Yujia Zhou
LegalOne: A Family of Foundation Models for Reliable Legal Reasoning
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive general capabilities, their direct application in the legal domain is often hindered by a lack of precise domain knowledge and complexity of performing rigorous multi-step judicial reasoning. To address this gap, we present LegalOne, a family of foundational models specifically tailored for the Chinese legal domain. LegalOne is developed through a comprehensive three-phase pipeline designed to master legal reasoning. First, during mid-training phase, we propose Plasticity-Adjusted Sampling (PAS) to address the challenge of domain adaptation. This perplexity-based scheduler strikes a balance between the acquisition of new knowledge and the retention of original capabilities, effectively establishing a robust legal foundation. Second, during supervised fine-tuning, we employ Legal Agentic CoT Distillation (LEAD) to distill explicit reasoning from raw legal texts. Unlike naive distillation, LEAD utilizes an agentic workflow to convert complex judicial processes into structured reasoning trajectories, thereby enforcing factual grounding and logical rigor. Finally, we implement a Curriculum Reinforcement Learning (RL) strategy. Through a progressive reinforcement process spanning memorization, understanding, and reasoning, LegalOne evolves from simple pattern matching to autonomous and reliable legal reasoning. Experimental results demonstrate that LegalOne achieves state-of-the-art performance across a wide range of legal tasks, surpassing general-purpose LLMs with vastly larger parameter counts through enhanced knowledge density and efficiency. We publicly release the LegalOne weights and the LegalKit evaluation framework to advance the field of Legal AI, paving the way for deploying trustworthy and interpretable foundation models in high-stakes judicial applications.
Beyond Exposure: Optimizing Ranking Fairness with Non-linear Time-Income Functions
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Ranking is central to information distribution in web search and recommendation. Nowadays, in ranking optimization, the fairness to item providers is viewed as a crucial factor alongside ranking relevance for users. There are currently numerous concepts of fairness and one widely recognized fairness concept is Exposure Fairness. However, it relies primarily on exposure determined solely by position, overlooking other factors that significantly influence income, such as time. To address this limitation, we propose to study ranking fairness when the provider utility is influenced by other contextual factors and is neither equal to nor proportional to item exposure. We give a formal definition of Income Fairness and develop a corresponding measurement metric. Simulated experiments show that existing-exposure-fairness-based ranking algorithms fail to optimize the proposed income fairness. Therefore, we propose the Dynamic-Income-Derivative-aware Ranking Fairness algorithm, which, based on the marginal income gain at the present timestep, uses Taylor-expansion-based gradients to simultaneously optimize effectiveness and income fairness. In both offline and online settings with diverse time-income functions, DIDRF consistently outperforms state-of-the-art methods.
ATACompressor: Adaptive Task-Aware Compression for Efficient Long-Context Processing in LLMs
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Long-context inputs in large language models (LLMs) often suffer from the "lost in the middle" problem, where critical information becomes diluted or ignored due to excessive length. Context compression methods aim to address this by reducing input size, but existing approaches struggle with balancing information preservation and compression efficiency. We propose Adaptive Task-Aware Compressor (ATACompressor), which dynamically adjusts compression based on the specific requirements of the task. ATACompressor employs a selective encoder that compresses only the task-relevant portions of long contexts, ensuring that essential information is preserved while reducing unnecessary content. Its adaptive allocation controller perceives the length of relevant content and adjusts the compression rate accordingly, optimizing resource utilization. We evaluate ATACompressor on three QA datasets: HotpotQA, MSMARCO, and SQUAD-showing that it outperforms existing methods in terms of both compression efficiency and task performance. Our approach provides a scalable solution for long-context processing in LLMs. Furthermore, we perform a range of ablation studies and analysis experiments to gain deeper insights into the key components of ATACompressor.
MulFeRL: Enhancing Reinforcement Learning with Verbal Feedback in a Multi-turn Loop
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning with Verifiable Rewards (RLVR) is widely used to improve reasoning in multiple domains, yet outcome-only scalar rewards are often sparse and uninformative, especially on failed samples, where they merely indicate failure and provide no insight into why the reasoning fails. In this paper, we investigate how to leverage richer verbal feedback to guide RLVR training on failed samples, and how to convert such feedback into a trainable learning signal. Specifically, we propose a multi-turn feedback-guided reinforcement learning framework. It builds on three mechanisms: (1) dynamic multi-turn regeneration guided by feedback, triggered only on failed samples, (2) two complementary learning signals for within-turn and cross-turn optimization, and (3) structured feedback injection into the model's reasoning process. Trained on sampled OpenR1-Math, the approach outperforms supervised fine-tuning and RLVR baselines in-domain and generalizes well out-of-domain.
Beyond Experience Retrieval: Learning to Generate Utility-Optimized Structured Experience for Frozen LLMs
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are largely static and often redo reasoning or repeat mistakes. Prior experience reuse typically relies on external retrieval, which is similarity-based, can introduce noise, and adds latency. We introduce SEAM (Structured Experience Adapter Module), a lightweight, executor-specific plug-in that stores experience in its parameters and generates a structured, instance-tailored experience entry in a single forward pass to guide a frozen LLM executor. SEAM is trained for utility via executor rollouts and GRPO while keeping the executor frozen, and it can be further improved after deployment with supervised fine-tuning on logged successful trajectories. Experiments on mathematical reasoning benchmarks show consistent accuracy gains across executors with low overhead. Extensive ablations and analyses further elucidate the mechanisms underlying SEAM's effectiveness and robustness.
A Federated and Parameter-Efficient Framework for Large Language Model Training in Medicine
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong performance on medical benchmarks, including question answering and diagnosis. To enable their use in clinical settings, LLMs are typically further adapted through continued pretraining or post-training using clinical data. However, most medical LLMs are trained on data from a single institution, which faces limitations in generalizability and safety in heterogeneous systems. Federated learning (FL) is a promising solution for enabling collaborative model development across healthcare institutions. Yet applying FL to LLMs in medicine remains fundamentally limited. First, conventional FL requires transmitting the full model during each communication round, which becomes impractical for multi-billion-parameter LLMs given the limited computational resources. Second, many FL algorithms implicitly assume data homogeneity, whereas real-world clinical data are highly heterogeneous across patients, diseases, and institutional practices. We introduce the model-agnostic and parameter-efficient federated learning framework for adapting LLMs to medical applications. Fed-MedLoRA transmits only low-rank adapter parameters, reducing communication and computation overhead, while Fed-MedLoRA+ further incorporates adaptive, data-aware aggregation to improve convergence under cross-site heterogeneity. We apply the framework to clinical information extraction (IE), which transforms patient narratives into structured medical entities and relations. Accuracy was assessed across five patient cohorts through comparisons with BERT models, and LLaMA-3 and DeepSeek-R1, GPT-4o models. Evaluation settings included (1) in-domain training and testing, (2) external validation on independent cohorts, and (3) a low-resource new-site adaptation scenario using real-world clinical notes from the Yale New Haven Health System.
ctELM: Decoding and Manipulating Embeddings of Clinical Trials with Embedding Language Models
Jan 26, 2026Abstract:Text embeddings have become an essential part of a variety of language applications. However, methods for interpreting, exploring and reversing embedding spaces are limited, reducing transparency and precluding potentially valuable generative use cases. In this work, we align Large Language Models to embeddings of clinical trials using the recently reported Embedding Language Model (ELM) method. We develop an open-source, domain-agnostic ELM architecture and training framework, design training tasks for clinical trials, and introduce an expert-validated synthetic dataset. We then train a series of ELMs exploring the impact of tasks and training regimes. Our final model, ctELM, can accurately describe and compare unseen clinical trials from embeddings alone and produce plausible clinical trials from novel vectors. We further show that generated trial abstracts are responsive to moving embeddings along concept vectors for age and sex of study subjects. Our public ELM implementation and experimental results will aid the alignment of Large Language Models to embedding spaces in the biomedical domain and beyond.
Chinese Court Simulation with LLM-Based Agent System
Aug 24, 2025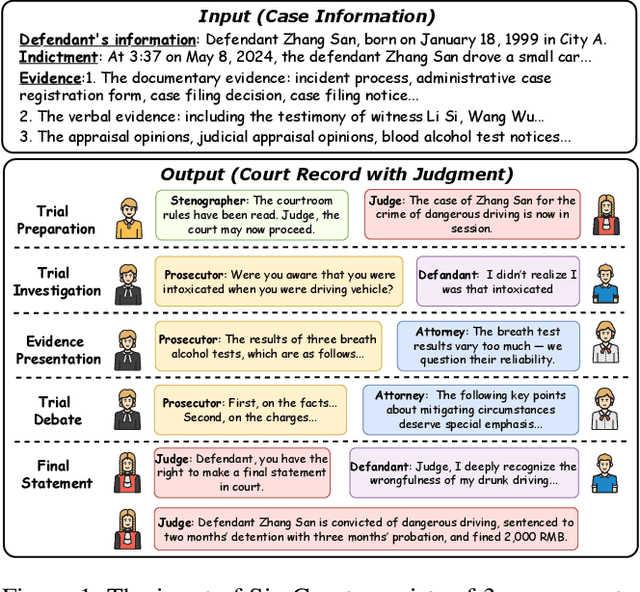

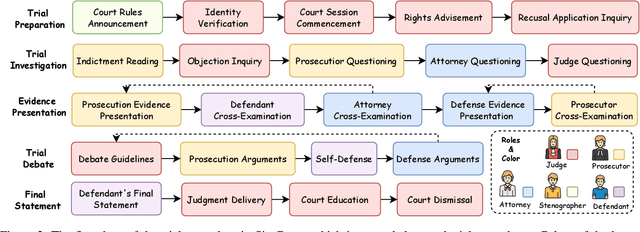

Abstract:Mock trial has long served as an important platform for legal professional training and education. It not only helps students learn about realistic trial procedures, but also provides practical value for case analysis and judgment prediction. Traditional mock trials are difficult to access by the public because they rely on professional tutors and human participants. Fortunately, the rise of large language models (LLMs) provides new opportunities for creating more accessible and scalable court simulations. While promising, existing research mainly focuses on agent construction while ignoring the systematic design and evaluation of court simulations, which are actually more important for the credibility and usage of court simulation in practice. To this end, we present the first court simulation framework -- SimCourt -- based on the real-world procedure structure of Chinese courts. Our framework replicates all 5 core stages of a Chinese trial and incorporates 5 courtroom roles, faithfully following the procedural definitions in China. To simulate trial participants with different roles, we propose and craft legal agents equipped with memory, planning, and reflection abilities. Experiment on legal judgment prediction show that our framework can generate simulated trials that better guide the system to predict the imprisonment, probation, and fine of each case. Further annotations by human experts show that agents' responses under our simulation framework even outperformed judges and lawyers from the real trials in many scenarios. These further demonstrate the potential of LLM-based court simulation.
Augmenting Multi-Agent Communication with State Delta Trajectory
Jun 24, 2025Abstract:Multi-agent techniques such as role playing or multi-turn debates have been shown to be effective in improving the performance of large language models (LLMs) in downstream tasks. Despite their differences in workflows, existing LLM-based multi-agent systems mostly use natural language for agent communication. While this is appealing for its simplicity and interpretability, it also introduces inevitable information loss as one model must down sample its continuous state vectors to concrete tokens before transferring them to the other model. Such losses are particularly significant when the information to transfer is not simple facts, but reasoning logics or abstractive thoughts. To tackle this problem, we propose a new communication protocol that transfers both natural language tokens and token-wise state transition trajectory from one agent to another. Particularly, compared to the actual state value, we find that the sequence of state changes in LLMs after generating each token can better reflect the information hidden behind the inference process, so we propose a State Delta Encoding (SDE) method to represent state transition trajectories. The experimental results show that multi-agent systems with SDE achieve SOTA performance compared to other communication protocols, particularly in tasks that involve complex reasoning. This shows the potential of communication augmentation for LLM-based multi-agent systems.
ValueSim: Generating Backstories to Model Individual Value Systems
May 28, 2025Abstract:As Large Language Models (LLMs) continue to exhibit increasingly human-like capabilities, aligning them with human values has become critically important. Contemporary advanced techniques, such as prompt learning and reinforcement learning, are being deployed to better align LLMs with human values. However, while these approaches address broad ethical considerations and helpfulness, they rarely focus on simulating individualized human value systems. To address this gap, we present ValueSim, a framework that simulates individual values through the generation of personal backstories reflecting past experiences and demographic information. ValueSim converts structured individual data into narrative backstories and employs a multi-module architecture inspired by the Cognitive-Affective Personality System to simulate individual values based on these narratives. Testing ValueSim on a self-constructed benchmark derived from the World Values Survey demonstrates an improvement in top-1 accuracy by over 10% compared to retrieval-augmented generation methods. Further analysis reveals that performance enhances as additional user interaction history becomes available, indicating the model's ability to refine its persona simulation capabilities over time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge