-tuned 1B parameter large language model (StockLLM) as the backbone, a novel candidate selection method leveraging LLM feedback, and a training objective that maximizes similarity between queries and historically significant sequences. This enables our retriever, FinSeer, to uncover meaningful patterns while minimizing noise in complex financial data. We also construct new datasets integrating financial indicators and historical stock prices to train FinSeer and ensure robust evaluation. Experimental results demonstrate that our RAG framework outperforms bare StockLLM and random retrieval, highlighting its effectiveness, while FinSeer surpasses existing retrieval methods, achieving an 8\% higher accuracy on BIGDATA22 and retrieving more impactful sequences. This work underscores the importance of tailored retrieval models in financial forecasting and provides a novel framework for future research.
The FinBen: An Holistic Financial Benchmark for Large Language Models
Feb 20, 2024



Abstract:LLMs have transformed NLP and shown promise in various fields, yet their potential in finance is underexplored due to a lack of thorough evaluations and the complexity of financial tasks. This along with the rapid development of LLMs, highlights the urgent need for a systematic financial evaluation benchmark for LLMs. In this paper, we introduce FinBen, the first comprehensive open-sourced evaluation benchmark, specifically designed to thoroughly assess the capabilities of LLMs in the financial domain. FinBen encompasses 35 datasets across 23 financial tasks, organized into three spectrums of difficulty inspired by the Cattell-Horn-Carroll theory, to evaluate LLMs' cognitive abilities in inductive reasoning, associative memory, quantitative reasoning, crystallized intelligence, and more. Our evaluation of 15 representative LLMs, including GPT-4, ChatGPT, and the latest Gemini, reveals insights into their strengths and limitations within the financial domain. The findings indicate that GPT-4 leads in quantification, extraction, numerical reasoning, and stock trading, while Gemini shines in generation and forecasting; however, both struggle with complex extraction and forecasting, showing a clear need for targeted enhancements. Instruction tuning boosts simple task performance but falls short in improving complex reasoning and forecasting abilities. FinBen seeks to continuously evaluate LLMs in finance, fostering AI development with regular updates of tasks and models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge