Zhongming Zhao
for the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative
MethConvTransformer: A Deep Learning Framework for Cross-Tissue Alzheimer's Disease Detection
Jan 01, 2026Abstract:Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder characterized by progressive cognitive decline and widespread epigenetic dysregulation in the brain. DNA methylation, as a stable yet dynamic epigenetic modification, holds promise as a noninvasive biomarker for early AD detection. However, methylation signatures vary substantially across tissues and studies, limiting reproducibility and translational utility. To address these challenges, we develop MethConvTransformer, a transformer-based deep learning framework that integrates DNA methylation profiles from both brain and peripheral tissues to enable biomarker discovery. The model couples a CpG-wise linear projection with convolutional and self-attention layers to capture local and long-range dependencies among CpG sites, while incorporating subject-level covariates and tissue embeddings to disentangle shared and region-specific methylation effects. In experiments across six GEO datasets and an independent ADNI validation cohort, our model consistently outperforms conventional machine-learning baselines, achieving superior discrimination and generalization. Moreover, interpretability analyses using linear projection, SHAP, and Grad-CAM++ reveal biologically meaningful methylation patterns aligned with AD-associated pathways, including immune receptor signaling, glycosylation, lipid metabolism, and endomembrane (ER/Golgi) organization. Together, these results indicate that MethConvTransformer delivers robust, cross-tissue epigenetic biomarkers for AD while providing multi-resolution interpretability, thereby advancing reproducible methylation-based diagnostics and offering testable hypotheses on disease mechanisms.
GENEVIC: GENetic data Exploration and Visualization via Intelligent interactive Console
Apr 04, 2024

Abstract:Summary: The vast generation of genetic data poses a significant challenge in efficiently uncovering valuable knowledge. Introducing GENEVIC, an AI-driven chat framework that tackles this challenge by bridging the gap between genetic data generation and biomedical knowledge discovery. Leveraging generative AI, notably ChatGPT, it serves as a biologist's 'copilot'. It automates the analysis, retrieval, and visualization of customized domain-specific genetic information, and integrates functionalities to generate protein interaction networks, enrich gene sets, and search scientific literature from PubMed, Google Scholar, and arXiv, making it a comprehensive tool for biomedical research. In its pilot phase, GENEVIC is assessed using a curated database that ranks genetic variants associated with Alzheimer's disease, schizophrenia, and cognition, based on their effect weights from the Polygenic Score Catalog, thus enabling researchers to prioritize genetic variants in complex diseases. GENEVIC's operation is user-friendly, accessible without any specialized training, secured by Azure OpenAI's HIPAA-compliant infrastructure, and evaluated for its efficacy through real-time query testing. As a prototype, GENEVIC is set to advance genetic research, enabling informed biomedical decisions. Availability and implementation: GENEVIC is publicly accessible at https://genevic-anath2024.streamlit.app. The underlying code is open-source and available via GitHub at https://github.com/anath2110/GENEVIC.git.
Drug Repurposing for COVID-19 using Graph Neural Network with Genetic, Mechanistic, and Epidemiological Validation
Sep 23, 2020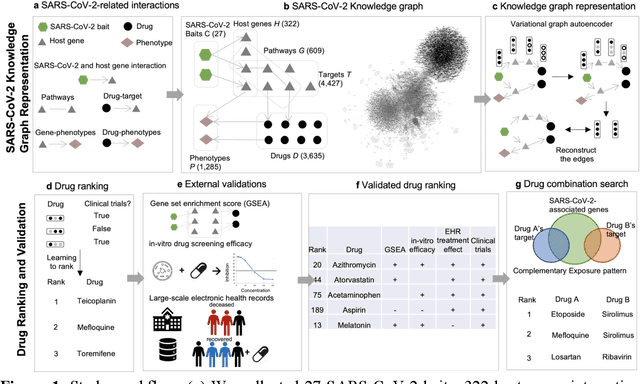
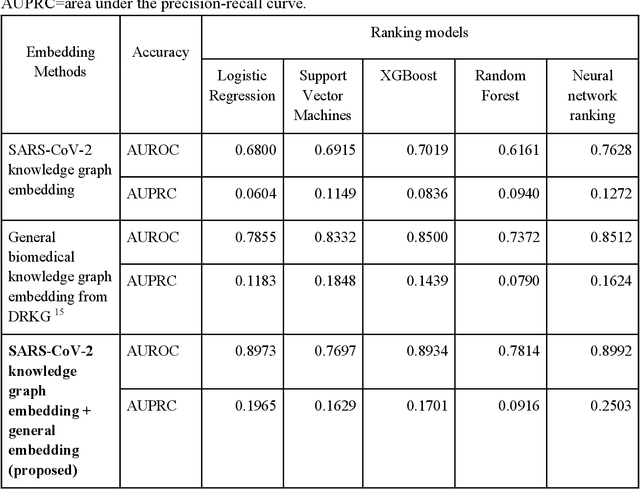
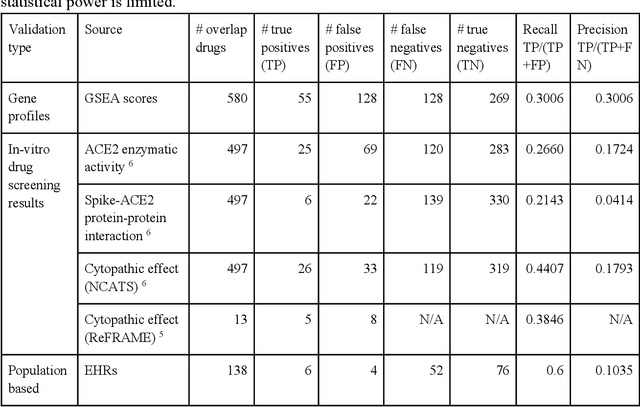
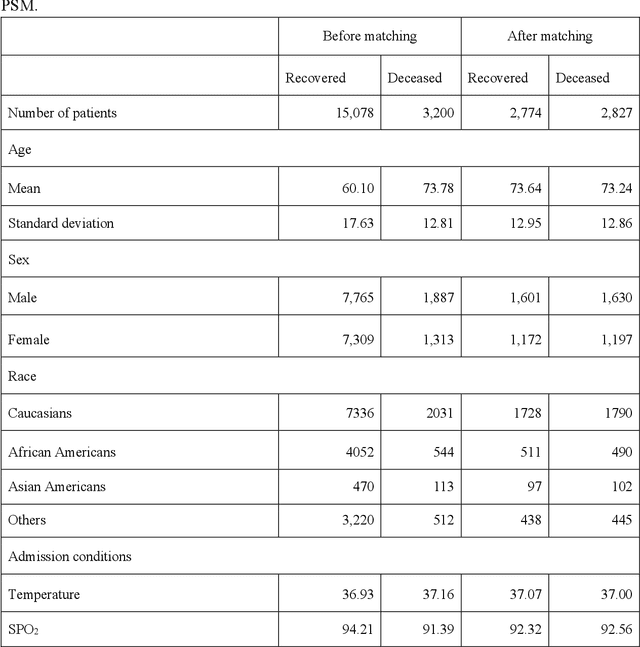
Abstract:Amid the pandemic of 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) infected by SARS-CoV-2, a vast amount of drug research for prevention and treatment has been quickly conducted, but these efforts have been unsuccessful thus far. Our objective is to prioritize repurposable drugs using a drug repurposing pipeline that systematically integrates multiple SARS-CoV-2 and drug interactions, deep graph neural networks, and in-vitro/population-based validations. We first collected all the available drugs (n= 3,635) involved in COVID-19 patient treatment through CTDbase. We built a SARS-CoV-2 knowledge graph based on the interactions among virus baits, host genes, pathways, drugs, and phenotypes. A deep graph neural network approach was used to derive the candidate representation based on the biological interactions. We prioritized the candidate drugs using clinical trial history, and then validated them with their genetic profiles, in vitro experimental efficacy, and electronic health records. We highlight the top 22 drugs including Azithromycin, Atorvastatin, Aspirin, Acetaminophen, and Albuterol. We further pinpointed drug combinations that may synergistically target COVID-19. In summary, we demonstrated that the integration of extensive interactions, deep neural networks, and rigorous validation can facilitate the rapid identification of candidate drugs for COVID-19 treatment.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge