Xiaoqian Jiang
Department of Health Data Science and Artificial Intelligence, McWilliams School of Biomedical Informatics, UT Health Houston, TX
From Performance to Practice: Knowledge-Distilled Segmentator for On-Premises Clinical Workflows
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Deploying medical image segmentation models in routine clinical workflows is often constrained by on-premises infrastructure, where computational resources are fixed and cloud-based inference may be restricted by governance and security policies. While high-capacity models achieve strong segmentation accuracy, their computational demands hinder practical deployment and long-term maintainability in hospital environments. We present a deployment-oriented framework that leverages knowledge distillation to translate a high-performing segmentation model into a scalable family of compact student models, without modifying the inference pipeline. The proposed approach preserves architectural compatibility with existing clinical systems while enabling systematic capacity reduction. The framework is evaluated on a multi-site brain MRI dataset comprising 1,104 3D volumes, with independent testing on 101 curated cases, and is further examined on abdominal CT to assess cross-modality generalizability. Under aggressive parameter reduction (94%), the distilled student model preserves nearly all of the teacher's segmentation accuracy (98.7%), while achieving substantial efficiency gains, including up to a 67% reduction in CPU inference latency without additional deployment overhead. These results demonstrate that knowledge distillation provides a practical and reliable pathway for converting research-grade segmentation models into maintainable, deployment-ready components for on-premises clinical workflows in real-world health systems.
ReCo-KD: Region- and Context-Aware Knowledge Distillation for Efficient 3D Medical Image Segmentation
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:Accurate 3D medical image segmentation is vital for diagnosis and treatment planning, but state-of-the-art models are often too large for clinics with limited computing resources. Lightweight architectures typically suffer significant performance loss. To address these deployment and speed constraints, we propose Region- and Context-aware Knowledge Distillation (ReCo-KD), a training-only framework that transfers both fine-grained anatomical detail and long-range contextual information from a high-capacity teacher to a compact student network. The framework integrates Multi-Scale Structure-Aware Region Distillation (MS-SARD), which applies class-aware masks and scale-normalized weighting to emphasize small but clinically important regions, and Multi-Scale Context Alignment (MS-CA), which aligns teacher-student affinity patterns across feature levels. Implemented on nnU-Net in a backbone-agnostic manner, ReCo-KD requires no custom student design and is easily adapted to other architectures. Experiments on multiple public 3D medical segmentation datasets and a challenging aggregated dataset show that the distilled lightweight model attains accuracy close to the teacher while markedly reducing parameters and inference latency, underscoring its practicality for clinical deployment.
FusionDP: Foundation Model-Assisted Differentially Private Learning for Partially Sensitive Features
Nov 05, 2025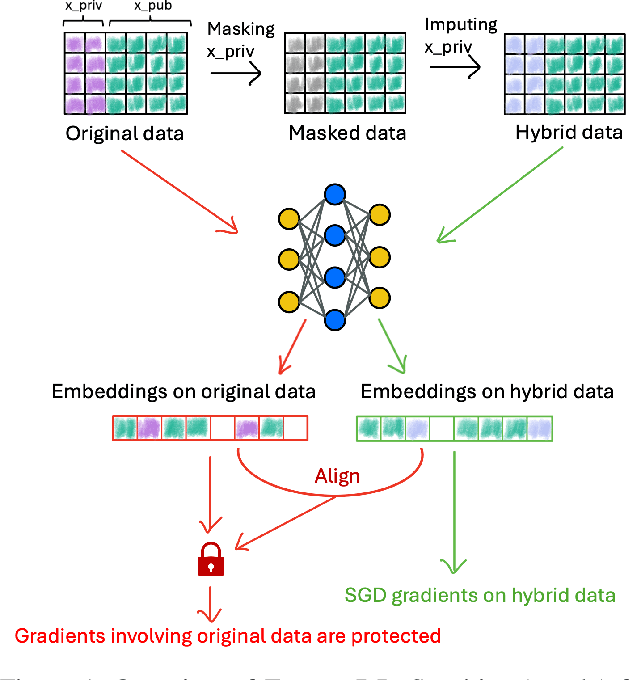
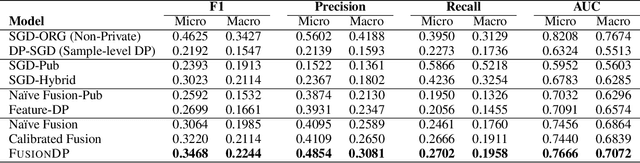
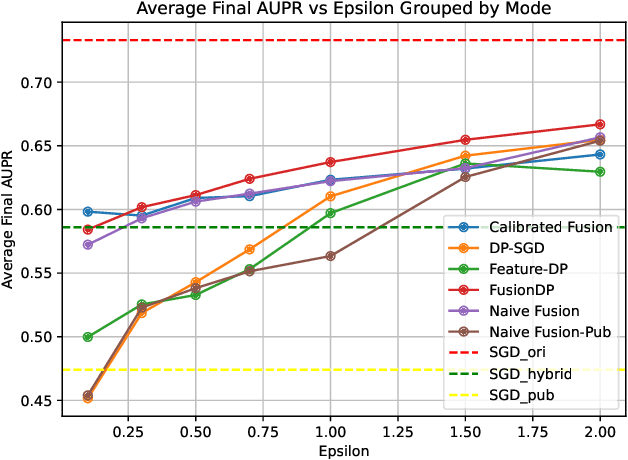
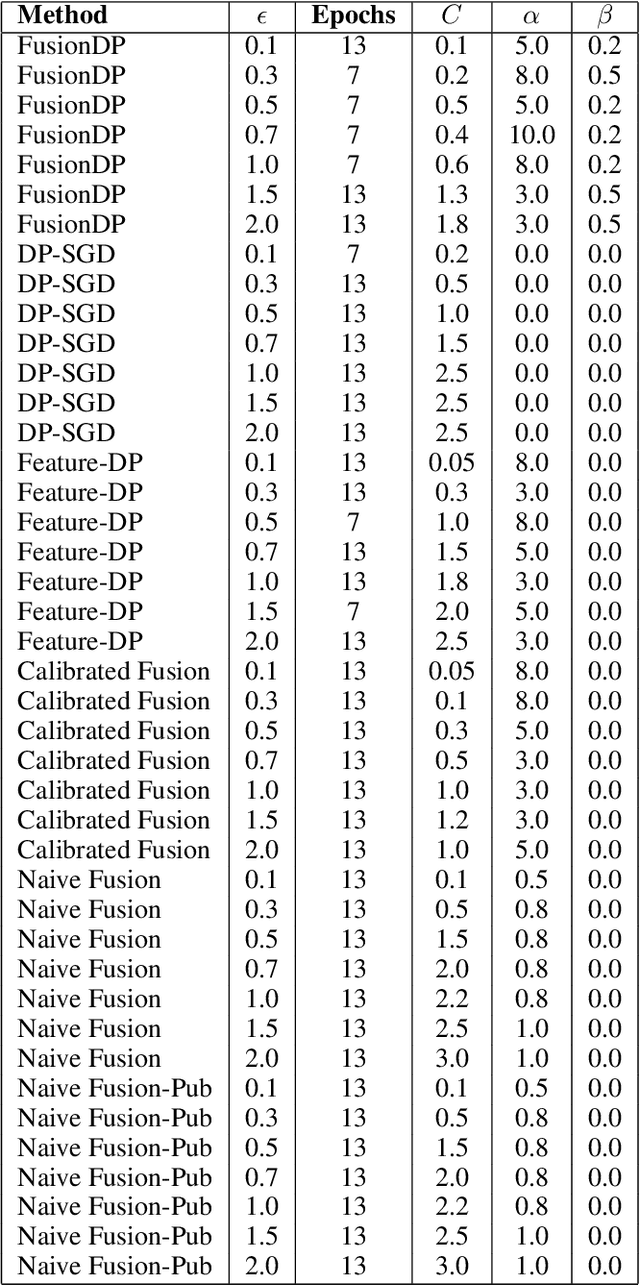
Abstract:Ensuring the privacy of sensitive training data is crucial in privacy-preserving machine learning. However, in practical scenarios, privacy protection may be required for only a subset of features. For instance, in ICU data, demographic attributes like age and gender pose higher privacy risks due to their re-identification potential, whereas raw lab results are generally less sensitive. Traditional DP-SGD enforces privacy protection on all features in one sample, leading to excessive noise injection and significant utility degradation. We propose FusionDP, a two-step framework that enhances model utility under feature-level differential privacy. First, FusionDP leverages large foundation models to impute sensitive features given non-sensitive features, treating them as external priors that provide high-quality estimates of sensitive attributes without accessing the true values during model training. Second, we introduce a modified DP-SGD algorithm that trains models on both original and imputed features while formally preserving the privacy of the original sensitive features. We evaluate FusionDP on two modalities: a sepsis prediction task on tabular data from PhysioNet and a clinical note classification task from MIMIC-III. By comparing against privacy-preserving baselines, our results show that FusionDP significantly improves model performance while maintaining rigorous feature-level privacy, demonstrating the potential of foundation model-driven imputation to enhance the privacy-utility trade-off for various modalities.
Empowering Clinical Trial Design through AI: A Randomized Evaluation of PowerGPT
Sep 15, 2025



Abstract:Sample size calculations for power analysis are critical for clinical research and trial design, yet their complexity and reliance on statistical expertise create barriers for many researchers. We introduce PowerGPT, an AI-powered system integrating large language models (LLMs) with statistical engines to automate test selection and sample size estimation in trial design. In a randomized trial to evaluate its effectiveness, PowerGPT significantly improved task completion rates (99.3% vs. 88.9% for test selection, 99.3% vs. 77.8% for sample size calculation) and accuracy (94.1% vs. 55.4% in sample size estimation, p < 0.001), while reducing average completion time (4.0 vs. 9.3 minutes, p < 0.001). These gains were consistent across various statistical tests and benefited both statisticians and non-statisticians as well as bridging expertise gaps. Already under deployment across multiple institutions, PowerGPT represents a scalable AI-driven approach that enhances accessibility, efficiency, and accuracy in statistical power analysis for clinical research.
FairACE: Achieving Degree Fairness in Graph Neural Networks via Contrastive and Adversarial Group-Balanced Training
Apr 15, 2025Abstract:Fairness has been a significant challenge in graph neural networks (GNNs) since degree biases often result in un-equal prediction performance among nodes with varying degrees. Existing GNN models focus on prediction accuracy, frequently overlooking fairness across different degree groups. To addressthis issue, we propose a novel GNN framework, namely Fairness- Aware Asymmetric Contrastive Ensemble (FairACE), which inte-grates asymmetric contrastive learning with adversarial training to improve degree fairness. FairACE captures one-hop local neighborhood information and two-hop monophily similarity to create fairer node representations and employs a degree fairness regulator to balance performance between high-degree and low-degree nodes. During model training, a novel group-balanced fairness loss is proposed to minimize classification disparities across degree groups. In addition, we also propose a novel fairness metric, the Accuracy Distribution Gap (ADG), which can quantitatively assess and ensure equitable performance across different degree-based node groups. Experimental results on both synthetic and real-world datasets demonstrate that FairACE significantly improves degree fairness metrics while maintaining competitive accuracy in comparison to the state-of-the-art GNN models.
Privacy-Preserving Model and Preprocessing Verification for Machine Learning
Jan 14, 2025
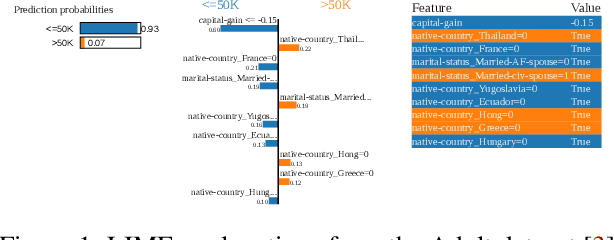
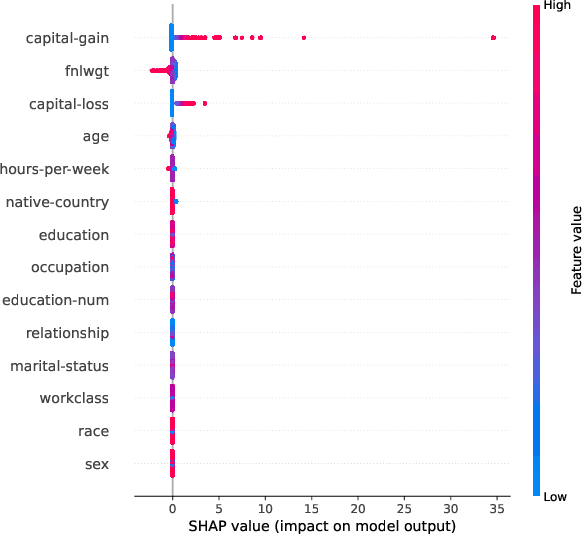
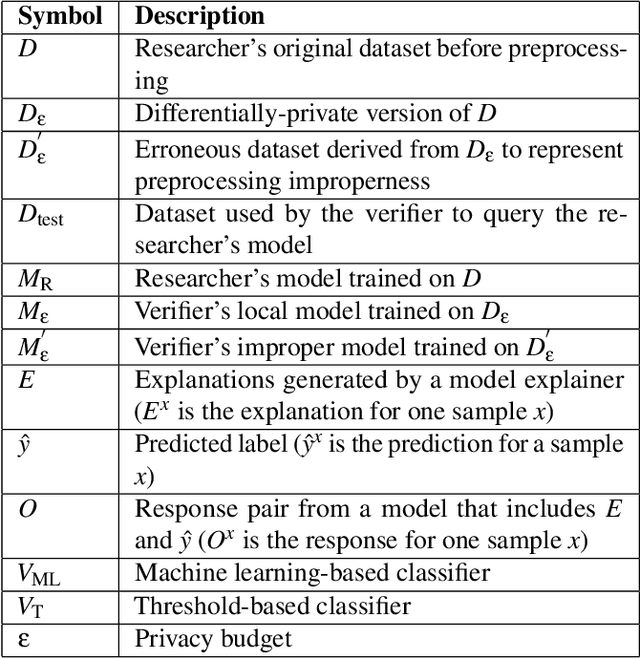
Abstract:This paper presents a framework for privacy-preserving verification of machine learning models, focusing on models trained on sensitive data. Integrating Local Differential Privacy (LDP) with model explanations from LIME and SHAP, our framework enables robust verification without compromising individual privacy. It addresses two key tasks: binary classification, to verify if a target model was trained correctly by applying the appropriate preprocessing steps, and multi-class classification, to identify specific preprocessing errors. Evaluations on three real-world datasets-Diabetes, Adult, and Student Record-demonstrate that while the ML-based approach is particularly effective in binary tasks, the threshold-based method performs comparably in multi-class tasks. Results indicate that although verification accuracy varies across datasets and noise levels, the framework provides effective detection of preprocessing errors, strong privacy guarantees, and practical applicability for safeguarding sensitive data.
CDEMapper: Enhancing NIH Common Data Element Normalization using Large Language Models
Nov 30, 2024Abstract:Common Data Elements (CDEs) standardize data collection and sharing across studies, enhancing data interoperability and improving research reproducibility. However, implementing CDEs presents challenges due to the broad range and variety of data elements. This study aims to develop an effective and efficient mapping tool to bridge the gap between local data elements and National Institutes of Health (NIH) CDEs. We propose CDEMapper, a large language model (LLM) powered mapping tool designed to assist in mapping local data elements to NIH CDEs. CDEMapper has three core modules: (1) CDE indexing and embeddings. NIH CDEs were indexed and embedded to support semantic search; (2) CDE recommendations. The tool combines Elasticsearch (BM25 similarity methods) with state of the art GPT services to recommend candidate CDEs and their permissible values; and (3) Human review. Users review and select the NIH CDEs and values that best match their data elements and value sets. We evaluate the tool recommendation accuracy against manually annotated mapping results. CDEMapper offers a publicly available, LLM-powered, and intuitive user interface that consolidates essential and advanced mapping services into a streamlined pipeline. It provides a step by step, quality assured mapping workflow designed with a user-centered approach. The evaluation results demonstrated that augmenting BM25 with GPT embeddings and a ranker consistently enhances CDEMapper mapping accuracy in three different mapping settings across four evaluation datasets. This work opens up the potential of using LLMs to assist with CDE recommendation and human curation when aligning local data elements with NIH CDEs. Additionally, this effort enhances clinical research data interoperability and helps researchers better understand the gaps between local data elements and NIH CDEs.
Information Extraction from Clinical Notes: Are We Ready to Switch to Large Language Models?
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:Backgrounds: Information extraction (IE) is critical in clinical natural language processing (NLP). While large language models (LLMs) excel on generative tasks, their performance on extractive tasks remains debated. Methods: We investigated Named Entity Recognition (NER) and Relation Extraction (RE) using 1,588 clinical notes from four sources (UT Physicians, MTSamples, MIMIC-III, and i2b2). We developed an annotated corpus covering 4 clinical entities and 16 modifiers, and compared instruction-tuned LLaMA-2 and LLaMA-3 against BiomedBERT in terms of performance, generalizability, computational resources, and throughput to BiomedBERT. Results: LLaMA models outperformed BiomedBERT across datasets. With sufficient training data, LLaMA showed modest improvements (1% on NER, 1.5-3.7% on RE); improvements were larger with limited training data. On unseen i2b2 data, LLaMA-3-70B outperformed BiomedBERT by 7% (F1) on NER and 4% on RE. However, LLaMA models required more computing resources and ran up to 28 times slower. We implemented "Kiwi," a clinical IE package featuring both models, available at https://kiwi.clinicalnlp.org/. Conclusion: This study is among the first to develop and evaluate a comprehensive clinical IE system using open-source LLMs. Results indicate that LLaMA models outperform BiomedBERT for clinical NER and RE but with higher computational costs and lower throughputs. These findings highlight that choosing between LLMs and traditional deep learning methods for clinical IE applications should remain task-specific, taking into account both performance metrics and practical considerations such as available computing resources and the intended use case scenarios.
Artificial Intelligence in Extracting Diagnostic Data from Dental Records
Jul 23, 2024Abstract:This research addresses the issue of missing structured data in dental records by extracting diagnostic information from unstructured text. The updated periodontology classification system's complexity has increased incomplete or missing structured diagnoses. To tackle this, we use advanced AI and NLP methods, leveraging GPT-4 to generate synthetic notes for fine-tuning a RoBERTa model. This significantly enhances the model's ability to understand medical and dental language. We evaluated the model using 120 randomly selected clinical notes from two datasets, demonstrating its improved diagnostic extraction accuracy. The results showed high accuracy in diagnosing periodontal status, stage, and grade, with Site 1 scoring 0.99 and Site 2 scoring 0.98. In the subtype category, Site 2 achieved perfect scores, outperforming Site 1. This method enhances extraction accuracy and broadens its use across dental contexts. The study underscores AI and NLP's transformative impact on healthcare delivery and management. Integrating AI and NLP technologies enhances documentation and simplifies administrative tasks by precisely extracting complex clinical information. This approach effectively addresses challenges in dental diagnostics. Using synthetic training data from LLMs optimizes the training process, improving accuracy and efficiency in identifying periodontal diagnoses from clinical notes. This innovative method holds promise for broader healthcare applications, potentially improving patient care quality.
Robust Privacy Amidst Innovation with Large Language Models Through a Critical Assessment of the Risks
Jul 23, 2024


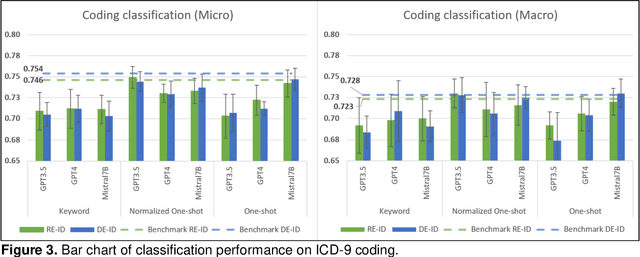
Abstract:This study examines integrating EHRs and NLP with large language models (LLMs) to improve healthcare data management and patient care. It focuses on using advanced models to create secure, HIPAA-compliant synthetic patient notes for biomedical research. The study used de-identified and re-identified MIMIC III datasets with GPT-3.5, GPT-4, and Mistral 7B to generate synthetic notes. Text generation employed templates and keyword extraction for contextually relevant notes, with one-shot generation for comparison. Privacy assessment checked PHI occurrence, while text utility was tested using an ICD-9 coding task. Text quality was evaluated with ROUGE and cosine similarity metrics to measure semantic similarity with source notes. Analysis of PHI occurrence and text utility via the ICD-9 coding task showed that the keyword-based method had low risk and good performance. One-shot generation showed the highest PHI exposure and PHI co-occurrence, especially in geographic location and date categories. The Normalized One-shot method achieved the highest classification accuracy. Privacy analysis revealed a critical balance between data utility and privacy protection, influencing future data use and sharing. Re-identified data consistently outperformed de-identified data. This study demonstrates the effectiveness of keyword-based methods in generating privacy-protecting synthetic clinical notes that retain data usability, potentially transforming clinical data-sharing practices. The superior performance of re-identified over de-identified data suggests a shift towards methods that enhance utility and privacy by using dummy PHIs to perplex privacy attacks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge